Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Questions > I want to know an answer for this. Mind map o...
Start Learning for Free
I want to know an answer for this. Mind map of nutrition in animals. Please answer it soon?
Most Upvoted Answer
I want to know an answer for this. Mind map of nutrition in animals. P...
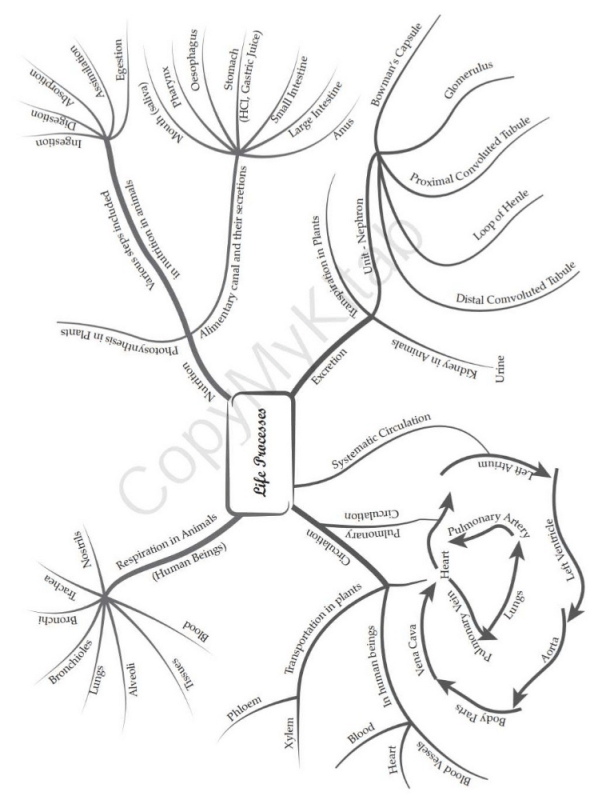
Nutrition in Animals: Mind Map
Nutrition in animals refers to the process by which animals obtain and utilize nutrients for growth, maintenance, and reproduction. It involves the ingestion, digestion, absorption, and assimilation of food. In this mind map, we will explore the different aspects of nutrition in animals.
1. Types of Nutrients:
- Carbohydrates: Provide energy and structural support.
- Proteins: Essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues.
- Lipids: Serve as a concentrated source of energy and insulation.
- Vitamins: Act as coenzymes and antioxidants.
- Minerals: Required for various physiological functions.
2. Modes of Nutrition:
- Autotrophic Nutrition: Organisms synthesize their own food using sunlight or inorganic substances.
- Heterotrophic Nutrition: Organisms obtain nutrients by consuming organic matter.
3. Heterotrophic Nutrition:
- Holozoic Nutrition: Ingestion of solid food followed by digestion and absorption.
- Saprophytic Nutrition: Decomposers obtain nutrients from dead organic matter.
- Parasitic Nutrition: Organisms derive nutrients from a living host.
- Symbiotic Nutrition: Two organisms live in close association, benefiting each other.
4. Digestive System:
- Ingestion: Intake of food through the mouth.
- Digestion: Mechanical and chemical breakdown of food.
- Absorption: Uptake of nutrients into the bloodstream.
- Assimilation: Utilization of nutrients by cells for growth and maintenance.
- Egestion: Elimination of undigested waste materials.
5. Digestive Processes:
- Mechanical Digestion: Physical breakdown of food into smaller particles.
- Chemical Digestion: Enzymatic breakdown of complex molecules into simpler forms.
- Enzymes: Biological catalysts that speed up digestion.
6. Digestive Structures:
- Mouth: Teeth and saliva initiate digestion.
- Esophagus: Transports food from the mouth to the stomach.
- Stomach: Secretes gastric juices for protein digestion.
- Small Intestine: Main site of digestion and absorption.
- Large Intestine: Absorbs water and forms feces.
7. Nutrient Absorption:
- Villi: Finger-like projections in the small intestine that increase surface area for absorption.
- Capillaries: Blood vessels surrounding the villi that absorb nutrients.
- Lacteals: Lymphatic vessels that absorb dietary fats.
8. Energy Balance:
- Caloric Intake: Energy obtained from food.
- Caloric Expenditure: Energy used for basal metabolic rate, physical activity, and thermogenesis.
- Energy Balance: Equilibrium between caloric intake and expenditure, leading to weight maintenance.
9. Nutritional Disorders:
- Malnutrition: Imbalance of nutrients, leading to undernutrition or overnutrition.
- Deficiency Diseases: Result from inadequate intake or absorption of specific nutrients.
- Obesity: Excessive accumulation of body fat, often caused by a high-calorie diet.
In conclusion, nutrition in animals involves the intake and utilization of various nutrients through different modes of nutrition. The digestive system plays a key role in the breakdown and absorption of nutrients, which are then assimilated for growth and maintenance. Understanding nutrition in animals is crucial for their overall health
Nutrition in animals refers to the process by which animals obtain and utilize nutrients for growth, maintenance, and reproduction. It involves the ingestion, digestion, absorption, and assimilation of food. In this mind map, we will explore the different aspects of nutrition in animals.
1. Types of Nutrients:
- Carbohydrates: Provide energy and structural support.
- Proteins: Essential for growth, repair, and maintenance of body tissues.
- Lipids: Serve as a concentrated source of energy and insulation.
- Vitamins: Act as coenzymes and antioxidants.
- Minerals: Required for various physiological functions.
2. Modes of Nutrition:
- Autotrophic Nutrition: Organisms synthesize their own food using sunlight or inorganic substances.
- Heterotrophic Nutrition: Organisms obtain nutrients by consuming organic matter.
3. Heterotrophic Nutrition:
- Holozoic Nutrition: Ingestion of solid food followed by digestion and absorption.
- Saprophytic Nutrition: Decomposers obtain nutrients from dead organic matter.
- Parasitic Nutrition: Organisms derive nutrients from a living host.
- Symbiotic Nutrition: Two organisms live in close association, benefiting each other.
4. Digestive System:
- Ingestion: Intake of food through the mouth.
- Digestion: Mechanical and chemical breakdown of food.
- Absorption: Uptake of nutrients into the bloodstream.
- Assimilation: Utilization of nutrients by cells for growth and maintenance.
- Egestion: Elimination of undigested waste materials.
5. Digestive Processes:
- Mechanical Digestion: Physical breakdown of food into smaller particles.
- Chemical Digestion: Enzymatic breakdown of complex molecules into simpler forms.
- Enzymes: Biological catalysts that speed up digestion.
6. Digestive Structures:
- Mouth: Teeth and saliva initiate digestion.
- Esophagus: Transports food from the mouth to the stomach.
- Stomach: Secretes gastric juices for protein digestion.
- Small Intestine: Main site of digestion and absorption.
- Large Intestine: Absorbs water and forms feces.
7. Nutrient Absorption:
- Villi: Finger-like projections in the small intestine that increase surface area for absorption.
- Capillaries: Blood vessels surrounding the villi that absorb nutrients.
- Lacteals: Lymphatic vessels that absorb dietary fats.
8. Energy Balance:
- Caloric Intake: Energy obtained from food.
- Caloric Expenditure: Energy used for basal metabolic rate, physical activity, and thermogenesis.
- Energy Balance: Equilibrium between caloric intake and expenditure, leading to weight maintenance.
9. Nutritional Disorders:
- Malnutrition: Imbalance of nutrients, leading to undernutrition or overnutrition.
- Deficiency Diseases: Result from inadequate intake or absorption of specific nutrients.
- Obesity: Excessive accumulation of body fat, often caused by a high-calorie diet.
In conclusion, nutrition in animals involves the intake and utilization of various nutrients through different modes of nutrition. The digestive system plays a key role in the breakdown and absorption of nutrients, which are then assimilated for growth and maintenance. Understanding nutrition in animals is crucial for their overall health
Community Answer
I want to know an answer for this. Mind map of nutrition in animals. P...

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Similar Class 10 Doubts
I want to know an answer for this. Mind map of nutrition in animals. Please answer it soon?
Question Description
I want to know an answer for this. Mind map of nutrition in animals. Please answer it soon? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about I want to know an answer for this. Mind map of nutrition in animals. Please answer it soon? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for I want to know an answer for this. Mind map of nutrition in animals. Please answer it soon?.
I want to know an answer for this. Mind map of nutrition in animals. Please answer it soon? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about I want to know an answer for this. Mind map of nutrition in animals. Please answer it soon? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for I want to know an answer for this. Mind map of nutrition in animals. Please answer it soon?.
Solutions for I want to know an answer for this. Mind map of nutrition in animals. Please answer it soon? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 10.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of I want to know an answer for this. Mind map of nutrition in animals. Please answer it soon? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
I want to know an answer for this. Mind map of nutrition in animals. Please answer it soon?, a detailed solution for I want to know an answer for this. Mind map of nutrition in animals. Please answer it soon? has been provided alongside types of I want to know an answer for this. Mind map of nutrition in animals. Please answer it soon? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice I want to know an answer for this. Mind map of nutrition in animals. Please answer it soon? tests, examples and also practice Class 10 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























