NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 - Biotechnology & Its Applications
Q1: Which part of the plant is best suited for making virus-free plants and why?
Ans: The meristem is the plant part that is best suited for making virus-free plants. This is because even when the plant is infected: with a virus, the meristem (apical and axillary) remains infection free; it can be removed. grown in vitro to obtain virus-free plants.
Q2: What is the major advantage of producing plants by micropropagation?
Ans: Advantages of producing plants by micropropagation:
- The number of plants can be obtained in very less time and in less space.
- Plants can be obtained throughout the year.
- Sterile plants can be multiplied by this method.
- An economical and easy method of plant propagation.
Q3: Find out what the various components of the medium used for propagation of an explant in vitro are?
Ans: The various components of the medium used for propagation of explants in vitro are carbon sources such as sucrose, vitamins, amino acids, inorganic salts, agar-agar, water and certain growth hormones such as auxins and gibberellins.
Q4: Crystals of Bt toxin produced by some bacteria do not kill the bacteria themselves because−
(a) bacteria are resistant to the toxin
(b) toxin is immature
(c) toxin is inactive
(d) bacteria encloses toxin in a special sac
Ans: (c) toxin is inactive: In bacteria, the toxin is present in an inactive form, called prototoxin, which gets converted into active form when it enters the body of an insect.
 Bt Toxin
Bt Toxin
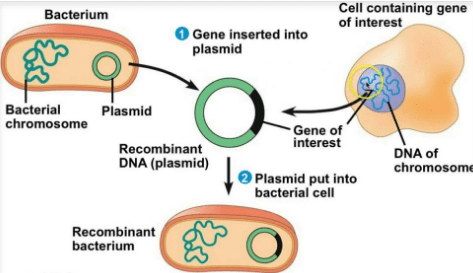
Q5: What are transgenic bacteria? Illustrate using any one example.
Ans: Transgenic bacteria contain foreign gene that is intentionally introduced into its genome. They are manipulated to express the desirable gene for the production of various commercially important products.
 Transgenic Bacteria
Transgenic Bacteria
An example of transgenic bacteria is E.coli. In the plasmid of E.coli, the two DNA sequences corresponding to A and B chain of human insulin are inserted, so as to produce the respective human insulin chains.
Hence, after the insertion of insulin gene into the bacterium, it becomes transgenic and starts producing chains of human insulin. Later on, these chains are extracted from E.coli and combined to form human insulin.
Formation of insulin
Q6: Compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of production of genetically modified crops.
Ans: The advantages of GM crops are:
- More tolerance to biotic and abiotic stresses (hormones, nutrition and cold, drought, salt, heat).
- Resistance to pests, thereby less relayed on chemical pesticides (pest-resistant crops).
- Increases fertility of soil with the efficiency of mineral usage prevents early exhaustion of fertility of the soil.
- Enhanced nutritional value of food, e.g., vitamin-A enriched rice (Golden rice), protein enriched vegetables like spinach, brocolli etc.
In addition to these uses, GM has been used to create special plants to supply alternative resources to industries, in the form of starches, fuels and pharmaceuticals.
The disadvantage of GM crops are:
- Transgenic genes in GM crops endanger native species.
- They cause damage to natural environment by reducing biodiversity.
- They may cause human health problems by altered genes
- Development of new strains of bacteria with are antibiotic resistance or other drug resistance.
Q7: What are Cry proteins? Name an organism that produces it. How has man exploited this protein to his benefit?
Ans: Cry proteins are encoded by cry genes. These proteins are toxins, which are produced by Bacillus thuringiensis bacteria. This bacterium contains these proteins in their inactive form. When the inactive toxin protein is ingested by the insect, it gets activated by the alkaline pH of the gut.
 Cry Protein
Cry Protein
This results in the lysis of epithelial cell and eventually the death of the insect. Therefore, man has exploited this protein to develop certain transgenic crops with insect resistance such as Bt cotton, Bt corn, etc.
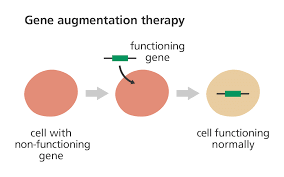
Q8: What is gene therapy? Illustrate using the example of adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
Ans: Gene therapy is a technique for correcting a defective gene through gene manipulation. It involves the delivery of a normal gene into the individual to replace the defective gene, for example, the introduction of gene for adenosine deaminase (ADA) in ADA deficient individual.
The adenosine deaminase enzyme is important for the normal functioning of the immune system. The individual suffering from this disorder can be cured by transplantation of bone marrow cells. The first step involves the extraction of lymphocyte from the patient’s bone marrow.
 Gene Therapy
Gene Therapy
Then, a functional gene for ADA is introduced into lymphocytes with the help of retrovirus. These treated lymphocytes containing ADA gene are then introduced into the patient’s bone marrow. Thus, the gene gets activated producing functional T lymphocytes and activating the patient’s immune system.
Q9: Diagrammatically represent the experimental steps in cloning and expressing a human gene (say the gene for growth hormone) into a bacterium like E. coli?
Ans: DNA cloning is a method of producing multiple identical copies of specific template DNA. It involves the use of a vector to carry the specific foreign DNA fragment into the host cell. The mechanism of cloning and transfer of gene for growth hormone into E.coli is represented below.
Human Gene
Q10: Can you suggest a method to remove oil (hydrocarbon) from seeds based on your understanding of rDNA technology and chemistry of oil?
Ans: Recombinant DNA technology (rDNA) is a technique used for manipulating the genetic material of an organism to obtain the desired result.
For example, this technology is used for removing oil from seeds. The constituents of oil are glycerol and fatty acids. Using rDNA, one can obtain oilless seeds by preventing the synthesis of either glycerol or fatty acids. This is done by removing the specific gene responsible for the synthesis.
Q11: Find out from internet what is golden rice.
Ans: Golden rice is a genetically modified variety of rice, Oryza sativa, which has been developed as a fortified food for areas where there is a shortage of dietary vitamin A.
It contains a precursor of pro-vitamin A, called beta-carotene, which has been introduced into the rice through genetic engineering. The rice plant naturally produces betacarotene pigment in its leaves.
 Golden SeedHowever, it is absent in the endosperm of the seed. This is because beta-carotene pigment helps in the process of photosynthesis while photosynthesis does not occur in endosperm.
Golden SeedHowever, it is absent in the endosperm of the seed. This is because beta-carotene pigment helps in the process of photosynthesis while photosynthesis does not occur in endosperm.
Since betacarotene is a precursor of provitamin A, it is introduced into the rice variety to fulfil the shortage of dietary vitamin A. It is simple and a less expensive alternative to vitamin supplements.
However, this variety of rice has faced a significant opposition from environment activists. Therefore, they are still not available in market for human consumption.
Q12: Does our blood have proteases and nucleases?
Ans: No, human blood does not include the enzymes, nucleases and proteases. In human beings, blood serum contains different types of protease inhibitors, which protect the blood proteins from being broken down by the action of proteases. The enzyme, nucleases, catalyses the hydrolysis of nucleic acids that is absent in blood.
Q13: Consult internet and find out how to make orally active protein pharmaceutical. What is the major problem to be encountered?
Ans:
- Orally active protein pharmaceuticals contain biologically active materials such as peptides or proteins, antibodies, and polymeric beads. It is administrated orally into the body through various formulations.
- It involves the encapsulation of protein or peptide in liposomes or formulations using penetration enhancers. These proteins or peptides are used for treatment of various diseases and are also used as vaccines.
- However, the oral administration of these peptides or proteins has some problems related to it. Once these proteins are ingested, the proteases present in the stomach juices denature the protein. As a result, their effect will be nullified.
- Hence, it is necessary to protect the therapeutic protein from digestive enzymes, if taken orally. This is the reason for the proteins to be injected directly into the target site.
|
65 videos|386 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 - Biotechnology & Its Applications
| 1. How is biotechnology used in agriculture? |  |
| 2. What are the ethical considerations surrounding biotechnology? |  |
| 3. How is biotechnology used in medicine? |  |
| 4. What are the career opportunities in biotechnology? |  |
| 5. How can biotechnology help in environmental conservation? |  |

















