NEET Exam > NEET Questions > A cubical vessel of height 1m is full of wate...
Start Learning for Free
A cubical vessel of height 1m is full of water.The minimum work done in taking out water from vessel will be 1)5000J 2)10000J 3)5J 4)10J?
Most Upvoted Answer
A cubical vessel of height 1m is full of water.The minimum work done i...
The best way -to make a hole in the bottom of the vessel,in this case, the work is equal to zero.
But let's look at other ways
Drain the water
at the beginning potential energy of water is mgh/2, and then we raise the water to a level h, so work is:
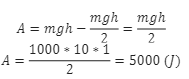
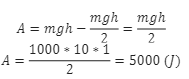
Community Answer
A cubical vessel of height 1m is full of water.The minimum work done i...
Problem:
A cubical vessel of height 1m is full of water. Determine the minimum work done in taking out water from the vessel.
Solution:
Step 1: Understanding the Problem
To find the minimum work done in taking out water from the vessel, we need to consider the potential energy of the water in the vessel.
Step 2: Identifying the Key Information
- The vessel is cubical in shape.
- The height of the vessel is 1m.
- The vessel is full of water.
Step 3: Analyzing the Problem
The potential energy of an object is given by the formula PE = mgh, where m is the mass of the object, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height of the object.
In this case, the water in the vessel has a certain mass and is at a height of 1m. To take out the water, we need to bring it to ground level, which means the height will become zero. Therefore, the change in height (h) will be 1m.
Step 4: Applying the Formula
Using the formula PE = mgh, we can calculate the potential energy of the water in the vessel.
PE = m * g * h
Since we are only interested in finding the minimum work done, we can assume that the mass of the water is 1kg (as the density of water is approximately 1000 kg/m^3).
PE = 1kg * 9.8 m/s^2 * 1m
PE = 9.8 J
Therefore, the minimum work done in taking out the water from the vessel is 9.8 Joules (J).
Step 5: Answer
The minimum work done in taking out water from the vessel is 9.8 J.
Summary:
The minimum work done in taking out water from a cubical vessel of height 1m is 9.8 Joules (J). This is calculated using the formula for potential energy, where the mass of the water is assumed to be 1kg.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
A cubical vessel of height 1m is full of water.The minimum work done in taking out water from vessel will be 1)5000J 2)10000J 3)5J 4)10J?
Question Description
A cubical vessel of height 1m is full of water.The minimum work done in taking out water from vessel will be 1)5000J 2)10000J 3)5J 4)10J? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about A cubical vessel of height 1m is full of water.The minimum work done in taking out water from vessel will be 1)5000J 2)10000J 3)5J 4)10J? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A cubical vessel of height 1m is full of water.The minimum work done in taking out water from vessel will be 1)5000J 2)10000J 3)5J 4)10J?.
A cubical vessel of height 1m is full of water.The minimum work done in taking out water from vessel will be 1)5000J 2)10000J 3)5J 4)10J? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about A cubical vessel of height 1m is full of water.The minimum work done in taking out water from vessel will be 1)5000J 2)10000J 3)5J 4)10J? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A cubical vessel of height 1m is full of water.The minimum work done in taking out water from vessel will be 1)5000J 2)10000J 3)5J 4)10J?.
Solutions for A cubical vessel of height 1m is full of water.The minimum work done in taking out water from vessel will be 1)5000J 2)10000J 3)5J 4)10J? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A cubical vessel of height 1m is full of water.The minimum work done in taking out water from vessel will be 1)5000J 2)10000J 3)5J 4)10J? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A cubical vessel of height 1m is full of water.The minimum work done in taking out water from vessel will be 1)5000J 2)10000J 3)5J 4)10J?, a detailed solution for A cubical vessel of height 1m is full of water.The minimum work done in taking out water from vessel will be 1)5000J 2)10000J 3)5J 4)10J? has been provided alongside types of A cubical vessel of height 1m is full of water.The minimum work done in taking out water from vessel will be 1)5000J 2)10000J 3)5J 4)10J? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A cubical vessel of height 1m is full of water.The minimum work done in taking out water from vessel will be 1)5000J 2)10000J 3)5J 4)10J? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























