Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > Explain isotherm of CO2 ?
Start Learning for Free
Explain isotherm of CO2 ?
Verified Answer
Explain isotherm of CO2 ?
Carbon dioxide has been studied in detail by Andrews. At different temperatures, he studied the behaviour of the gas. Keeping temperature constant, the various pressures were plotted against volumes, as obtained from his experiments.These P as V plots at constant temperature are called isotherms. Andrews obtained a number of typical isotherms from his experiments on carbon dioxide as shown below. These isotherms can be roughly classified as follows:
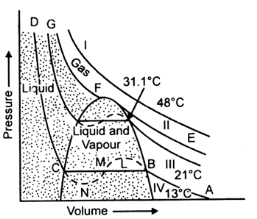

A) Isotherms at a temperature much above the critical temperature (31deg1degC): These are very much like the ideal gas isotherms (Isotherm I).
(B) Isotherms at a temperature just above the critical temperature : They have a point of inflexion which is not found in the ideal gas isotherms (Isotherm II).
(C) Isotherms at a temperature just above the critical temperature : These show a straight horizontal part along which the gas gets converted to the liquid state (Isotherms III and IV).
This is the case of discontinuous liquefaction as the properties of the substance in the gaseous and liquid forms are markedly different from each other.
In each of these isotherms, like isotherm (IV) at 13degC, it is clear that with the increase of pressure, the volume of the gas decreases along AB according to Boyle’s law and at B, the liquefaction starts. On decreasing the volume further, there is no change of pressure (along BC) until point C is reached where the whole of the gas has been liquefied.
Curve CD is almost vertical showing that liquid obtained is slightly compressible.
At higher temperature, say 21degC, curve III is a similar isotherm except that horizontal position is shorter. If the temperature is further raised, the horizontal part of the isotherm becomes shorter and shorter until it is reduced to a point F as in curve II at the critical temperature.
Liquefaction of a gas does not occur at all along the isotherm above the critical temperature. It is only along the critical temperature isotherm that a gas undistinguishably continues into the liquid state.
All gases behave similarly except that the length of horizontal portions and peak of the dotted parabola (F) are different depending on the nature of the gas.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 11 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 11 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
Explain isotherm of CO2 ?
What is an Isotherm of CO2?
An isotherm of CO2 refers to a graphical representation of the relationship between the pressure and the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) adsorbed on a solid material at a constant temperature. Isotherms are essential for understanding the adsorption behavior of CO2 and are widely used in various fields, including environmental science, chemical engineering, and material science.
The Significance of Isotherms
Isotherms provide valuable insights into the adsorption capacity, selectivity, and affinity of a material for CO2. These characteristics are crucial for the development of carbon capture and storage technologies, as well as for designing efficient gas separation processes. By studying the isotherms of CO2, researchers can determine the optimal conditions for adsorption and evaluate the performance of different materials.
Understanding the Graph
When plotting an isotherm of CO2, the pressure of CO2 is typically represented on the x-axis, while the amount of adsorbed CO2 is plotted on the y-axis. The resulting graph shows how the amount of CO2 adsorbed changes with varying pressures at a constant temperature.
Types of Isotherms
Different types of isotherms can be observed depending on the adsorption behavior of the material. Here are some common types:
1. Langmuir Isotherm: The Langmuir isotherm assumes that adsorption occurs on a homogeneous surface with a finite number of identical active sites. It follows the equation: q = (Q * b * P) / (1 + b * P), where q is the amount of adsorbed CO2, Q is the maximum adsorption capacity, b is the Langmuir constant, and P is the pressure of CO2.
2. BET Isotherm: The BET (Brunauer-Emmett-Teller) isotherm is applicable to multilayer adsorption on a solid surface. It accounts for the formation of multiple layers of adsorbate molecules. The equation is more complex than the Langmuir isotherm but provides valuable information about the surface area and adsorption energies.
Interpreting Isotherms
Isotherms can provide crucial information about the adsorption process. By analyzing the shape of the curve, one can determine the adsorption capacity, the presence of multiple layers, and the strength of the adsorbent-adsorbate interaction. These insights help researchers select suitable materials for various applications, such as CO2 capture from flue gases or natural gas purification.
Conclusion
Isotherms of CO2 are powerful tools for understanding the adsorption behavior of materials. By studying these graphs, researchers can gain insights into the capacity, selectivity, and affinity of solids for CO2. This knowledge is vital for developing efficient carbon capture technologies and designing effective gas separation processes.
An isotherm of CO2 refers to a graphical representation of the relationship between the pressure and the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) adsorbed on a solid material at a constant temperature. Isotherms are essential for understanding the adsorption behavior of CO2 and are widely used in various fields, including environmental science, chemical engineering, and material science.
The Significance of Isotherms
Isotherms provide valuable insights into the adsorption capacity, selectivity, and affinity of a material for CO2. These characteristics are crucial for the development of carbon capture and storage technologies, as well as for designing efficient gas separation processes. By studying the isotherms of CO2, researchers can determine the optimal conditions for adsorption and evaluate the performance of different materials.
Understanding the Graph
When plotting an isotherm of CO2, the pressure of CO2 is typically represented on the x-axis, while the amount of adsorbed CO2 is plotted on the y-axis. The resulting graph shows how the amount of CO2 adsorbed changes with varying pressures at a constant temperature.
Types of Isotherms
Different types of isotherms can be observed depending on the adsorption behavior of the material. Here are some common types:
1. Langmuir Isotherm: The Langmuir isotherm assumes that adsorption occurs on a homogeneous surface with a finite number of identical active sites. It follows the equation: q = (Q * b * P) / (1 + b * P), where q is the amount of adsorbed CO2, Q is the maximum adsorption capacity, b is the Langmuir constant, and P is the pressure of CO2.
2. BET Isotherm: The BET (Brunauer-Emmett-Teller) isotherm is applicable to multilayer adsorption on a solid surface. It accounts for the formation of multiple layers of adsorbate molecules. The equation is more complex than the Langmuir isotherm but provides valuable information about the surface area and adsorption energies.
Interpreting Isotherms
Isotherms can provide crucial information about the adsorption process. By analyzing the shape of the curve, one can determine the adsorption capacity, the presence of multiple layers, and the strength of the adsorbent-adsorbate interaction. These insights help researchers select suitable materials for various applications, such as CO2 capture from flue gases or natural gas purification.
Conclusion
Isotherms of CO2 are powerful tools for understanding the adsorption behavior of materials. By studying these graphs, researchers can gain insights into the capacity, selectivity, and affinity of solids for CO2. This knowledge is vital for developing efficient carbon capture technologies and designing effective gas separation processes.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Question Description
Explain isotherm of CO2 ? for Class 11 2025 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Explain isotherm of CO2 ? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Explain isotherm of CO2 ?.
Explain isotherm of CO2 ? for Class 11 2025 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Explain isotherm of CO2 ? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Explain isotherm of CO2 ?.
Solutions for Explain isotherm of CO2 ? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Explain isotherm of CO2 ? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Explain isotherm of CO2 ?, a detailed solution for Explain isotherm of CO2 ? has been provided alongside types of Explain isotherm of CO2 ? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Explain isotherm of CO2 ? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















