UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Polity for UPSC CSE > List of Constitutional Bodies
List of Constitutional Bodies | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
When you hear about the UPSC or Election Commission, somebody may add that these are Constitutional bodies. Many consider the constitutional bodies as more ‘prestigious’ or ‘powerful’ than other organizations or institutions in India. You should already be knowing about many Constitutional Posts like the President of India, Prime Minister of India, Governors, etc.
But what exactly is a Constitutional Body?

What is a Constitutional Body?
- Those bodies whose formation is prescribed by the Indian Constitution itself are known as Constitutional Bodies.
- They derive their powers and authority from the Indian Constitution.
- A constitutional amendment is often required to change any powers or functions related to such bodies.
List of Constitutional Bodies
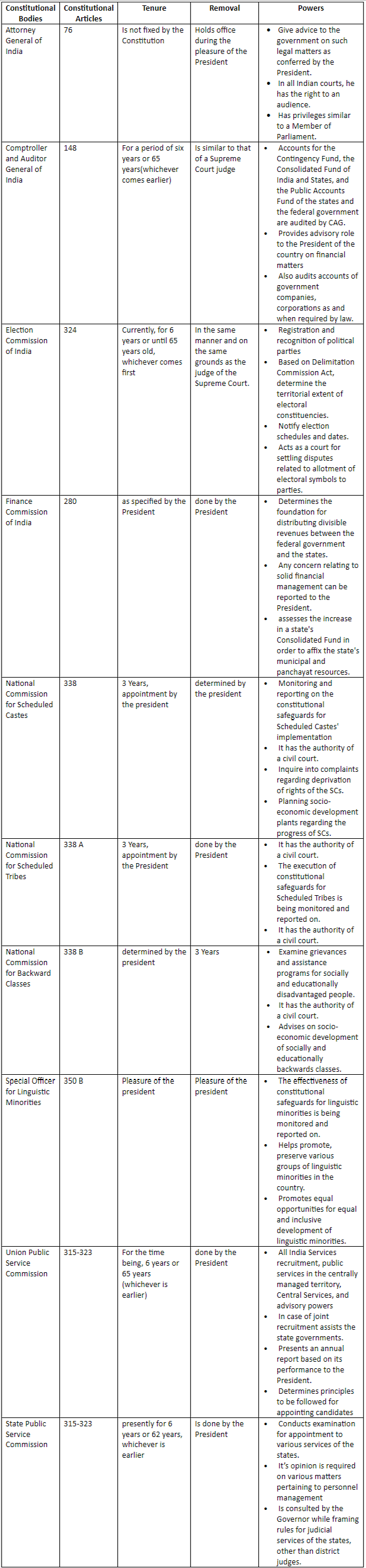
Conclusion
To manage diverse state functions, the state necessitates several authorities. Consequently, the constitution outlines the establishment of crucial authorities, along with their respective roles, responsibilities, powers, and the necessary qualifications for leaders and officials, collectively referred to as constitutional bodies.
- Constitutional bodies are entities whose establishment is mandated by the Indian Constitution.
- Their powers and authority find their basis in the Indian Constitution.
- Modifying the authority or functions of these entities often requires a constitutional amendment.
The document List of Constitutional Bodies | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Polity for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
154 videos|994 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on List of Constitutional Bodies - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the role of the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) in India? |  |
Ans. The Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) is a constitutional body responsible for conducting recruitment examinations and selecting candidates for various civil services and posts in the government of India. It conducts prestigious exams like the Civil Services Examination, Indian Forest Service Examination, Engineering Services Examination, and many others.
| 2. How can I apply for UPSC exams? |  |
Ans. To apply for UPSC exams, candidates need to visit the official website of the UPSC and fill out the online application form. The application process usually includes providing personal details, educational qualifications, uploading documents, and paying the required application fee. The detailed instructions for application and the examination schedule can be found on the UPSC website.
| 3. What are the eligibility criteria for appearing in UPSC exams? |  |
Ans. The eligibility criteria for UPSC exams vary depending on the specific examination. However, in general, candidates must be Indian citizens and meet certain age limits. They should also possess a minimum educational qualification as specified by the UPSC for each examination. It is important to carefully read the official notification or advertisement for the specific exam to understand the eligibility requirements.
| 4. How many attempts can I make for UPSC exams? |  |
Ans. The number of attempts for UPSC exams depends on the category to which a candidate belongs. For the General category, the maximum number of attempts is six. However, there are relaxations in the number of attempts for candidates from other categories. For example, candidates belonging to the Other Backward Classes (OBC) can attempt the exam nine times, while there is no restriction on the number of attempts for candidates from Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST) categories.
| 5. What is the selection process for UPSC exams? |  |
Ans. The selection process for UPSC exams involves multiple stages. It typically includes a preliminary examination, a main examination, and a personal interview. The preliminary examination consists of two objective-type papers, while the main examination consists of written papers and an interview. Candidates who qualify the preliminary examination are eligible to appear for the main examination. The final selection is based on the candidate's performance in the main examination and interview, along with the marks obtained in the preliminary examination (which is considered for qualifying purposes only).
Related Searches

















