Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > Two discrete spherical particles (P and Q) of...
Start Learning for Free
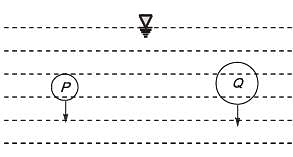
Two discrete spherical particles (P and Q) of equal mass density are independently released in water. Particle P and particle Q have diameters of 0.5 mm and 1.0 mm. respectively. Assume Stake’s law is valid.
The drag force on particle Q will be ________ tim es the drag force on particle P. (round off to the nearest integer).
The drag force on particle Q will be ________ tim es the drag force on particle P. (round off to the nearest integer).
Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Two discrete spherical particles (P and Q) of equal mass density are i...
ρ sity of water
ρb = density of particle
Diameter of P = D1 = 0.5 mm
Diameter of Q = D2 = 1 mm
∴
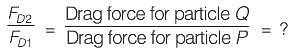
Let’s take basic case of Stake’s law i.e. a particle of diameter d moving, downward in fluid.
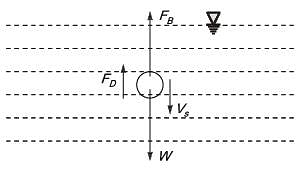
FB = Buoyancy force
FD = Drag force
Vs = Setting velocity
W = weigth of particle
Wg = FB + FD
mg - FB = 3πμDVs
(ρb - ρ)Vsphere = 3πμDVs
∵ Volume of sphere,
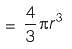
∴
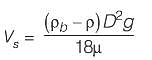
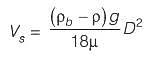
Now,
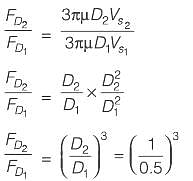
∴
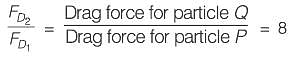
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Two discrete spherical particles (P and Q) of equal mass density are i...
Assuming that the particles are solid and have the same mass density, the larger particle Q will have a greater mass than the smaller particle P.
The mass of a spherical particle can be calculated using the formula:
Mass = (4/3) * π * (radius)^3 * density
Since the mass density is the same for both particles, we can compare their masses by comparing their volumes.
The volume of a sphere can be calculated using the formula:
Volume = (4/3) * π * (radius)^3
Let's calculate the volumes of particles P and Q:
Volume of particle P = (4/3) * π * (0.25 mm)^3 ≈ 0.0654 mm^3
Volume of particle Q = (4/3) * π * (0.5 mm)^3 ≈ 0.5236 mm^3
As we can see, the volume of particle Q is approximately 8 times greater than the volume of particle P.
Since the particles have the same mass density, the larger particle Q will have a mass approximately 8 times greater than the smaller particle P.
The mass of a spherical particle can be calculated using the formula:
Mass = (4/3) * π * (radius)^3 * density
Since the mass density is the same for both particles, we can compare their masses by comparing their volumes.
The volume of a sphere can be calculated using the formula:
Volume = (4/3) * π * (radius)^3
Let's calculate the volumes of particles P and Q:
Volume of particle P = (4/3) * π * (0.25 mm)^3 ≈ 0.0654 mm^3
Volume of particle Q = (4/3) * π * (0.5 mm)^3 ≈ 0.5236 mm^3
As we can see, the volume of particle Q is approximately 8 times greater than the volume of particle P.
Since the particles have the same mass density, the larger particle Q will have a mass approximately 8 times greater than the smaller particle P.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
Two discrete spherical particles (P and Q) of equal mass density are independently released in water. Particle P and particle Q have diameters of 0.5 mm and 1.0 mm. respectively. Assume Stake’s law is valid.The drag force on particle Q will be ________ tim es the drag force on particle P. (round off to the nearest integer).Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Two discrete spherical particles (P and Q) of equal mass density are independently released in water. Particle P and particle Q have diameters of 0.5 mm and 1.0 mm. respectively. Assume Stake’s law is valid.The drag force on particle Q will be ________ tim es the drag force on particle P. (round off to the nearest integer).Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Two discrete spherical particles (P and Q) of equal mass density are independently released in water. Particle P and particle Q have diameters of 0.5 mm and 1.0 mm. respectively. Assume Stake’s law is valid.The drag force on particle Q will be ________ tim es the drag force on particle P. (round off to the nearest integer).Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Two discrete spherical particles (P and Q) of equal mass density are independently released in water. Particle P and particle Q have diameters of 0.5 mm and 1.0 mm. respectively. Assume Stake’s law is valid.The drag force on particle Q will be ________ tim es the drag force on particle P. (round off to the nearest integer).Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?.
Two discrete spherical particles (P and Q) of equal mass density are independently released in water. Particle P and particle Q have diameters of 0.5 mm and 1.0 mm. respectively. Assume Stake’s law is valid.The drag force on particle Q will be ________ tim es the drag force on particle P. (round off to the nearest integer).Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Two discrete spherical particles (P and Q) of equal mass density are independently released in water. Particle P and particle Q have diameters of 0.5 mm and 1.0 mm. respectively. Assume Stake’s law is valid.The drag force on particle Q will be ________ tim es the drag force on particle P. (round off to the nearest integer).Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Two discrete spherical particles (P and Q) of equal mass density are independently released in water. Particle P and particle Q have diameters of 0.5 mm and 1.0 mm. respectively. Assume Stake’s law is valid.The drag force on particle Q will be ________ tim es the drag force on particle P. (round off to the nearest integer).Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Two discrete spherical particles (P and Q) of equal mass density are independently released in water. Particle P and particle Q have diameters of 0.5 mm and 1.0 mm. respectively. Assume Stake’s law is valid.The drag force on particle Q will be ________ tim es the drag force on particle P. (round off to the nearest integer).Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Two discrete spherical particles (P and Q) of equal mass density are independently released in water. Particle P and particle Q have diameters of 0.5 mm and 1.0 mm. respectively. Assume Stake’s law is valid.The drag force on particle Q will be ________ tim es the drag force on particle P. (round off to the nearest integer).Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Two discrete spherical particles (P and Q) of equal mass density are independently released in water. Particle P and particle Q have diameters of 0.5 mm and 1.0 mm. respectively. Assume Stake’s law is valid.The drag force on particle Q will be ________ tim es the drag force on particle P. (round off to the nearest integer).Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Two discrete spherical particles (P and Q) of equal mass density are independently released in water. Particle P and particle Q have diameters of 0.5 mm and 1.0 mm. respectively. Assume Stake’s law is valid.The drag force on particle Q will be ________ tim es the drag force on particle P. (round off to the nearest integer).Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Two discrete spherical particles (P and Q) of equal mass density are independently released in water. Particle P and particle Q have diameters of 0.5 mm and 1.0 mm. respectively. Assume Stake’s law is valid.The drag force on particle Q will be ________ tim es the drag force on particle P. (round off to the nearest integer).Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Two discrete spherical particles (P and Q) of equal mass density are independently released in water. Particle P and particle Q have diameters of 0.5 mm and 1.0 mm. respectively. Assume Stake’s law is valid.The drag force on particle Q will be ________ tim es the drag force on particle P. (round off to the nearest integer).Correct answer is '8'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























