Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > A single phase overhead transmission line del...
Start Learning for Free
A single phase overhead transmission line delivers a power of 5500 kW to a load at 11 kV. The receiving end voltage leads the current by 45°. The resistance and the inductive reactance of the transmission line are 10 Ω and 10 Ω respectively. The sending end voltages is
- a)12 kV
- b)15 kV
- c)21 kV
- d)22 kV
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A single phase overhead transmission line delivers a power of 5500 kW ...
Concept:
Short Transmission Line:
When the length of the overhead transmission line is up to about 50 km and the line voltage is comparatively up to 20 kV.
Due to smaller lengths and lower voltage, the capacitance effect is small and may be neglected.
Considered a short transmission line of resistance R and Reactance XL over a length.
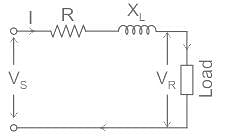
Vs is the sending end voltage
VR is the receiving end voltage
I is the load current.
cos ϕR is receiving end power factor
and, cos ϕs is sending end power factor
The phasor diagram of the system can be drawn by taking load current as a reference,
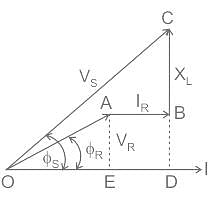
From the phasor,
(OC)2 = (OD)2 + (DC)2
(OC)2 = (OE + ED)2 + (DB + BC)2
V2S = (VR cos ϕR + IR)2 + (VR sin ϕR + IXL)2
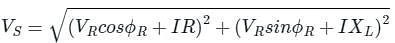
Calculation:
Given, P = 5500 kW
VR = 11 kV
R = 10 Ω
XL = 10 Ω
P = VR I cos ϕR
cos ϕR = cos (45°) = 0.707
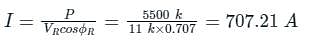
From above concept,
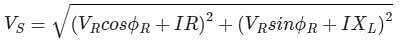
sin ϕR = 0.707
(VR cos ϕR + IR) = (11000 × 0.707) + (707.21 × 10) = 14849 volt
(VR sin ϕR + IXL) = (11000 × 0.707) + (707.21 × 10) = 14849 volt

⇒ VS = 21 kV
Short Transmission Line:
When the length of the overhead transmission line is up to about 50 km and the line voltage is comparatively up to 20 kV.
Due to smaller lengths and lower voltage, the capacitance effect is small and may be neglected.
Considered a short transmission line of resistance R and Reactance XL over a length.

Vs is the sending end voltage
VR is the receiving end voltage
I is the load current.
cos ϕR is receiving end power factor
and, cos ϕs is sending end power factor
The phasor diagram of the system can be drawn by taking load current as a reference,

From the phasor,
(OC)2 = (OD)2 + (DC)2
(OC)2 = (OE + ED)2 + (DB + BC)2
V2S = (VR cos ϕR + IR)2 + (VR sin ϕR + IXL)2
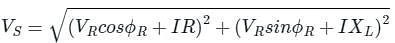
Calculation:
Given, P = 5500 kW
VR = 11 kV
R = 10 Ω
XL = 10 Ω
P = VR I cos ϕR
cos ϕR = cos (45°) = 0.707
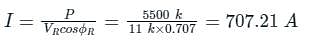
From above concept,
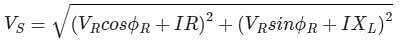
sin ϕR = 0.707
(VR cos ϕR + IR) = (11000 × 0.707) + (707.21 × 10) = 14849 volt
(VR sin ϕR + IXL) = (11000 × 0.707) + (707.21 × 10) = 14849 volt

⇒ VS = 21 kV
Most Upvoted Answer
A single phase overhead transmission line delivers a power of 5500 kW ...
Concept:
Short Transmission Line:
When the length of the overhead transmission line is up to about 50 km and the line voltage is comparatively up to 20 kV.
Due to smaller lengths and lower voltage, the capacitance effect is small and may be neglected.
Considered a short transmission line of resistance R and Reactance XL over a length.

Vs is the sending end voltage
VR is the receiving end voltage
I is the load current.
cos ϕR is receiving end power factor
and, cos ϕs is sending end power factor
The phasor diagram of the system can be drawn by taking load current as a reference,

From the phasor,
(OC)2 = (OD)2 + (DC)2
(OC)2 = (OE + ED)2 + (DB + BC)2
V2S = (VR cos ϕR + IR)2 + (VR sin ϕR + IXL)2
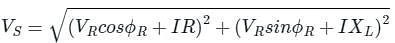
Calculation:
Given, P = 5500 kW
VR = 11 kV
R = 10 Ω
XL = 10 Ω
P = VR I cos ϕR
cos ϕR = cos (45°) = 0.707
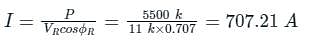
From above concept,
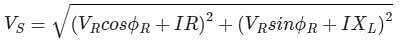
sin ϕR = 0.707
(VR cos ϕR + IR) = (11000 × 0.707) + (707.21 × 10) = 14849 volt
(VR sin ϕR + IXL) = (11000 × 0.707) + (707.21 × 10) = 14849 volt

⇒ VS = 21 kV
Short Transmission Line:
When the length of the overhead transmission line is up to about 50 km and the line voltage is comparatively up to 20 kV.
Due to smaller lengths and lower voltage, the capacitance effect is small and may be neglected.
Considered a short transmission line of resistance R and Reactance XL over a length.

Vs is the sending end voltage
VR is the receiving end voltage
I is the load current.
cos ϕR is receiving end power factor
and, cos ϕs is sending end power factor
The phasor diagram of the system can be drawn by taking load current as a reference,

From the phasor,
(OC)2 = (OD)2 + (DC)2
(OC)2 = (OE + ED)2 + (DB + BC)2
V2S = (VR cos ϕR + IR)2 + (VR sin ϕR + IXL)2
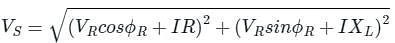
Calculation:
Given, P = 5500 kW
VR = 11 kV
R = 10 Ω
XL = 10 Ω
P = VR I cos ϕR
cos ϕR = cos (45°) = 0.707
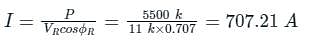
From above concept,
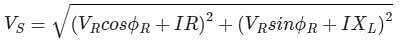
sin ϕR = 0.707
(VR cos ϕR + IR) = (11000 × 0.707) + (707.21 × 10) = 14849 volt
(VR sin ϕR + IXL) = (11000 × 0.707) + (707.21 × 10) = 14849 volt

⇒ VS = 21 kV
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A single phase overhead transmission line delivers a power of 5500 kW ...
Degrees. The resistance and inductive reactance of the line are 0.5 ohm and 1 ohm respectively.
To calculate the sending end voltage and the power loss in the transmission line, we can use the following formulas:
Sending end voltage:
V_s = V_r + I * (R + jX)
Power loss in the transmission line:
P_loss = 3 * I^2 * R
Given:
Power, P = 5500 kW
Load voltage, V_r = 11 kV
Phase angle, δ = 45 degrees
Resistance, R = 0.5 ohm
Inductive reactance, X = 1 ohm
First, we need to convert the power from kW to W and the load voltage from kV to V:
P = 5500 * 1000 = 5,500,000 W
V_r = 11 * 1000 = 11,000 V
We can calculate the current using the power and the load voltage:
P = 3 * V_r * I * cos(δ)
5,500,000 = 3 * 11,000 * I * cos(45)
I * cos(45) = 5,500,000 / (3 * 11,000)
I * cos(45) = 55/3
I = (55/3) / cos(45)
I ≈ 12,903.3 A
Next, we can calculate the imaginary part of the current using the power factor (sin(δ)):
I * sin(δ) = P / (3 * V_r * sin(δ))
I * sin(45) = 5,500,000 / (3 * 11,000 * sin(45))
I * sin(45) = 55/3
I = (55/3) / sin(45)
I ≈ 12,903.3 A
Now, we can calculate the sending end voltage using the load voltage, current, resistance, and reactance:
V_s = V_r + I * (R + jX)
V_s = 11,000 + 12,903.3 * (0.5 + j * 1)
V_s = 11,000 + 12,903.3 * (0.5 + j)
V_s = 11,000 + 6,451.65 + j * 12,903.3
V_s ≈ 17,451.65 + j * 12,903.3 V
Finally, we can calculate the power loss in the transmission line using the current and resistance:
P_loss = 3 * I^2 * R
P_loss = 3 * (12,903.3)^2 * 0.5
P_loss = 3 * 166,811,810.89 * 0.5
P_loss ≈ 249,217,716.335 W
Therefore, the sending end voltage is approximately 17,451.65 + j * 12,903.3 V and the power loss in the transmission line is approximately 249,217,716.335 W.
To calculate the sending end voltage and the power loss in the transmission line, we can use the following formulas:
Sending end voltage:
V_s = V_r + I * (R + jX)
Power loss in the transmission line:
P_loss = 3 * I^2 * R
Given:
Power, P = 5500 kW
Load voltage, V_r = 11 kV
Phase angle, δ = 45 degrees
Resistance, R = 0.5 ohm
Inductive reactance, X = 1 ohm
First, we need to convert the power from kW to W and the load voltage from kV to V:
P = 5500 * 1000 = 5,500,000 W
V_r = 11 * 1000 = 11,000 V
We can calculate the current using the power and the load voltage:
P = 3 * V_r * I * cos(δ)
5,500,000 = 3 * 11,000 * I * cos(45)
I * cos(45) = 5,500,000 / (3 * 11,000)
I * cos(45) = 55/3
I = (55/3) / cos(45)
I ≈ 12,903.3 A
Next, we can calculate the imaginary part of the current using the power factor (sin(δ)):
I * sin(δ) = P / (3 * V_r * sin(δ))
I * sin(45) = 5,500,000 / (3 * 11,000 * sin(45))
I * sin(45) = 55/3
I = (55/3) / sin(45)
I ≈ 12,903.3 A
Now, we can calculate the sending end voltage using the load voltage, current, resistance, and reactance:
V_s = V_r + I * (R + jX)
V_s = 11,000 + 12,903.3 * (0.5 + j * 1)
V_s = 11,000 + 12,903.3 * (0.5 + j)
V_s = 11,000 + 6,451.65 + j * 12,903.3
V_s ≈ 17,451.65 + j * 12,903.3 V
Finally, we can calculate the power loss in the transmission line using the current and resistance:
P_loss = 3 * I^2 * R
P_loss = 3 * (12,903.3)^2 * 0.5
P_loss = 3 * 166,811,810.89 * 0.5
P_loss ≈ 249,217,716.335 W
Therefore, the sending end voltage is approximately 17,451.65 + j * 12,903.3 V and the power loss in the transmission line is approximately 249,217,716.335 W.
Attention Electrical Engineering (EE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electrical Engineering (EE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electrical Engineering (EE).

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
A single phase overhead transmission line delivers a power of 5500 kW to a load at 11 kV. The receiving end voltage leads the current by 45°. The resistance and the inductive reactance of the transmission line are 10 Ω and 10 Ω respectively. The sending end voltages isa)12 kVb)15 kVc)21 kVd)22 kVCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A single phase overhead transmission line delivers a power of 5500 kW to a load at 11 kV. The receiving end voltage leads the current by 45°. The resistance and the inductive reactance of the transmission line are 10 Ω and 10 Ω respectively. The sending end voltages isa)12 kVb)15 kVc)21 kVd)22 kVCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about A single phase overhead transmission line delivers a power of 5500 kW to a load at 11 kV. The receiving end voltage leads the current by 45°. The resistance and the inductive reactance of the transmission line are 10 Ω and 10 Ω respectively. The sending end voltages isa)12 kVb)15 kVc)21 kVd)22 kVCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A single phase overhead transmission line delivers a power of 5500 kW to a load at 11 kV. The receiving end voltage leads the current by 45°. The resistance and the inductive reactance of the transmission line are 10 Ω and 10 Ω respectively. The sending end voltages isa)12 kVb)15 kVc)21 kVd)22 kVCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
A single phase overhead transmission line delivers a power of 5500 kW to a load at 11 kV. The receiving end voltage leads the current by 45°. The resistance and the inductive reactance of the transmission line are 10 Ω and 10 Ω respectively. The sending end voltages isa)12 kVb)15 kVc)21 kVd)22 kVCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about A single phase overhead transmission line delivers a power of 5500 kW to a load at 11 kV. The receiving end voltage leads the current by 45°. The resistance and the inductive reactance of the transmission line are 10 Ω and 10 Ω respectively. The sending end voltages isa)12 kVb)15 kVc)21 kVd)22 kVCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A single phase overhead transmission line delivers a power of 5500 kW to a load at 11 kV. The receiving end voltage leads the current by 45°. The resistance and the inductive reactance of the transmission line are 10 Ω and 10 Ω respectively. The sending end voltages isa)12 kVb)15 kVc)21 kVd)22 kVCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A single phase overhead transmission line delivers a power of 5500 kW to a load at 11 kV. The receiving end voltage leads the current by 45°. The resistance and the inductive reactance of the transmission line are 10 Ω and 10 Ω respectively. The sending end voltages isa)12 kVb)15 kVc)21 kVd)22 kVCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A single phase overhead transmission line delivers a power of 5500 kW to a load at 11 kV. The receiving end voltage leads the current by 45°. The resistance and the inductive reactance of the transmission line are 10 Ω and 10 Ω respectively. The sending end voltages isa)12 kVb)15 kVc)21 kVd)22 kVCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A single phase overhead transmission line delivers a power of 5500 kW to a load at 11 kV. The receiving end voltage leads the current by 45°. The resistance and the inductive reactance of the transmission line are 10 Ω and 10 Ω respectively. The sending end voltages isa)12 kVb)15 kVc)21 kVd)22 kVCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A single phase overhead transmission line delivers a power of 5500 kW to a load at 11 kV. The receiving end voltage leads the current by 45°. The resistance and the inductive reactance of the transmission line are 10 Ω and 10 Ω respectively. The sending end voltages isa)12 kVb)15 kVc)21 kVd)22 kVCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A single phase overhead transmission line delivers a power of 5500 kW to a load at 11 kV. The receiving end voltage leads the current by 45°. The resistance and the inductive reactance of the transmission line are 10 Ω and 10 Ω respectively. The sending end voltages isa)12 kVb)15 kVc)21 kVd)22 kVCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A single phase overhead transmission line delivers a power of 5500 kW to a load at 11 kV. The receiving end voltage leads the current by 45°. The resistance and the inductive reactance of the transmission line are 10 Ω and 10 Ω respectively. The sending end voltages isa)12 kVb)15 kVc)21 kVd)22 kVCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























