Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Question Answers - Our Environment
Q1: Define environment?
Ans: The biotic and abiotic factors which surrounds any living organism is considered as its environment. It can be generally defined as a community of organisms living in a particular environment and the physical elements in that environment with which they interact.
Q2: What is a food chain?
Ans: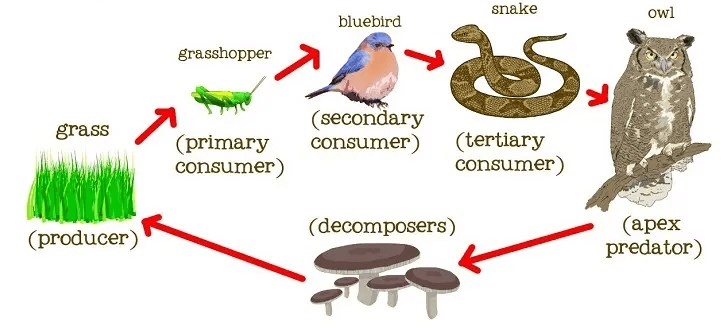 The process of eating autotrophs by herbivores and herbivores being eaten by other animals is considered as food chain.
The process of eating autotrophs by herbivores and herbivores being eaten by other animals is considered as food chain.
Q3: Define "biodegradable" and "non-biodegradable" substances. Explain the environmental impact of non-biodegradable waste. Provide examples of each type of waste and their effects on ecosystems.
Ans: Biodegradable substances are materials that can be broken down naturally by biological processes into simpler, non-harmful substances.
Non-biodegradable substances are materials that persist in the environment for long periods and do not degrade easily. The environmental impact of non-biodegradable waste is significant and has far-reaching consequences. 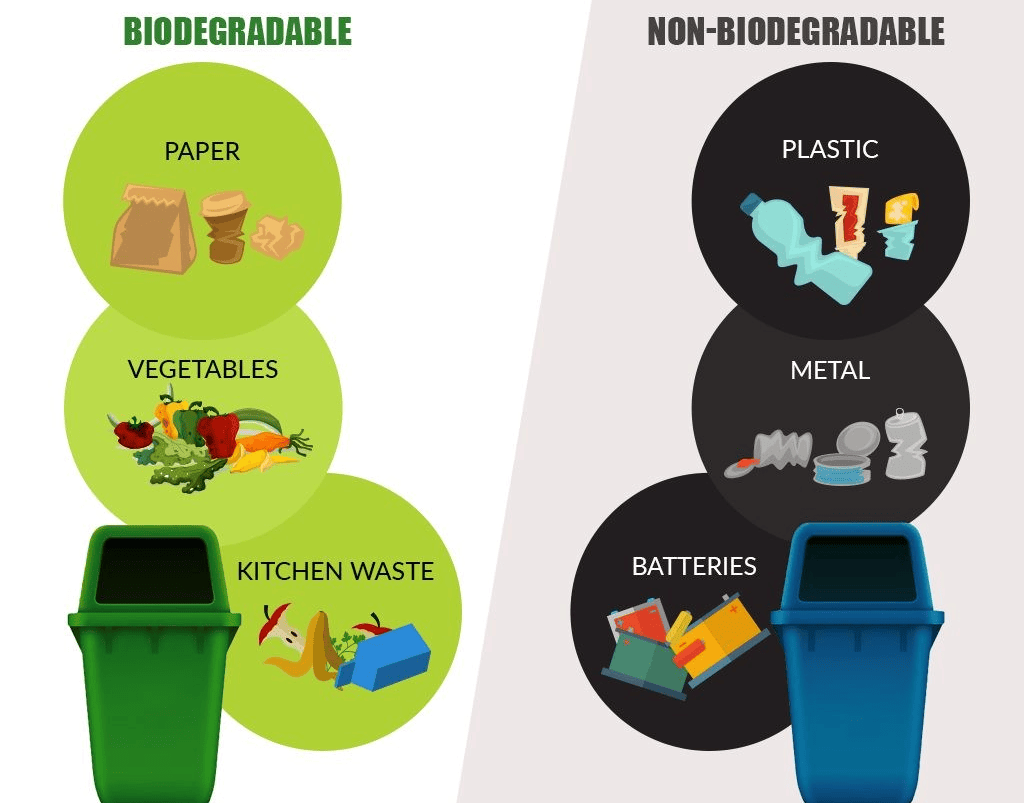 Environmental Impact of Non-Biodegradable Waste:
Environmental Impact of Non-Biodegradable Waste:
i. Accumulation: Non-biodegradable waste, such as plastics and synthetic materials, accumulates in the environment, leading to pollution and aesthetic degradation.
ii. Soil and Water Contamination: Non-biodegradable waste can leach harmful chemicals into soil and water, affecting the quality of these resources.
iii. Wildlife Harm: Animals may ingest or become entangled in non-biodegradable waste, causing injury or death. Marine animals are particularly vulnerable to plastic pollution.
iv. Microplastic Formation: Non-biodegradable plastics break down into microplastics, which can enter the food chain and have adverse effects on ecosystems and human health.
Examples of Biodegradable and Non-Biodegradable Waste:
Biodegradable: Food waste, paper, wood, organic matter. These materials break down naturally, contributing to nutrient cycles.
Non-Biodegradable: Plastics, synthetic fibers, glass, metal, certain chemicals. These materials persist in the environment, causing pollution and harm.
Q4: What is pollution?
Ans: Pollution is the introduction of substances (or energy) that cause adverse changes in the environment and living entities.
Q5: Explain the effects of human activity on the environment?
Ans: Any type of change that people make in our environment affects the animals, plants and the land. Some changes are helpful. Some may be harmful to the environment. 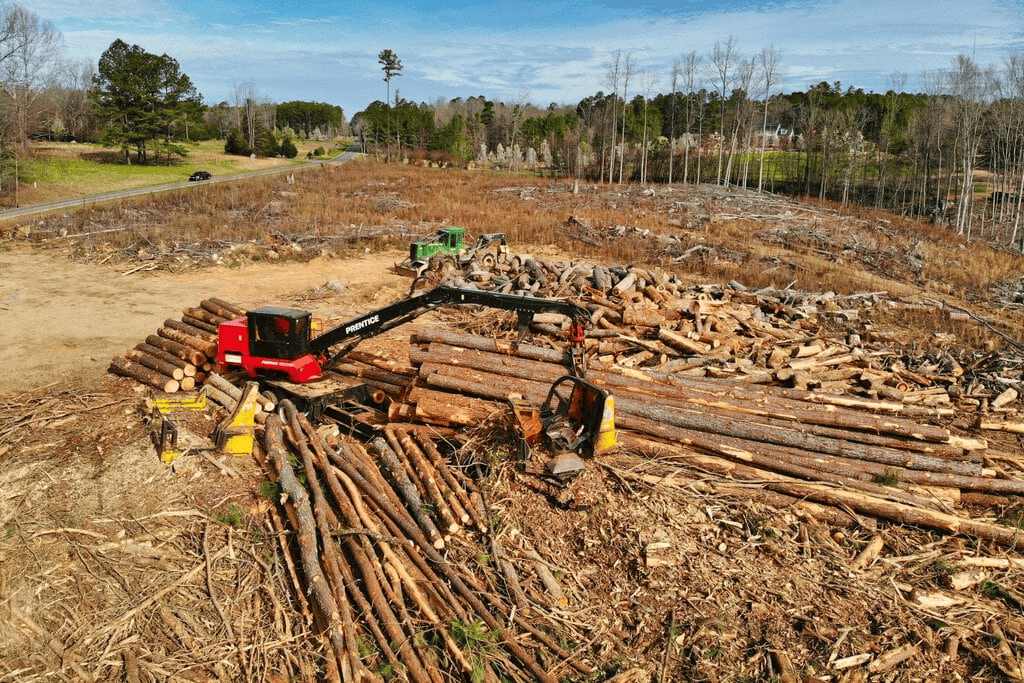 Clearing land for farming, construction of homes, roads, and shopping centers is helpful to people, but animal habitats and plants may be destroyed. Clearing of land may result in soil erosion and the eventual loss of topsoil.
Clearing land for farming, construction of homes, roads, and shopping centers is helpful to people, but animal habitats and plants may be destroyed. Clearing of land may result in soil erosion and the eventual loss of topsoil.
Q6: We often observe domestic waste decomposing in the bylanes of residential colonies. Suggest ways to make the residents realise that the improper disposal of their waste is harmful to the environment.
Ans: Some of the ways to make people realise that the improper disposal of waste is harmful to the environment includes making people aware of negative impacts of waste disposal. They can be made aware by:
(i) Conducting seminars about the negative effects of the wastes on environment.
(ii) Usage of pamphlets and posters for providing information.
(iii) Forming an eco-club in the society for spreading awareness about the ill effects of waste on the surroundings such as :
- Improper disposal of waste will release harmful gases in the environment that make it unclean and unhygienic for the living organisms.
- The waste will flow to water bodies along with rainwater and become a threat to aquatic life and pollute the water bodies.
- It provides space for breeding of the mosquitoes and which results in spread of malaria, filariasis, dengue, etc.
- Hazardous chemicals from wastes get into the soil and can harm the plants when they take up the contamination through their roots. This will affect the health of other animals and humans and will have negative impact on environment.
Q7: What are the after-effects of ozone depletion?
Ans: 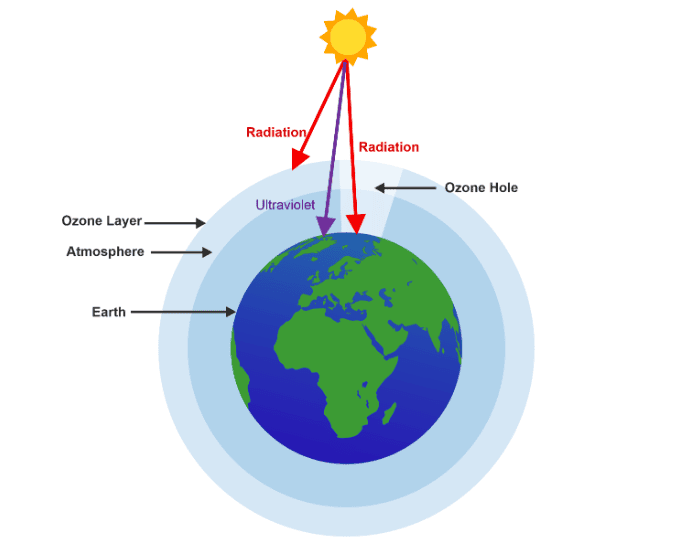 Ozone depletion will create holes in the stratosphere, which will allow the UV rays to enter the earth. The UV ray that reaches the skin can cause disastrous effect.
Ozone depletion will create holes in the stratosphere, which will allow the UV rays to enter the earth. The UV ray that reaches the skin can cause disastrous effect.
Q8: Why is it necessary to manage our garbage?
Ans: Healthy living requires a clean surrounding hence it is very essential to dispose our garbage in a proper way. Proper managing of our garbage can keep us free from much communicable disease.
Q9: What happens when higher energy ultraviolet radiations act on the oxygen at the higher level of the atmosphere?
Ans: When high energy ultraviolet radiations react with oxygen present in stratosphere (the higher level of atmosphere) it splits into its constituent atoms. Since these atoms produced are very reactive, they react with molecular oxygen (O2) to form ozone (O3).
Q10: What are the advantages of cloth bags over plastic bags during shopping?
Ans: Cloth bags are better than the plastic bags because they:
- can be used to carry many things
- can be reused
- are made of biodegradable materials
- do not pollute the environment.
Q11: Why does following a vegetarian diet help us obtain more energy?
Ans:
A vegetarian diet helps us obtain more energy because it involves consuming food directly from plants, which are the primary producers in the food chain. Plants convert sunlight into chemical energy through photosynthesis, making them the most direct and efficient source of energy available to consumers.
According to the 10 percent energy transfer rule, only about 10% of the energy stored in one trophic level is passed on to the next level. For example, when a herbivore eats a plant, only about 10% of the plant's energy is transferred to the herbivore. Similarly, when a carnivore eats the herbivore, it again receives only about 10% of the herbivore's energy. This means that as we move up each level in the food chain, there is a significant reduction in the amount of available energy.
By following a vegetarian diet, we consume food directly from the first trophic level (plants). Since plants retain the highest amount of energy derived from the sun, eating them allows us to receive more of that energy with minimal loss.
In contrast, a non-vegetarian diet involves consuming animals that are further up the food chain, where energy has already been lost at each step due to metabolic processes, heat, and waste.
Therefore, eating a vegetarian diet keeps us closer to the original source of energy, providing us with a greater amount of available energy compared to diets that rely on consuming animals. This higher energy availability can result in improved energy levels and more efficient use of resources within an ecosystem.
Q12:
(a) From the following group of organisms create a food chain which is most advantageous for human beings in terms of energy.
Hawk, Rat, Cereal plant, Goat, Snake, Human being
(b) State the possible disadvantage if the cereal plant is growing in soil rich in pesticides.
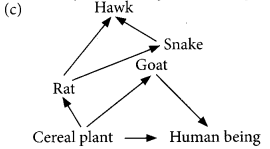
(c) Construct a food web using the organisms mentioned above.
Ans:
(a) A food chain which is most advantageous for human beings in terms of energy is:
Cereal plant → Human being
(b) If the cereal plant is growing in soil rich in pesticides, these pesticides are absorbed by growing plants along with water and minerals, when animals eat these cereal plants, these poisonous chemical pesticides go into their bodies through food. This increase in concentration of harmful pesticides in the body of living organisms at each trophic level of a food chain is called biological magnification. Pesticides are lethal to non-target species also. The extensive use of pesticides in agriculture can change the community of microorganisms living in soil.
Q13: What is meant by trophic level in a food chain? Construct a terrestrial food chain with trophic levels. The energy flow in a food chain is always unidirectional. Why?
Ans: The various steps representing organisms in a food chain at which the transfer of food and energy takes place are called trophic levels.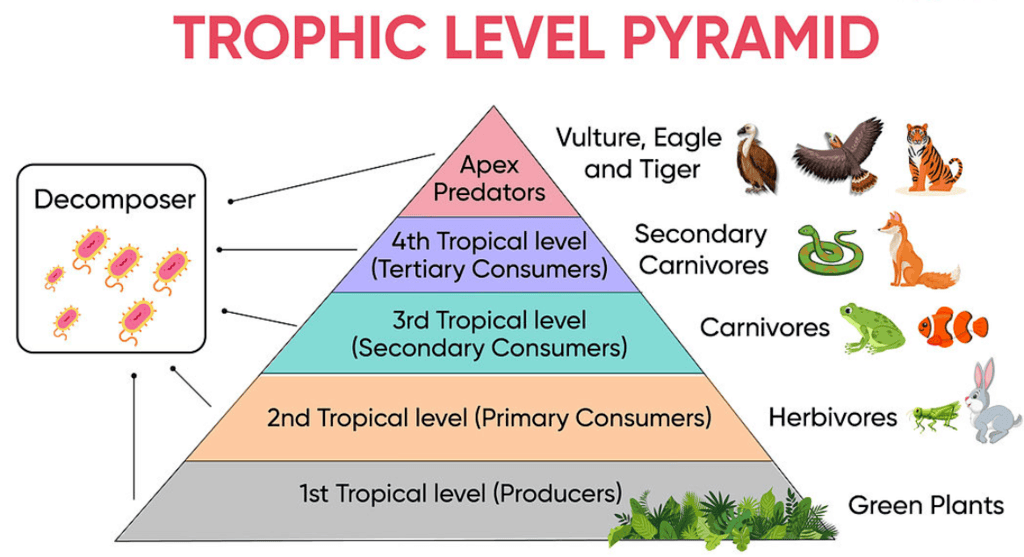 Four trophic levels in a terrestrial food chain:
Four trophic levels in a terrestrial food chain:
Grass → Rabbit → Wild cat → Tiger
There is a unidirectional flow of energy from sun to producers and subsequenty to series of different types of consumers, i.e.,
Solar radiations → Producers → Herbivores → Carnivores
It cannot pass in reverse direction, there is always a decrease in the flow of energy and content with rise in trophic level. Large quantity of energy is lost at each step in the form of heat and is also used up in various metabolic activities.
Q14: Describe how decomposers facilitate recycling of matter in order to maintain balance in the ecosystem.
Ans: Decomposers are micro-organisms that obtain energy from the chemical breakdown of dead organisms of animals or plants. These micro-organisms breakdown the complex organic substances of dead organisms into simple inorganic substances that go into the soil and are used up once more by the plants. Decomposers thus, help in recycling of matter.
Q15: What will happen if we kill all the organisms in one trophic level?
Ans: If we kill all the organisms in one trophic level, the following effects will take place:
- The population of organisms in previous trophic level will increase.
- The organisms in next trophic level will not be able to get the food, so they will migrate to some other ecosystem or die.
- It will cause an ecological imbalance in the food chain.
Q16: How is ozone formed in the higher level of the atmosphere? “Damage to ozone layer is a cause of concern”. Justify this statement.
Ans: Ozone is formed due to action of UV rays on oxygen molecules to form free oxygen atom which subsequently combines with another molecule of oxygen to form ozone. The reaction is: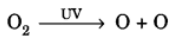
O + O2 → O3 (Ozone)
Ozone depletion is a cause of concern because it protects us from the harmful ultraviolet radiations of the Sun by absorbing them. The UV rays can cause skin cancer, ageing, cataract, etc. to human beings if they are not absorbed by ozone due to ozone depletion.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Question Answers - Our Environment
| 1. How does pollution impact our environment? |  |
| 2. What are some ways to reduce our carbon footprint? |  |
| 3. Why is recycling important for the environment? |  |
| 4. How does deforestation contribute to climate change? |  |
| 5. What are the effects of plastic pollution on marine life? |  |






















