NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Non keratinised stratified squamous epitheliu...
Start Learning for Free
Non keratinised stratified squamous epithelium is found in :-
- a)Skin
- b)Stomach
- c)Oesophagus
- d)Intestine
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Non keratinised stratified squamous epithelium is found in :-a)Skinb)S...
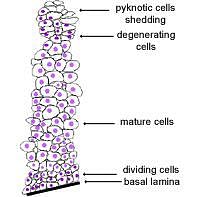
Stratified epithelia contain two or more layers of cells.
The function of this type of epithelium is mostly protective - the higher the number of layers, the more protective it is. It is good at withstanding abrasion. This type of epithelium is constantly renewing itself. Cells in the bottom layer divide, and the daughter cells move towards surface maturing and then degenerating.
This type of epithelium can either be keratinising (i.e. the skin) or non-keratinising (i.e. the oesophagus).
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
Most Upvoted Answer
Non keratinised stratified squamous epithelium is found in :-a)Skinb)S...
Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium is a type of tissue that lines the surfaces of organs and structures in the body. It is characterized by multiple layers of cells that are flat and irregularly shaped. This type of epithelium does not contain keratin, which is a tough, fibrous protein found in the skin, hair, and nails. Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium is found in several locations in the body, including the esophagus.
The esophagus is a muscular tube that connects the throat to the stomach. It plays a crucial role in the process of swallowing and transporting food from the mouth to the stomach. The inner lining of the esophagus is composed of non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. This type of epithelium is well suited for its function in the esophagus for several reasons.
1. Protection: The esophagus is exposed to friction and mechanical stress as food passes through it. The multiple layers of cells in non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium provide a protective barrier against damage, preventing the underlying tissues from being disrupted.
2. Flexibility: The cells in non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium are not rigid and are able to stretch and accommodate the movement of food as it passes through the esophagus. This flexibility allows for efficient swallowing and transport of food.
3. Secretion: Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium contains specialized cells that secrete mucus. The mucus helps to lubricate the esophagus, reducing friction and facilitating the movement of food.
4. Absorption: While the primary function of the esophagus is not absorption, some substances, such as alcohol and certain medications, can be absorbed through the lining of the esophagus. The thinness and permeability of non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium allow for limited absorption to occur.
Overall, the presence of non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium in the esophagus is essential for its function in swallowing and transporting food. It provides protection, flexibility, secretion, and limited absorption capabilities, ensuring the efficient and safe passage of food from the mouth to the stomach.
The esophagus is a muscular tube that connects the throat to the stomach. It plays a crucial role in the process of swallowing and transporting food from the mouth to the stomach. The inner lining of the esophagus is composed of non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. This type of epithelium is well suited for its function in the esophagus for several reasons.
1. Protection: The esophagus is exposed to friction and mechanical stress as food passes through it. The multiple layers of cells in non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium provide a protective barrier against damage, preventing the underlying tissues from being disrupted.
2. Flexibility: The cells in non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium are not rigid and are able to stretch and accommodate the movement of food as it passes through the esophagus. This flexibility allows for efficient swallowing and transport of food.
3. Secretion: Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium contains specialized cells that secrete mucus. The mucus helps to lubricate the esophagus, reducing friction and facilitating the movement of food.
4. Absorption: While the primary function of the esophagus is not absorption, some substances, such as alcohol and certain medications, can be absorbed through the lining of the esophagus. The thinness and permeability of non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium allow for limited absorption to occur.
Overall, the presence of non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium in the esophagus is essential for its function in swallowing and transporting food. It provides protection, flexibility, secretion, and limited absorption capabilities, ensuring the efficient and safe passage of food from the mouth to the stomach.
Community Answer
Non keratinised stratified squamous epithelium is found in :-a)Skinb)S...
Lining of buccal cavity and oesophagus contain non keratinised, where as the rest of the alimentary canal is lined by cuboidal epithelium.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Non keratinised stratified squamous epithelium is found in :-a)Skinb)Stomachc)Oesophagusd)IntestineCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Non keratinised stratified squamous epithelium is found in :-a)Skinb)Stomachc)Oesophagusd)IntestineCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Non keratinised stratified squamous epithelium is found in :-a)Skinb)Stomachc)Oesophagusd)IntestineCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Non keratinised stratified squamous epithelium is found in :-a)Skinb)Stomachc)Oesophagusd)IntestineCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Non keratinised stratified squamous epithelium is found in :-a)Skinb)Stomachc)Oesophagusd)IntestineCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Non keratinised stratified squamous epithelium is found in :-a)Skinb)Stomachc)Oesophagusd)IntestineCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Non keratinised stratified squamous epithelium is found in :-a)Skinb)Stomachc)Oesophagusd)IntestineCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Non keratinised stratified squamous epithelium is found in :-a)Skinb)Stomachc)Oesophagusd)IntestineCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Non keratinised stratified squamous epithelium is found in :-a)Skinb)Stomachc)Oesophagusd)IntestineCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Non keratinised stratified squamous epithelium is found in :-a)Skinb)Stomachc)Oesophagusd)IntestineCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Non keratinised stratified squamous epithelium is found in :-a)Skinb)Stomachc)Oesophagusd)IntestineCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Non keratinised stratified squamous epithelium is found in :-a)Skinb)Stomachc)Oesophagusd)IntestineCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Non keratinised stratified squamous epithelium is found in :-a)Skinb)Stomachc)Oesophagusd)IntestineCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























