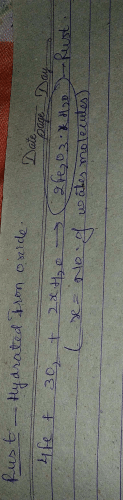Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Questions > What os chemical formula of rust?
Start Learning for Free
What os chemical formula of rust?
Verified Answer
What os chemical formula of rust?
Fe2O3
Several forms of rust are distinguishable visually and by spectroscopy, and form under different circumstances.Rust consists of hydrated iron(III) oxides Fe2O3. nH2O, iron(III) oxide-hydroxide (FeO(OH), Fe(OH)3. Rusting is the common term for corrosion of iron and its alloys, such as steel.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 10 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 10 courses
Community Answer
What os chemical formula of rust?
The Chemical Formula of Rust
Rust is a type of corrosion that occurs on iron or steel surfaces when they are exposed to oxygen and moisture for an extended period of time. The chemical formula for rust is Fe2O3, which represents a compound made up of two iron (Fe) atoms bonded to three oxygen (O) atoms. Let's delve into the details of how rust forms and the chemical reactions involved.
Formation of Rust
Rust formation involves a series of chemical reactions that occur when iron or steel is exposed to air and water. The process can be summarized as follows:
1. Oxidation of Iron: Iron reacts with oxygen in the presence of moisture to form iron(II) ions (Fe2+). This process is known as oxidation and is represented by the equation:
4Fe + 3O2 + 6H2O → 4Fe(OH)3
2. Formation of Iron(II) Hydroxide: The iron(II) ions react with water to form iron(II) hydroxide (Fe(OH)2), which is an intermediate product in the formation of rust.
2Fe(OH)3 → Fe2O3 + 3H2O
3. Oxidation of Iron(II) Hydroxide: The iron(II) hydroxide further reacts with oxygen to form hydrated iron(III) oxide, commonly known as rust.
4Fe(OH)2 + O2 → 2Fe2O3 + 4H2O
Composition of Rust
Rust is primarily composed of hydrated iron(III) oxide, Fe2O3·xH2O, where "x" represents the number of water molecules associated with each Fe2O3 unit. The presence of water in rust is crucial as it enables the oxidation process to occur. The exact composition of rust can vary depending on environmental factors such as humidity and temperature.
Visual Appearance of Rust
Rust typically appears as a reddish-brown or orange-brown flaky substance on the surface of iron or steel. It is characterized by its brittle nature and tendency to crumble easily. The formation of rust not only alters the appearance of the metal but also weakens its structural integrity.
Prevention and Removal of Rust
To prevent rust formation, protective measures such as applying paint, varnish, or a rust-resistant coating can be employed to create a barrier between the metal surface and the environment. Additionally, using galvanized steel or stainless steel, which are more resistant to corrosion, can be effective in preventing rust.
When rust has already formed, it can be removed through various methods including mechanical techniques like sanding or wire brushing, chemical treatments using rust removers or rust converters, or electrolytic rust removal processes.
In conclusion, the chemical formula for rust is Fe2O3, representing the compound iron(III) oxide. Rust formation involves oxidation of iron in the presence of oxygen and moisture, resulting in the formation of iron(II) hydroxide and subsequent conversion to rust. Understanding the chemical reactions involved in rust formation is crucial for preventing and

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
What os chemical formula of rust?
Question Description
What os chemical formula of rust? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about What os chemical formula of rust? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What os chemical formula of rust?.
What os chemical formula of rust? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about What os chemical formula of rust? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What os chemical formula of rust?.
Solutions for What os chemical formula of rust? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 10.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What os chemical formula of rust? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What os chemical formula of rust?, a detailed solution for What os chemical formula of rust? has been provided alongside types of What os chemical formula of rust? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What os chemical formula of rust? tests, examples and also practice Class 10 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.