NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Plant mitosis is generally controlled bya)Cyt...
Start Learning for Free
Plant mitosis is generally controlled by
- a)Cytokinin
- b)Genetic make-up
- c)Cytochrome
- d)Auxin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Plant mitosis is generally controlled bya)Cytokininb)Genetic make-upc)...
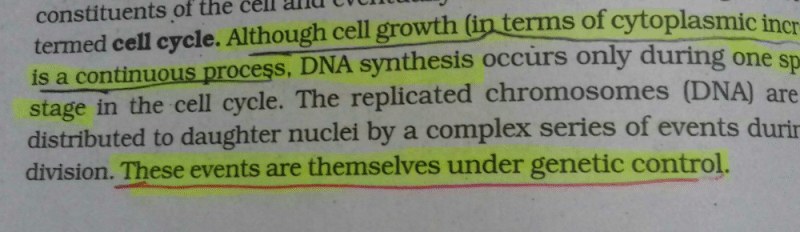
In plant cell, mitosis cell division is generally controlled by cytokinin hormone. Auxinis also required for cell division in plant.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
Most Upvoted Answer
Plant mitosis is generally controlled bya)Cytokininb)Genetic make-upc)...
Plant mitosis is generally controlled by cytokinin.
Plant mitosis is the process of cell division in plants, where a single cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells. This process is essential for plant growth, development, and reproduction. The control of plant mitosis involves various factors, including hormones, genetic make-up, and signaling molecules.
Cytokinin:
Cytokinin is a class of plant hormones that play a crucial role in regulating cell division and growth. It promotes cell division in the meristematic tissues of plants, which are responsible for continuous growth and development. Cytokinins are synthesized in the root tips, shoot tips, and developing seeds.
Role of cytokinin in plant mitosis:
Cytokinin controls plant mitosis by regulating the progression of the cell cycle. The cell cycle consists of several stages, including interphase (G1, S, G2) and mitotic phase (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase). Cytokinins primarily influence the G1 to S transition, which is the phase where the cell prepares for DNA replication.
Cytokinins stimulate the synthesis of cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), which are proteins involved in cell cycle regulation. These proteins control the progression from one phase to another by phosphorylating specific target proteins. By promoting cyclin and CDK synthesis, cytokinins accelerate the cell cycle and enhance cell division.
Cytokinins also regulate the activity of proteins called cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CKIs). CKIs inhibit the activity of CDKs, thereby slowing down the cell cycle and suppressing cell division. Cytokinins can suppress the expression of CKIs, allowing the cell cycle to proceed and promoting cell division.
In addition to their role in cell cycle regulation, cytokinins also influence other aspects of plant development, such as shoot and root growth, differentiation of tissues, and organ formation.
Conclusion:
Plant mitosis is primarily controlled by cytokinin, a plant hormone that regulates the cell cycle and promotes cell division. Cytokinins stimulate the synthesis of cyclins and CDKs, which drive the progression of the cell cycle. They also suppress the expression of CKIs, allowing the cell cycle to proceed and promoting cell division. Understanding the role of cytokinin in plant mitosis is crucial for studying plant growth and development.
Plant mitosis is the process of cell division in plants, where a single cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells. This process is essential for plant growth, development, and reproduction. The control of plant mitosis involves various factors, including hormones, genetic make-up, and signaling molecules.
Cytokinin:
Cytokinin is a class of plant hormones that play a crucial role in regulating cell division and growth. It promotes cell division in the meristematic tissues of plants, which are responsible for continuous growth and development. Cytokinins are synthesized in the root tips, shoot tips, and developing seeds.
Role of cytokinin in plant mitosis:
Cytokinin controls plant mitosis by regulating the progression of the cell cycle. The cell cycle consists of several stages, including interphase (G1, S, G2) and mitotic phase (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase). Cytokinins primarily influence the G1 to S transition, which is the phase where the cell prepares for DNA replication.
Cytokinins stimulate the synthesis of cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), which are proteins involved in cell cycle regulation. These proteins control the progression from one phase to another by phosphorylating specific target proteins. By promoting cyclin and CDK synthesis, cytokinins accelerate the cell cycle and enhance cell division.
Cytokinins also regulate the activity of proteins called cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CKIs). CKIs inhibit the activity of CDKs, thereby slowing down the cell cycle and suppressing cell division. Cytokinins can suppress the expression of CKIs, allowing the cell cycle to proceed and promoting cell division.
In addition to their role in cell cycle regulation, cytokinins also influence other aspects of plant development, such as shoot and root growth, differentiation of tissues, and organ formation.
Conclusion:
Plant mitosis is primarily controlled by cytokinin, a plant hormone that regulates the cell cycle and promotes cell division. Cytokinins stimulate the synthesis of cyclins and CDKs, which drive the progression of the cell cycle. They also suppress the expression of CKIs, allowing the cell cycle to proceed and promoting cell division. Understanding the role of cytokinin in plant mitosis is crucial for studying plant growth and development.
Community Answer
Plant mitosis is generally controlled bya)Cytokininb)Genetic make-upc)...

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Question Description
Plant mitosis is generally controlled bya)Cytokininb)Genetic make-upc)Cytochromed)AuxinCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Plant mitosis is generally controlled bya)Cytokininb)Genetic make-upc)Cytochromed)AuxinCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Plant mitosis is generally controlled bya)Cytokininb)Genetic make-upc)Cytochromed)AuxinCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Plant mitosis is generally controlled bya)Cytokininb)Genetic make-upc)Cytochromed)AuxinCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Plant mitosis is generally controlled bya)Cytokininb)Genetic make-upc)Cytochromed)AuxinCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Plant mitosis is generally controlled bya)Cytokininb)Genetic make-upc)Cytochromed)AuxinCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Plant mitosis is generally controlled bya)Cytokininb)Genetic make-upc)Cytochromed)AuxinCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Plant mitosis is generally controlled bya)Cytokininb)Genetic make-upc)Cytochromed)AuxinCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Plant mitosis is generally controlled bya)Cytokininb)Genetic make-upc)Cytochromed)AuxinCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Plant mitosis is generally controlled bya)Cytokininb)Genetic make-upc)Cytochromed)AuxinCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Plant mitosis is generally controlled bya)Cytokininb)Genetic make-upc)Cytochromed)AuxinCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Plant mitosis is generally controlled bya)Cytokininb)Genetic make-upc)Cytochromed)AuxinCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















