Laxmikant Summary: National Commission for Protection of Child Rights | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Establishment |

|
| Composition |

|
| Functions |

|
| Powers |

|
| Working |

|
| Functions under other Acts |

|
| State Commission for Protection of Child Rights |

|
| Children's Courts |

|
Introduction
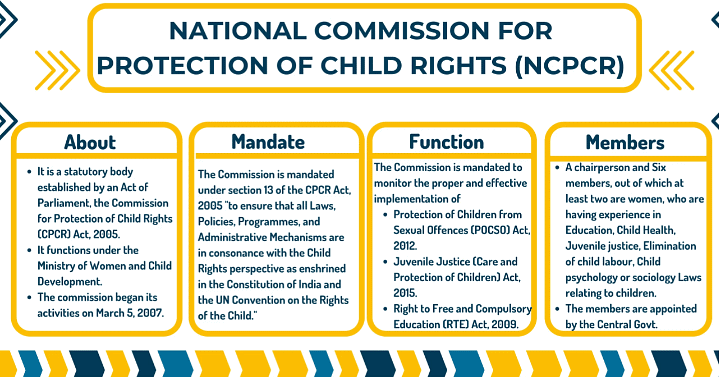
The NCPCR, established in 2007 under the Commission for Protection of Child Rights Act, 2005, operates under the Ministry of Women and Child Development, Government of India. With a focus on safeguarding children's rights, it reviews and monitors their status, recommends measures, and conducts inquiries into violations. Comprising a Chairperson and members, NCPCR plays a crucial role in advocating for the well-being of children in various situations.
Establishment
The National Commission for Protection of Child Rights, formed in 2007 under the Commission for Protection of Child Rights Act, 2005, is a statutory (non-constitutional) body. Mandated to protect, promote, and defend child rights in India, it adheres to the rights outlined in the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child, adopted in 1989 and ratified by the Government of India in 1992.

According to this Convention, a child is defined as an individual below eighteen years of age. The Commission focuses on the effective implementation of laws and programs related to children, ensuring alignment with constitutional and international perspectives on child rights.
The Commission, operating autonomously, falls under the administrative purview of the Ministry of Women and Child Development, Government of India.
Composition
The Commission is constituted as a multi-member body with a Chairperson and six members, where at least two must be women. The Chairperson, renowned for outstanding contributions to children's welfare, and the six members, chosen for their eminence and expertise in specific fields related to child well-being, are appointed by the Central Government. The appointment of the Chairperson involves a recommendation from a three-member selection committee chaired by the minister-in-charge of the Ministry or the Department of Women and Child Development.

The salaries, allowances, and service conditions for both the Chairperson and members are determined by the Central Government, and these conditions cannot be altered to their disadvantage post-appointment. Each member serves a three-year term, with a maximum of two terms. The upper age limit for the Chairperson is 65 years, while for members, it is 60 years.
The Chairperson or a member can resign at any time, and the Central Government has the authority to remove the Chairperson on grounds of proven misbehavior or incapacity. Removal can also occur under various circumstances, including insolvency, engaging in paid employment outside official duties, refusal or incapability to act, declaration of unsound mind, abuse of office, conviction leading to imprisonment, or absence from three consecutive Commission meetings.
Functions
1. To examine and review the safeguards provided by laws for the protection of child rights and recommend effective implementation measures.
2. To present reports to the Central Government, annually and at other intervals, on the working of these safeguards.
3. To inquire into violations of child rights and recommend initiation of proceedings in such cases.
4. To examine factors inhibiting the enjoyment of rights of children affected by various situations and recommend remedial measures.
5. To address matters concerning children in need of special care, including those in distress, marginalized, in conflict with the law, without family, and children of prisoners, recommending remedial measures.
6. To study international instruments, review existing policies, programs, and activities on child rights, and make recommendations for effective implementation.
7. To undertake and promote research in the field of child rights.
8. To promote child rights literacy, raise awareness of safeguards, and spread awareness among various sections of society.
9. To inspect juvenile custodial homes and institutions, taking remedial action with the authorities when needed.
10. To inquire into complaints and take suo moto notice of matters related to deprivation, violation of child rights, non-implementation of laws, non-compliance of policy decisions, and perform other functions necessary for the promotion of child rights.
Powers
- While inquiring into any matter, the Commission possesses all the powers of a civil court trying a suit, particularly in:
- Summoning and enforcing the attendance of any person for examination under oath.
- Requiring the discovery and production of any document.
- Receiving evidence on affidavits.
- Requisitioning any public record from any court or office.
- Issuing summons for the examination of witnesses or documents.
Working
The Commission, upon completing an inquiry, may take the following actions:
- Recommend the initiation of proceedings for prosecution or suitable action against the concerned person to the relevant government or authority.
- Seek necessary directions, orders, or writs from the concerned Supreme Court or High Court.
- Recommend to the concerned government or authority the grant of necessary interim relief to the victim.
The Commission submits its annual or special reports to the Central Government and the respective State Government. These reports, along with a memorandum of action taken on the Commission's recommendations and reasons for non-acceptance within one year, are laid before the respective legislatures.
Functions under other Acts
In addition to the aforementioned functions, the Commission has been assigned additional functions under three Acts related to children:
1. The Right of Children to Free and Compulsory Education (RTE) Act, 2009: According to this Act, the Commission is tasked with:
- (i) Examining and reviewing safeguards for rights under the Act and recommending effective implementation measures.
- (ii) Inquiring into complaints related to a child's right to free and compulsory education.
- (iii) Taking necessary steps post-inquiry.

2. The Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012: This Act outlines the following provisions regarding the Commission's additional functions:
- (i) Monitoring the implementation of POCSO Act provisions.
- (ii) Having the same powers during inquiries into offenses under this Act as provided under the Commissions for the Protection of Child Rights Act, 2005.
- (iii) Including activities under this Act in the annual report referred to in the Commissions for the Protection of Child Rights Act, 2005.
3. The Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection) Act, 2015: Pertaining to additional functions, this Act stipulates:
- (i) Monitoring the implementation of this Act's provisions.
- (ii) Having the same powers during inquiries into offenses under this Act as provided under the Commissions for the Protection of Child Rights Act, 2005.
- (iii) Including activities under this Act in the annual report referred to in the Commissions for the Protection of Child Rights Act, 2005.
State Commission for Protection of Child Rights
The Commissions for Protection of Child Rights Act of 2005 allows for the establishment of the State Commission for Protection of Child Rights at the state level. This commission is created through an Official Gazette Notification by the state government.

Composition
The State Commission is a multi-member body comprising a chairperson and six members, with at least two being women. The chairperson, appointed by the state government, should be an eminent individual with notable contributions to children's welfare. The six members are selected based on their eminence, ability, integrity, and experience in specific fields related to child rights.
The chairperson and members hold office for three years, with specific age limits for eligibility. Removal from office can occur under various circumstances, including proven misbehavior or incapacity.
Functions of the Commission
- Examine and review safeguards for child rights, recommending effective implementation measures.
- Present reports to the state government on the working of these safeguards annually.
- Inquire into violations of child rights and recommend proceedings in such cases.
- Examine factors hindering children's rights in various situations and suggest remedial measures.
- Address matters related to children in need of special care and recommend appropriate measures.
- Study treaties, international instruments, and review existing policies on child rights.
- Undertake and promote research in the field of child rights.
- Spread child rights literacy and awareness of available safeguards.
- Inspect juvenile custodial homes or other institutions where children are detained and recommend remedial action.
- Inquire into complaints and take suo-motu notice of issues related to child rights.
- Perform other functions deemed necessary for the promotion of child rights.
Powers
The state commission, during inquiries, possesses the powers of a civil court, including summoning individuals, requiring document production, receiving evidence on affidavits, requisitioning public records, and issuing summons for examinations.
Working
Upon completing an inquiry, the state commission may recommend prosecution or suitable action, approach the courts for necessary directions, or recommend interim relief for victims. Annual or special reports are submitted to the state government, including a memorandum of action taken on recommendations and reasons for non-acceptance.
Children's Courts
The Commissions for Protection of Child Rights Act (2005) includes provisions for establishing Children's Courts dedicated to the prompt adjudication of offenses against children or violations of child rights.

Under this act, the state government has the authority to designate either a specific court in the state or, for each district, a Court of Session to function as a Children's Court. However, the establishment of these courts requires the approval of the Chief Justice of the respective state's High Court.
For each Children's Court, the state government must appoint a public prosecutor or designate an advocate with at least seven years of practice as a special public prosecutor to handle cases within that court.
|
151 videos|780 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Laxmikant Summary: National Commission for Protection of Child Rights - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the composition of the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights? |  |
| 2. What are the functions of the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights? |  |
| 3. What powers does the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights have? |  |
| 4. How does the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights work? |  |
| 5. What are the functions of the State Commission for Protection of Child Rights? |  |















