NEET Previous Year Questions(2016-25): Molecular Basis of Inheritance | Biology Class 12 PDF Download
2025
Q1: Which chromosome in the human genome has the highest number of genes? (NEET 2025)
(a) Chromosome 1
(b) Chromosome 10
(c) Chromosome X
(d) Chromosome Y
Ans: (a)
- Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 total), with 22 pairs being autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes (X and Y).
- Chromosomes carry genes, which are the functional units of heredity made up of DNA. Each chromosome contains a unique set of genes that determine various biological functions.
- Chromosome 1 is the largest human chromosome and contains the highest number of genes compared to other chromosomes in the human genome.
- Chromosome 1 is the largest of all human chromosomes and contains approximately 2968 genes, making it the chromosome with the highest number of genes.
- Chromosome Y has the fewest 231 genes.
Q2: Match List-I with List-II: (NEET 2025)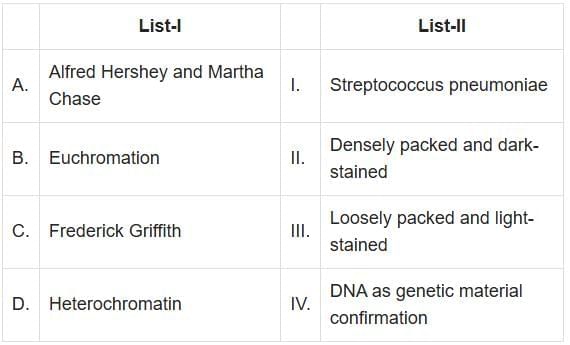
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
(b) A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I
(c) A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
(d) A-IV, B-II, C-I, D-III
Ans: (a)
A. Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase - IV. DNA as genetic material confirmation: Hershey and Chase conducted the famous "blender experiment" which confirmed that DNA, and not protein, is the genetic material in bacteriophages.
- The unequivocal proof that DNA is the genetic material came from the experiments of Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase (1952).
- They worked with viruses that infect bacteria called bacteriophages.
- The experiment used the T2 bacteriophage, a type of virus that infects bacteria. The bacteriophage consists of a protein coat and DNA.
- B. Euchromatin - III. Loosely packed and light-stained: Euchromatin is a form of chromatin that is loosely packed and appears light under a microscope, allowing active gene transcription.
- C. Frederick Griffith - I. Streptococcus Pneumoniae: Griffith's experiments involved Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria, leading to the discovery of the phenomenon of transformation.
- The "Transforming Principle" is a term used to describe the substance responsible for transformation in bacteria, which was first identified by Frederick Griffith in 1928.
- Griffith's experiments involved two strains of the bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae, a virulent smooth strain (S) and a non-virulent rough strain (R).
- D. Heterochromatin - II. Densely packed and dark-stained: Heterochromatin is tightly packed chromatin that appears dark under a microscope and is generally transcriptionally inactive.
Q3: Which of the following are the post-transcriptional events in an eukaryotic cell? (NEET 2025)
A. Transport of pre-mRNA to the cytoplasm prior to splicing
B. Removal of introns and joining of exons.
C. Addition of methyl group at 5' end of hnRNA.
D. Addition of adenine residues at 3' end of hnRNA.
E. Base pairing of two complementary RNAs.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) B, C, E only
(b) C, D, E only
(c) A, B, C only
(d) B, C, D only
Ans: (d)
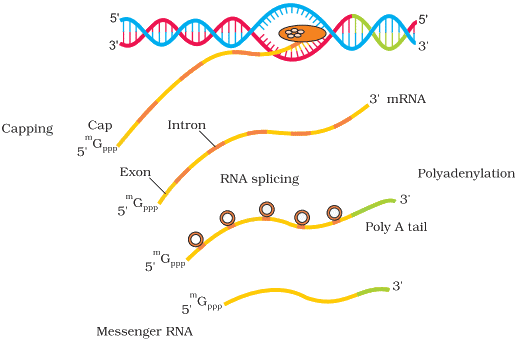
Option B: Removal of introns and joining of exons:
- This process is known as RNA splicing, where non-coding sequences (introns) are removed and coding sequences (exons) are joined together.
- Splicing is essential for producing a continuous coding sequence that can be translated into a functional protein.
Option C: Addition of methyl group at 5’ end of hnRNA:
- This modification is known as 5’ capping. A methylated guanine nucleotide is added to the 5’ end of the hnRNA.
- The 5’ cap protects the RNA from enzymatic degradation and aids in ribosome binding during translation.
Option D: Addition of adenine residues at 3’ end of hnRNA:
- This process is called polyadenylation, where a poly(A) tail (a sequence of adenine residues) is added to the 3’ end of the hnRNA.
- The poly(A) tail enhances RNA stability and facilitates its export from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
Other options:
Option A: Transport of pre-mRNA to cytoplasm prior to splicing:
- This is incorrect because splicing occurs in the nucleus, and only mature mRNA (after splicing) is transported to the cytoplasm.
Option E: Base pairing of two complementary RNAs:
- This is not a post-transcriptional event in eukaryotic cells. Base pairing of complementary RNAs occurs in processes like RNA interference (RNAi) or double-stranded RNA formation in viral replication.
Q4: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2025)
Statement I: In the RNA world, RNA is considered the first genetic material evolved to carry out essential life processes. RNA acts as a genetic material and also as a catalyst for some important biochemical reactions in living systems. Being reactive, RNA is unstable.
Statement II: DNA evolved from RNA and is a more stable genetic material. Its double helical strands being complementary, resist changes by evolving repairing mechanism.
(a) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
Ans: (c)
- Statement I: The statement accurately describes RNA as the first genetic material in the RNA world. Its dual role as a genetic material and a catalytic molecule is well-documented, but its instability due to high reactivity is a limitation. This makes the statement correct.
- Statement II: DNA evolved as a more stable alternative to RNA. Its double-helical complementary strands and repair mechanisms make it less prone to changes or mutations. This stability is a key factor in its role as the primary genetic material in most living organisms today. This makes the statement correct.
Q5: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2025)
Statement I: Transfer RNAs and ribosomal RNA do not interact with mRNA.
Statement II: RNA interference (RNAi) takes place in all eukaryotic organisms as a method of cellular defence.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
Ans: (b)
Statement I: "Transfer RNAs and ribosomal RNA do not interact with mRNA" is incorrect:
- tRNA: During protein synthesis, tRNAs interact with mRNA by recognizing specific codons on the mRNA via their anticodon regions. This interaction ensures the correct amino acids are added to the growing polypeptide chain.
- rRNA: Ribosomal RNA is a structural and functional component of ribosomes. It plays a critical role in catalyzing peptide bond formation and in aligning the mRNA during translation. Without rRNA, the interaction between mRNA and ribosomes would not occur.
Statement II: "RNA interference (RNAi) takes place in all eukaryotic organisms as a method of cellular defense" is correct:
- RNAi is a conserved mechanism found across eukaryotic organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi.
- It plays a role in defending cells against viral infections by degrading viral RNA and in regulating the expression of endogenous genes by silencing specific mRNAs.
- RNAi is mediated by small RNA molecules such as siRNA (small interfering RNA) and miRNA (microRNA), which guide RNA-induced silencing complexes (RISC) to target mRNA for degradation or translational repression.
Q6: Who proposed that the genetic code for amino acids should be made up of three nucleotides? (NEET 2025)
(a) Jacque Monod
(b) Franklin Stahl
(c) George Gamow
(d) Francis Crick
Ans: (c)
- The genetic code refers to the set of rules by which information encoded in DNA or RNA is translated into proteins, the functional molecules in cells.
- Proteins are composed of amino acids, and the sequence of amino acids is determined by the sequence of nucleotides in the genetic material.
- The concept of the genetic code being made up of three nucleotides, known as codons, was first proposed by George Gamow, a physicist.
George Gamow:
- George Gamow proposed the idea of the triplet code in 1954. He theorized that a combination of three nucleotides could encode one amino acid.
- He argued that there are only 4 bases and if they have to code for 20 amino acids, the code should constitute a combination of bases.
- He suggested that in order to code for all 20 amino acids, the code should be made up of three nucleotides. This was a very bold proposition, because a permutation combination of 43 (4 × 4 × 4) would generate 64 codons; generating many more codons than required.
Other Options:
- Francis Crick: James Watson and Francis Crick are credited with discovering the double helix structure of DNA in 1953.
- Jacques Monod: Jacques Monod was a molecular biologist known for his work on gene regulation, particularly the lac operon in bacteria.
- Franklin Stahl: Franklin Stahl is known for his work on DNA replication, specifically the Meselson-Stahl experiment that demonstrated the semi-conservative mechanism of DNA replication.
Q7: Histones are enriched with- (NEET 2025)
(a) Phenylalanine & Leucine
(b) Phenylalanine & Arginine
(c) Lysine & Arginine
(d) Leucine & Lysine
Ans: (c)
- The nucleosome is the basic structural unit of chromatin in eukaryotic cells. It plays a critical role in the packaging of DNA into a compact, dense shape, which allows for efficient storage and regulation of genetic information.
- A nucleosome consists of a segment of DNA wound around a core of histone proteins.
- Histones are rich in the basic amino acid residues lysine and arginine. Both the amino acid residues carry positive charges in their side chains.
- Histones are organised to form a unit of eight molecules called histone octamer.
- The histone core around which DNA is wrapped is composed of eight histone molecules: two each of histone proteins H2A, H2B, H3, and H4.
- The negatively charged DNA is wrapped around the positively charged histone octamer to form a structure called nucleosome
- A typical nucleosome contains 200 bp of DNA helix.
Q8: Which factor is important for termination of transcription? (NEET 2025)
(a) ρ(rho)
(b) γ(gamma)
(c) α(alpha)
(d) σ(sigma)
Ans: (a)
Transcription is the process by which a DNA sequence is copied into RNA. It is carried out by RNA polymerase and includes three main stages: initiation, elongation, and termination.
- Initiation: In this stage, RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region of the DNA, forming a transcription initiation complex. In prokaryotes, this process often involves the transient association of a sigma factor (σ) with the RNA polymerase core enzyme, which helps in recognizing and binding to the promoter sequence.
- Elongation: Once the initiation complex is formed, RNA polymerase begins moving along the DNA template, synthesizing RNA in the 5' to 3' direction. During elongation, RNA polymerase does not require the transient association of initiation or termination factors. It simply catalyzes the addition of ribonucleotides to the growing RNA chain based on the complementary base pairing with the DNA template.
- Termination: In the termination stage, RNA polymerase recognizes specific sequences in the DNA template that signal the end of the gene or transcription unit. In prokaryotes, termination often involves the transient association of a termination factor (ρ) with the RNA polymerase complex, leading to the release of the newly synthesized RNA molecule and dissociation of RNA polymerase from the DNA template.
Other Options:
- α (Alpha): Alpha subunits are part of the core RNA polymerase enzyme complex and are involved in the assembly and stability of RNA polymerase. They play a role in initiating transcription but are not involved in termination.
- σ (Sigma): Sigma factors are essential for the initiation of transcription. They help RNA polymerase recognize and bind to specific promoter sequences but dissociate from RNA polymerase after initiation. Sigma factors are not involved in transcription termination.
- γ (Gamma): Gamma is not a factor associated with transcription in prokaryotes.
2024
Q1: A transcription unit in DNA is defined primarily by the three regions in DNA and these are with respect to upstream and down stream end; (NEET 2024)
(a) Repressor, Operator gene, Structural gene
(b) Structural gene, Transposons, Operator gene
(c) Inducer, Repressor, Structural gene
(d) Promotor, Structural gene, Terminator
Ans: (d)
A transcription unit in DNA is critical for the process of transcription, wherein a particular segment of DNA is copied into RNA (especially mRNA) by the enzyme RNA polymerase. This unit is composed of sequences that include both coding regions, which are directly transcribed into RNA, and regulatory regions, which ensure that transcription is initiated and terminated at the correct locations on the DNA.
The correct answer is: Option D: Promotor, Structural gene, Terminator
Here's a detailed explanation of each component:
Promoter: The promoter is a sequence in DNA that signals the RNA polymerase to start transcription. It is located at the upstream end (5' end) of the gene. Promoters are essential for transcription initiation and are typically found just before the genes they regulate.
Structural gene: This region of the transcription unit is actually expressed or translated into protein (or functional RNA), depending on the kind of gene. These genes contain the functional sequences that are copied during the transcription process.
Terminator: The terminator is found at the downstream end (3' end) of the transcription unit and includes sequences that signal the RNA polymerase enzyme to stop transcription. This ensures that the newly synthesized RNA contains only the necessary genetic message.
The other options contain components that do not accurately define the typical structure of a transcription unit:
Option A mixes regulatory proteins and DNA regions, which does not accurately represent the structural components of a transcription unit.
Option B includes "transposons" which are genetic elements that can move around within the genomes but are not typically part of the transcription unit.
Option C again refers to regulatory proteins (inducer and repressor) along with structural genes, confusing the functions of proteins and DNA regions.
Therefore, Option D correctly represents the standard components of a transcription unit in the context of gene transcription in DNA.
Q2: Match List I with List II (NEET 2024)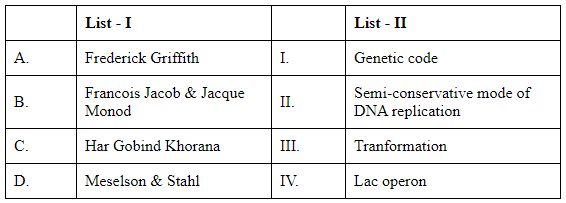
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III, B-II, C-I, D-IV
(b) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(c) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(d) A-IV, B-II, C-II, D-III
Ans: (b)
To solve this matching question, let's discuss each scientist(s) and their contribution:
A. Frederick Griffith: Known for discovering the "transforming principle," which showed that a substance from dead bacteria could genetically transform living bacteria. This process is called transformation. The correct match for Frederick Griffith is III. Transformation.
B. Francois Jacob & Jacques Monod: They are famous for their work on the lac operon, a set of genes involved in lactose metabolism in bacteria. Their study elucidated how genes are regulated and expressed in cells. The correct match for Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod is IV. Lac operon.
C. Har Gobind Khorana: Known for his research on the genetic code and its role in protein synthesis. Khorana was one of the scientists who elucidated how the sequence of nucleotides in nucleic acids is translated into protein sequences. The correct match for Har Gobind Khorana is I. Genetic code.
D. Meselson & Stahl: Famous for their experiment confirming the semi-conservative mechanism of DNA replication, where each new DNA molecule consists of one old strand and one newly synthesized strand. The correct match for Meselson and Stahl is II. Semi-conservative mode of DNA replication.
Comparing this information with the options provided:
Option A: A-III, B-II, C-I, D-IV (Incorrect: B does not match II)
Option B: A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II (Correct: All matches are accurate)
Option C: A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I (Incorrect: A, B, C, and D do not match correctly)
Option D: A-IV, B-II, C-II, D-III (Incorrect: A, C, and D do not match correctly)
Therefore, the correct answer is Option B.
Q3: Which of the following statement is correct regarding the process of replication in E.coli? (NEET 2024)
(a) 'The DNA dependent DNA polymerase catalyses polymerization in one direction that is 3' → 5'
(b) The DNA dependent RNA polymerase catalyses polymerization in one direction, that is 5' → 3'
(c) The DNA dependent DNA polymerase catalyses polymerization in 5' → 3' as well as 3' → 5' direction
(d) The DNA dependent DNA polymerase catalyses polymerization in 5' → 3' direction.
Ans: (d)
The correct statement regarding the process of replication in E.coli is found in Option D: 'The DNA dependent DNA polymerase catalyses polymerization in 5' → 3' direction.' To elaborate:
- Replication in E.coli involves synthesising new DNA strands from a DNA template.
- This process is catalysed by an enzyme called DNA polymerase.
- DNA polymerases add nucleotides to the growing DNA strand during replication.
- These enzymes can only add nucleotides to the 3' end of the DNA strand, resulting in synthesis in the 5' to 3' direction.
The directional limitation arises from the structure of deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs), which have:
- A 5' phosphate group
- A 3' hydroxyl group
- A nitrogenous base
DNA strands form through phosphodiester bonds between the 3' hydroxyl group of one nucleotide and the 5' phosphate group of the next. Thus, nucleotides can only be added to the 3' end of the growing strand. The other options are incorrect for the following reasons:
- Option A incorrectly states the direction of synthesis, which is impossible with the mechanics of DNA polymerases.
- Option B refers to DNA dependent RNA polymerase, which is involved in transcription, not replication, and synthesises RNA in the 5' to 3' direction.
- Option C incorrectly claims that DNA polymerase can synthesise in both directions, contradicting its inherent directional nature.
Understanding the precise mechanics of the enzyme clarifies that Option D accurately describes how DNA dependent DNA polymerase facilitates DNA replication in E.coli.
Q4: Which one is the correct product of DNA dependent RNA polymerase to the given template? (NEET 2024)
3'TACATGGCAAATATCCATTCA5'
(a) 5'AUGUACCGUUUAUAGGUAAGU3'
(b) 5'AUGUAAAGUUUAUAGGUAAGU3'
(c) 5'AUGUACCGUUUAUAGGGAAGU3'
(d) 5'ATGTACCGTTTATAGGTAAGT3'
Ans: (a)
DNA-dependent RNA polymerase is an enzyme responsible for transcribing DNA into RNA. During transcription, the RNA polymerase reads the template strand of DNA and synthesizes a complementary RNA strand. A key point in this process is that RNA polymerase builds RNA by replacing thymine (T) with uracil (U).
The provided DNA template is: 3'TACATGGCAAATATCCATTCA5'
To find the correct RNA sequence, we need to identify the complementary base for each base in the template strand while considering RNA bases. Remember, in RNA:
A (Adenine) pairs with U (Uracil)
T (Thymine) pairs with A (Adenine)
C (Cytosine) pairs with G (Guanine)
G (Guanine) pairs with C (Cytosine)
The complementary RNA sequence to the DNA template is generated as follows:
3'T --> 5'A
3'A --> 5'U
3'C --> 5'G
3'G --> 5'C
3'T --> 5'A
3'A --> 5'U
3'T --> 5'A
3'G --> 5'C
3'G --> 5'C
3'C --> 5'G
3'A --> 5'U
3'A --> 5'U
3'T --> 5'A
3'A --> 5'U
3'T --> 5'A
3'C --> 5'G
3'C --> 5'G
3'A --> 5'U
3'T --> 5'A
3'T --> 5'A
3'C --> 5'G'
This constructs the RNA sequence: 5'AUGUACCGUUUAUAGGUAAGU3'
Thus, Option A correctly represents the RNA sequence transcribed by DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from the given DNA template:
Option A: 5'AUGUACCGUUUAUAGGUAAGU3'
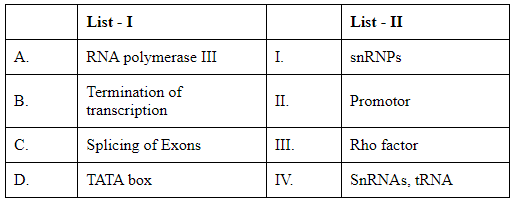
Q5: Match List I with List II: (NEET 2024)
 Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A-II, B-IV, C-I, D-III
(b) A-III, B-II, C-IV, D-I
(c) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(d) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
Ans: (d)
The goal is to correctly match the terms in List I with the descriptions in List II. Let's analyze and match each term from List I with its appropriate partner in List II:
List I:
A. RNA polymerase III: This enzyme is primarily responsible for transcribing DNA to synthesize tRNA, 5S rRNA, and other small RNAs.
B. Termination of transcription: In prokaryotes, specific termination factors such as the Rho factor are involved in stopping transcription. In eukaryotes, different mechanisms and sequences are used.
C. Splicing of Exons: The process involving the removal of introns and joining of exons during mRNA processing. Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) are critical components in this process.
D. TATA box: A DNA sequence within the promoter region, which is crucial for forming the transcription initiation complex.
List II:
I. snRNPs: Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in mRNA splicing.
II. Promoter: A region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene, typically containing sequences like the TATA box.
III. Rho factor: A protein essential for terminating transcription in prokaryotes.
IV. SnRNAs, tRNA: Molecules transcribed primarily by RNA polymerase III.
Matching these descriptions:
A (RNA polymerase III) matches with IV (SnRNAs, tRNA).
B (Termination of transcription) matches with III (Rho factor).
C (Splicing of Exons) matches with I (snRNPs).
D (TATA box) matches with II (Promoter).
Therefore, the correct matches according to options listed are: Option D: A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
Q6: The lactose present in the growth medium of bacteria is transported to the cell by the action of (NEET 2024)
(a) Beta-galactosidase
(b) Acetylase
(c) Permease
(d) Polymerase
Ans: (c)
Lactose, a disaccharide made of glucose and galactose, requires specific mechanisms to enter bacterial cells for metabolism. The protein responsible for this transport is permease. Key points about lactose permease:
- It is encoded by the lacY gene, part of the lac operon, a well-known example of gene regulation in bacteria.
- In bacteria like Escherichia coli, lactose permease facilitates the transport of lactose across the cell membrane when lactose is present outside the cell.
- Once inside, lactose can be used as a source of energy and carbon.
Other options can be ruled out because:
- Beta-galactosidase (Option A) breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose but does not transport it.
- Acetylase (Option B) adds acetyl groups to molecules and is unrelated to sugar transport.
- Polymerase (Option D) synthesises RNA and DNA, which is also not related to transporting sugars like lactose.
Thus, lactose permease (Option C) is essential for transporting lactose into bacterial cells, confirming it as the correct choice.
Q7: Match List-I with List-II (NEET 2024)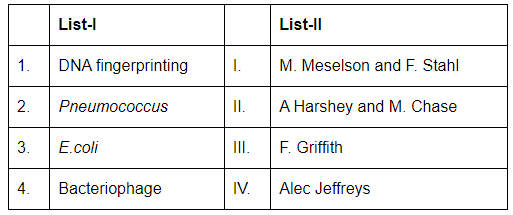 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
(b) A-IV, B-III, C-I, D-II
(c) A-II, B-III, C-I, D-IV
(d) A-III, B-II, C-I, D-IV
Ans: (b)
1. DNA fingerprinting: DNA fingerprinting was developed by Alec Jeffreys. He is credited with the invention of this technique, which is used for identifying individuals based on their unique DNA patterns. Therefore, A-IV.
2. Pneumococcus: The work involving Pneumococcus and the concept of transformation in bacteria was done by Frederick Griffith. His experiment showed that genetic material could be transferred between bacteria. Therefore, B-III.
3. E.coli: The Meselson-Stahl experiment demonstrated the semi-conservative replication of DNA using E. coli bacteria. This experiment was done by Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl. Therefore, C-I.
4. Bacteriophage: The famous experiment on the bacteriophage (a virus that infects bacteria) was conducted by Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase, which confirmed that DNA, not protein, is the genetic material. Therefore, D-II.
Thus, the correct match is:
- A-IV: DNA fingerprinting was developed by Alec Jeffreys.
- B-III: Pneumococcus was studied by Frederick Griffith.
- C-I: E. coli was used in the Meselson-Stahl experiment.
- D-II: Bacteriophage research was done by Hershey and Chase.
Q8: Which of the following is not the characteristic feature of the genetic code? (NEET 2024)
(a) The codon is triplet
(b) The code is nearly universal
(c) The code has punctuations
(d) Some amino acids are coded by more than one codon, hence the code is degenerate
Ans: (c)
1. The codon is triplet: This is a correct characteristic of the genetic code. Each codon consists of three nucleotides, which correspond to a
specific amino acid or a stop signal during protein synthesis.
2. The code is nearly universal: This is correct. The genetic code is nearly universal, meaning that the same codons generally specify the same amino acids in almost all organisms, from bacteria to humans.
3. The code has punctuations: This is incorrect. The genetic code does not contain punctuations like commas or periods. However, it does have start and stop codons that signal the beginning and end of protein synthesis, but these are not considered punctuations in the traditional sense.
4. Some amino acids are coded by more than one codon, hence the code is degenerate: This is correct. The genetic code is degenerate, meaning that multiple codons can code for the same amino acid.
Thus, the incorrect characteristic is C: "The code has punctuations."
Q9: Which of the following techniques was used to elucidate the double helix model of DNA? (NEET 2024)
(a) γ-radiation
(b) Electromagnetic radiation
(c) UV-Vis spectroscopy
(d) X-ray diffraction
Ans: (d)
The double helix model of DNA was elucidated using X-ray diffraction. This technique was employed by Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins, whose X-ray diffraction images of DNA provided critical evidence of its helical structure. The famous Photo 51 captured by Franklin was instrumental in helping James Watson and Francis Crick propose the double helix model of DNA in 1953.
X-ray diffraction helped determine the helical structure and the dimensions of DNA, which ultimately led to the understanding that DNA consists of two strands wound around each other in a double helix.
The other techniques listed:
γ-radiation, electromagnetic radiation, and UV-Vis spectroscopy were not directly involved in elucidating the double helix structure of DNA.
Q10: Which experimental material was used by Taylor and colleagues to prove that DNA in chromosomes replicates semiconservatively? (NEET 2024)
(a) Vicia faba
(b) Pisum sativum
(c) Solanum tuberosum
(d) Oryza sativa
Ans: (a)
Taylor and colleagues used Vicia faba (broad bean) as their experimental material to prove that DNA replication in chromosomes occurs semiconservatively. In their famous experiment, they labeled the DNA with radioactive isotopes (using tritiated thymidine) and observed the pattern of DNA replication in the cells of the broad bean. They demonstrated that during DNA replication, each chromosome retains one strand from the original DNA molecule and synthesizes a new complementary strand, thus confirming the semiconservative model of DNA replication.
Q11: In the lac operon, the i gene codes for: (NEET 2024)
(a) Inducer
(b) Repressor
(c) β-galactosidase
(d) Permease
Ans: (b)
In the lac operon, the i gene codes for the repressor protein. This repressor binds to the operator region of the operon and prevents transcription of the structural genes when lactose (or an inducer) is not present. When lactose is available, it binds to the repressor, causing it to change shape and release from the operator, allowing transcription to proceed and enabling the cell to metabolize lactose.
- Inducer: This is the molecule (like lactose or allolactose) that binds to the repressor and inactivates it, not the product of the i gene.
- β-galactosidase: This enzyme is encoded by the lacZ gene, not the i gene.
- Permease: This enzyme is encoded by the lacY gene, also not by the i gene.
Thus, the i gene codes for the repressor protein.
Q12: Given below are statements regarding RNA polymerase in prokaryotes: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: In prokaryotes, RNA polymerase is capable of catalysing the process of elongation during transcription.
Statement II: RNA polymerase associates transiently with 'Rho' factor to initiate transcription.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is True but Statement II is False
(b) Statement I is False but Statement II is True
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are True
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are False
Ans: (a)
- Statement I: In prokaryotes, RNA polymerase is capable of catalyzing the process of elongation during transcription: This statement is true. RNA polymerase in prokaryotes is responsible for both initiation and elongation during transcription. Once it binds to the promoter and initiates transcription, it catalyzes the elongation of the RNA molecule by adding nucleotides in the 5' to 3' direction.
- Statement II: RNA polymerase associates transiently with 'Rho' factor to initiate transcription: This statement is false. Rho factor is involved in the termination of transcription, not the initiation. It helps in terminating transcription by causing the RNA polymerase to dissociate from the DNA when a specific sequence is reached. The initiation of transcription in prokaryotes primarily involves the interaction of RNA polymerase with the promoter region and the sigma factor, not the Rho factor.
Thus, Statement I is true, and Statement II is false, making the correct answer (a).
Q13: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: In the lac operon, the z gene codes beta-galactosidase which is primarily responsible for the hydrolysis of lactose into galactose and glucose.
Statement II: In addition to lactose, glucose or galactose can also induce the lac operon.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is True but Statement II is False
(b) Statement I is False but Statement II is True
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are True
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are False
Ans: (a)
- Statement I: In the lac operon, the z gene codes beta-galactosidase which is primarily responsible for the hydrolysis of lactose into galactose and glucose: This statement is true. The lacZ gene in the lac operon encodes beta-galactosidase, an enzyme that hydrolyzes lactose into glucose and galactose. This is a crucial step in the breakdown of lactose for use by the cell.
- Statement II: In addition to lactose, glucose or galactose can also induce the lac operon: This statement is false. The lac operon is primarily induced by lactose (or more specifically allolactose, a derivative of lactose). Glucose and galactose do not act as inducers for the lac operon. In fact, the presence of glucose can inhibit the operon via catabolite repression, a mechanism that prevents the lac operon from being activated when glucose is available. Galactose is an intermediate in the metabolism of lactose, but it does not directly induce the lac operon.
Thus, Statement I is true, and Statement II is false, making the correct answer (a).
Q14: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2024)
Statement I: In eukaryotes, there are three RNA polymerases in the nucleus in addition to the RNA polymerase found in the organelle.
Statement II: All the three RNA polymerases in the eukaryotic nucleus have different roles.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect.
(b) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect.
Ans: (c)
Statement I: In eukaryotes, there are three RNA polymerases in the nucleus in addition to the RNA polymerase found in the organelle: This statement is correct. In eukaryotic cells, there are three RNA polymerases in the nucleus:
- RNA polymerase I: Synthesizes ribosomal RNA (rRNA), except for 5S rRNA.
- RNA polymerase II: Synthesizes messenger RNA (mRNA) and other non-coding RNAs like small nuclear RNA (snRNA).
- RNA polymerase III: Synthesizes transfer RNA (tRNA), 5S rRNA, and other small RNAs.
In addition to these, RNA polymerase is also found in mitochondria and chloroplasts (in plants) where it is responsible for transcribing mitochondrial and plastid genomes.
Statement II: All the three RNA polymerases in the eukaryotic nucleus have different roles: This statement is correct. Each of the three RNA polymerases has a specific function in the transcription of different types of RNA. As mentioned:
- RNA polymerase I transcribes rRNA.
- RNA polymerase II transcribes mRNA and some other small RNAs.
- RNA polymerase III transcribes tRNA and 5S rRNA.
Therefore, both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
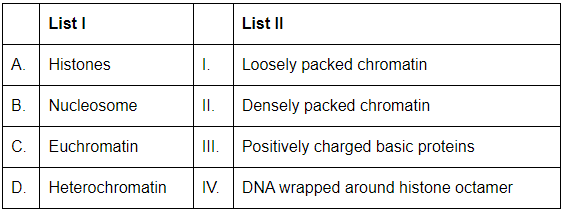
Q15: Match List I with List II: (NEET 2024)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-IV, B-III, C- II, D- I
(b) A-III, B-I, C- IV, D- II
(c) A-II, B-III, C- IV, D- I
(d) A-III, B-IV, C- I, D- II
Ans: (d)
A. Histones: Histones are positively charged basic proteins that help in the packaging of DNA into chromatin. Thus, A-III is the correct match.
B. Nucleosome: A nucleosome consists of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer. This is the basic structural unit of chromatin. Thus, B-IV is the correct match.
C. Euchromatin: Euchromatin is loosely packed chromatin, which is more active in transcription because it allows better access to DNA for transcription factors and RNA polymerase. Thus, C-I is the correct match.
D. Heterochromatin: Heterochromatin is densely packed chromatin and is generally transcriptionally inactive. Thus, D-II is the correct match.
Thus, the correct matching is:
- A-III: Histones are positively charged basic proteins.
- B-IV: Nucleosome is DNA wrapped around a histone octamer.
- C-I: Euchromatin is loosely packed chromatin.
- D-II: Heterochromatin is densely packed chromatin.
2023
Q1: Unequivocal proof that DNA is the genetic material was first proposed by (NEET 2023)
(a) Frederick Griffith
(b) Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase
(c) Avery, Macleoid and McCarthy
(d) Wilkins and Franklin
Ans: (b)
- The first unequivocal proof that DNA is the genetic material came from the experiments conducted by Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase in 1952. They used bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) and radioactively labeled the protein and DNA of the phage separately in two different sets of experiments. They found that it was the DNA, not the protein, of the phage that was injected into the bacteria and carried the genetic information necessary for the production of new phage particles.
- Avery, Macleoid and McCarty gave the biochemical characterisation of Transforming Principle.
- The transformation experiments by using Pneumococcus was conducted by Frederick Griffith.
- Wilkins and Franklin produced X-ray diffraction data of DNA.
So, the correct answer is : Option B : Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase.
Q2: What is the role of RNA polymerase III in the process of transcription in Eukaryotes? (NEET 2023)
(a) Transcription of rRNAs (28S, 18S and 5.8S)
(b) Transcription of tRNA, 5S rRNA and snRNA
(c) Transcription of precursor of mRNA
(d) Transcription of only snRNAs
Ans: (b)
In eukaryotes, there are two additional complexities – (i) There are at least three RNA polymerases in the nucleus (in addition to the RNA polymerase found in the organelles). There is a clear cut division of labour. The RNA polymerase I transcribes rRNAs (28S, 18S, and 5.8S), whereas the RNA polymerase III is responsible for transcription of tRNA, 5srRNA, and snRNAs (small nuclear RNAs). The RNA polymerase II transcribes precursor of mRNA, the heterogeneous nuclear RNA (hnRNA).
Q3: Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) refers to (NEET 2023)
(a) All genes that are expressed as RNA.
(b) All genes that are expressed as proteins.
(c) All genes whether expressed or unexpressed.
(d) Certain important expressed genes.
Ans: (a)
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) are short sub-sequences of a cDNA sequence. They may identify expressed genes, so they are derived from mRNA which is transcribed from expressed genes. They serve as a kind of "tag" or marker for identifying the gene from which it was transcribed. Therefore, ESTs represent genes that are expressed as RNA. The other options listed do not accurately describe what ESTs are.
Q4: Match List I with List II. (NEET 2023)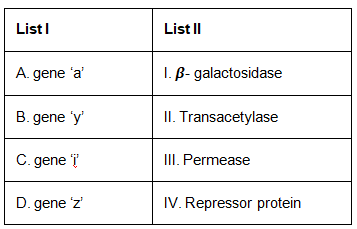
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
(b) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(c) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(d) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
Ans: (b)
The question relates to the lac operon model in E. coli, which is a well-studied example of gene regulation. In this model :
- Gene 'z' codes for beta-galactosidase (breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose)
- Gene 'y' codes for permease (transports lactose into the cell)
- Gene 'a' codes for transacetylase (may help in lactose metabolism, but its exact role is unclear)
- Gene 'i' codes for the repressor protein (binds to the operator to prevent transcription)
So, matching the List I (genes) with List II (proteins they code for) :
- A (Gene 'a') matches with II (Transacetylase)
- B (Gene 'y') matches with III (Permease)
- C (Gene 'i') matches with IV (Repressor protein)
- D (Gene 'z') matches with I (Beta-galactosidase)
Therefore, the correct option is : Option A : A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
Q6: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2023)
Statement I: In prokaryotes, the positively charged DNA is held with some negatively charged proteins in a region called nucleoid.
Statement II: In eukaryotes, the negatively charged DNA is wrapped around the positively charged histone octamer to form nucleosome.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
(c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is false.
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is true.
Ans: (d)
Statement I is incorrect. In prokaryotes, there is no well-defined nucleus or nucleosomes as found in eukaryotes. The DNA in prokaryotes is located in a region called the nucleoid, but it is not associated with histones or proteins in the same way as eukaryotic DNA.
Statement II is true. In eukaryotes, the negatively charged DNA is indeed wrapped around the positively charged histone octamer to form nucleosomes, which are the basic units of chromatin organization.
Q7: Which one of the following is the sequence on corresponding coding strand, if the sequence on mRNA formed is as follows 5’AUCGAUCGAUCGAUCGAUCGAUCG AUCG 3’? (NEET 2023)
(a) 5’ UAGCUAGCUAGCUAGCUAGCUAGCUAGC 3’
(b) 3’ UAGCUAGCUAGCUAGCUAGCUAGCUAGC 5’
(c) 5’ ATCGATCGATCGATCGATCGATCGATCG 3’
(d) 3’ ATCGATCGATCGATCGATCGATCGATCG 5’
Ans: (c)
The sequence on the mRNA is 5’AUCGAUCGAUCGAUCGAUCGAUCG AUCG 3’. The mRNA is synthesized from the template strand of DNA by complementary base pairing, following these rules: A pairs with U, U pairs with A, C pairs with G, and G pairs with C. The coding strand of DNA has the same sequence as the mRNA, except with T instead of U.
To find the sequence on the corresponding coding strand, we can use these rules to convert the mRNA sequence back to DNA :
5’ AUCGAUCGAUCGAUCGAUCGAUCG AUCG 3’ (mRNA)
5’ ATCGATCGATCGATCGATCGATCG ATCG 3’ (coding strand DNA)
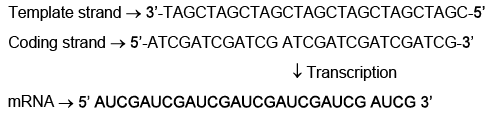
Q8: How many different proteins does the ribosome consist of? (NEET 2023)
(a) 20
(b) 80
(c) 60
(d) 40
Ans: (b)
The ribosome is made up of several proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). In eukaryotes, the ribosome consists of about 80 different proteins, while in prokaryotes, it consists of about 50-60 proteins. These proteins are associated with the large and small subunits of the ribosome, which play crucial roles in protein synthesis.
Thus, the correct answer is 80.
Q9: Which of the following is not a cloning vector? (NEET 2023)
(a) Probe
(b) BAC
(c) YAC
(d) PBR322
Ans: (a)
A cloning vector is a DNA molecule used to carry foreign genetic material into a host cell for replication or expression. The following are examples of cloning vectors:
- BAC (Bacterial Artificial Chromosome): A vector used to clone large DNA fragments, typically used for genomic library construction.
- YAC (Yeast Artificial Chromosome): A vector used for cloning very large fragments of DNA in yeast cells.
- PBR322: A plasmid vector commonly used for cloning small DNA fragments in bacteria.
On the other hand, a probe is a short, labeled DNA or RNA sequence used to detect the presence of complementary sequences in a sample (usually through hybridization), but it is not a cloning vector.
Thus, the correct answer is (a) Probe.
Q10: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2023)
Statement I: RNA mutates at a faster rate.
Statement II: Viruses having RNA genome and shorter life span mutate and evolve faster.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is false but Statement II is true.
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are true.
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are false.
(d) Statement I is true but Statement II is false.
Ans: (b)
Statement I: RNA mutates at a faster rate: This statement is true. RNA viruses tend to have a higher mutation rate compared to DNA viruses or organisms. This is because RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (which are used by RNA viruses to replicate their RNA genomes) lack the proofreading mechanisms that DNA polymerases have, leading to a higher rate of mutations during replication.
Statement II: Viruses having RNA genome and shorter life span mutate and evolve faster: This statement is true. RNA viruses, due to their higher mutation rate and shorter life spans (which lead to faster replication cycles), evolve more rapidly compared to DNA viruses. The fast mutation rate allows RNA viruses to adapt quickly to changes in their environment, including host immune responses or antiviral treatments.
Thus, both Statement I and Statement II are true. The correct answer is (b).
Q11: The last chromosome sequenced in the Human Genome Project was: (NEET 2023)
(a) Chromosome 6
(b) Chromosome 1
(c) Chromosome 22
(d) Chromosome 14
Ans: (b)
The Human Genome Project (HGP) aimed to map and sequence the entire human genome. The last chromosome to be sequenced was Chromosome 1. Chromosome 1 is the largest human chromosome and contains the most genes, making its sequencing a major challenge. The sequencing of Chromosome 1 was completed in 2006, which marked the final major milestone in the Human Genome Project.
Q12: The component that binds to the operator region of an operon and prevents RNA polymerase from transcribing the operon is:
(a) Promotor
(b) Regulator protein
(c) Repressor protein
(d) Inducer (NEET 2023)
Ans: (c)
In an operon, the repressor protein binds to the operator region of the DNA. This binding prevents RNA polymerase from transcribing the genes of the operon, thereby inhibiting gene expression. The repressor protein acts as a regulatory element in gene expression by blocking the transcription process in the presence or absence of specific molecules like inducers or co-repressors.
Promotor: The promoter is the region where RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription, not where the repressor binds.
Regulator protein: This is a broader term that can refer to any protein that regulates gene expression, but the repressor protein is the specific one that binds to the operator.
Inducer: An inducer molecule can bind to the repressor, changing its shape and preventing it from binding to the operator, thus allowing transcription.
Thus, the repressor protein is the correct component that binds to the operator region and prevents RNA polymerase from transcribing the operon.
Q13: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2023)
I: The process of copying genetic information from one strand of the DNA into RNA is termed as transcription.
II: A transcription unit in DNA is defined primarily by the three regions in the DNA i.e. a promoter, the structural gene, and a terminator.
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
(b) Statement I is false but Statement II is true
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
Ans: (c)
Statement I: The process of copying genetic information from one strand of the DNA into RNA is termed as transcription: This statement is true. Transcription is the process by which an RNA molecule is synthesized from a DNA template strand. During transcription, the enzyme RNA polymerase synthesizes RNA by copying the genetic code from the DNA into RNA, specifically messenger RNA (mRNA).
Statement II: A transcription unit in DNA is defined primarily by the three regions in the DNA i.e. a promoter, the structural gene, and a terminator: This statement is true. A transcription unit consists of:
- Promoter: The region where RNA polymerase binds to initiate transcription.
- Structural gene: The gene that gets transcribed into RNA.
- Terminator: The region where RNA polymerase stops transcription, ending the process.
Thus, both Statement I and Statement II are correct, making the correct answer (c).
Q14: Which scientist conducted an experiment with 32P and 35S labelled phages for demonstrating that DNA is the genetic material?
(a) James D. Watson and F.H.C Crick
(b) A.D. Hershey and M.J. Chase
(c) F. Griffith
(d) O.T. Avery, C.M. MacLeod and M. McCarty (NEET 2023)
Ans: (b)
A.D. Hershey and M.J. Chase conducted their famous experiment in 1952 using radioactively labeled bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) to demonstrate that DNA is the genetic material. In their experiment:
- They used 32P to label the DNA of the bacteriophage (because DNA contains phosphorus) and 35S to label the protein (because proteins contain sulfur).
- After the phages infected the bacteria, they observed that only the DNA (not the protein) entered the bacterial cells and directed the synthesis of new viral particles, thus proving that DNA, not protein, carries genetic information.
This experiment is one of the key pieces of evidence supporting the idea that DNA is the genetic material.
Thus, the correct answer is (B): A.D. Hershey and M.J. Chase.
Q15: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2023)
Statement I: RNA being unstable, it mutates at a faster rate.
Statement II: RNA can directly code for synthesis of proteins hence can easily express the characters.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect.
(b) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct.
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct.
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect.
Ans: (c)
Statement I: RNA being unstable, it mutates at a faster rate: This statement is correct. RNA molecules, especially those in viruses, tend to be less stable than DNA, and this instability contributes to a higher mutation rate. RNA viruses, in particular, have a higher mutation rate due to the lack of proofreading mechanisms during replication.
Statement II: RNA can directly code for the synthesis of proteins hence can easily express the characters: This statement is correct. RNA, specifically mRNA (messenger RNA), directly codes for the synthesis of proteins in the process of translation. This is a key aspect of genetic expression, where the information in the RNA is used to assemble amino acids into proteins, which are responsible for the traits and functions of an organism.
Thus, both Statement I and Statement II are correct, making the correct answer (c).
Q16: Which one of the following acts as an inducer for lac operon? (NEET 2023)
(a) Sucrose
(b) Lactose
(c) Glucose
(d) Galactose
Ans: (b)
In the lac operon system of E. coli, lactose acts as the inducer. When lactose is present in the environment, it binds to the repressor protein and causes a conformational change that prevents the repressor from binding to the operator region of the operon. This allows RNA polymerase to transcribe the genes required for lactose metabolism, specifically β-galactosidase, which breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose.
Sucrose, glucose, and galactose do not function as inducers for the lac operon.
Thus, lactose is the correct inducer for the lac operon.
Q17: With reference to Hershey and Chase experiments, select the correct statements: (NEET 2023)
A: Viruses grown in the presence of radioactive phosphorus contained radioactive DNA.
B: Viruses grown on radioactive sulphur contained radioactive proteins.
C: Viruses grown on radioactive phosphorus contained radioactive protein.
D: Viruses grown on radioactive sulphur contained radioactive DNA.
E: Viruses grown on radioactive protein contained radioactive DNA.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) (D) and (E) only
(b) (A) and (B) only
(c) (A) and (C) only
(d) (B) and (D) only
Ans: (b)
In the Hershey and Chase experiment (1952), they used radioactive isotopes to label the components of the bacteriophage (virus) and traced which component entered the bacterial cell during infection. They used 32P to label DNA (since DNA contains phosphorus) and 35S to label protein (since proteins contain sulfur but no phosphorus). The key results were:
- (A): Viruses grown in the presence of radioactive phosphorus contained radioactive DNA: This is true. The viral DNA was labeled with 32P (radioactive phosphorus) and was found to enter the bacterial cell, confirming that DNA carries the genetic information.
- (B): Viruses grown on radioactive sulphur contained radioactive proteins: This is true. The protein coat of the virus was labeled with 35S (radioactive sulfur) and remained outside the bacterial cell, confirming that the protein coat did not enter the host cell.
- (C): Viruses grown on radioactive phosphorus contained radioactive protein: This is false. The phosphorus label was incorporated into the DNA, not the protein.
- (D): Viruses grown on radioactive sulphur contained radioactive DNA: This is false. The sulfur label was incorporated into the protein, not the DNA.
- (E): Viruses grown on radioactive protein contained radioactive DNA: This is false. The radioactive sulfur label was in the protein, not the DNA.
Thus, the correct statements are (A) and (B), making the correct answer (b).
Q18: The salient features of genetic code are: (NEET 2023)
(A) The code is palindromic
(B) UGA acts as initiator codon
(C) The code is unambiguous and specific
(D) The code is nearly universal
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) and (D) only
(b) (B) and (C) only
(c) (A) and (B) only
(d) (C) and (D) only
Ans: (d)
(A) The code is palindromic: This statement is incorrect. The genetic code is not palindromic. A palindromic sequence refers to one that reads the same forwards and backwards, but this does not apply to the genetic code.
(B) UGA acts as the initiator codon: This statement is incorrect. UGA is actually a stop codon, not the initiator codon. The initiator codon is AUG, which codes for methionine.
(C) The code is unambiguous and specific: This statement is correct. The genetic code is unambiguous, meaning each codon specifies only one amino acid or a stop signal. It is also specific, meaning that each codon is assigned to a specific amino acid.
(D) The code is nearly universal: This statement is correct. The genetic code is nearly universal among all living organisms, meaning that the same codons usually specify the same amino acids across different species.
Thus, the correct features of the genetic code are (C) and (D), making the correct answer (4).
2022
Q1: The process of translation of mRNA to proteins begins as soon as: (NEET 2022)
(a) The larger subunit of ribosome encounters mRNA
(b) Both the subunits join together to bind with mRNA
(c) The tRNA is activated and the larger subunit of ribosome encounters mRNA
(d) The small subunit of ribosome encounters mRNA
Ans: (d)
When the small subunit of ribosome encounters an mRNA, the process of translation of the mRNA to protein begins. This process is followed by the binding of bigger/larger subunit.
t-RNA is activated by the addition of amino acid prior to the attachment or ribosome, in the first phase.
Q2: Read the following statements and choose the set of correct statements: (NEET 2022)
(A) Euchromatin is loosely packed chromatin
(B) Heterochromatin is transcriptionally active
(C) Histone octomer is wrapped by negatively charged DNA in nucleosome
(D) Histones are rich in lysine and arginine
(E) A typical nucleosome contains 400 bp of DNA helix
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (C), (D) Only
(b) (B), (E) Only
(c) (A), (C), (E) Only
(d) (B), (D), (E) Only
Ans: (a)
- Heterochromatin is transcriptionally inactive. A typical nucleosome contains 200 bp of DNA helix.
- Euchromatin is the loosely packed chromatin region.
- The negatively charged DNA is wrapped around the positively charged histone octamer to form a structure called nucleosome. Histones are rich in basic amino acid residues lysine and arginine.
Q3: DNA Polymorphism forms the basis of: (NEET 2022)
(a) DNA finger printing
(b) Both genetic mapping and DNA finger printing
(c) Translation
(d) Genetic mapping
Ans: (b)
Polymorphism in DNA sequence is the basis of genetic mapping of human genome as well as of DNA finger printing.
Q4: If the length of a DNA molecule is 1.1 metres, what will be the approximate number of base pairs? (NEET 2022)
(a) 6.6 x 109 bp
(b) 3.3 x 106 bp
(c) 6.6 x 106 bp
(d) 3.3 x 109 bp
Ans: (d)
The two chains of DNA are coiled in a right-handed helicle fashion. The pitch of the helix is 3.4 nm and has a diameter of 2 nm. In the B-form of DNA, the distance between a bp in a helix is approximately 0.34 nm which means there are about 10 nucleotides present in a complete turn.
The total length of DNA molecule in nm = 1.1 × 109 nm.
The approximate number of base pairs = 1.1 × 109/ 0.34
= 3.3 × 109
Q5: If a geneticist uses the blind approach for sequencing the whole genome of an organism, followed by assignment of function to different segments, the methodology adopted by him is called as : (NEET 2022)
(a) Sequence annotation
(b) Gene mapping
(c) Expressed sequence tags
(d) Bioinformatics
Ans: (a)
Sequencing the whole set of genome that contained all the coding and non-coding sequences and later assigning different regions in the sequence with functions is called sequence annotation.
Q6: In an E. coli strain, i gene gets mutated, and its product cannot bind the inducer molecule. If the growth medium is provided with lactose, what will be the outcome? (NEET 2022)
(a) RNA polymerase will bind the promoter region
(b) Only z gene will get transcribed
(c) z, y, a genes will be transcribed
(d) z, y, a genes will not be translated
Ans: (d)
Let us understand the genes of lac operon:
| Sl. No | Gene on the lac operon | Function |
| 1 | i gene | It is called the regulatory gene; it codes for the repressor of the lac operon. |
| 2 | Z gene | It encodes for beta-galactosidase; it acts on disaccharides like lactose and converts them into glucose and galactose. |
| 3 | y gene | It encodes for permease; it increases the permeability of the cell to beta galactosides. |
| 5 | a gene | It encodes for transacetylase. |
- In presence of an inducer (lactose) the repressor is inactivated by its interaction with the inducer. Thus, the RNA polymerase transcribes the operon into lac mRNA and the z, y, a gene will be translated into their corresponding products.
- If i gene gets mutated and its product can not bind the inducer then there is no interaction between the repressor and the inducer. The repressor will not be inactivated. Thus, the RNA polymerase will not transcribe the operon, and the z, y, and a gene will not be translated.
So, the correct answer is option (d).
Q7: Ten E.coli cells with 15N - dsDNA are incubated in medium containing 14N nucleotide. After 60 minutes, how many E.coli cells will have DNA totally free from 15N? (NEET 2022)
(a) 20 cells
(b) 40 cells
(c) 60 cells
(d) 80 cells
Ans: (c)
From 10 parent E.coli cells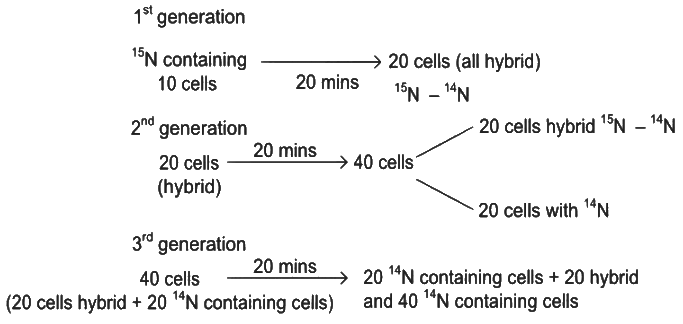
Therefore, after 60 minutes, 60 E.coli cells will have DNA totally free from 15N.
Q8: In lac operon, z gene codes for (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) Transacetylase
(b) β-galactosidase
(c) Permease
(d) Repressor
Ans: (b)
In lac operon, z gene codes for β-galactosidase.
Transacetylase, permease and repressor protein are coded by genes 'a', 'y' and 'i' respectively.
Q9: Given below are two statements (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Statement I : DNA polymerases catalyse polymerisation only in one direction, that is 5' → 3'.
Statement II : During replication of DNA, on one strand the replication is continuous while on other strand it is discontinuous.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(d) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
Ans: (b)
The DNA-dependent DNA polymerases catalyse polymerisation only in one direction, that is 5' → 3'. This creates some additional complications at the replicating fork. Consequently, on one strand (the template with polarity 3' → 5'), the replication is continuous, while on the other (the template with polarity 5' → 3'), it is discontinuous.
Q10: Match List - I with List - II. (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
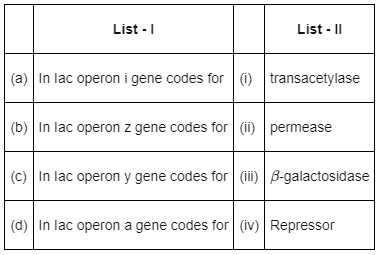
Choose the correct answer from the options given below
(a) (a) - (iii), (b) - (i), (c) - (iv), (d) - (ii)
(b) (a) - (iii), (b) - (ii), (c) - (i), (d) - (iv)
(c) (a) - (iv), (b) - (iii), (c) - (ii), (d) - (i)
(d) (a) - (iv), (b) - (i), (c) - (iii), (d) - (ii)
Ans: (c)
In Iac operon,
- The i gene codes for repressor protein.
- The z gene codes for β-galactosidase.
- The y gene codes for permease and the a gene codes for transacetylase.
Q11: Match List-I with List-II: (NEET 2022 Phase 2)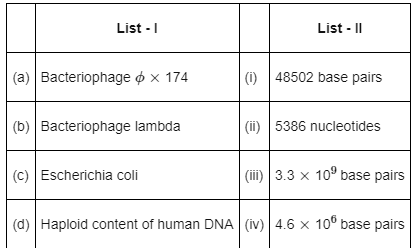
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (a)-(i), (b)-(ii), (c)-(iv), (d)-(iii)
(b) (a)-(i), (b)-(ii), (c)-(iii), (d)-(iv)
(c) (a)-(ii), (b)-(iv), (c)-(i), (d)-(iii)
(d) (a)-(ii), (b)-(i), (c)-(iv), (d)-(iii)
Ans: (d)
Genetic material of –
- Bacteriophage ∅ × 174 contains 5386 nucleotides
- Bacteriophage lambda contains 48502 base pairs
- Escherichia coli contains 4.6 × 106 base pairs
- Haploid content of human DNA contains 3.3 × 109 base pairs
Q12: Against the codon 5' UAC 3', what would be the sequence of anticodon on tRNA? (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) 5' GUA 3'
(b) 5' AUG 3'
(c) 5' ATG 3'
(d) 5' GTA 3'
Ans: (b)
- In the process of translation, the mRNA codon pairs with the tRNA anticodon to bring the correct amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain. The pairing between the codon and anticodon follows the complementary base-pairing rules, with adenine (A) pairing with uracil (U), and guanine (G) pairing with cytosine (C).
- In this case, the mRNA codon is given as 5' UAC 3'. To determine the tRNA anticodon sequence, we must follow the base-pairing rules:
- The U (uracil) in the codon pairs with A (adenine) in the anticodon.
- The A (adenine) in the codon pairs with U (uracil) in the anticodon.
- The C (cytosine) in the codon pairs with G (guanine) in the anticodon.
- Therefore, the anticodon sequence on the tRNA would be 5' AUG 3'.
Q13: If A and C make 30% and 20% of DNA, respectively, what will be the percentage composition of T and G?
(a) T : 20%, G : 20%
(b) T : 20%, G : 30%
(c) T : 30%, G : 20%
(d) T : 30%, G : 30% (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (c)
According to Chargaff’s rule, amount of Adenine (A) is equal to thymine and amount of cytosine (c) will be equal to that of Guanine.
So,
A = T = 30% + 30% = 60%
C = G = 20% + 20% = 40%
So, T and G will be 30% and 20% respectively.
2021
Q1: Complete the flow chart on central dogma (NEET 2021)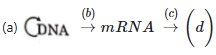
(a) (a) - Replication; (b) - Transcription;
(c) - Translation; (d) - Protein
(b) (a) - Transduction; (b) - Translation;
(c) - Replication; (d) - Protein
(c) (a) - Replication; (b) - Transcription;
(c) - Transduction; (d) - Protein
(d) (a) - Transcription; (b) - Replication;
(c) - Transcription; (d) - Transduction
Ans: (a)
- Formation of DNA from DNA is replication.
- Formation of mRNA from DNA is called Transcription.
- Formation of protein from mRNA is called Translation.
So,
(a) is Replication
(b) is Transcription
(c) is Translation
(d) is Protein
- Transduction is transfer of genetic material from one bacterium to another with the help of virus or a bacteriophage.
Q2: What is the role of RNA polymerase III in the process of transcription in eukaryotes? (NEET 2021)
(a) Transcribes precursor of mRNA
(b) Transcribes only snRNAs
(c) Transcribes rRNAs (28S, 18S, and 5.8S)
(d) Transcribes tRNA, 5s rRNA and snRNA
Ans: (d)
- RNA polymerase III transcribes tRNA, ScRNA, 5S rRNA and snRNA.
- RNA polymerase I transcribes 5.8S, 18S and 28S rRNA.
- RNA polymerase II transcribes hnRNA which is precursor of mRNA
Q3: DNA fingerprinting involves identifying differences in some specific regions in DNA sequence, called as (NEET 2021)
(a) Single nucleotides
(b) Polymorphic DNA
(c) Satellite DNA
(d) Repetitive DNA
Ans: (d)
- DNA fingerprinting involves identifying differences in some specific regions in DNA sequence called as repetitive DNA.
- The basis of DNA fingerprinting is VNTR (a satellite DNA as probe that show very high degree of polymorphism)
- Polymorphism is the variation at genetic level. Allelic sequence variation has traditionally been described as a DNA polymorphism.
Q4: Identify the correct statement. (NEET 2021)
(a) The coding strand in a transcription unit is copied to an mRNA.
(b) Split gene arrangement is characteristic of prokaryotes.
(c) In capping, methylguanosine triphosphate is added to the 3' end of hnRNA.
(d) RNA polymerase binds with the Rho factor to terminate the process of transcription in bacteria.
Ans: (d)
- Split gene arrangement is characteristic of eukaryotes.
- In capping 5-methyl guanosine triphosphate is added at 5' end of hnRNA.
- At 3' end poly-A tail is added.
- The non coding or template strand is copied to an mRNA. RNA polymerase associate with ρ factor (Rho factor) and it alters the specificity of the RNA polymerase to terminate the processes.
Q5: If Adenine makes 30% of the DNA molecule, what will be the percentage of Thymine, Guanine and Cytosine in it? (NEET 2021)
(a) T:30 ; G:20 ; C:20
(b) T:20 ; G:25 ; C:25
(c) T:20 ; G:30 ; C:20
(d) T:20 ; G:20 ; C:30
Ans: (a)
Chargaff rule - In DNA there is always equality in quantity between the bases A and T and between the bases G and C.
According to Chargaff's rule, for a double stranded DNA,
[A] = [T],
∵ [A] = 30%, ⇒ [T] = 30%
Since [C] = [G]
∴ 100 − [A + T]
= 100 − [30 + 30]
= 100 − 60 = 40%
and C = G = 20% each
∴ [A] = 30%
[T] = 30%
[G] = 20%
[C] = 20%
Q6: Which of the following RNAs is not required for the synthesis of protein? (NEET 2021)
(a) rRNA
(b) siRNA
(c) mRNA
(d) tRNA
Ans: (b)
- siRNA mainly protect the cell from exogenous mRNA attacks. It degrades the growing mRNA and stop gene expression. It is highly specific and reduces the synthesis of particular proteins by reducing the translation of specific messenger RNAs. Hence, siRNA is not required for protein synthesis but is used to reduce its synthesis.
- mRNA is messenger RNA that carries genetic information provided by DNA.
- tRNA carries amino acids to the mRNA during translation.
- rRNA is structural RNA that forms ribosomes which are involved in translation.
Q7: Which is the "Only enzyme" that has "Capability to catalyze Initiation, Elongation, and Termination in the process of transcription in prokaryotes? (NEET 2021)
(a) DNA Ligase
(b) DNase
(c) DNA dependent DNA polymerase
(d) DNA dependent RNA polymerase
Ans: (d)
Prokaryotes utilize one RNA polymerase for transcription of all types of RNA. The enzyme RNA polymerase is needed for RNA formation from DNA, i.e. DNA dependent RNA polymerase. It occurs in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells. RNA polymerase is the only enzyme which, has the capability to catalyse all initiation, elongation and termination in prokaryotes.
Q8: Which one of the following statements about Histones is wrong? (NEET 2021)
(a) Histones are rich in amino acids - Lysine and Arginine.
(b) Histones carry a positive charge in the side chain.
(c) Histones are organized to form a unit of 8 molecules.
(d) The pH of histones is slightly acidic.
Ans: (d)
- Histones are rich in basic amino acids residue lysine and arginine with charged side chain.
- There are five types of histone proteins i.e. H1, H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. Four of them occur in pairs to produce a unit of 8 molecules (histone octamer).
- The pH of histones is basic.
Q9: Statement I: The codon 'AUG codes for methionine and phenylalanine.
Statement II: AAA' and 'AAG are both codons that code for the amino acid lysine.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below. (NEET 2021)
(a) Statement I is correct but Statement II is false
(b) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is true
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
Ans: (b)
Statement I: The codon 'AUG' codes for methionine and phenylalanine.
- This statement is false,AUG codes only for methionine amino acid.
- One codon codes for specific amino acids only but one amino acid can be coded by more than one codon.
- So, codons are unambiguous and specific.
Statement II: AAA and 'AAG' both codons code for the amino acid lysine.
- This statement is true, one amino acid can be coded by more than one codon.
- Lysine amino acids can be coded by AAA and AAG both.
- So, codons are degenerate.
2020
Q1: If the distance between two consecutive base pairs is 0.34 nm and the total number of base pairs of a DNA double helix in a typical mammalian cell is 6.6 × 109 dp, then the length of the DNA is approximately. (NEET 2020)
(a) 2.2 meters
(b) 2.7 meters
(c) 2.0 meters
(d) 2.5 meters
Ans: (a)
The diploid content of human genome is 6.6 x 109 base pairs. The distance between two consecutive base pairs is 0.34 nm (0.34 x 10-9 m), so the length of DNA double helix in a typical mammalian cell is around 6.6 x 10-9 bp x 0.34 x 10-9m/bp = 2.2 metres.
Q2: The first phase of translation is: (NEET 2020)
(a) Aminoacylation of tRNA
(b) Recognition of an anti-codon
(c) Binding of mRNA to ribosome
(d) Recognition of DNA molecule
Ans: (a)
The first phase of translation involves activation of amino acid in the presence of ATP and linked to their cognate tRNA - a process commonly called as charging of tRNA or aminoacylation of tRNA.
Q3: Name the enzyme that facilitates opening of DNA helix during transcription. (NEET 2020)
(a) DNA polymerase
(b) RNA polymerase
(c) DNA ligase
(d) DNA helicase
Ans: (b)
- The enzyme that facilitates opening of the DNA helix during transcription is RNA polymerase.
- RNA polymerase is responsible for the synthesis of RNA from a DNA template during transcription. It binds to the DNA at a specific site called the promoter region and then unwinds the DNA helix to expose the template strand. This opening of the DNA helix is facilitated by the activity of RNA polymerase, which breaks the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs of the DNA.
- Once the DNA is unwound, RNA polymerase can begin the synthesis of RNA by adding complementary RNA nucleotides to the template strand. The RNA polymerase moves along the DNA strand, opening the helix as it goes, and synthesizing a new RNA molecule.
Therefore, option B, "RNA polymerase," is the correct answer.
Q4: Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) Adenine does not pair with thymine
(b) Adenine pairs with thymine through one H-bond
(c) Adenine pairs with thymine through two H-bonds
(d) Adenine pairs with thymine through three H-bonds (NEET 2020)
Ans: (c)
Based on the observation of Erwin Chargaff that for a double stranded DNA, the ratios between Adenine and Thymine and Guanine and Cytosine are constant and equals one. Adenine pairs with thymine through two H-bonds i.e., A = T and guanine pairs with cytosine with three H-bonds.
2019
Q1: Purines found both in DNA and RNA are (NEET 2019)
(a) Cytosine and thymine
(b) Adenine and thymine
(c) Adenine and guanine
(d) Guanine and cytosine
Ans: (c)
Adenine and guanine are purines which are common to both DNA and RNA.
Q2: Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) refers to (NEET 2019)
(a) Novel DNA sequences
(b) Genes expressed as RNA
(c) Polypeptide expression
(d) DNA polymorphism
Ans: (b)
Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) are genes that are expressed as RNA. It is used in sequencing of human genome.
Q3: Match the following genes of the Lac operon with their respective products. (NEET 2019)
| (A) I gene | (i) β - galactosidase |
| (B) z gene | (ii) Permease |
| (C) a gene | (iii) Repressor |
| (D) y gene | (iv) Transacetylase |
Select the correct option.
| (A) | (B) | (C) | (D) | |
| (a) | (iii) | (iv) | (i) | (ii) |
| (b) | (i) | (iii) | (ii) | (iv) |
| (c) | (iii) | (i) | (ii) | (iv) |
| (d) | (iii) | (i) | (iv) | (ii) |
Ans: (d)
In lac operon
- I gene → Repressor
- z gene → β-galactosidase
- y gene → Permease
- a gene → Transacetylase
Q4: Which of the following features of genetic code does allow bacteria to produce human insulin by recombinant DNA technology? (NEET 2019)
(a) Genetic code is specific.
(b) Genetic code is not ambiguous.
(c) Genetic code is redundant.
(d) Genetic code is nearly universal.
Ans: (d)
In recombinant DNA technology, a bacterium is able to produce human insulin because genetic code is nearly universal. Human insulin is used to treat diabetes.
Q5: Under which of the following conditions there will be no change in the reading frame of following mRNA? (NEET 2019)
5' AACAGCGGUGCUAUU 3'
(a) Deletion of GGU from 7th, 8th and 9th positions
(b) Insertion of G at 5th position
(c) Deletion of G from 5th position
(d) Insertion of A and G at 4th and 5th position respectively
Ans: (a)
In case of deletion of GGU from 7th, 8th and 9th position, there will be no change in reading frame of mRNA.
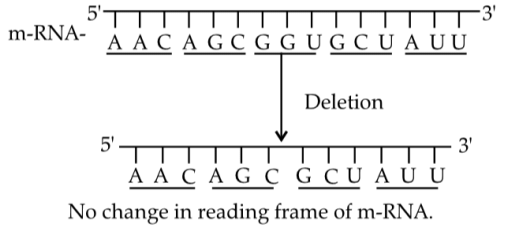
2018
Q1: Select the correct match. (NEET 2018)
(a) Alec Jeffreys - Streptococcus pneumoniae
(b) Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase - TMV
(c) Matthew Meselson and F. Stahl - Pisum sativum
(d) Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod - Lac operon
Ans: (d)
Francois Jacob and Jacque Monod proposed model of gene regulation known as operon model/lac operon. Alec Jeffreys gave DNA fingerprinting technique. Matthew Meselson and F. Stahl gave semiconservative DNA replication in E.coli. Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase proved DNA as genetic material not protein.
Q2: The experimental proof for semi-conservative replication of DNA was first shown in a (NEET 2018)
(a) Fungus
(b) Bacterium
(c) Plant
(d) Virus
Ans: (b)
Semi-conservative DNA replication was first shown in bacterium escherichia coli by Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl.
Q3: Select the correct statement. (NEET 2018)
(a) Franklin Stahl coined the term ‘‘ linkage ’’.
(b) Punnett square was developed by a British scientist.
(c) Spliceosomes take part in translation.
(d) Transduction was discovered by S. Altman.
Ans: (b)
- Punnet square was developed by a British geneticist Reginald C. Punnet.
- Franklin Stahl and Meselson proved semiconservative mode of DNA replication.
- Morgan coined the term linkage.
- Transduction was discovered by Zinder and Lederberg.
Q4: Select the correct match. (NEET 2018)
(a) Ribozyme - Nucleic acid
(b) F2 x Recessive parent - Dihybrid cross
(c) T.H. Morgan - Transduction
(d) G. Mendel - Transformation
Ans: (a)
Ribozyme is a catalytic RNA, which is nucleic acid.
Q5: Many ribosomes may associate with a single wiRNA to form multiple copies of a polypeptide simultaneously. Such strings of ribosomes are termed as (NEET 2018)
(a) Polysome
(b) Polyhedral bodies
(c) Plastidome
(d) Nucleosome
Ans: (a)
- Ribosomes may occur singly a monosomes or in rosettes and helical groups called polysomes. The different ribosomes of a polysome are connected with a strand of m-RNA.
- Nucleosome is a basic unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes.
- Plastidome are the plastids of a cell when they are referred to a functional unit.
- Polyhedral bodies are involved in carbon fixation are present in autotrophic bacteria.
Q6: All of the following are part of an operon except (NEET 2018)
(a) An operator
(b) Structural genes
(c) An enhancer
(d) A promoter
Ans: (c)
Operon concept is for prokaryotes and enchancer sequences are present in eukaryotes.
Q7: AGGTATCGCAT is a sequence from the coding strand of a gene. What will be the corresponding sequence of the transcribed mRNA? (NEET 2018)
(a) AGGUAUCGCAU
(b) UGGTUTCGCAT
(c) ACCUAUGCGAU
(d) UCCAUAGCGUA
Ans: (a)
Coding strand and mRNA have same nucleotide sequence except, ‘T’ - Thymine is replaced by ‘U’ - Uracil in mRNA.
2017
Q1: The final proof for DNA as the genetic material came from the experiments of (NEET 2017)
(a) Hershey and Chase
(b) Avery, MacLeod and McCarty
(c) Hargobind Khorana
(d) Griffith
Ans: (a)
Hershey and Chase proved that DNA as genetic material. They used bacteriophage for their experiment.
Q2: If there are 999 bases in an RNA that code for a protein with 333 amino acids, and the base at position 901 is deleted such that the length of the RNA becomes 998 bases, how many codons will be altered? (NEET 2017)
(a) 11
(b) 33
(c) 333
(d) 1
Ans: (b)
If deletion happen at 901st position than the remaining 98 bases specifying for 33 codons of amino acids will be altered.
Q3: During DNA replication, Okazaki fragments are used to elongate (NEET 2017)
(a) The lagging strand towards replication fork
(b) The leading strand away from replication fork
(c) The lagging strand away from the replication fork
(d) The leading strand towards replication fork
Ans: (c)
- Two DNA polymerase molecules simultaneously work at the DNA fork, one on the leading strand and the other on the lagging strand.
- DNA polymerase synthesizes each Okazaki fragment at lagging strand in 5′-3′ direction. As the replication fork opens further, new Okazaki fragments appear. The first Okazaki fragment appears away from the replication fork and thus the direction of elongation would be away from replication fork.
Q4: Which of the following RNAs should be most abundant in animal cell? (NEET 2017)
(a) tRNA
(b) mRNA
(c) miRNA
(d) rRNA
Ans: (d)
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is most abundant in animal cell. It constitutes 80% of total RNA of the cell.
Q5: Spliceosomes are not found in cells of (NEET 2017)
(a) Fungi
(b) Animals
(c) Bacteria
(d) Plants
Ans: (c)
Spliceosomes help in removal of introns. They will not occur in prokaryotes because prokaryotes do not have introns and thus, processing does not require splicing of mRNA.
Q6: The association of histone H1 with a nucleosome indicates that (NEET 2017)
(a) DNA replication is occurring
(b) The DNA is condensed into a chromatin fibre
(c) The DNA double helix is exposed
(d) Transcription is occurring
Ans: (b)
Histones help in packaging of DNA. In eukaryotes, DNA packaging is carried out with the help of positively charged basic proteins called histones. Histones are of five types - H1 H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. H1 is attached over the linker DNA. Histone contains a large proportion of the positively charged (basic) amino acids, lysine and arginine in their structure. DNA is negatively charged due to the phosphate groups on its backbone. The result of these opposite charges is strong attraction and therefore, high binding affinity between histones and DNA.
2016
Q1: Taylor conducted the experiments to prove semiconservative mode of chromosome replication on (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Vinca rosea
(b) Vicia faba
(c) Drosophila melanogaster
(d) E. coli
Ans: b
Taylor et al. (1957) conducted experiment on Vicia faba (broad bean) to prove semiconservative replication of DNA. He fed dividing cells of root tips of Vicia faba with radioactive 3H containing thymine instead of normal thymine and found that all the chromosomes became radioactive. Labelled thymine was then replaced with normal one. Next generation came to have radioactivity in one of the two chromatids of each chromosome while in subsequent generation radioactivity was present in 50% of the chromosomes. This is possible only if out of the two strands of a chromosome, one is formed afresh while the other is conserved at each replication.
Q2: The equivalent of a structural gene is (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Muton
(b) Cistron
(c) Operon
(d) Recon
Ans: (b)
Cislron (or gene) is a length ot DNA that contains the information for coding a specific Polypeptide chain or a functional RNA molecule transfer RNA or ribosomal RNA). Hence, cistron is a unit of function. Currently such a gene is called structural gene.
Q3: Which of the following rRNAs acts as structural RNA as well as ribozyme in bacteria? (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) 5S rRNA
(b) 18S rRNA
(c) 23S rRNA
(d) 5.8S rRNA
Ans: (c)
23S rRNA acts as structural RNA as well as ribozyme in bacteria.
Q4: A molecule that can act as a genetic material must fulfill the traits given below, except (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) It should be able to express itself in the form of ‘Mendelian characters’
(b) It should be able to generate its replica
(c) It should be unstable structurally and chemically
(d) It should provide the scope for slow changes that are required for evolution.
Ans: (c)
Genetic material should be structurally and chemically stable otherwise its expression will change and lead to loss of several metabolic functions, etc.
Q5: DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyses transcription on one strand of the DNA which is called the (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Template strand
(b) Coding strand
(c) Alpha strand
(d) Antistrand
Ans: (a)
The strand of DNA on which RNA polymerase binds to catalyse transcription is called template strand. It is also known as master or antisense strand. It lias the polarity of 3' → 5'.
Q6: Which one of the following is the starter codon? (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) UAA
(b) UAG
(c) AUG
(d) UGA
Ans: (c)
The start codon is the first codon of a messenger RNA (mRNA) transcript translated by a ribosome. The start codon always codes for methionine in eukaryotes and a modified Met (fMet) in prokaryotes. The most common start codon is AUG.
Q7: Which of the following is required as inducer (s) for the expression of Lac operon? (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Lactose
(b) Lactose and Galactose
(c) Glucose
(d) Galactose
Ans: (a)
In Lac operon, lactose is an inducer. It binds with suppressor and inactivates it. It allows RNA polymers access to the promoter and transcription proceeds.
Q8: A complex of ribosomes attached to a single strand of RNA is known as (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Polypeptide
(b) Okazaki fragment
(c) Polysome
(d) Polymer
Ans: (c)
A polysome or polyribosome is a complex of an mRNA molecule and two or more ribosomes, which is formed during the active translation process. They were initially named as ergosomes in 1963. However, further research by Jonathan Warner and Alex Rich characterized polysome
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions(2016-25): Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Biology Class 12
| 1. What is the role of DNA replication in the molecular basis of inheritance? |  |
| 2. How do mutations contribute to genetic variation in organisms? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of gene mutations that can occur in DNA? |  |
| 4. How does DNA packaging and epigenetic modifications regulate gene expression? |  |
| 5. How is the central dogma of molecular biology related to the process of gene expression? |  |

















