International Relations: September 2025 Current Affairs | Current Affairs & General Knowledge - CLAT PDF Download
China’s WTO Concession and Implications for India

Why in News?
China has announced at the UN General Assembly that it will no longer pursue Special and Differential Treatment (SDT) in future World Trade Organization (WTO) negotiations. This marks a significant shift in global trade dynamics and arises in the context of increasing US tariff pressures and criticism regarding the exploitation of SDT provisions. This development has direct implications for India, which heavily relies on SDT flexibilities to protect its agricultural and social welfare priorities.
Key Takeaways
- China's decision is a tactical retreat while preserving its developing country status.
- India's reliance on SDT is critical for safeguarding its agricultural interests and vulnerable populations.
- The shift could impact India's agricultural subsidies and food security measures.
Additional Details
- Special and Differential Treatment (SDT): These are provisions in WTO agreements that provide developing countries and Least Developed Countries (LDCs) with special rights and favorable treatment in trade negotiations. This includes longer implementation periods and preferential market access to help them participate effectively in global trade.
- Impact of China's Decision: While China’s move has been hailed as a reform by the WTO, many view it as a way to deflect criticism without relinquishing its agricultural and industrial advantages.
- External Pressures on India: With the US imposing tariffs on various goods, there are growing calls for India to abandon its developing country status, which it has relied upon for higher tariffs and compliance flexibilities.
- Agricultural Importance: Agriculture is crucial for India, employing around half of its workforce and ensuring food security for 1.4 billion citizens. India utilizes exemptions to subsidize low-income farmers, which is at risk due to potential phased reductions in subsidies.
- Global Hypocrisy: Developed nations have provided substantial subsidies to their own agricultural sectors, while criticizing India's support mechanisms, highlighting a disparity in global trade practices.
- Strategic Options for India: India needs to lead initiatives like the G33 coalition to protect its agricultural interests while also engaging in e-commerce talks and reforming its SDT framework to maintain essential protections.
In conclusion, while India faces increasing pressure to reduce its dependence on SDT, its demographic and developmental challenges necessitate a cautious approach. A well-calibrated strategy can ensure food security and enhance global competitiveness. By proactively engaging in WTO reforms, India can position itself as a key player in balancing growth and equity in international trade.
India-Pak Ties Through the Prism of the Indus Treaty

Why in News?
Recently, India has called for a review and renegotiation of the Indus Waters Treaty (IWT) and has suspended this 65-year-old agreement in light of the April Pahalgam terror attack. The issue of water sharing is becoming increasingly contentious, akin to topics like terrorism and Kashmir in India-Pakistan relations. Much of the discussion surrounding this topic has been driven by emotion rather than factual analysis.
Key Takeaways
- The Indus Waters Treaty allocates 80% of the Indus system's waters to Pakistan, a decision that has drawn criticism in India.
- India's then PM Nehru viewed the Treaty as a step towards peaceful coexistence, while critics argue it represents appeasement.
- Both nations have expressed dissatisfaction with the Treaty due to differing perspectives.
- Pakistan's actions often reflect insecurities regarding water control linked to its Kashmir agenda.
Additional Details
- Indus Waters Treaty (IWT): The Treaty comprises an agreement that gives India rights over eastern rivers while limiting its use of western rivers. This arrangement has been a point of contention, with Pakistan leveraging the Treaty’s dispute mechanisms to challenge Indian projects in Jammu and Kashmir.
- The enduring nature of the IWT is attributed to India's role as the upper riparian state, which has a significant impact on Pakistan, unlike the reverse situation.
- Experts suggest that had Pakistan been the upper riparian, the IWT might not have survived the numerous crises, including four wars and ongoing hostility.
- Despite its favorable terms under the IWT, Pakistan is resistant to any renegotiation, fearing it may weaken its position.
- India prioritizes the completion of water projects in Jammu and Kashmir, signaling its readiness to utilize its rights without disrupting flows.
- The Indus Waters Treaty remains a crucial aspect of India-Pakistan relations, with both countries needing to navigate their interests and insecurities regarding water resources.
- The ongoing discussions and potential renegotiations could reshape their bilateral ties amidst broader geopolitical concerns.
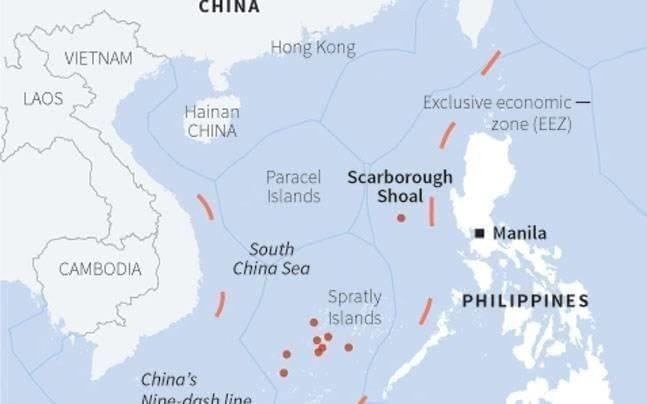
Scarborough Shoal in South China Sea
Why in News?
Recently, China's State Council has approved the establishment of a national nature reserve at Scarborough Shoal, known as Huangyan Dao in Chinese and Bajo de Masinloc or Panatag Shoal in the Philippines. This decision has significant implications for regional geopolitics and international relations.
Key Takeaways
- Scarborough Shoal is located approximately 200 km from Luzon (Philippines) and over 800 km from Hainan (China).
- The area is uninhabited yet strategically important, situated near vital shipping lanes that facilitate over $3 trillion in trade annually.
- The lagoon in Scarborough Shoal provides shelter for boats, while the surrounding waters are rich in fish stocks crucial for the local communities in Zambales and Pangasinan.
Additional Details
- Sovereignty Claims: Both China and the Philippines assert ownership over Scarborough Shoal, leading to ongoing tensions.
- 2016 Arbitration Ruling: The Permanent Court of Arbitration in The Hague deemed China's nine-dash line claim invalid, recognizing Scarborough as a traditional fishing ground under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS). However, China has rejected this ruling.
- Philippines' Position: The Philippines argues that Scarborough Shoal lies within its Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), rendering China's reserve declaration "illegitimate and unlawful."
- International Response: Nations such as the US, Japan, Australia, and Canada have conducted naval patrols and drills in support of the Philippines and to uphold freedom of navigation in the contested waters.
This situation at Scarborough Shoal underscores the complexities of territorial disputes in the South China Sea, involving historical claims, international law, and geopolitical strategies that affect regional stability.
France Recognises Palestine: Implications for Israel and Gaza War

Why in News?
Recently, at the UN General Assembly, France, alongside the UK, Canada, Australia, and several European nations, recognized the statehood of Palestine. This decision has been met with strong criticism from Israel, which views it as a reward for terrorism.
Key Takeaways
- The recognition of Palestine impacts diplomatic relations but has minimal immediate effects on the ongoing Gaza conflict.
- Israel continues military operations despite growing international support for Palestine.
- Palestinian statehood remains contested due to Israeli occupation and lack of defined territory.
- India has a longstanding commitment to supporting Palestinian statehood.
Additional Details
- Impact of Palestine Recognition: The growing recognition of Palestinian statehood adds diplomatic pressure on Israel but does not alter the current situation in Gaza. Israel's offensive continues, as Prime Minister Netanyahu has stated that the war will persist regardless of any hostage releases.
- International Dynamics: While some European countries are limiting military exports to Israel, the US has reaffirmed its support, recently approving $6.4 billion in arms sales. Germany also plays a significant role, together with the US, supplying over 90% of Israel’s defense imports.
- Criteria for Statehood: According to the 1933 Montevideo Convention, statehood requires defined territory, a permanent population, a government, and the capacity for international relations. Palestine struggles with these criteria due to Israeli occupation.
- Territory Status: Palestinian territories, including the West Bank, East Jerusalem, and Gaza, are largely controlled by Israel, complicating the prospect of sovereignty.
- Population Impact: The ongoing Gaza war has caused significant loss of life, with estimates of over 65,000 deaths and widespread famine, severely threatening the population's survival.
- Governance Issues: The Palestinian Authority governs limited areas in the West Bank, while Hamas controls Gaza, leading to challenges in governance and calls for reform.
- International Recognition: Although Palestine has gained global recognition, effective control over land and governance remains compromised, limiting its diplomatic engagement to lobbying efforts.
- Israel's Response: In reaction to increasing global recognition of Palestine, Israel has intensified military operations, with Netanyahu asserting that a Palestinian state "will never be established."
- India's Support: India has shown consistent support for Palestine, being the first non-Arab state to recognize the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) in 1974 and supporting its status at various international forums.
- Policy Approach: India advocates for a negotiated two-state solution, aiming for a sovereign and independent Palestinian state alongside Israel, with East Jerusalem as its capital, based on pre-1967 borders.
In conclusion, while the recognition of Palestine by France and other nations signals moral support, its practical implications for the ongoing Gaza war and the quest for a peaceful resolution remain limited, particularly given the current geopolitical dynamics.
India-EFTA Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement (TEPA) - A Strategic Leap Forward

Why in News?
The recent signing of the Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement (TEPA) between India and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA), which includes Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein, marks India's first comprehensive trade pact with advanced European economies. This agreement represents a significant advancement in India's global trade diplomacy.
Key Takeaways
- Investment of approximately $100 billion over 15 years, aimed at creating up to 1 million direct jobs in India.
- Elimination or reduction of tariffs on 92.2% of tariff lines, impacting 99.6% of India's exports by value.
- Boost for key sectors such as textiles, gems and jewellery, organic chemicals, and industrial goods.
- Commitments from EFTA across various service sectors, enhancing collaboration in numerous fields.
Additional Details
- Investment and Job Creation: EFTA's commitment to invest $100 billion will enhance India's attractiveness as a long-term investment destination.
- Market Access: The agreement will provide duty-free treatment for all non-agricultural products, benefitting multiple sectors.
- Strategic Collaborations: EFTA's strengths in precision engineering, pharmaceuticals, and renewable energy align with India's technological needs.
- Climate Goals: TEPA supports India's aim for net-zero emissions by 2070, offering access to European green finance and technology.
- Nuclear Energy Potential: India's significant thorium reserves present opportunities for developing safe and clean thorium-based nuclear energy.
In conclusion, TEPA transcends a mere trade agreement; it establishes a strategic partnership encompassing trade, investment, technology, and sustainability. By leveraging European expertise and capital alongside India's demographic advantages, TEPA sets a new standard for global cooperation and paves the way for a more energy-secure, innovation-driven, and climate-resilient India.
Let Griger counters, not guesses, shape Iran Actions

Why in News?
The nuclear issue has resurfaced as a critical topic in global geopolitics, particularly following the U.S. strikes on Iran's Fordow nuclear site in June 2025. In response to Iranian violations of the 2015 nuclear deal, the E3 countries (Britain, France, Germany) invoked the "snapback" clause, which could reinstate stringent UN sanctions. The situation is exacerbated by the withdrawal of International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) staff from Iran, creating a void of verified information. In this context, it is essential that diplomacy is based on verification rather than speculation.
Key Takeaways
- The snapback clause has been triggered for the first time since 2015, raising the potential for renewed UN sanctions.
- The lack of IAEA verification has led to a vacuum of reliable information, increasing risks across global markets and regional stability.
- India faces significant challenges related to oil supply and the safety of its citizens in West Asia amidst the unfolding crisis.
Additional Details
- Importance of IAEA Verification: Access by the IAEA replaces speculation with factual data, establishing a foundation for diplomatic negotiations.
- Market Stability: IAEA oversight in conflict zones, as seen in Ukraine, has helped stabilize markets; similar measures in Iran could alleviate volatility.
- Iran’s Sovereignty Concerns: Iran believes that IAEA inspections threaten its sovereignty and could lead to military strikes, as previous attacks have followed IAEA disclosures.
- Risks of NPT Withdrawal: If Iran withdraws from the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), it would eliminate the IAEA's legal authority to inspect, leading to potential military escalations and global instability.
The Iran nuclear situation represents a pivotal moment for global non-proliferation and regional stability. It necessitates credible verification, structured dialogue, and ongoing diplomacy rather than mere speculation. For India, the implications extend beyond international order principles, touching on energy security, the safety of its diaspora, and regional peace. By leveraging its credibility in multilateral forums and its technical expertise, India can play a constructive role. The current crisis is a test of whether global powers can prioritize collective security over unilateral actions and competing interests to prevent escalation.
Indo-China Border Dispute: Challenges in Defining the Line of Actual Control

Why in News?
The India-China border dispute has remained unresolved despite decades of discussions and agreements since 1993, particularly regarding the definition of the Line of Actual Control (LAC), which continues to fuel tensions between the two nations.
Key Takeaways
- The India-China border dispute is one of the most intricate territorial conflicts in Asia.
- Efforts to define the LAC have resulted in recurring confrontations, highlighting the complexities of the issue.
- Historical negotiations and agreements have failed to bring about a clear resolution.
Additional Details
- Early Efforts: The border negotiations gained traction after Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi's visit to Beijing in 1988, marking a significant shift in bilateral relations.
- Border Peace and Tranquillity Agreement (BPTA): Signed in September 1993 during Prime Minister P.V. Narasimha Rao's visit, this agreement emphasized peaceful consultation and the non-use of force.
- 1996 Agreement: This agreement introduced military confidence-building measures but highlighted the failure to achieve a mutual understanding of the LAC.
- Attempts to clarify the LAC between 2000 and 2002 through map exchanges failed, leading to ongoing disputes over key areas like Depsang and Pangong Tso.
- The current structural problem arises from the unwillingness of both nations to concede territory in strategically sensitive regions, exacerbated by China's infrastructure advantages.
While the agreements from 1993 and 1996 temporarily alleviated tensions, the ongoing inability to define the LAC has kept the border situation unstable. Both countries have developed mechanisms to avert escalation, yet a lack of political resolve to finalize the boundary complicates peace efforts. The recurring standoffs underscore the urgent need to either clarify the LAC or implement robust measures to prevent patrol confrontations from escalating into conflicts.
H-1B $100,000 Entry Fee Explained: Payers, Exemptions, and Grey Areas

Why in News?
The White House has announced a new entry fee of $100,000 for H-1B visa holders, effective from September 21, 2025. This decision has raised concerns, especially among Indian tech workers and students, who represent the largest group of H-1B visa users. The fee targets only new entrants to the US, while those currently in the country who are extending or changing their status are exempt.
Key Takeaways
- The $100,000 fee is mandatory for all H-1B petitions for workers outside the US.
- Employers must pay this fee upfront to secure approval for new H-1B applications.
- Waivers may be granted by the Secretary of Homeland Security based on national interest.
- Uncertainty remains regarding which sectors may qualify for fee exemptions.
Additional Details
- Implementation Date: The fee requirement will come into effect on September 21, 2025.
- Exemptions: Current visa holders extending or changing their status do not have to pay the fee.
- The measure will be reviewed after 12 months to consider possible extensions.
- Impact on Sectors: Historically prioritized sectors like healthcare, defense, and critical technology may receive waivers, but details remain unclear.
- Universities and non-profit organizations, typically cap-exempt under H-1B rules, face ambiguity regarding their status under this new fee structure.
- This new entry fee has sparked significant debate in the context of US immigration politics, which has become increasingly contentious. The issue of immigration surged in voter concern from 2.1% in 2012 to 14.6% in 2024. Former President Donald Trump's rhetoric has often framed immigration as a threat to American jobs, a narrative that now extends to skilled migration through the H-1B program.
- Critics argue that the H-1B program is exploited to hire less expensive labor rather than top talent, as evidenced by data showing that a significant percentage of Indian applicants in FY2023 received salaries below the US median for IT jobs.
- Conversely, industry leaders assert that H-1B visas are crucial for bridging the skills gap in STEM fields, emphasizing the disparity in STEM graduates between the US and countries like India and China.
- As the largest user of the H-1B system, India could face substantial disruption due to this new fee, impacting pathways for young graduates and potentially leading to an increase in offshoring work.
- Major tech firms and consulting companies are likely to experience significant cost increases, which may hinder their hiring capabilities going forward.
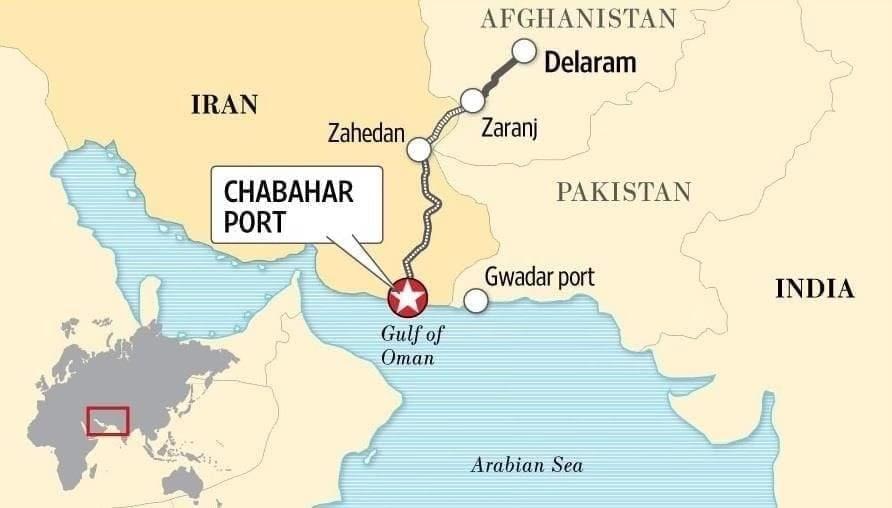
US Revokes Sanctions Waiver on Chabahar Port
Why in News?
The U.S. has ended the 2018 waiver that allowed India to utilize Iran’s Chabahar Port for the reconstruction efforts in Afghanistan. This decision has been enacted with a revocation notice issued within 10 days.
Key Takeaways
- The Chabahar Port is a significant strategic asset for India in the region.
- The revocation of the waiver poses challenges for India's economic interests in Afghanistan.
- This move could potentially strain diplomatic relations between India, the U.S., and Iran.
Additional Details
- Chabahar Port: A deep-water port located in the Sistan-Baluchistan province of Iran, on the Gulf of Oman, at the entrance of the Strait of Hormuz. It is notable for being the only Iranian port with direct access to the Indian Ocean.
- Distance: Chabahar is 550 nautical miles from Kandla Port in Gujarat and 786 nautical miles from Mumbai.
- Structure: The port comprises two terminals: Shahid Beheshti and Shahid Kalantari.
- Strategic Importance: Its proximity to Afghanistan and its position on the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) enhance its potential as a major commercial hub, linking the Indian Ocean and Persian Gulf with the Caspian Sea and further to northern Europe via Russia.
The revocation of the sanctions waiver by the U.S. could jeopardize India’s investments in Chabahar, estimated at ₹200 crores, and disrupt future development projects. It also threatens to cut off India’s only direct maritime access to Afghanistan and Central Asia, thereby weakening its strategic position against China’s Gwadar Port in Pakistan. Furthermore, this situation may create diplomatic tensions between India and its strategic partner Iran, as well as with the United States, which is a significant trade partner.
U.K., Australia and Canada Recognise Palestine State in Seismic Shift

Why in News?
On September 22, 2025, Britain, Australia, and Canada formally recognised Palestine as a sovereign state. This significant development marks a pivotal shift in Western foreign policy, especially among G-7 nations, and follows nearly two years of conflict in Gaza that escalated after Hamas's attack on October 7, 2023. While this move is celebrated by Palestinians, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu condemned it as an "absurd reward for terrorism."
Key Takeaways
- This recognition represents the first instance of G-7 nations officially acknowledging Palestine, diverging from the long-standing Western support for Israel.
- It highlights a stark change in policy, as Western nations had previously deferred recognition pending a negotiated two-state solution.
- The decision is influenced by ongoing violence in Gaza and a perceived urgency for peace.
- The U.K. carries a "special responsibility" due to its historical role in the region, particularly the 1917 Balfour Declaration.
Additional Details
- Reviving Peace Hopes: Leaders, including U.K. Deputy PM Keir Starmer, view this recognition as a means to reinvigorate the two-state solution discussions.
- International Pressure: Increased calls for accountability regarding humanitarian issues in Gaza have prompted action from these governments.
- Alignment with Europe: Portugal's simultaneous announcement of recognition, along with expected support from France, reflects a united European front.
- Israel's Reaction: Netanyahu has expressed strong opposition, claiming that recognition undermines Israel's existence and framing it as a reward for terrorism.
- Historical Context: The legacy of the Balfour Declaration and ongoing stalemates in peace negotiations impact the current dynamics.
- Geopolitical Implications: This shift could create divisions between U.S. policies and those of its allies, influence developing nations' views on justice and decolonization, and affect regional power balances.
The recognition of Palestine by the U.K., Australia, and Canada transcends mere symbolism; it may initiate a wave of similar acknowledgments from other Western nations. While it renews hopes for a two-state resolution, it also risks exacerbating tensions with Israel and the United States.
The Saudi-Pakistan Deal Upends India’s Strategic Thought

Why in News?
The recent establishment of a Strategic Mutual Defence Agreement between Pakistan and Saudi Arabia has significant implications for the geopolitical landscape of South Asia, particularly affecting India's strategic calculations.
Key Takeaways
- The agreement includes a clause that treats aggression against one party as an attack on both, reminiscent of collective defense commitments.
- This development highlights India’s vulnerabilities in its diplomatic efforts and the complexities of its relations in West Asia.
- Riyadh's renewed ties with Islamabad signify a shift in regional alliances, particularly in the context of recent military confrontations and changing global dynamics.
Additional Details
- Context of the Agreement: The deal emerges following the April 2025 terror attack in Pahalgam, which has escalated tensions between India and Pakistan, leading to India's military and diplomatic responses.
- Saudi-Pakistan Relationship: Historically, Saudi Arabia has relied on Pakistan for military support; however, this relationship has faced challenges, such as Pakistan's refusal to contribute troops to Saudi operations in Yemen in 2015.
- The current agreement signals a strategic recalibration by Riyadh, reflecting a desire for greater autonomy and a re-evaluation of its alliances amidst global uncertainties.
- The pact also illustrates the ideological and military bonds that Pakistan shares with Arab states, despite India's expanding influence in the region.
In conclusion, this agreement between Saudi Arabia and Pakistan not only reinforces Islamabad's position but also serves as a critical reminder for India regarding the necessity of adapting its strategic approaches in a rapidly changing international environment. Failing to engage proactively could result in India losing ground to rivals adept at navigating global complexities.
India’s Strategic Autonomy in a Multipolar World
Why in News?
The discussion surrounding India's strategic autonomy has gained prominence as the country navigates its foreign policy in an increasingly multipolar world, particularly in the context of its relations with major powers like the United States, China, and Russia. This relevance is underscored by ongoing territorial disputes in regions like the South China Sea and the evolving geopolitical landscape.
Key Takeaways
- India's stance in the South China Sea emphasizes strategic autonomy by advocating for freedom of navigation under UNCLOS.
- Bilateral tensions with China include border clashes and disputes over oil exploration in contested waters.
- India employs a balanced approach through alliances like the Quad while engaging in cooperation via BRICS and SCO.
Additional Details
- Historical Context: India's strategic autonomy emerged from its colonial past and was institutionalized during Nehru's Non-Alignment Movement.
- Evolution of Strategic Autonomy: The concept has shifted from non-alignment to a doctrine of multi-alignment, showcasing India's adaptability in a changing global order.
- India and the United States: The partnership has deepened through defense cooperation and joint initiatives like the Quad, though friction points remain regarding trade and ties with Russia.
- Relations with China: Despite security challenges, China remains a key trading partner, prompting India to strengthen its border security and deepen Indo-Pacific ties.
- Engagement with Russia: India maintains a historical defense relationship with Russia, continuing cooperation despite international pressures.
- Global South Context: India has asserted its role as a voice for the Global South, balancing its relationships while emphasizing pragmatism.
- Technological Dimensions: India faces internal constraints such as political polarization and economic vulnerabilities, necessitating a focus on modern domains like cyber security and data sovereignty.
In conclusion, India's strategic autonomy is characterized by its ability to maintain independence in foreign policy, navigating the complexities of global alliances while safeguarding national interests. The evolution of this doctrine reflects India's resilience and adaptability in a multipolar world.
US to Update MTCR Export Control Policies

Why in News?
The United States is set to reinterpret the 1987 Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR) with the aim of increasing exports of heavy attack drones, such as the MQ-9 Reaper, to allied nations.
Key Takeaways
- The MTCR was established by G-7 countries to prevent the proliferation of missile technology.
- The US plans to classify large unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) as "aircraft" rather than missile systems.
- This reinterpretation aims to position the US as a leading drone supplier globally.
Additional Details
- Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR): Established in 1987 by G-7 countries (Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, UK, USA), the MTCR seeks to prevent the spread of missiles and UAVs that could deliver nuclear, chemical, or biological weapons.
- Membership: Currently, 35 countries are members of the MTCR, with India joining in 2016.
- Categories:
- Category I items: Complete missile/UAV systems with payloads over 500 kg and ranges exceeding 300 km, along with major subsystems and production facilities (exports presumed denied).
- Category II items: Less sensitive or dual-use components/technologies, where exports are subject to national discretion under strict licensing.
- This policy change will allow for Foreign Military Sales (FMS) of heavy attack drones to countries like Saudi Arabia and India, while still ensuring US oversight on regional stability, end-use monitoring, technology security, and human rights compliance.
- This move is also expected to enhance India–US space and defence cooperation by lowering barriers for joint ventures and technology partnerships.
This reinterpretation of the MTCR represents a significant shift in US export policy, reflecting its strategic interests in maintaining an advantage in the global drone market.
India–Europe Energy Dynamics: India’s Rising Diesel Exports to Europe Amid EU’s Upcoming Ban on Russian Crude Products

Why in News?
The European Union (EU) plans to implement a ban on imports of fuels refined from Russian crude starting January 21, 2026. In anticipation of this ban, Europe is currently stockpiling petroleum products, especially diesel. During this period, India has emerged as a significant swing supplier of petroleum products to Europe, altering the energy dynamics between India and Europe.
Key Takeaways
- The EU's ban on Russian crude products will lead to increased demand for alternatives, with India stepping in as a major supplier.
- India's petroleum exports to Europe have surged significantly, reflecting the growing dependence of Europe on Indian refined fuels.
Additional Details
- India's Petroleum Exports to Europe: The petroleum industry is crucial for India's economy, contributing significantly to foreign exchange earnings. In the period from April to January 2024, exports to Europe were valued at $18.4 billion, with a notable increase in export volumes.
- Export Growth: In July 2024, exports rose 26% to reach 266,000 barrels per day (bpd). The major products exported include diesel (238,000 bpd) and aviation fuel (81,000 bpd).
- Historical Growth: Between 2018-19 and 2023-24, India's petroleum exports to Europe surged by over 253,000% in volume and nearly 250% in value.
- Global Context: Major petroleum exporters globally include Saudi Arabia (16.2%), Russia (9.14%), and Canada (8.48%), while India has established itself as an emerging player in refined product exports.
- Types of Exports: India exports various crude oil derivatives such as diesel, gasoline, naphtha, kerosene, as well as refined products like aviation turbine fuel and petrochemicals.
- Strategic Importance: The consistent energy demand in Europe alongside India's advanced refining capabilities offers mutual benefits, reinforcing India's position as a reliable global energy supplier.
India's increasing role as a swing supplier of petroleum products is significant for Europe's energy security as it transitions away from Russian crude. To capitalize on this opportunity, India should focus on strengthening its global energy trade and preparing for policy shifts like the 2026 EU ban through market diversification and diplomatic engagement.
Power of Siberia 2 Pipeline

Why in News?
Russia has recently announced a “legally binding” memorandum with China to construct the Power of Siberia 2 pipeline. This development underscores the strengthening ties between Russia and China amidst ongoing Western sanctions.
Key Takeaways
- The Power of Siberia 2 pipeline is a strategic initiative aimed at enhancing energy cooperation between Russia and China.
- This project is part of a broader effort to counter Western influence and sanctions.
What are Power of Siberia Pipelines?
- Power of Siberia 1:
- Operational pipeline from eastern Siberia to northern China.
- Commercial exports began in December 2019.
- Specifications:
- Length: Over 5,100 km (3,968 km in Russia).
- Diameter: 1,420 mm.
- Capacity: 61 bcm/year (38 bcm contracted to China).
- Designed to withstand temperatures as low as -62°C, constructed using 2.25 million tonnes of steel.
- Gas Source & Route:
- Supplies from Chayanda field (Yakutia) and later the Kovykta field.
- Gas passes through the Amur Gas Processing Plant.
- Two tunnels cross under the Amur River into China, linking to the Heihe–Shanghai pipeline.
- Timeline:
- Construction began in 2014 and is expected to complete with full deliveries of 38 bcm by 2025.
- Power of Siberia 2:
- A planned 2,600 km pipeline exporting 50 bcm/year from the Yamal and western Siberia fields to China via Mongolia (Soyuz Vostok segment).
- Status: Gazprom–CNPC signed a binding memorandum; however, pricing, financing, and timelines are still under negotiation. Deliveries may start by 2030.
Geopolitical Significance
- Political Symbolism:
- This project symbolizes the growing partnership between Russia and China, indicating a shift away from Western LNG supplies and reflecting defiance against sanctions.
- Strategic Showcase:
- Analysts describe the project as political theatre, highlighting Russia's increasing dependence on China while simultaneously giving China greater strategic leverage.
This pipeline initiative represents not only an energy collaboration but also a significant geopolitical maneuver in the context of current international relations.
Kokrajhar-Gelephu and Banarhat-Samtse Railway Lines to Bhutan

Why in News?
India and Bhutan have inaugurated their first-ever railway links, connecting Kokrajhar–Gelephu (69 km, Assam–Bhutan) and Banarhat–Samtse (20 km, West Bengal–Bhutan). This initiative marks a significant milestone in enhancing connectivity between the two nations.
Key Takeaways
- Agreements for the railway links were signed during Prime Minister Modi's visit to Bhutan in March 2024 and were formalized in 2025.
- The Kokrajhar–Gelephu line includes 6 stations and is designed to accommodate Vande Bharat trains, with an expected completion time of 4 years.
- The Banarhat–Samtse line features 2 stations and various infrastructures such as bridges and underpasses, with a completion timeline of 3 years.
- Both railway lines will be fully electrified, providing Bhutan direct access to India's extensive railway network.
Additional Details
- Bilateral Relations: This project strengthens ties with Bhutan, which is India's closest neighbor and the largest recipient of Indian development assistance.
- Strategic Security: The railway lines enhance regional security and serve as a counterbalance to China's growing influence in South Asia.
- Economic Integration: Supports Bhutan's trade (with 80% of it being with India), boosts hydropower exports, and aids in industrial development.
- Tourism & Culture: Facilitates improved people-to-people exchanges, particularly linking Gelephu's Mindfulness City to Samtse's industrial hub.
- Act East Policy: This initiative advances India’s policy through cross-border infrastructure in the eastern and northeastern regions.
- Rail Diplomacy: Positions Indian Railways as a strategic enabler of connectivity and diplomacy in the region.
The introduction of these railway lines not only enhances transportation and trade but also symbolizes the deepening of India-Bhutan relations, paving the way for future collaborative ventures.
|
98 videos|939 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on International Relations: September 2025 Current Affairs - Current Affairs & General Knowledge - CLAT
| 1. What are the key implications of China's WTO concessions for India? |  |
| 2. How does the Indus Treaty influence India-Pakistan relations? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the Scarborough Shoal dispute in the South China Sea? |  |
| 4. What are the potential consequences of France and other countries recognizing Palestine? |  |
| 5. How does the India-EFTA TEPA enhance India's trade strategy? |  |





















