NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Conductivity and molar conductivity formula?
Start Learning for Free
Conductivity and molar conductivity formula?
Verified Answer
Conductivity and molar conductivity formula?
about the specific conductivity and molar conductivity. The conductance of material is the property of materials due to which a material allows the flow of ions through itself and thus conducts electricity. It is generally defined as the reciprocal of resistance of that material. SI unit of conductance is S (Siemens). Specific conductivity (better known as conductivity) is the measure of the ability of that material to conduct electricity. It is represented by the symbol “К”. Hence, by definition,
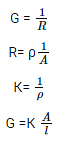
Where,
К = conductivity,
ρ = resistivity of the material
G= conductance
R= resistance
l = length
A= area of cross section
The conductance of a material depends on the nature of the material, no. of valence electrons for a material and temperature. Metals are good conductors of electricity due to their valence electrons. We observe that the conductance of materials decreases with increase in temperature.
Water in its pure state is known to have very low conductivity due to the presence of hydroxyl ions. The presence of electrolytes further enhances the conductivity as they furnish their ions in the solution. The conductance of electricity by ions present in the solution is called electrolytic or ionic conductance.Specific conductivity or conductivity of an electrolytic solution at any given concentration is the conductance of one unit volume of solution kept between two platinum electrodes with the unit area of cross-section and at a distance of unit length.The conductivity of electrolytic solutions depends on:
The nature and the concentration of the electrolyte added
The size of the ions produced and their salvation.
Solvent nature and viscosity.
Temperature.
Due to charge, concentration and size of the ions in which electrolytes dissociate or ease with which the ions move under a potential gradient, the conductivity of solutions of different electrolytes differs with the same solvent and at a given temperature. Hence we define a more common term molar conductivity for an electrolyte solution. The molar conductivity of a solution at a given concentration is the conductance of the volume of solution containing one mole of electrolyte kept between two electrodes with the unit area of cross section and distance of unit length. In general terms, it is defined as the ratio of specific conductivity and the concentration of the electrolyte. The symbol Ʌm denotes it.
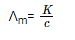
Where,
К = specific conductivity
c= concentration of electrolyte.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
Most Upvoted Answer
Conductivity and molar conductivity formula?
Conductivity and Molar Conductivity
Conductivity and molar conductivity are important concepts in the field of chemistry that help us understand the ability of substances to conduct electricity in solution. These properties are particularly relevant in the study of electrolytes, which are substances that dissociate into ions when dissolved in a solvent.
Conductivity
Conductivity is a measure of how well a substance conducts electricity. It is defined as the reciprocal of resistivity and is represented by the symbol σ. Conductivity is influenced by factors such as the concentration of ions, the mobility of the ions, and the temperature of the solution. The unit of conductivity is Siemens per meter (S/m).
Molar Conductivity
Molar conductivity is the conductivity of a solution containing one mole of solute in a volume of one liter. It is represented by the symbol Λm and is measured in Siemens per meter squared per mole per liter (S·m²·mol⁻¹·L⁻¹). Molar conductivity is a useful parameter to compare the conductivity of different solutions at the same concentration.
The Relationship between Conductivity and Molar Conductivity
The molar conductivity of a solution is directly proportional to its conductivity. The relationship between these two properties can be expressed using the equation:
Λm = κ / c
where Λm is the molar conductivity, κ is the conductivity, and c is the concentration of the solution. This equation shows that molar conductivity decreases with increasing concentration, as the number of ions per unit volume decreases.
Applying the Kohlrausch Law
The Kohlrausch Law states that the molar conductivity of an electrolyte at infinite dilution is the sum of the molar conductivities of its constituent ions. This law allows us to determine the molar conductivity of individual ions in a solution by measuring the molar conductivity of the electrolyte at different concentrations.
The Kohlrausch Law equation:
Λm = Λm⁰ - (A⁺ × Λm⁺⁺) - (A⁻ × Λm⁻⁻)
where Λm is the molar conductivity of the electrolyte, Λm⁰ is the molar conductivity at infinite dilution, A⁺ and A⁻ are the concentrations of the cation and anion, and Λm⁺⁺ and Λm⁻⁻ are the molar conductivities of the cation and anion at infinite dilution, respectively.
Conclusion
Conductivity and molar conductivity are important properties that help us understand the ability of substances to conduct electricity in solution. By studying these properties, scientists can gain insights into the behavior of electrolytes and their constituent ions. The relationship between conductivity and molar conductivity, as well as the application of the Kohlrausch Law, allows for the determination of molar conductivities of individual ions in a solution.
Conductivity and molar conductivity are important concepts in the field of chemistry that help us understand the ability of substances to conduct electricity in solution. These properties are particularly relevant in the study of electrolytes, which are substances that dissociate into ions when dissolved in a solvent.
Conductivity
Conductivity is a measure of how well a substance conducts electricity. It is defined as the reciprocal of resistivity and is represented by the symbol σ. Conductivity is influenced by factors such as the concentration of ions, the mobility of the ions, and the temperature of the solution. The unit of conductivity is Siemens per meter (S/m).
Molar Conductivity
Molar conductivity is the conductivity of a solution containing one mole of solute in a volume of one liter. It is represented by the symbol Λm and is measured in Siemens per meter squared per mole per liter (S·m²·mol⁻¹·L⁻¹). Molar conductivity is a useful parameter to compare the conductivity of different solutions at the same concentration.
The Relationship between Conductivity and Molar Conductivity
The molar conductivity of a solution is directly proportional to its conductivity. The relationship between these two properties can be expressed using the equation:
Λm = κ / c
where Λm is the molar conductivity, κ is the conductivity, and c is the concentration of the solution. This equation shows that molar conductivity decreases with increasing concentration, as the number of ions per unit volume decreases.
Applying the Kohlrausch Law
The Kohlrausch Law states that the molar conductivity of an electrolyte at infinite dilution is the sum of the molar conductivities of its constituent ions. This law allows us to determine the molar conductivity of individual ions in a solution by measuring the molar conductivity of the electrolyte at different concentrations.
The Kohlrausch Law equation:
Λm = Λm⁰ - (A⁺ × Λm⁺⁺) - (A⁻ × Λm⁻⁻)
where Λm is the molar conductivity of the electrolyte, Λm⁰ is the molar conductivity at infinite dilution, A⁺ and A⁻ are the concentrations of the cation and anion, and Λm⁺⁺ and Λm⁻⁻ are the molar conductivities of the cation and anion at infinite dilution, respectively.
Conclusion
Conductivity and molar conductivity are important properties that help us understand the ability of substances to conduct electricity in solution. By studying these properties, scientists can gain insights into the behavior of electrolytes and their constituent ions. The relationship between conductivity and molar conductivity, as well as the application of the Kohlrausch Law, allows for the determination of molar conductivities of individual ions in a solution.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Conductivity and molar conductivity formula?
Question Description
Conductivity and molar conductivity formula? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Conductivity and molar conductivity formula? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Conductivity and molar conductivity formula?.
Conductivity and molar conductivity formula? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Conductivity and molar conductivity formula? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Conductivity and molar conductivity formula?.
Solutions for Conductivity and molar conductivity formula? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Conductivity and molar conductivity formula? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Conductivity and molar conductivity formula?, a detailed solution for Conductivity and molar conductivity formula? has been provided alongside types of Conductivity and molar conductivity formula? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Conductivity and molar conductivity formula? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























