UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Polity for UPSC CSE > Laxmikant Summary: Law Commission of India
Laxmikant Summary: Law Commission of India | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Historical Background |

|
| Commissions Constituted So Far |

|
| Composition |

|
| Functions |

|
| Working |

|
| Role |

|
Introduction
The Law Commission of India functions as a non-statutory advisory entity, established periodically by the Central Government for a designated term. Its primary role is to propose legislative measures aimed at consolidating and codifying laws. It's important to note that although the Commission provides recommendations, these are not legally obligatory for the government to follow.
 Law Commission of India
Law Commission of India
Historical Background
- Under the British regime in the 19th century, four Law Commissions were established.
- These commissions played a significant role in enriching the Indian Statute Book.
- They made recommendations for a range of legislations, adapting the prevailing English laws to suit Indian conditions.
 Pre-independence Law Commissions
Pre-independence Law Commissions
- Key legislative contributions from these commissions include:
- Indian Penal Code
- Criminal Procedure Code
- Civil Procedure Code
- Indian Contract Act
- Indian Evidence Act
- Transfer of Property Act
- These laws, among others, are the outcomes of the work carried out by these four Commissions.
Commissions Constituted So Far
- Post-Independence, the Constitution of India introduced separate chapters on Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policy, reshaping law reform.
- Article 372 states that pre-Constitution laws remain in force until amended or repealed.
- There were calls for a new Law Commission to update outdated laws to meet changing national needs.
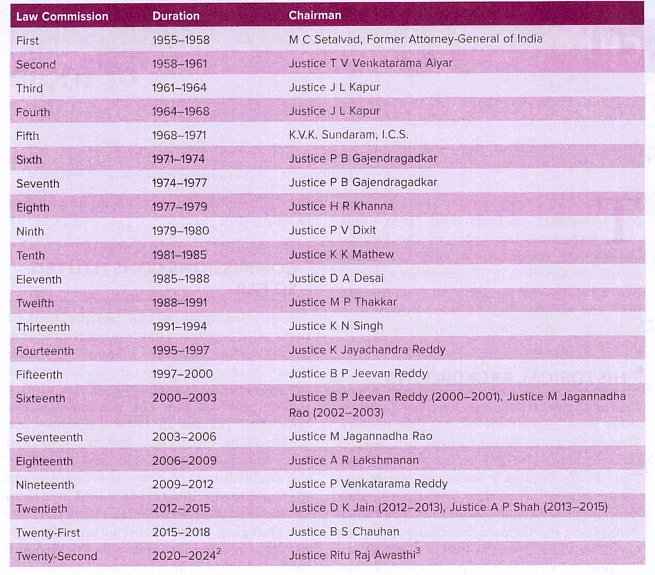 Law Commissions Appointed so far
Law Commissions Appointed so far
- In response, the government established the First Law Commission of independent India in 1955.
- Commission Head: Me Setalvad, then Attorney-General of India.
- Commission Term: Three years.
- Subsequently, twenty-one Law Commissions have been constituted since 1955, each with a three-year term and varying terms of reference.
Composition
- The composition of the Commission is not fixed, varying for each Commission based on the topics referred for consideration.
- Generally includes a Chairman, full-time members, a Member-Secretary, and part-time members.
- Chairman and full-time members can be serving or retired judges of the Supreme Court or High Courts, legal experts, jurists, or law professors.
- The Member-Secretary, from the Indian Legal Service, holds the rank of Additional Secretary or Secretary to the Government of India.

- Part-time members are appointed from eminent members of the bar, scholars in the academic field, or individuals with specialized knowledge in a specific branch of law.
- The Commission's regular staff consists of about a dozen research personnel with different ranks and varied experiences.
- A small group of secretarial staff manages the administrative side of the Commission's operations.
Functions
- Identify and recommend the immediate repeal of laws that are no longer necessary or relevant.
- Examine existing laws in the context of Directive Principles of State Policy, proposing improvements and reforms. Recommend legislations to implement Directive Principles and achieve objectives outlined in the Constitution's Preamble.
- Convey views to the Government on any law or judicial administration matter referred to by the Government.
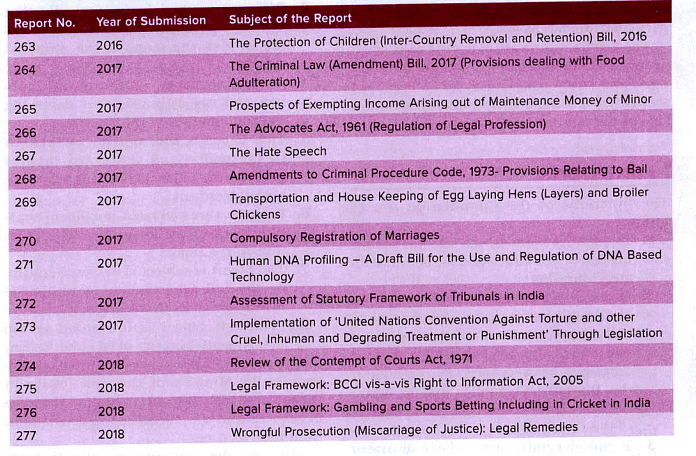 Reports submitted by the 21st Law Commission of India (2015-2018)
Reports submitted by the 21st Law Commission of India (2015-2018)
- Consider requests to provide research to foreign countries, as referred to by the Government.
- Take measures to utilize law and the legal process in the service of the poor.
- Revise Central Acts of general importance to simplify, eliminate anomalies, ambiguities, and inequities.
Working
- Projects initiated in Commission meetings.
- Priorities discussed, topics identified, and preparatory work assigned to members.
- Different methodologies adopted for data collection and research, considering the proposed reform's scope.
- A working paper, outlining the problem and suggesting reform measures, emerges as the outcome.
- The paper is circulated to the public and concerned interest groups to elicit reactions and suggestions.
 Union Minister Shri kiren Rijiju
Union Minister Shri kiren Rijiju
- Responses are evaluated, and information is organized for proper incorporation into the report.
- The report undergoes close scrutiny by the full Commission in prolonged meetings for finalization.
- The final report is forwarded to the Government (Ministry of Law and Justice).
- Commission reports are considered by the Ministry of Law and Justice in consultation with the concerned administrative ministries and are periodically submitted to Parliament.
- To date, the Commission has submitted 277 reports on various subjects.
Role
The Commission's crucial role is highlighted in the following points:
- Government benefits from specialized recommendations on different legal aspects entrusted to the Commission.
- Commission engages in legal research and reviews existing laws for proposing reforms and enacting new legislations, addressing procedural delays, expediting case disposal, and reducing litigation costs.
- Various Commissions have made a significant contribution to the progressive development and codification of the country's legal framework.
The document Laxmikant Summary: Law Commission of India | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Polity for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
170 videos|999 docs|259 tests
|
FAQs on Laxmikant Summary: Law Commission of India - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the Law Commission of India? |  |
The Law Commission of India is a statutory body established by the Indian government to recommend legal reforms and improvements in existing laws. It is responsible for conducting research, undertaking studies, and preparing reports on various legal issues for the government's consideration.
| 2. What is the historical background of the Law Commission of India? |  |
The Law Commission of India was first established in 1955, under the chairmanship of Mr. M.C. Setalvad. It was initially constituted for a period of three years but has been regularly reconstituted since then. The commission plays a crucial role in bringing reforms to the Indian legal system.
| 3. How is the Law Commission of India composed? |  |
The Law Commission of India consists of a chairman and several members, including legal experts, academicians, and eminent jurists. The chairman is usually a retired judge of the Supreme Court of India or a retired Chief Justice of a High Court. The members are appointed by the government based on their expertise and experience in the legal field.
| 4. What are the functions of the Law Commission of India? |  |
The Law Commission of India has various functions, including conducting studies and research on legal issues referred to it by the government, examining and reviewing existing laws, proposing reforms and amendments to the laws, and preparing reports on matters related to legal policy and legislation. It also advises the government on legal matters as and when required.
| 5. How does the Law Commission of India work? |  |
The Law Commission of India works by receiving references from the government on legal issues, conducting extensive research and analysis on those issues, consulting with stakeholders, and preparing reports with recommendations for legal reforms. These reports are then submitted to the government for consideration and action. The commission also engages in public consultations and seeks inputs from experts and the general public during its functioning.
Related Searches















