Kingdom Protista: Euglenoids, Slime Moulds & Protozoans | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Biological classification is an important topic for NEET aspirants and should be well understood to develop an understanding and relation between different organisms and their characteristics. Let us take a glance at one of the important topics, “Kingdom Protista”, in this NCERT based notes.
Euglenoids
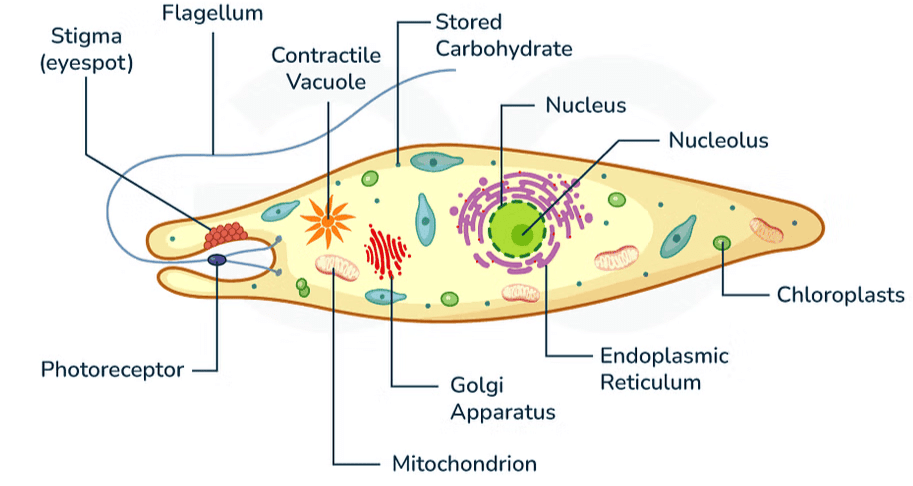 Euglena
Euglena
- Most euglenoids are freshwater organisms found in stagnant water.
- Instead of a cell wall, they have a flexible, protein-rich layer called a pellicle.
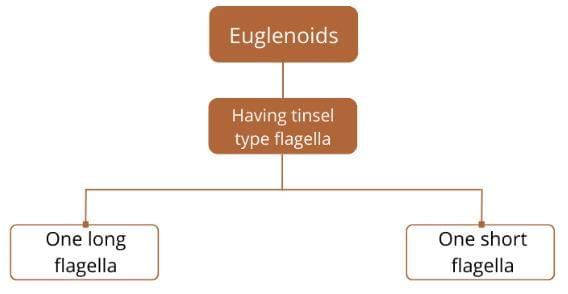
- The flagella bear hair (tinsels). So the flagella are tinsel type.
- They are photosynthetic in the presence of sunlight but can act as heterotrophs by consuming smaller organisms when deprived of light.
- The pigments in euglenoids are similar to those found in higher plants.
- Example: Euglena.
Slime Moulds
 Slime Mould
Slime Mould
Slime moulds are a type of protist that feeds on decaying organic material. They move along decaying twigs and leaves, engulfing organic matter.
- Under favourable conditions, slime moulds form an aggregation called plasmodium, which can grow and spread over several feet.
- When conditions become unfavourable, the plasmodium differentiates and forms fruiting bodies at its tips, which bear spores.
- The spores have true walls and are extremely resistant, allowing them to survive for many years, even in adverse conditions.
- The spores are dispersed by air currents.
Protozoans
Protozoans are heterotrophs, meaning they obtain their food by consuming other organisms. They can be found living as predators or parasites. Scientists believe that protozoans are primitive relatives of animals.There are four major groups of protozoans:
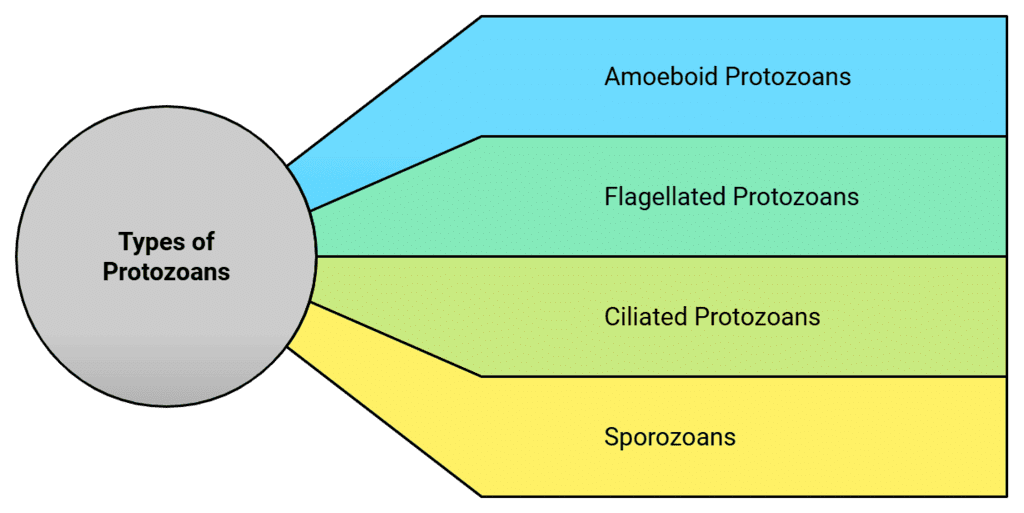 Types of Protozoans
Types of Protozoans
Don’t want to read and yet learn the concept? Here’s an interesting video to learn the concepts in depth: Kingdom Protista: Protozoans
(i) Amoeboid Protozoans:
- These organisms inhabit freshwater, seawater, or moist soil.
- They move and capture prey by extending pseudopodia(false feet), similar to the way Amoeba does.
- Some marine amoeboid protozoans have silica shells on their surfaces.
- Some species, like Entamoeba, are parasitic.
(ii) Flagellated Protozoans:
- Members of this group can be either free-living or parasitic.
- They are characterized by the presence of flagella.
- Parasitic flagellated protozoans can cause diseases, such as sleeping sickness caused by Trypanosoma.
(iii) Ciliated Protozoans:
- These organisms are aquatic and are known for their active movement due to the presence of thousands of cilia.
- They have a cavity called a gullet that opens to the outside of the cell surface.
- The coordinated movement of cilia steers water laden with food into the gullet.
- An example of a ciliated protozoan is Paramecium.
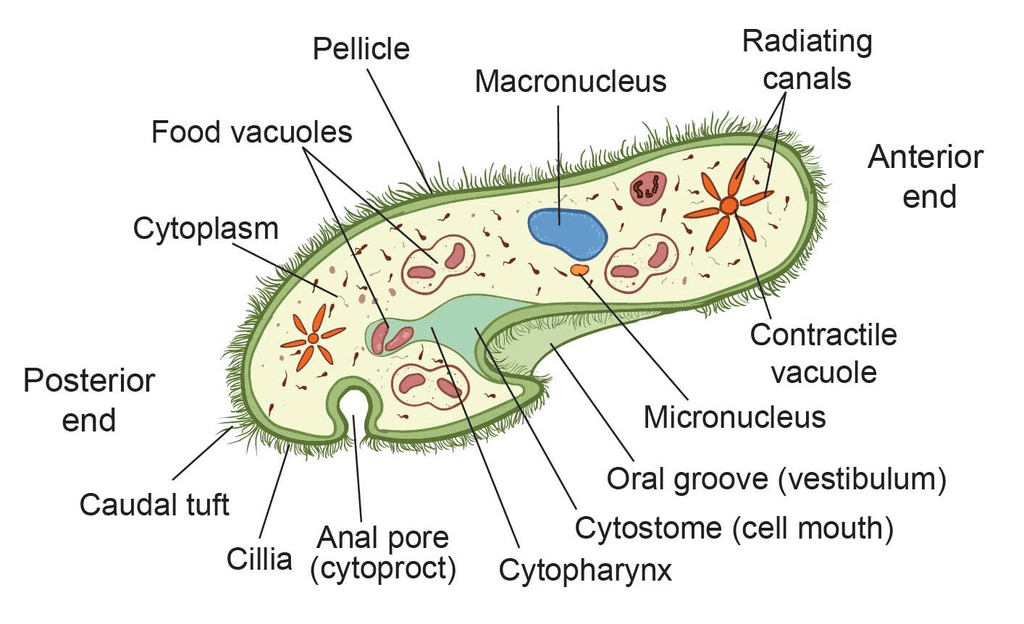 Paramoecium
Paramoecium
(iv) Sporozoans:
- This group includes diverse organisms that have an infectious spore-like stage in their life cycle.
- The most notorious sporozoan is Plasmodium, the malarial parasite, which causes malaria, a disease with a significant impact on the human population.
Now you can try answering the questions from Kingdom Protista asked in NEET:
Q.1. Pseudopodia help amoeboids in _______
(a) locomotion
(b) Ingestion of food
(c) locomotion and ingestion of food
(d) performing metabolic reactions
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Pseudopodia help amoeboids in both locomotion and ingestion of food. Pseudopodia are temporary extensions in amoeba that help them to move to as well as intake food by surrounding it with temporary extensions.
Q.2.The thalloid body of a slime mould (Myxomycetes) is known as:
(a) protonema
(b) Plasmodium
(c) fruiting body
(d) mycelium
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Slime moulds (Myxomycetes) have a thalloid, multinucleated, and creeping mass called Plasmodium. It moves over decaying leaves and twigs to feed on organic matter.This vegetative stage is not a mycelium (fungal), protonema (bryophyte), or fruiting body (reproductive structure), but specifically referred to as Plasmodium.
Attempt this test to check your knowledge about Kingdom Protista:
Test: Kingdom Protista
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Kingdom Protista: Euglenoids, Slime Moulds & Protozoans - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are Euglenoids and what distinguishes them from other protists? |  |
| 2. What are the main types of Slime Moulds and their ecological importance? |  |
| 3. How do Protozoans differ from Euglenoids and Slime Moulds? |  |
| 4. What are some common examples of Protozoans and their habitats? |  |
| 5. How do Euglenoids, Slime Moulds, and Protozoans contribute to the environment? |  |

















