UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > NCERT Video Summary: Class 6 to Class 12 (English) > NCERT Summary: The Early Societies (Theme 10: Displacing Indigenous Peoples)
NCERT Summary: The Early Societies (Theme 10: Displacing Indigenous Peoples) | NCERT Video Summary: Class 6 to Class 12 (English) - UPSC PDF Download
Displacing Indigenous Peoples
- The American empires of Spain and Portugal did not expand after the 17th century.
- The countries like Holland, France and England began to expand their trading activities and to establish colonies in America, Africa and Asia after 17th century.
- The word ‘Settler’ is used for the Dutch in South Africa, the British in Ireland. New Zealand and Australia and the Europeans in America.
- The native people led a simple life. They did not claim their rights over land.
- The continent of North America extends from Arctic Circle to the Tropic of Cancer and from the Pacific to the Atlantic Ocean.
- The inhabitants of North America used to live in groups before the advent of the Europeans.
- The original inhabitants of North America came from Asia about 30,000 years ago.
- The inhabitants of North America grew vegetables and maize. They ate fish and meat also.
- The people of North America believed in subsistence economy.
- People spoke numerous languages, but none of them is available to us in written form.
- Accounts of historical antecedents were recorded by each tribe.
- They used to transfer their historical knowledge orally to the next generation.
- Technique of clothes weaving was also known to the inhabitants.
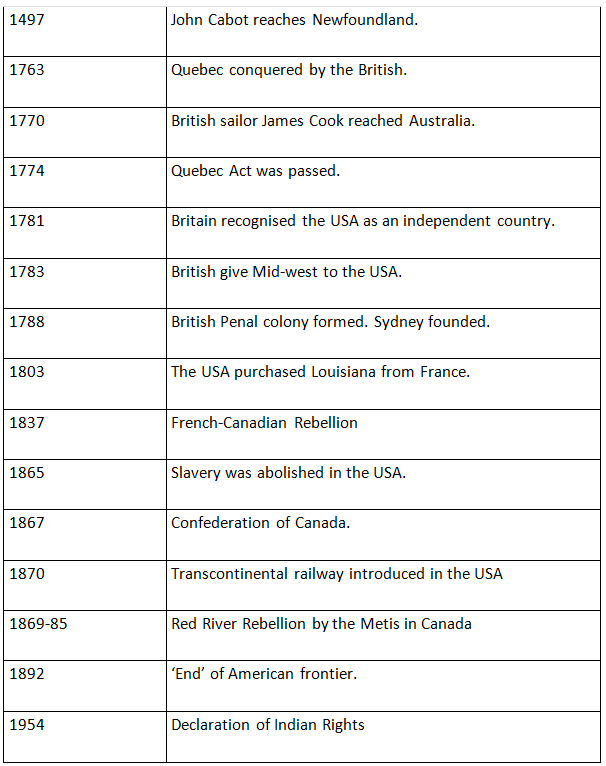
- In 1492, Christopher Columbus discovered the continent of America.
- News of discovery of gold and silver mines in America spread throughout the world.
- The Hopis were a native tribe who lived near California.
- Wampum belts are made of colored shells, sewn together.
- At the end of 18th century Canada came into existence.
- England had 13 colonies on the eastern coast of America.
- In the 1840’s, traces of gold were found in the USA, in California. It led to the ‘Gold Rush’, when thousands of Europeans hurried to America in the hope of making a quick fortune. It also led to the building of railway lines across the continent.
- British colonies in America declared a war against England in 1776 to gain independence.
- The War of Independence of the colonies continued till 1783.
- In 1860, the USA had an undeveloped economy. In 1890, it was the leading industrial power in the world.
- Invention of barbed wire in 1873 brought out revolution in American agriculture.
- The American President Abraham Lincoln played a key role in the abolition of the slavery.
- Explorer William Jansz of Dutch reached Australia in 1606.
- A.J. Tasman followed the route of William Jansz and named Tasmania after his name.
- A.J. Tasman discovered New Zealand.
- Another British explorer, James Cook reached the island of Botany Bay in 1770 and named it New South Wales.
- In Australia, economic prosperity of the mining industry played a crucial role.
- Canberra was declared the capital of Australia in 1911.
- The process of economic development enhanced with rearing of Marino sheep.
Important terms
- Colonial: Belonging to a country that controls another country.
- Oral History: To write history or to dictate others so that it could have been recorded.
- Native: Citizens of the colonized countries. ‘The Hopis’ are California’s native tribes.
- Subsistence Economy: It means to produce as much as required for the fulfillment of their basic necessities.
- Settler: People who settle at a place of which they are not inhabitants.
- Wampum Belt: A belt made of colored shells.
- Indigenous people: People belonging naturally to a place.
- Multiculturalism: A policy that implies a treatment of equality for the cultures of native Europeans and Asian emigrants.
- Terra Nullius: A policy that implies recognizing no one’s right over a given piece of land.
Timeline
The document NCERT Summary: The Early Societies (Theme 10: Displacing Indigenous Peoples) | NCERT Video Summary: Class 6 to Class 12 (English) - UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course NCERT Video Summary: Class 6 to Class 12 (English).
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
494 videos|387 docs
|
FAQs on NCERT Summary: The Early Societies (Theme 10: Displacing Indigenous Peoples) - NCERT Video Summary: Class 6 to Class 12 (English) - UPSC
| 1. How did early societies displace indigenous peoples? |  |
Ans. Early societies displaced indigenous peoples through various means such as colonization, forced migration, and land seizures. They often used military force and coercion to take control of indigenous lands and resources, leading to the displacement and marginalization of indigenous communities.
| 2. What were the consequences of displacing indigenous peoples in early societies? |  |
Ans. The displacement of indigenous peoples in early societies had severe consequences. It resulted in the loss of ancestral lands and resources, cultural assimilation, and the breakdown of indigenous social structures. Indigenous communities faced marginalization, poverty, and loss of identity, leading to long-term social and economic inequalities.
| 3. How did colonization contribute to the displacement of indigenous peoples? |  |
Ans. Colonization played a significant role in the displacement of indigenous peoples. European powers, through colonial expansion, took control of vast territories inhabited by indigenous communities. They enforced their own laws, exploited resources, and imposed their cultural norms, often leading to the displacement and marginalization of indigenous peoples.
| 4. Were indigenous peoples completely displaced by early societies? |  |
Ans. While early societies did displace many indigenous peoples, it is important to note that complete displacement was not always achieved. Some indigenous communities managed to resist or adapt to the changes brought by early societies, while others were integrated or assimilated into the dominant cultures. However, the overall impact of displacement on indigenous peoples was significant.
| 5. How is the displacement of indigenous peoples relevant today? |  |
Ans. The displacement of indigenous peoples in early societies continues to have relevance today. Many indigenous communities around the world still face the consequences of historical displacement, including land rights issues, cultural preservation, and socio-economic disparities. Recognizing and addressing these issues is crucial for promoting justice, equality, and the rights of indigenous peoples.
Related Searches





















