NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Hexafluorocobaltate ( lll) is found to b high...
Start Learning for Free
Hexafluorocobaltate ( lll) is found to b high spin complex . The probable hybrid state of cobalt in it is sp3d2. Can u explain how ?
Verified Answer
Hexafluorocobaltate ( lll) is found to b high spin complex . The proba...
Biodegradable substances include food scraps, cotton, wool, wood, human and animal waste, manufactured products based on natural materials (such as paper, and vegetable-oil based soaps). See also degradable and photodegradable.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
Most Upvoted Answer
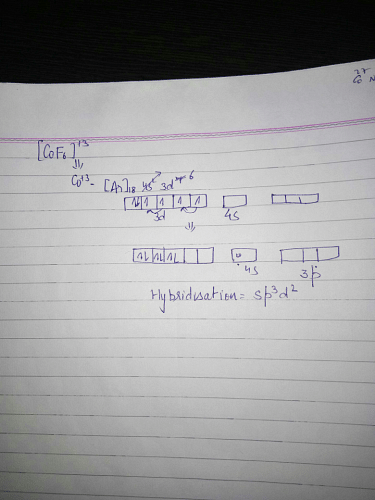
Hexafluorocobaltate ( lll) is found to b high spin complex . The proba...
Community Answer
Hexafluorocobaltate ( lll) is found to b high spin complex . The proba...
Probable Hybrid State of Cobalt in Hexafluorocobaltate (III)
The hybridization of an atom refers to the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals. In the case of cobalt in hexafluorocobaltate (III), the probable hybrid state is sp3d2. Let's explore why this is the case:
The Central Atom: Cobalt (Co)
- Cobalt is a transition metal with the electronic configuration [Ar] 3d7 4s2.
- In order to form stable compounds, cobalt undergoes hybridization to achieve a more favorable arrangement of its valence electrons.
Electronic Configuration of Cobalt in Hexafluorocobaltate (III)
- Hexafluorocobaltate (III) refers to the complex ion [CoF6]3-, where cobalt is in the +3 oxidation state.
- The 3+ charge on the cobalt ion indicates the loss of three electrons, resulting in the electronic configuration [Ar] 3d6.
- The six fluoride ions (F-) each contribute one electron, resulting in a total of six additional electrons in the complex.
Determining the Hybridization State
To determine the hybridization state of cobalt in hexafluorocobaltate (III), we need to consider the following factors:
1. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory
- VSEPR theory predicts that the arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom is determined by minimizing electron-electron repulsion.
- In the case of hexafluorocobaltate (III), the complex has an octahedral geometry, with the six fluorine atoms surrounding the central cobalt atom.
2. Ligand Field Theory
- Ligand field theory explains the behavior of transition metal complexes by considering the interaction between the metal and the ligands.
- In this case, the fluoride ions act as ligands and donate their electron pairs to the cobalt ion.
3. Crystal Field Theory
- Crystal field theory describes the splitting of d orbitals in a transition metal complex due to the presence of ligands.
- In an octahedral field, the d orbitals split into two sets of different energies: the lower energy set (t2g) and the higher energy set (eg).
4. High Spin Complex
- Hexafluorocobaltate (III) is a high spin complex, meaning that the electrons occupy the available orbitals in a way that maximizes their spin.
- In a high spin complex, the electron configuration is determined by filling the orbitals with parallel spins before pairing electrons.
- In this case, the six electrons in the 3d subshell of cobalt will occupy the available d orbitals in a high spin manner.
5. Hybridization State
- Considering the octahedral geometry, the cobalt ion will undergo hybridization to form six hybrid orbitals.
- The combination of one 3s, three 3p, and two 3d orbitals gives rise to a set of six sp3d2 hybrid orbitals.
- These hybrid orbitals will then overlap with the ligand orbitals to form sigma bonds.
Conclusion
The hybridization of an atom refers to the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals. In the case of cobalt in hexafluorocobaltate (III), the probable hybrid state is sp3d2. Let's explore why this is the case:
The Central Atom: Cobalt (Co)
- Cobalt is a transition metal with the electronic configuration [Ar] 3d7 4s2.
- In order to form stable compounds, cobalt undergoes hybridization to achieve a more favorable arrangement of its valence electrons.
Electronic Configuration of Cobalt in Hexafluorocobaltate (III)
- Hexafluorocobaltate (III) refers to the complex ion [CoF6]3-, where cobalt is in the +3 oxidation state.
- The 3+ charge on the cobalt ion indicates the loss of three electrons, resulting in the electronic configuration [Ar] 3d6.
- The six fluoride ions (F-) each contribute one electron, resulting in a total of six additional electrons in the complex.
Determining the Hybridization State
To determine the hybridization state of cobalt in hexafluorocobaltate (III), we need to consider the following factors:
1. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory
- VSEPR theory predicts that the arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom is determined by minimizing electron-electron repulsion.
- In the case of hexafluorocobaltate (III), the complex has an octahedral geometry, with the six fluorine atoms surrounding the central cobalt atom.
2. Ligand Field Theory
- Ligand field theory explains the behavior of transition metal complexes by considering the interaction between the metal and the ligands.
- In this case, the fluoride ions act as ligands and donate their electron pairs to the cobalt ion.
3. Crystal Field Theory
- Crystal field theory describes the splitting of d orbitals in a transition metal complex due to the presence of ligands.
- In an octahedral field, the d orbitals split into two sets of different energies: the lower energy set (t2g) and the higher energy set (eg).
4. High Spin Complex
- Hexafluorocobaltate (III) is a high spin complex, meaning that the electrons occupy the available orbitals in a way that maximizes their spin.
- In a high spin complex, the electron configuration is determined by filling the orbitals with parallel spins before pairing electrons.
- In this case, the six electrons in the 3d subshell of cobalt will occupy the available d orbitals in a high spin manner.
5. Hybridization State
- Considering the octahedral geometry, the cobalt ion will undergo hybridization to form six hybrid orbitals.
- The combination of one 3s, three 3p, and two 3d orbitals gives rise to a set of six sp3d2 hybrid orbitals.
- These hybrid orbitals will then overlap with the ligand orbitals to form sigma bonds.
Conclusion
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Hexafluorocobaltate ( lll) is found to b high spin complex . The probable hybrid state of cobalt in it is sp3d2. Can u explain how ?
Question Description
Hexafluorocobaltate ( lll) is found to b high spin complex . The probable hybrid state of cobalt in it is sp3d2. Can u explain how ? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Hexafluorocobaltate ( lll) is found to b high spin complex . The probable hybrid state of cobalt in it is sp3d2. Can u explain how ? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Hexafluorocobaltate ( lll) is found to b high spin complex . The probable hybrid state of cobalt in it is sp3d2. Can u explain how ?.
Hexafluorocobaltate ( lll) is found to b high spin complex . The probable hybrid state of cobalt in it is sp3d2. Can u explain how ? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Hexafluorocobaltate ( lll) is found to b high spin complex . The probable hybrid state of cobalt in it is sp3d2. Can u explain how ? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Hexafluorocobaltate ( lll) is found to b high spin complex . The probable hybrid state of cobalt in it is sp3d2. Can u explain how ?.
Solutions for Hexafluorocobaltate ( lll) is found to b high spin complex . The probable hybrid state of cobalt in it is sp3d2. Can u explain how ? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Hexafluorocobaltate ( lll) is found to b high spin complex . The probable hybrid state of cobalt in it is sp3d2. Can u explain how ? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Hexafluorocobaltate ( lll) is found to b high spin complex . The probable hybrid state of cobalt in it is sp3d2. Can u explain how ?, a detailed solution for Hexafluorocobaltate ( lll) is found to b high spin complex . The probable hybrid state of cobalt in it is sp3d2. Can u explain how ? has been provided alongside types of Hexafluorocobaltate ( lll) is found to b high spin complex . The probable hybrid state of cobalt in it is sp3d2. Can u explain how ? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Hexafluorocobaltate ( lll) is found to b high spin complex . The probable hybrid state of cobalt in it is sp3d2. Can u explain how ? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























