UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Polity for UPSC CSE > Laxmikanth Summary: Attorney General of India
Laxmikanth Summary: Attorney General of India | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
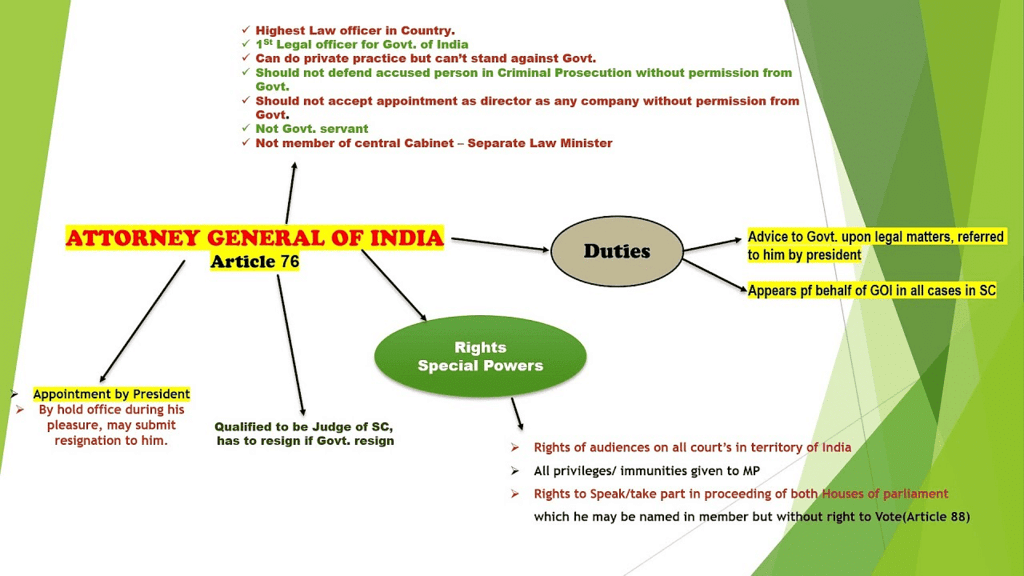
- The Constitution of India, specifically in Article 76, has established the position of the Attorney General.
- The Attorney General is recognized as the highest legal officer in the country.
- This role involves providing legal advice to the government and representing it in court cases.
- The Attorney General plays a crucial part in ensuring that the laws and constitution are upheld.
- They also have the responsibility of overseeing legal matters and guiding other government legal representatives.
 Attorney General of India
Attorney General of India
Appointment and Term
- The Attorney General (AG) is appointed by the President.
- To qualify for the AG position, a person must meet certain criteria:
- Must be a citizen of India.
- Must have served as a judge of a high court for at least five years.
- Alternatively, must have worked as an advocate in a high court for ten years.
- Can also be an eminent jurist, according to the President's opinion.
- The term of office for the AG is not set by the Constitution.
- There are no specific rules in the Constitution regarding how the AG can be removed.
- The AG serves at the pleasure of the President, meaning the President can remove them at any time.
- The AG can also leave their position by giving a resignation to the President.
- Traditionally, the AG tends to resign when the government or council of ministers resigns or is changed, since the AG is appointed based on their advice.
- The salary of the AG is not fixed by the Constitution.
- The AG receives a salary that the President decides.
Duties and Functions
The Attorney General (AG) serves as the main legal advisor to the Government of India. His or her responsibilities include:
- Providing legal advice to the Government of India on matters referred by the President.
- Carrying out other legal duties assigned by the President.
- Performing functions given by the Constitution or other laws.
The President has specifically assigned the following roles to the AG:
- To represent the Government of India in all cases before the Supreme Court that involve the Government.
- To act on behalf of the Government in any references made by the President to the Supreme Court under Article 143 of the Constitution.
- To appear in any High Court case involving the Government of India, when requested by the Government.
Question for Laxmikanth Summary: Attorney General of IndiaTry yourself: Who appoints the Attorney General for India?View Solution
Rights and Limitations
- In carrying out his or her official responsibilities, the Attorney General (AG) has the right to be heard in all courts within India.
- The AG can speak and participate in the meetings of both Houses of Parliament, as well as their joint sessions and any committee of Parliament where he or she is a member, although the AG does not have the right to vote.
- The AG enjoys all the rights and protections that a member of Parliament receives.
- To prevent any conflicts or complications in duty, the following restrictions are imposed on the AG:
- The AG must not give advice or represent anyone against the Government of India.
- The AG should not provide advice or represent the Government of India in cases where he or she is required to give advice or appear for the Government.
- The AG cannot defend individuals accused in criminal cases without the approval of the Government of India.
- The AG must not take on a role as a director in any company or corporation without obtaining permission from the Government of India.
- The AG should not advise any ministry, department of the Government of India, statutory organization, or public sector undertaking unless the request comes through the Ministry of Law and Justice, Department of Legal Affairs.
- It is important to note that the AG is not a full-time lawyer for the Government. He or she is not classified as a government employee and is allowed to engage in private legal work.
Solicitor General of India
 Solicitor General of India
Solicitor General of India
- In addition to the Attorney General (AG), there are other legal officers in the Government of India.
- These officers include the Solicitor General of India and the Additional Solicitor General of India.
- They provide help to the AG in carrying out their official duties.
- It is important to note that only the position of the AG is established by the Constitution.
- In simpler terms, Article 76 does not mention the roles of the Solicitor General or the Additional Solicitor General.
- The AG is not part of the Central Cabinet.
- There is a separate Law Minister in the Central Cabinet who handles legal issues for the government.
Question for Laxmikanth Summary: Attorney General of India
Try yourself:
What is the role and responsibilities of the Attorney General of India?View Solution
The document Laxmikanth Summary: Attorney General of India | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Polity for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
142 videos|777 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on Laxmikanth Summary: Attorney General of India - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the process of appointment for the Solicitor General of India? |  |
Ans. The Solicitor General of India is appointed by the President of India on the advice of the Attorney General. The appointment is generally made from among the senior advocates with a significant experience in litigation.
| 2. What are the key duties and functions of the Solicitor General of India? |  |
Ans. The Solicitor General represents the Government of India in legal matters, advises on legal issues, and appears in court on behalf of the government in important cases. Additionally, they assist the Attorney General in fulfilling their responsibilities.
| 3. What rights does the Solicitor General of India possess? |  |
Ans. The Solicitor General has the right to appear before the Supreme Court and High Courts on behalf of the government, participate in legal proceedings, and provide legal opinions to the government. They also have the authority to represent the government in matters of significant national importance.
| 4. Are there any limitations on the powers of the Solicitor General of India? |  |
Ans. Yes, the Solicitor General's powers are limited to representing the government in legal matters. They cannot take on private cases or represent individuals without the government’s consent, ensuring that their duties are aligned with government interests.
| 5. How does the role of the Solicitor General differ from that of the Attorney General of India? |  |
Ans. The Attorney General is the chief legal advisor to the government and has a broader scope of responsibilities, including advising the government on legal matters and representing it in all courts. The Solicitor General, on the other hand, primarily assists the Attorney General and represents the government in specific cases.
Related Searches

















