International Relations: February 2025 UPSC Current Affairs | UPSC Mains: International Relations PDF Download
Paris AI Summit 2025

Why in News?
The Prime Minister (PM) of India visited France to co-chair the Paris Artificial Intelligence (AI) Action Summit 2025. Additionally, the 2nd India-France AI Policy Roundtable took place alongside the summit.
Key Takeaways
- The AI Action Summit serves as a global platform for world leaders, policymakers, technology experts, and industry representatives to discuss AI governance, ethics, and societal impacts.
- This summit in Paris marks the third edition following the Bletchley Park Summit (UK 2023) and the Seoul Summit (South Korea 2024).
Additional Details
- Bletchley Park Declaration: Comprising 28 countries, it advocated for safe, human-centric, and responsible AI.
- The declaration from 27 nations reaffirmed international cooperation and proposed the establishment of a network of AI Safety Institutes.
Key Outcomes of the Paris Artificial Intelligence (AI) Summit 2025
- Joint Declaration on Inclusive and Sustainable AI: A statement titled ‘Inclusive and Sustainable Artificial Intelligence for People and the Planet’ was signed by 58 countries, including India and China, but notably excluding the US and UK.
- Public Interest AI Platform and Incubator: Launched to foster collaboration between public and private sectors, aiming to create a trustworthy AI ecosystem through enhanced data capacity, transparency, and funding.
- Human-Centric AI and Global Priorities: The summit stressed the importance of ethical AI that safeguards human rights while addressing inequalities driven by AI.
- Global priorities highlighted included AI accessibility, transparency, job creation, sustainability, and international governance.
- It emphasized bridging the digital divide, ensuring AI safety, promoting green AI, and fostering global cooperation.
- Alignment with Existing Multilateral AI Initiatives: It focused on aligning with global frameworks such as UN General Assembly Resolutions, UNESCO AI Ethics Recommendations, and strategies from the African Union, OECD, G7, and G20.
- India’s Stance: India promoted open-source and sustainable AI, emphasizing clean energy and workforce upskilling, aiming to establish itself as the central platform for responsible AI development as the 2024 lead chair of the Global Partnership on AI (GPAI).
Key Outcomes of the 2nd India-France AI Policy Roundtable
- AI Governance & Ethics: The discussions emphasized equitable benefit-sharing, techno-legal frameworks, and AI safety.
- Topics included Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for AI, foundation models, global governance, and AI's role in addressing global challenges.
- Cross-Border AI Collaboration: There was a focus on data sovereignty, interoperable AI infrastructure, and the need for mechanisms to address cross-border data flow issues.
- AI for Global Challenges: The integration of AI in multilingual models and federated computing was discussed, along with the promotion of energy-efficient AI models and responsible computing practices to mitigate AI's high energy footprint.
Challenges Related to the Development of AI
- High Energy Consumption: AI's energy demands could escalate data centers' power consumption from 1-2% to 3-4% by 2030, potentially reaching 21% of global energy needs. The rise in energy demand is projected to incur a social cost of USD 125-140 billion due to increased carbon emissions.
- For context, a ChatGPT query reportedly uses ten times more energy than a Google search, and AI data centers may consume as much electricity as India's total current consumption (1,580 terawatt-hours).
- People-Centric AI vs. AI-Centric Development: Balancing ethical, inclusive AI with automation-driven development remains a challenge, with concerns over job loss and data privacy risks.
- Insecure and Low-Cost AI Models: Models like DeepSeek pose risks of data breaches, misinformation, and cybersecurity threats. Weak regulatory oversight exacerbates bias and security issues, necessitating robust governance.
Way Forward
- Sustainable AI Infrastructure: Promote energy-efficient AI models, utilize renewable-powered data centers, and optimize algorithms to reduce carbon footprints.
- Encourage green computing and smart grids driven by AI to enhance sustainability.
- Ethical and Inclusive AI Policies: Ensure equity, transparency, and accountability in AI, focusing on data privacy, bias mitigation, and algorithmic fairness.
- Strengthening AI Regulations and Security: Implement strict oversight on AI models, particularly those that are insecure, to combat cyber threats and misinformation.
- Capacity Building and Workforce Readiness: Enhance AI education, skilling programs, and research institutions to mitigate job displacement and build a skilled workforce.
- AI for Public Good: Leverage AI in sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, governance, and disaster management to foster economic and social progress while minimizing associated risks.
The Paris AI Summit 2025 highlighted the crucial need for international collaboration and ethical governance in utilizing AI technologies, addressing both the potential benefits and the significant challenges they pose.
World Economic Forum Annual Meeting 2025

Why in News?
The 2025 World Economic Forum (WEF) took place in Davos, Switzerland, where global leaders convened to address urgent global issues under the theme “Collaboration for the Intelligent Age.”
Key Takeaways
- Sustainability: The meeting emphasized that sustainability is crucial for business resilience, advocating that companies should align their growth strategies with global sustainability goals to achieve both profitability and societal impact.
- Emerging Technologies: The discussions highlighted the dual nature of Artificial Intelligence and green technologies, presenting both opportunities and challenges. Establishing responsible AI frameworks and maintaining an ethical balance with progress are essential for improving supply chains, reducing emissions, and enhancing transparency.
- Partnerships: It was stressed that addressing global challenges necessitates multi-sectoral partnerships to develop impactful solutions, with the potential to unlock USD 12 trillion in market opportunities by 2030.
- Climate Action: The need for urgent climate action was highlighted, ensuring that decarbonization efforts include a fair transition for workers and communities.
Additional Details
- India at the 2025 WEF: India secured over Rs 20 lakh crore in investment commitments, with Maharashtra receiving nearly 80% of the total funding.
- States' Contributions:
- Telangana: Secured Rs 1.79 lakh crore in investment.
- Kerala: Focused on its industrial transformation.
- Uttar Pradesh: Outlined its vision to become a USD 1 trillion economy by 2029 with a goal of zero poverty.
In summary, the 2025 WEF underscored the interconnectedness of sustainability, technology, and collaborative efforts in addressing global challenges. The emphasis on responsible practices and significant investment commitments indicates a proactive approach towards future growth and climate responsibility.
India-UK Agreements in Aero India 2025

Why in News?
India and the United Kingdom (UK) have signed several defence agreements aimed at enhancing their defence cooperation. Additionally, the recent India-UK Energy Dialogue focused on establishing a sustainable, resilient, and inclusive energy future.
Key Takeaways
- Defence Partnership Initiative (DP-I) aims to bolster bilateral defence collaboration.
- Contract for supplying Laser Beam Riding MANPADs (LBRM) has been established, starting with High Velocity Missiles (STARStreak) launchers.
- India's first Advanced Short-Range Air-to-Air Missile (ASRAAM) assembly facility will be set up in Hyderabad.
- Integrated Full Electric Propulsion System (IFEP) development for India's next-gen Landing Platform Dock (LPD) fleet is agreed upon.
- The second phase of the ASPIRE programme supports 24/7 power supply and industrial energy efficiency.
Additional Details
- Defence Partnership Initiative (DP-I): Launched to enhance bilateral defence collaboration, focusing on technology transfer and joint exercises.
- ASPIRE Phase-2: An initiative to accelerate smart power and renewable energy in India, ensuring reliability and promoting decarbonization.
- Trade Relations: India was the UK's 11th largest trading partner in 2024, with bilateral trade valued at £42 billion.
- Education Cooperation: Mutual Recognition of Academic Qualifications signed in July 2022 facilitates academic exchanges, with Indian student enrollments in UK universities reaching 185,000 in 2022-23.
- People-to-People Ties: The Migration and Mobility Partnership (MMP) facilitates professional movement, while the Young Professional Scheme allows graduates to work and live in each country for two years.
In conclusion, India and the UK are significantly deepening their strategic partnership in defence and clean energy through various agreements and collaborative initiatives. These efforts are aligned with India's goals for self-reliance and contribute to mutual economic benefits while promoting global sustainability and security.
Mains Question
Q: Analyse the importance of international cooperation for achieving self-reliance in defence technology.
India-Sri Lanka Fishing Dispute
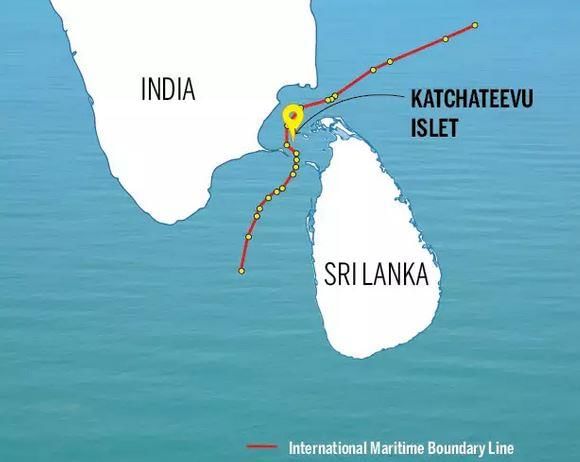
Why in News?
The Sri Lankan Navy recently apprehended several Indian fishermen for illegally fishing in the Palk Bay, which is considered Sri Lankan waters. This incident has reignited the longstanding fishing dispute between India and Sri Lanka. Notably, in 2024, the number of Indian fishermen arrested in Sri Lanka surpassed 500 for the first time in a decade, highlighting the escalating tensions.
Key Takeaways
- The dispute is marked by recurrent arrests of Indian fishermen entering Sri Lankan waters.
- Historical fishing rights beyond the International Maritime Boundary Line (IMBL) claimed by Indian fishermen lead to frequent clashes.
- Overfishing and environmental concerns, particularly bottom trawling, exacerbate tensions.
- Sri Lanka's national security concerns include potential threats from Tamil militant groups.
Additional Details
- Recurrent Arrests: Indian fishermen often stray into Sri Lankan waters due to engine failures or sudden weather changes, resulting in arrests and the destruction of their fishing vessels.
- Violation of IMBL: The IMBL divides the Palk Bay between India and Sri Lanka, but fishing rights are contested, with Indian fishermen asserting historical rights to fish in these areas.
- Depletion of Fish Stocks: Overfishing on the Indian side compels fishermen to enter Sri Lankan waters, which the Sri Lankan government views as poaching, threatening local livelihoods.
- Bottom-Trawling: Sri Lanka opposes the environmentally harmful fishing method of bottom trawling employed by Indian fishermen, advocating for sustainable fishing practices.
- Political Ramifications: Allegations against the Sri Lankan Navy's actions have led to diplomatic tensions, influencing India's stance on Sri Lanka's human rights issues.
- Economic Consequences: The estimated annual loss for Sri Lanka due to Indian poaching stands at USD 730 million, highlighting the economic implications of the dispute.
The fishing conflict between India and Sri Lanka poses significant challenges, including livelihood issues for fishermen, enforcement difficulties, and environmental degradation. Effective resolution measures, including enhanced maritime regulation enforcement and alternative livelihood programs, are essential for sustainable management of marine resources in the region.
US Agency for International Development

Why in News?
The recent decision by President Donald Trump to impose a 90-day freeze on foreign aid has led to the suspension of programs managed by the US Agency for International Development (USAID) globally. Additionally, the US will not participate in the 2025 G20 Foreign Ministers' meeting scheduled to take place in Johannesburg, South Africa.
Key Takeaways
- USAID is the primary agency for US global humanitarian and development assistance.
- In 2024, USAID received an allocation of USD 44.2 billion, constituting only 0.4% of the total US federal budget but representing 42% of all humanitarian aid tracked by the UN.
- Top recipients of USAID aid include Ukraine, Ethiopia, Jordan, Somalia, and Afghanistan.
Additional Details
- What is USAID? USAID focuses on providing global humanitarian and development assistance, funding areas such as healthcare, food aid, disaster relief, and policy advocacy.
- USAID and India: India has been associated with USAID since 1951, starting with the India Emergency Food Aid Act. The relationship has evolved from food aid to infrastructure development, capacity building, and economic reforms, with a focus on education, immunization, polio eradication, and HIV/TB prevention. In the past decade, India has received approximately USD 1.5 billion from USAID, representing about 0.2% to 0.4% of USAID's total global funding.
- The implications of the US's aid freeze are significant for India. As India positions itself as a bridge between the Global North and South, a reduction in US involvement in the G20 could allow China and Russia to increase their influence, potentially altering global economic dynamics and affecting India's standing.
- While financial aid from USAID has decreased, contributions still exceeded USD 50 million in 2024. A permanent funding cut may impact crucial health initiatives in India, such as vaccination programs and infectious disease control, necessitating a reallocation of domestic resources to maintain health, environmental, and governance projects.
India-Bhutan Ties and Subnational Diplomacy

Why in News?
Following the King of Bhutan visit to India, both countries committed to strengthening India and Bhutan ties in which Subnational diplomacy by states like Assam can further strengthen economic and cultural relations.
What were the Key Outcomes of the Visit?
- Strengthened Cooperation: Bhutan expressed gratitude for India’s continued support for its 13th Five Year Plan (2024-29) and for India's contributions to Bhutan’s Economic Stimulus Programme.
- Economic Development: India has assured continued support for the Mindfulness City project, a sustainable economic hub.
- Hydropower Cooperation: Significant progress has been made in the 1020 MW Punatshangchhu-II hydro project and both countries agreed to expedite the completion of the Punatsangchhu-I project.
- Cross-Border Connectivity: The Integrated Check Post (ICP) at Darranga, Assam, was inaugurated to boost tourism and economic activities in Bhutan's eastern region and Assam's border areas.
|
88 videos|124 docs
|





















