NEET Previous Year Questions(2016-25): Principles of Inheritance & Variation | Biology Class 12 PDF Download
2025
Q1: What is the pattern of inheritance for polygenic traits? (NEET 2025)
(a) Autosomal dominant pattern
(b) X-linked recessive inheritance pattern
(c) Mendelian inheritance pattern
(d) Non-Mendelian inheritance pattern
Ans: (d)
- Polygenic traits are traits controlled by multiple genes, often located on different chromosomes. These genes collectively contribute to the phenotype, and their effects are additive.
- Unlike single-gene traits studied by Mendel, polygenic traits do not follow simple dominant-recessive inheritance. Instead, they exhibit a Non-Mendelian inheritance pattern.
- Examples of polygenic traits include skin color, height, eye color, and weight in humans. These traits show a continuous range of variation rather than discrete categories.
- Environmental factors also play a significant role in the expression of polygenic traits.
- Polygenic traits are inherited in a manner that does not conform to Mendel’s laws of inheritance. The phenotypes result from the interaction of multiple genes, each with a small, cumulative effect.
Other Options:
- Mendelian inheritance pattern: This applies to single-gene traits where one gene determines the phenotype, with clear dominant and recessive alleles. Polygenic traits do not follow this pattern, as they are influenced by multiple genes and exhibit a range of phenotypes.
- Autosomal dominant pattern: In this inheritance pattern, a single copy of a dominant allele on an autosome is sufficient to express the trait.
- X-linked recessive inheritance pattern: This pattern refers to traits caused by recessive alleles on the X chromosome. These traits are often seen more in males due to their single X chromosome.
Q2: With the help of given pedigree, find out the probability for the birth of a child having no disease and being a carrier (has the disease mutation in one allele of the gene) in F3 generation. (NEET 2025)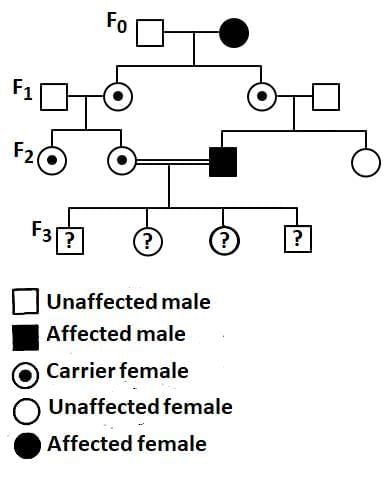
(a) 1/8
(b) Zero
(c) 1/4
(d) 1/2
Ans: (c)
- A pedigree chart is a diagram that shows the occurrence and appearance of phenotypes of a particular gene or organism and its ancestors, often used to determine inheritance patterns.
- Carriers are individuals who have one recessive allele (disease mutation) and one normal allele. They do not show symptoms of the disease but can pass the mutation to their offspring.
X-linked Recessive Mutation:
- Typically, X-linked recessive traits are more common in males because they only have one X chromosome.
- Affected males pass the trait to all their daughters, who are carriers, and to none of their sons.
- Carrier females (having one normal and one affected X chromosome) can pass the trait to both sons and daughters.
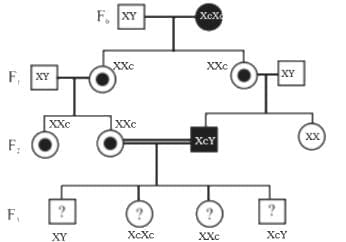
Thus, the correct answer is 1/4 (XXc)
Q3: Genes R and Y follow independent assortment. If RRYY produce round yellow seed and rryy produce wrinkled green seeds, what will be then phenotypic ratio of the F2 generation? (NEET 2025)
(a) Phenotypic ratio - 9 : 3 : 3 : 1
(b) Phenotypic ratio - 9 :7
(c) Phenotypic ratio - 1 : 2 : 1
(d) Phenotypic ratio - 3 : 1
Ans: (a)
In pea plants:
- The round seed (R) is dominant over the wrinkled seed (r)
- The yellow color (Y) seed is dominant over the green color seed (y)
The cross is in the following,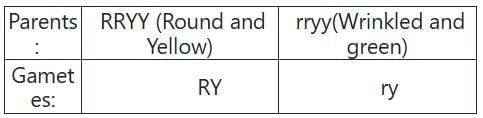 F1: RrYy (Round and yellow)
F1: RrYy (Round and yellow)
Selfing of F1: RrYy (Round and yellow) X RrYy (Round and yellow)
Gametes: RY, Ry, rY, ry X RY, Ry, rY, ry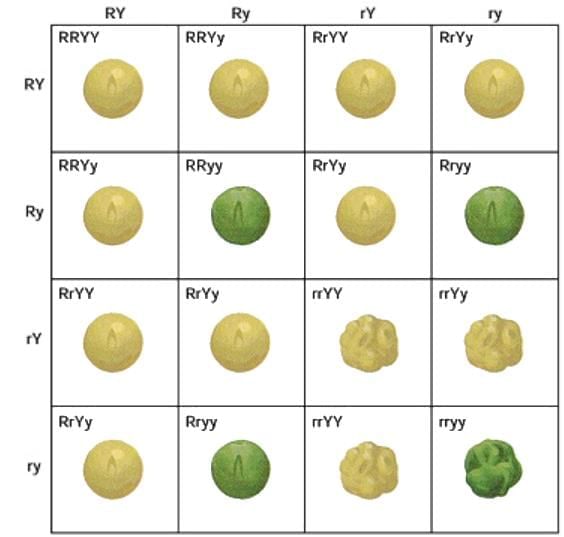
The phenotypic ratio produced is 9: 3: 3: 1.
- 9 - Round yellow
- 3 - Round green
- 3 - Wrinkled yellow
- 1 - Wrinkled green
Therefore, in F2 generation two new combination of seeds Round yellow and wrinkled green seeds would be produced that differ from the parent type.
2024
Q1:A pink flowered Snapdragon plant was crossed with a red flowered Snapdragon plant. What type of phenotype/s is/are expected in the progeny?
(a) Only red flowered plants
(b) Red flowered as well as pink flowered plants
(c) Only pink flowered plants
(d) Red, Pink as well as white flowered plants
Ans: (b)
Pink colour flower in snapdragon have genotype Rr
Red flowered snapdragon have genotype RR when they both are crossed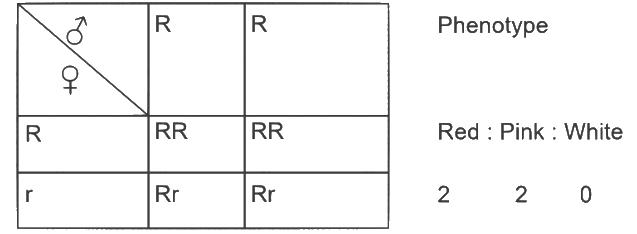 So the progeny that we get are red and pink flowered plants only.
So the progeny that we get are red and pink flowered plants only.
Q2: In a plant, black seed color (BB/Bb) is dominant over white seed color (bb). In order to find out the genotype of the black seed plant, with which of the following genotype will you cross it? (NEET 2024)
(a) BB
(b) bb
(c) Bb
(d) BB/Bb
Ans: (b)
To determine the genotype of a black seed plant that could either be homozygous dominant (BB) or heterozygous (Bb), you need to perform a test cross. A test cross involves crossing the individual in question with a homozygous recessive individual. In this scenario, that would be a plant with white seed color, or genotype bb.
A test cross is used because it can reveal whether the black seed plant carries the recessive b allele. When crossed with a homozygous recessive (bb) plant:
By observing the seed colors of the offspring, you can determine whether the black seed plant was homozygous dominant or heterozygous. If any white seeds appear among the offspring, the black seed plant must be heterozygous (Bb). If no white seeds appear, the black seed plant is likely homozygous dominant (BB).
Therefore, the correct option for crossing to determine the genotype of the black seed plant is: Option B bb
Q3: Which one of the following can be explained on the basis of Mendel's Law of Dominance? (NEET 2024)
A. Out of one pair of factors one is dominant and the other is recessive.
B. Alleles do not show any expression and both the characters appear as such in F2 generation.
C. Factors occur in pairs in normal diploid plants.
D. The discrete unit controlling a particular character is called factor.
E. The expression of only one of the parental characters is found in a monohybrid cross.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A, B and C only
(b) A, C, D and E only
(c) B, C and D only
(d) A, B, C, D and E
Ans: (b)
The correct answer is: Option B: A, C, D and E only Explanation:
Mendel's Law of Dominance states that in a heterozygote, the dominant allele will mask the expression of the recessive allele. Let's analyze the options:
A. Out of one pair of factors one is dominant and the other is recessive: This is the core principle of Mendel's Law of Dominance.
C. Factors occur in pairs in normal diploid plants: This is a fundamental concept in genetics, as diploid organisms have two copies of each chromosome, thus two copies of each gene (factors).
D. The discrete unit controlling a particular character is called factor: Mendel used the term "factor" to describe what we now know as genes.
E. The expression of only one of the parental characters is found in a monohybrid cross: This is a direct consequence of the law of dominance, where the dominant trait masks the expression of the recessive trait in the F1 generation of a monohybrid cross.
Option B is incorrect:
B. Alleles do not show any expression and both the characters appear as such in F2 generation: This statement is incorrect. While the recessive allele is not expressed in the F1 generation, it reappears in the F2 generation in a 3:1 ratio (dominant:recessive). This is due to the Law of Segregation, not the Law of Dominance.
Q4: Match List I with List II (NEET 2024)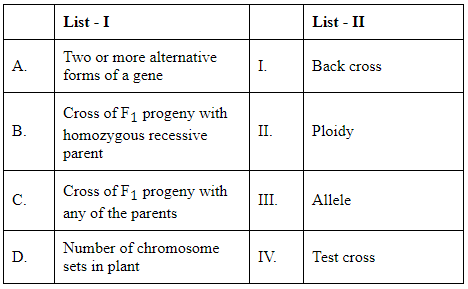
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(b) A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV
(c) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(d) A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
Ans: (c)
Let's analyze each term in List-I with the definitions presented in List-II:
A. Two or more alternative forms of a gene: These are called alleles. Thus, A matches with III 'Allele'.
B. Cross of F1 progeny with homozygous recessive parent: This specific type of cross is known as a test cross, often used to determine the genotype of an individual having dominant phenotype. Therefore, B matches with IV 'Test cross'.
C. Cross of F1 progeny with any of the parents: This is defined as a back cross, which can be used for multiple purposes, including the testing of the parental genes in the offspring. So, C matches with I 'Back cross'.
D. Number of chromosome sets in plant: This describes how many sets of chromosomes are present, i.e., the level of ploidy of the organism. Therefore, D matches with II 'Ploidy'.
From the analysis:
- A matches with III
B matches with IV
C matches with I
D matches with II
Accordingly, the correct answer that matches all the descriptions is: Option C: A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II.
Q5: As per ABO blood grouping system, the blood group of father is B+ , mother is A+ and child is O+ . Their respective genotype can be
A. IBi / IAi / ii
B. IBIB/ IAIA/ ii
C. IAIB/ iIA/ IBi
D. IAi/IBi/IAi
E. iIB / iIA / IAIB
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below : (NEET 2024)
(a) A only
(b) B only
(c) C & B only
(d) D & E only
Ans: (a)
The ABO blood group is determined by alleles IA, IB, and i, which are responsible for producing A, B, and O blood types, respectively. The IA and IB alleles are codominant, meaning both can be expressed if both are present, whereas the i allele is recessive.
Given the blood types in the problem statement:
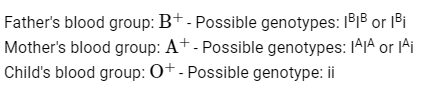 To find the correct pairing:
To find the correct pairing:
The child has an O blood type, meaning their genotype must be ii, indicating they inherited an i allele from each parent. Therefore, both parents must have at least one i allele.
Given this information:
Father's Genotype: It must include i since the child inherited i. Thus, the father's genotype could be IBi.
Mother's Genotype: It must also include i for the same reason, so the mother's genotype could be IAi.
Child's Genotype: It is confirmed as ii.
Matching this analysis with the provided options:
Option A: IBi/IAi/ii - This matches the reasoning provided.
Option B: IBIB/IAIA/ii - This is incorrect because it suggests that neither parent has a recessive i allele to pass to the child, which is necessary for the child’s blood type O.
Option C: iIB/iIA/IAIB - This is incorrect and does not match the required genotypes for the child to inherit ii.
Option D: IAi/IBi/IAi - This includes a typo in the children's genotype and misalignment with blood types.
Option E: iIB/iIA/IAIB - This is incorrect, mismatches the inheritance mechanism.
So the correct pairing based on the genotypes and blood groups mentioned, along with genetic laws, would be Option "A",
So the answer is: Option A
Q6: Match List I with List II : (NEET 2024)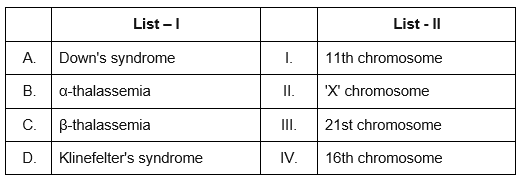
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
(b) A-II, B-III, C-IV, D-I
(c) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(d) A-IV, B-I, C-II, D-III
Ans: (c)
Sol: To correctly match List I with List II concerning medical conditions and their associated chromosomes, it's essential to have some understanding of genetics and chromosome abnormalities related with each condition. Here's the correct matching based on that information:
Down's syndrome: This genetic disorder is characterized by an extra copy (trisomy) of the 21st chromosome, which makes it associated with 21st chromosome (III).
α -thalassemia: This condition is related to a mutation or deletion in the alpha globin genes located on the 16th chromosome (IV).
β -thalassemia: This is a blood disorder caused due to mutations in the beta globin gene found on the 11th chromosome (I).
Klinefelter's syndrome: This syndrome arises from the presence of an extra X chromosome in males (usually XXY), so it is related to abnormality in the 'X' chromosome (II).
Given these matches:
A - III
B - IV
C - I
D - II
The correct option based on the details above is: Option C: A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
2023
Q1: The phenomenon of pleiotropism refers to (NEET 2023)
(a) Presence of several alleles of a single gene controlling a single crossover
(b) Presence of two alleles, each of the two genes controlling a single trait
(c) A single gene affecting multiple phenotypic expression
(d) More than two genes affecting a single character
Ans: (c)
When a single gene affects multiple phenotypic expression, the gene is called pleiotropic gene and the phenomenon is called pleiotropism.
Q2: Which of the following statements are correct about Klinefelter’s Syndrome? (NEET 2023)
A. This disorder was first described by Langdon Down (1866).
B. Such an individual has overall masculine development. However, the feminine developement is also expressed.
C. The affected individual is short statured.
D. Physical, psychomotor and mental development is retarded.
E. Such individuals are sterile.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A and B only
(b) C and D only
(c) B and E only
(d) A and E only
Ans: (c)
B. Such an individual has overall masculine development. However, the feminine development is also expressed. People with Klinefelter syndrome are male (XY), but they often have certain physical characteristics that may be typically associated with female development, such as wider hips, less body hair, and sometimes breast tissue development.
E. Such individuals are sterile. Often, individuals with Klinefelter syndrome produce little to no sperm and are therefore usually infertile. However, there are cases where fertility treatments can help some men with Klinefelter syndrome to father children.
For the other options :
A. This disorder was first described by Langdon Down (1866). This is incorrect. Klinefelter's syndrome was first described by Dr. Harry Klinefelter in the 1940s, not by Langdon Down.
C. The affected individual is short statured. This is incorrect. In fact, individuals with Klinefelter's syndrome are often taller than average.
D. Physical, psychomotor and mental development is retarded. This is also incorrect. While individuals with Klinefelter syndrome may have some learning difficulties or delays, particularly with language and speech, it is not accurate or appropriate to say that their physical, psychomotor, and mental development is "retarded". They may face some challenges, but with support they can lead healthy, productive lives.
Q3: Broad palm with single palm crease is visible in a person suffering from- (NEET 2023)
(a)Down’s Syndrome
(b) Turner’s Syndrome
(c) Klinefelter’s Syndrome
(d) Thalassemia
Ans: (a)
A broad palm with a single palmar crease, also known as a "simian crease," is often associated with Down's Syndrome. Down's Syndrome is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. It is characterized by certain physical features, including a flat facial profile, an upward slant to the eyes, and a single palmar crease.
So, the correct answer is : Option D : Down's syndrome.
Q4: Which one of the following symbols represents mating between relatives in human pedigree analysis? (NEET 2023)
(a) 
(b) 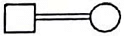
(c) 
(d) 
Ans: (b)
The symbol representing mating between relatives (consanguineous mating) in human pedigree analysis is 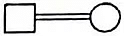
Q5: Frequency of recombination between gene pairs on same chromosome as a measure of the distance between genes to map their position on chromosome, was used for the first time by (NEET 2023)
(a) Thomas Hunt Morgan
(b) Sutton and Boveri
(c) Alfred Sturtevant
(d) Henking
Ans: (c)
- Alfred Sturtevant used the frequency of recombination between gene pairs on the same chromosome as a measure of the distance between genes and ‘mapped’ their position on the chromosome.
- Sutton and Boveri proposed chromosomal theory of inheritance.
- Henking discovered X-chromosome.
- Thomas Hunt Morgan proved chromosomal theory of inheritance and proposed the concept of linkage.
2022
Q1: XO type of sex determination can be found in: (NEET 2022)
(a) Birds
(b) Grasshoppers
(c) Monkeys
(d) Drosophila
Ans: (b)
Grasshopper is an example of XO type of sex determination in which the males have only one X-chromosome besides the autosomes, whereas females have a pair of X-chromosomes.
Q2: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2022)
Statement I : Mendel studied seven pairs of contrasting traits in pea plants and proposed the Laws of Inheritance
Statement II : Seven characters examined by Mendel in his experiment on pea plants were seed shape and colour, flower colour, pod shape and colour, flower position and stem height
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(d) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
Ans: (b)
Gregor J. Mendel, conducted hybridisation experiments on garden peas and selected 14 true breeding pea plant varieties (seven contrasting traits). Contrasting traits studied were smooth or wrinkled seeds, yellow or green seeds, inflated on constricted pods, green or yellow pods, tall or dwarf plants, violet or white flowers and axial or terminal flower positions.
Q3: Which of the following occurs due to the presence of autosome linked dominant trait? (NEET 2022)
(a) Haemophilia
(b) Thalessemia
(c) Sickle cell anaemia
(d) Myotonic dystrophy
Ans: (d)
- Haemophilia is a X-linked recessive disorder. Thalassemia is an autosomal recessive disorder. Sickle cell anaemia is an autosomal recessive disorder.
- Myotonic dystrophy is an autosomal dominant disorder i.e. it occurs due to the presence of autosomal linked dominant trait.
Q4: Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason(R). (NEET 2022)
Assertion (A): Mendel's law of Independent assortment does not hold good for the genes that are located closely on the same chromosome.
Reason (R): Closely located genes assort independently. In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(b) (A) is correct but (R) is not correct
(c) (A) is not correct but (R) is correct
(d) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
Ans: (b)
Closely located genes do not show independent assortment. Mendel's law of independent assortment holds good for those genes which are located on different chromosomes.
Q5:If a colour blind female marries a man whose mother was also colour blind, what are the chances of her progeny having colour blindness?
(a) 25%
(b) 50%
(c) 75%
(d) 100% (NEET 2022)
Ans: (d)
If mother of man is colour blind, then man will also be colour blind as colour blindness is a X-linked recessive trait and shows criss-cross inheritance.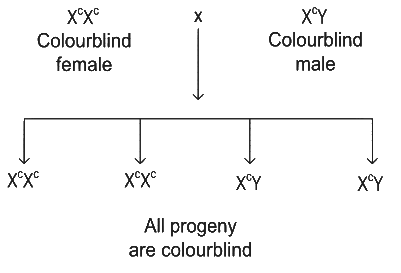
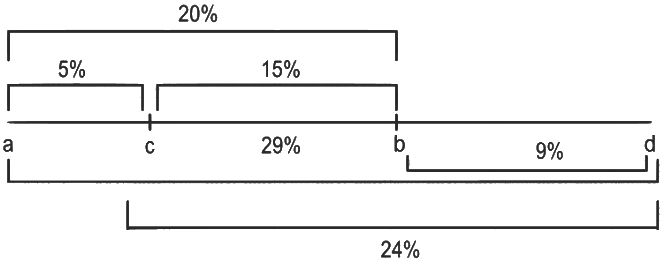
Q6: The recombination frequency between the genes a & c 5&, b & c is 15%, b & d is 9%, a & b is 20%, c & d is 25% and a & d is 29%. What will be the sequence of these genes on a linear chromosome?
(a) a, d, b, c
(b) d, b, a, c
(c) a, b, c, d
(d) a, c, b, d (NEET 2022)
Ans: (d)
1% recombination frequency = 1 centi Morgan
To place the genes on a linear chromosome, decreasing order of recombination frequency will be considered.
Q5: If a geneticist uses the blind approach for sequencing the whole genome of an organism, followed by assignment of function to different segments, the methodology adopted by him is called as: (NEET 2022)
(a) Gene mapping
(b) Expressed sequence tags
(c) Bioinformatics
(d) Sequence annotation
Ans: d
In sequence annotation, the whole set of genome containing all coding and non-coding sequences is sequenced and the functions are assigned to different segments. It could be used for marking specific features in a DNA, RNA or protein sequence with descriptive information about structure or function. It helps in describing regions or sites of interest in the protein sequence, such as enzyme active sites, secondary structure or other characteristics reported in the cited references.
Q6: Given below are two statements: (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Statement I : Sickle cell anaemia and haemophilia are autosomal dominant traits.
Statement II : Sickle cell anaemia and haemophilia are disorders of the blood.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(d) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
Ans: (a)
- Sickle cell anaemia is autosomal recessive disorder, whereas, haemophilia is sex linked recessive disorder.
- Both sickle cell anaemia and haemophilia are the genetic disorders related to blood.
Q7: In meiosis, crossing over and exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes are catalyzed by the enzyme
(a) Polymerase
(b) Phosphorylase
(c) Recombinase
(d) Transferase (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (c)
Crossing over and exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes occurs during pachytene stage of meiosis. The enzyme involved in this process is recombinase.
Q8: The chromosomal theory of inheritance was proposed by (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) Robert Brown
(b) Thomas Morgan
(c) Sutton and Boveri
(d) Gregor Mendel
Ans: (c)
Sutton and Boveri proposed chromosomal theory of inheritance. Thomas Morgan experimentally verified the chromosomal theory of inheritance. Gregor Mendel proposed laws of inheritance.
Q9: What is the expected percentage of F2 progeny with yellow and inflated pod in dihybrid cross experiment involving pea plants with green coloured, inflated pod and yellow coloured constricted pod? (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) 9%
(b) 100%
(c) 56.25%
(d) 18.75%
Ans: (d)
(G) Green pod colour is dominant over yellow pod colour (g)
(I) Inflated pod is dominant over constricted pod (i)
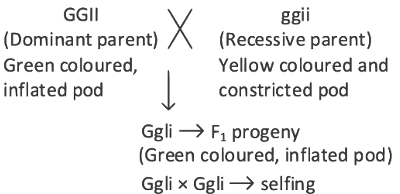
Expected percentage of F2 progeny with yellow – inflated pod in this cross is
1/4 x 3/4 x 100 = 18.75%
Q10: If a female individual is with small round head, furrowed tongue, partially open mouth and broad palm with characteristic palm crease. Also the physical, psychomotor and mental development is retarded. The karyotype analysis of such an individual will show :
(a) Trisomy of chromosome 21
(b) 47 chromosomes with XXY sex chromosomes
(c) 45 chromosomes with XO sex chromosomes
(d) 47 chromosomes with XYY sex chromosomes (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
Ans: (a)
- The symptoms described in the question are characteristic of Down syndrome, a genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21. This results in a trisomy of chromosome 21.
- Option A : Trisomy of chromosome 21 - Individuals with Down syndrome typically exhibit a range of physical and developmental features, such as a small round head, furrowed tongue, partially open mouth, and a broad palm with a characteristic single palmar crease. They also tend to have delayed physical, psychomotor, and mental development. Karyotype analysis of an individual with Down syndrome will show three copies of chromosome 21 instead of the normal two copies.
The other options describe different chromosomal abnormalities:
- Option B : 47 chromosomes with XXY sex chromosomes - This karyotype is characteristic of Klinefelter syndrome, a condition in which males have an extra X chromosome. Affected individuals have 47 chromosomes, and their symptoms are different from those described in the question.
- Option C : 45 chromosomes with XO sex chromosomes - This karyotype is characteristic of Turner syndrome, a condition in which females have only one X chromosome. Affected individuals have 45 chromosomes, and their symptoms are different from those described in the question.
- Option D : 47 chromosomes with XYY sex chromosomes - This karyotype is characteristic of XYY syndrome, a condition in which males have an extra Y chromosome. Affected individuals have 47 chromosomes, and their symptoms are different from those described in the question.
Q11: A normal girl, whose mother is haemophilic marries a male with no ancestral history of haemophilia. What will be the possible phenotypes of the offspring? (NEET 2022 Phase 2)
(a) Haemophilic son and haemophilic daughter.
(b) Haemophilic son and carrier daughter.
(c) Normal daughter and normal son.
(d) Normal son and haemophilic daughter.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) (b) and (d) only
(b) (a) and (b) only
(c) (b) and (c) only
(d) (a) and (d) only
Ans: (c)
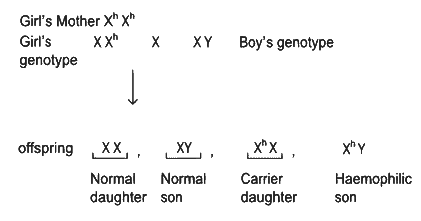
Hence (b) & (c) are correct which makes option (c) as correct option.
2021
Q1: The production of gametes by the parents, formation of zygotes, the F1 and F2 plants, can be understood from a diagram called: (NEET 2021)
(a) Punnett square
(b) Net square
(c) Bullet square
(d) Punch square
Ans: (a)
Punnett square is a tool that helps to show all possible allelic combinations of gametes in a cross of parents with known genotypes in order to predict the probability of their offspring possessing certain sets of alleles. For a cross involving two genes, a Punnett square is still a good strategy.
Q2: In a cross between a male and female, both heterozygous for sickle cell anaemia gene, what percentage of the progeny will be diseased? (NEET 2021)
(a) 25%
(b) 100%
(c) 50%
(d) 75%
Ans: (a)
The genotype of both male and female, heterozygous for sickle-cell anaemia gene can be represented as HbA HbS
Thus,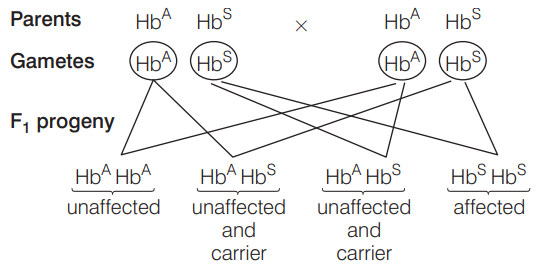
Total number of affected progenies = 1
∴ Percentage of diseased/affected progenies = 1/4 x 100 = 25%
Q3: Now-a-days it is possible to detect the mutated gene causing cancer by allowing radioactive probe to hybridise its complimentary DNA in a clone of cells, followed by its detection using autoradiography because: (NEET 2021)
(a) mutated gene does not appear on photographic film as the probe has complementarity with it
(b) mutated gene partially appears on a photographic film
(c) mutated gene completely and clearly appears on a photographic film
(d) mutated gene does not appear on a photographic film as the probe has no complementarity with it
Ans: (d)
- Autoradiography allows the detection/localisation of radioactive isotope within a biological sample.
- Probe is a radiolabelled ss DNA or ss RNA depending on the technique. To identify the mutated gene probe is allowed to hybridise to its complementary DNA in a clone of cells followed by detection using autoradiography. The mutated gene will not appear on the photographic film, because the probe does not have complementarity with the mutated gene.
2020
Q1: Experimental verification of the chromosomal theory of inheritance was done by: (NEET 2020)
(a) Boveri
(b) Morgan
(c) Mendel
(d) Sutton
Ans: (b)
Experimental verification of the chromosomal theory of inheritance was done by Morgan. Sutton and Boveri proposed chromosomal theory of inheritance but it was experimentally verified by T.H. Morgan.
Q2: Select the correct match (NEET 2020)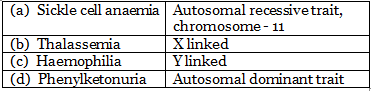
(a) a
(b) b
(c) c
(d) d
Ans: (a)
Phenylketonuria is an inborn error of metabolism is also inherited as the autosomal recessive trait. Sickle cell anemia is an autosomes linked recessive trait that can be transmitted from parents to the offspring when both the partners are carrier for the gene (or heterozygous).
Q3: How many true breeding pea plant varieties did mendel select as pairs, which were similar except in one character with contrasting traits? (NEET 2020)
(a) 14
(b) 8
(c) 4
(d) 2
Ans: (a)
A true breeding line refers to the plant that has been self pollinated continuously and produced generations that were stable in the inheritance of the character. Mendel selected 14 true-breeding pea plant varieties, as pairs which were similar except for one character with contrasting traits.
Q4: Embryological support for evolution was disapproved by (NEET 2020)
(a) Oparin
(b) Alfred Wallace
(c) Karl Ernst von Baer
(d) Charles Darwin
Ans: (d)
Embryological support for evolution was disapproved by Karl Ernst von Baer, he noted that embryos never pass through the adult stages of other animals during embryonic development.
2019
Q1: In Antirrhinum (Snapdragon), a red flower was crossed with a white flower and in F1 generation all pink flowers were obtained. When pink flowers were soiled, the F2 generation showed white, red and pink flowers. Choose the incorrect statements from the following. (NEET 2019)
(a) Law of segregation does not apply in this experiment.
(b) This experiment docs not follow the Principle of Dominance.
(c) Pink colour in is due to incomplete dominance.
(d) Ratio of F2 is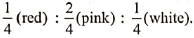
Ans: (a)
Law of segregation applies in this case as when pink (lowers obtained in F1, are selfed then red and while (lowers are obtained in F2 which indicates that there is no mixing of gametes.
Q2: The frequency of recombination between gene present on the same chromosome as a measure of the distance between genes was explained by (NEET 2019)
(a) Sutton Boveri
(b) T.H. Morgan
(c) Gregor J.Mendel
(d) Alfred Sturtevant
Ans: (d)
Alfred Sturtevant explained chromosomal mapping on the basis of recombination frequency which is directly proportional to distance between two genes on same chromosome.
Q3: What is the genetic disorder in which an individual has an overall masculine development, gynaecomastia, and is sterile? (NEET 2019)
(a) Down’s syndrome
(b) Turner’s syndrome
(c) Klinefelter’s syndrome
(d) Edward syndrome
Ans: (c)
Klinefelter’s Syndrome has an additional copy of X-chromosome in male. They have trisomy of sex chromosome as 44 + XXY (47). They show overall masculine development, gynaecomastia and are sterile.
Q4: What map unit (Centimorgan) is adopted in the construction of genetic maps? (NEET 2019)
(a) A unit of distance between genes on chromosomes, representing 50% cross over.
(b) A unit of distance between two expressed genes, representing 10% cross over.
(c) A unit of distance between two expressed genes, representing 100% cross over.
(d) A unit of distance between genes on chromosomes, representing 1% cross over.
Ans: (d)
A centimorgan or map unit is a unit for measuring genetic linkage. It is defined as the distance between chromosome positions (also termed loci or markers) for which the expected average number of intervening chromosomal crossovers in a single generation is 1 percent.
Q5: A gene locus has two alleles A, a. If the frequency of dominant allele A is 0.4, then what will be the frequency of homozygous dominant, heterozygous and homozygous recessive individuals in the population? (NEET 2019)
(a) 0.16(AA); 0.48 (Aa); 0.36(aa)
(b) 0.16 (AA); 0.36(Aa); 0.48(aa)
(c) 0.36 (AA); 0.48 (Aa); 0.16 (aa)
(d) 0.16 (AA); 0.24 (Aa); 0.36 (aa)
Ans: (a)
Frequency of dominant allele (say p) = 0.4
Frequency of recessive allele (say q) = 1 – 0.4 = 0.6
Frequency of homozygous dominant dividuals (AA) = p2 = (0.4)2 = 0.16
Frequency of heterozygous individuals (Aa) = 2pq = 2(0.4) (0.6) = 0.48
Frequency of homozygous recessive individuals (aa) = q2 = (0.6)2 = 0.36
Q6: Select the incorrect statement. (NEET 2019)
(a) Human males have one of their sex- chromosome much shorter than other.
(b) Male fruit fly is heterogametic.
(c) In male grasshoppers, 50% of sperms have no sex-chromosome.
(d) In domesticated fowls sex of progeny depends on the type of sperm rather than egg.
Ans: (d)
The type of sex determination in birds is called female heterogamety and male homogamety. Thus, the sex of the progeny depends on the type of egg rather than the type of sperm. The female birds have two different sex chromosomes designated as Z and W while male birds have two similar sex chromosomes and called ZZ.
2018
Q1: Which of the following pairs is wrongly matched? (NEET 2018)
(a) Starch synthesis in pea : Multiple alleles
(b) ABO blood grouping : Co-dominance
(c) XO type sex determination: Grasshopper
(d) T.H. Morgan : Linkage
Ans: (a)
The gene for starch synthesis in pea seeds can produce more than one effect which implies it is a pleiotropic gene.
Q2: Which of the following characteristics represent ‘inheritance of blood groups’ in humans? (NEET 2018)
(i) Dominance
(ii) Co-dominance
(iii) Multiple allele
(iv) Incomplete dominance
(v) Polygenic inheritance
(a) (ii), (iii) and (v)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii), (iv) and (v)
(d) (i), (iii) and (v)
Ans: (b)
ABO blood group system in human beings is an example of dominance, co-dominance and multiple allelism.
IA IO IB IO or i - Alleles shows dominant-recessive relationship.
lA IB - Codominance is a phenomenon in which alleles of a gene do not show dominant recessive relationship and express themselves independently when present together.
IA IO IB IO or i - More than two alternate forms of a gene present on the same locus are called as multiple alleles and the mode of inheritance in the alleles is called multiple allelism.
Q3: A woman has an X-linked condition on one of her X chromosomes. This chromosome can be inherited by (NEET 2018)
(a) Only daughters
(b) Only sons
(c) Only grandchildren
(d) Both sons and daughters.
Ans: (d)
Woman acts as a carrier when she has the X-linked condition on one of her X-chromosomes. Both son and daughter inherit X-chromosome from mother. Hence, one of the two daughters will be carrier and one of the two sons will be diseased. It can be explained by the given cross :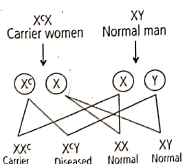
where XC is the X-chromosome carrying the gene for the condition.
2017
Q1: Thalassemia and sickle cell anaemia are caused due to a problem in globin molecule synthesis. Select the correct statement. (NEET 2017)(a) Both are due to a quantitative defect in globin chain synthesis.
(b) Thalassemia is due to less synthesis of globin molecules.
(c) Sickle cell anaemia is due to a quantitative problem of globin molecules.
(d) Both are due to a qualitative defect in globin chain synthesis.
Ans: (b)
Sickle cell anaemia is caused due to point mutation in which at the 6th position of beta globin chain, glutamic acid is replaced by valine, Huts, it is a qualitative defect in functioning of globin molecules.
Thalassemia is caused due to either mutation or deletion which ultimately results in reduced rate of synthesis of one of the globin chains lltal make up haemoglobin. Hence, it is a quantitative defect in functioning of globin molecules.
Q2: The genotypes of a husband and wife are IAIB and IAi.
Among the blood types of their children, how many different genotypes and phenotypes arc possible? (NEET 2017)
(a) 3 genotypes; 4 phenotypes
(b) 4 genotypes; 3 phenotypes
(c) 4 genotypes; 4 phenotypes
(d) 3 genotypes; 3 phenotype
Ans: (b)
If the genotypes of husband and wife are IA and IAi respectively, then the probabilities of genotypes and phenotypes among their children can be worked out as: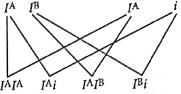
Genotype: IA IA IAi IA IAIB IBi
Phenotype: A A AB B
Thus, there are four possible genotypes, viz., IA IA , IAi, IAIB and IBi and three possible phenotypes, viz.,A, AB and B among the children.
Q3: A disease caused by an autosomal primary non disjunction is (NEET 2017)
(a) Klinefelter’s syndrome
(b) Turner’s syndrome
(c) Sickle cell anaemia
(d) Down’s syndrome.
Ans: (d)
Down’s syndrome is an autosomal aneuploidy, caused by the presence of an extrachromosome number 21. Both the chromosomes of the pair 21 pass into a single egg due to non disjunction during oogenesis.
Q4: Which one from those given below is the perf for Mendel’s hybridisation experiments? (NEET 2017)
(a) 1840-1850
(b) 1857-1869
(c) 1870-1877
(d) 1856-1863
Ans: (d)
The correct period for Mendel's hybridization experiments is Option D, 1856 – 1863. Gregor Mendel conducted his experiments on plant hybridization using pea plants between these years. During this period, he meticulously crossbred peas and observed the inheritance patterns of certain traits, which led to the formation of the fundamental laws of genetics, known as Mendel's Laws of Inheritance.
Q5: Among the following characters, which one was not considered by Mendel in his experiments on pea? (NEET 2017)
(a) Trichomes-Glandular or non-glandular
(b) Seed-Green or yellow
(c) Pod-Inflated or constricted
(d) Stem-Tall or dwarf
Ans: (a)
During his experiments Mendel have taken seven characters in a pea plant. In which nature of trichomes i.e., glandular or non-glandular was not considered by Mendel.
2016
Q1: The mechanism that causes a gene to m< from one linkage group to another is called (NEET 2016 Phase 2)
(a) Inversion
(b) Duplication
(c) Translocation
(d) Crossing-over.
Ans: (c)
Translocation i s a chromosomal abnormality caused by rearrangement of parts between non-homologous chromosomes. It may cause a gene to move from one linkage group to another.
Q2: If a colour-blind man marries a woman who is homozygous for normal colour vision, probability of their son being colour-blind (NEET 2016)
(a) 0
(b) 0.5
(c) 0.75
(d) 1
Ans: (a)
Genotype o f colour blind man - X°Y
Genotype of women homozygous XX
for normal woman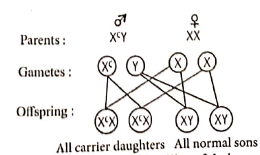
Hence, there is zero (0) probability of their son to be colour-blind.
Q3: In a test cross involving F1 dihybrid flies, more parental-type offspring were produced than the recombinant-type offspring. This indicates (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) The two genes are linked and present on the same chromosome
(b) Both of the characters are controlled by more than one gene
(c) The two genes are located on two different chromosomes
(d) Chromosomes failed to separate during meiosis
Ans: (a)
If in a dihybrid test cross more parental combinations appear as compared to the recombinants in F2 generation, then it is indicative of involvement of linkage. Linkage is the tendency of two different genes on the same chromosome to remain together during the separation of homologous chromosomes at meiosis. During complete linkage no recombinants are formed whereas in incomplete linkage few recombinants are produced along with parental combinations.
Q4: Which of the following most appropriately describes haemophilia? (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
(a) Chromosomal disorder
(b) Dominant gene disorder
(c) Recessive gene disorder
(d) X-linked recessive gene disorder
Ans: (d)
Haemophilia is a sex-linked disease. It occurs due to the presence of a recessive sex linked gene h, which is carried by X-chromosome.
Q5: Match the terms in column I with their description m column II and choose the correct option. (NEET 2016 Phase 1)
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Dominance | (i) Many genes govern a single character |
| B. Codominance | (ii) In a heterozygous organism only one allele expresses itself |
| C. Pleiotropy | (iii) In a heterozygous organism both alleles express themselves fully |
| D. Polygenic | (iv) A single gene inheritance influences many characters |
A | B | C | D | |
(a) | (iv) | (i) | (ii) | (iii) |
(b) | (iv) | (iii) | (i) | (ii) |
(c) | (ii) | (i) | (iv) | (iii) |
(d) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) | (i) |
Ans: (d)
Let's match the terms in Column-I with their descriptions in Column-II:
- (a) Dominance: Describes a relationship between alleles of a gene, where one allele masks the expression of another allele at the same locus.
- (b) Codominance: Occurs when both alleles at a locus are expressed and the phenotype is a combination or simultaneous expression of both alleles.
- (c) Pleiotropy: Occurs when one gene influences multiple different phenotypic traits.
- (d) Polygenic inheritance: This term refers to a situation where a single trait is controlled by more than one gene (often, many genes contribute to the phenotype).
Now we match them with the descriptions:
- (a) - (ii) "In a heterozyous organism only one allele expresses itself" aligns with the concept of Dominance.
- (b) - (iii) "In a heterozyous organism both alleles express themselves fully" is correct for Codominance.
- (c) - (iv) "A single gene influences many characters" corresponds to Pleiotropy.
- (d) - (i) "Many genes govern a single character" is the definition of Polygenic inheritance.
Therefore, the correct match is:
Option A
(a) - (ii), (b) - (iii), (c) - (iv), (d) - (i)
Q6: A cell at telophase stage is observed t student in a plant brought from the field, tells his teacher that this cell is not like c cells at telophase stage. There is no form; of cell plate and thus the cell is containing more number of chromosomes as compared to other dividing cells. This would result in (NEET 2016)
(a) Somaclonal variation
(b) Polyteny
(c) Aneuploidy
(d) polyploidy
Ans: (d)
Polyploidy is the phenomenon of occurrence of more than two sets of chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell. Polyploidy is more common in plants. Polyploidy arises as a result of total non-disjunction of chromosomes during mitosis or meiosis.
Q7: Pick out the correct statements. (NEET 2016)
(1) Haemophilia is a sex-linked recessive Disease.
(2) Down’s syndrome is due to anetiploidy
(3) Phenylketonuria is an autosomal recessive gene disorder.
(4) Sickle cell anaemia is an X-Iinked recessive gene disorder.
(a) (1), (3) and (4) are correct.
(b) (1), (2) and (3) are correct.
(c) (1) and (4) are correct.
(d) (2) and (4) are correct.
Ans: (b)
Sickle-cell anaemia is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder. It can be transmitted from parents to the offspring when both the partners are carriers of the gene (or heterozygous).
Q8: A tall true breeding garden pea plant is crossed with a dwarf true breeding garden pea plant When the F1 plants were selfed the resulting genotypes in the ratio of (NEET 2016)
(a) 3 : 1 : : Tall; Dwarf
(b) 3 : 1 Dwarf : Tall
(c) 1 : 2 : 1 : : Tall homozygous : Tall heterozygous : Dwarf
(d) 1 : 2 : 1 : : Tall heterozygous : Tall homozygous : Dwarf.
Ans: (c)
When a tall true breeding garden pea plant is crossed with a dwarf true breeding garden pea plant and the F1 plants were soiled the resulting genotypes were in the ratio of 1 : 2 : 1 i.e„ Tall homozygous: Tall heterozygous : Dwarf
It can be illustrated as given below: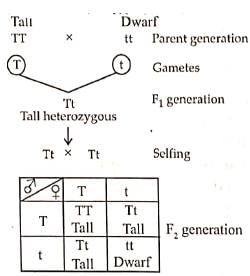
Phenotypic ratio : 3 : 1 : : Tall: Dwarf
Genotypic ratio -1 :2:1:: TT : T t : tt
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on NEET Previous Year Questions(2016-25): Principles of Inheritance & Variation - Biology Class 12
| 1. What are the basic principles of inheritance? |  |
| 2. How do variations occur in offspring? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between genotype and phenotype? |  |
| 4. How do genetic disorders arise in individuals? |  |
| 5. How can inheritance patterns be studied in humans? |  |

















