Physical Geography of India - 2 | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| The Indian Desert / Marusthali Region |

|
| The Coastal Plains |

|
| The Islands |

|
| Mains Questions |

|
The Indian Desert / Marusthali Region
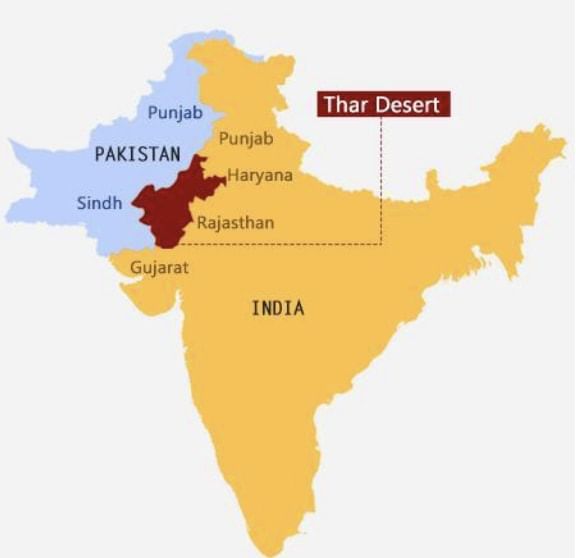 Thar Desert
Thar Desert
- The Great Indian Desert or the Thar Desert lies to the northwest of the Aravalli hills.
- It is a land of undulating topography with longitudinal sand dunes and barchans (crescent-shaped dunes).
- It receives below 50 mm precipitation per year and thus has an arid climate with low vegetation cover.
- The underlying rock structure of the desert is an extension of the Peninsular plateau.
- Most of the rivers in this region are ephemeral. The Luni river flowing in the southern part of the desert empties into a dry inland basin and thus is an example of an endorheic river basin.
- Endorheic basin- Sometimes streams disappear into the ground after flowing for some distance, resulting in inland drainage by joining a lake or playa.
The Coastal Plains
- India has a long coastline of about 7516.6 km.
- On the basis of the location and active geomorphological processes, it can be broadly divided into two:
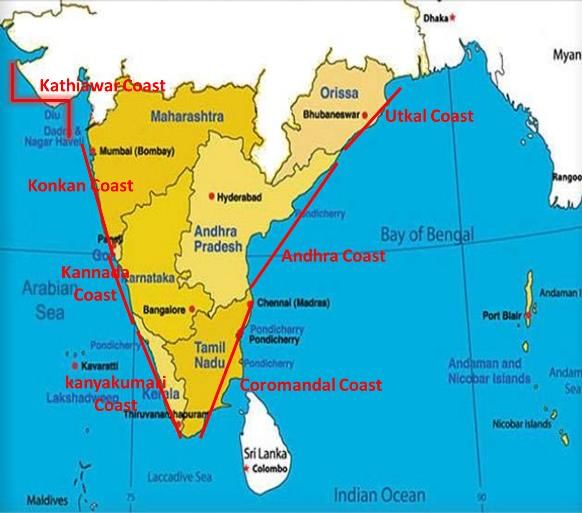 The Coastal Plains of India
The Coastal Plains of India
(a) Western Coastal Plains
- These are submerged coastal plains with narrow continental shelf.
- This submergence has resulted in a narrow coastal belt and provides natural conditions for the development of ports and harbours.
- Kandla, Mazagaon, Cochin, etc. are some of the important natural ports located along the west.
- Extending from the Gujarat coast in the north to the Kerala coast in the south, the western coast may be divided into the following divisions – The Kachchh and Kathiawar coast in Gujarat, the Konkan coast in Maharashtra, Goa and Karnataka, and the Malabar coast in Kerala. The Karnataka coastal plain is also known as Kanara coast.
- The rivers here are fast-flowing and carry less sediments, thus they do not form any deltas.
- The Malabar coast has got certain distinguishing features in the form of ‘Kayals’(backwaters), which are used for fishing, inland navigation and also due to its special attraction for tourists.
(b) Eastern Coastal Plains
- These are emergent coast plains.
- The Eastern coastal plain is broader than the Western coastal plain.
- They have well-developed deltas that are formed by the rivers flowing eastward into the Bay of Bengal.
- Example: deltas of the Mahanadi, the Godavari, the Krishna and the Kaveri.
- It has less number of ports and harbours because of its emergent nature.
- The continental shelf here is narrow.
The Islands
There are two major island groups in India :
(a) In the Bay of Bengal
- It includes the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- These island groups consist of about 572 islands/islets. These are situated roughly between 6°N - 14°N and 92°E - 94°E.
- The entire group of islands is divided into two broad categories:
(i) The Andaman in the North
(ii) The Nicobar in the South
They are separated by a water body called the Ten-degree channel. - These islands are believed to be an elevated portion of submarine mountains.
- Some smaller islands are volcanic in origin. Barren Island, the only active volcano in India is also situated in the Nicobar Islands.
- Baratang island is the only place in India with mud volcanoes.
- The coastal line has some coral deposits and beaches.
- These islands receive convectional rainfall and have an equatorial type of vegetation.
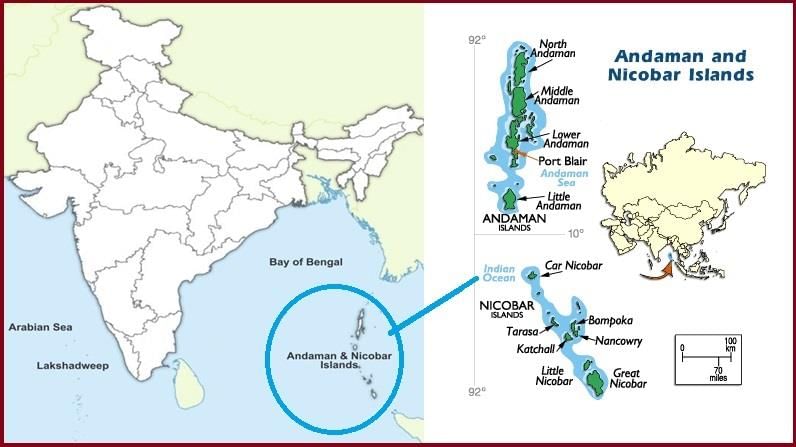 Andaman and Nicobar Islands
Andaman and Nicobar Islands
(b) In the Arabian sea
- These Islands include Lakshadweep Islands.
- These are scattered between 8°N-12°N and 71°E -74°E longitude and are located at a distance of 280 km-480 km off the coast of Kerala.
- The entire island group is built of coral deposits.
- There are approximately 36 islands of which 11 are inhabited.
- Largest Island: Minicoy (453 sq. km. Area).
- The entire group of islands is broadly divided by the Eleventh-degree channel.
- North of the Eleventh-degree channel is the Amini Island group and to the south is the Cannanore Island group.
- The Islands of this archipelago have storm beaches consisting of unconsolidated pebbles, shingles, cobbles and boulders.
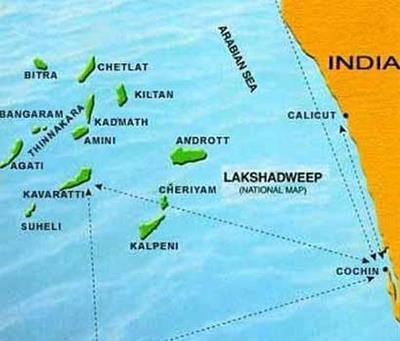 Lakshadweep Island
Lakshadweep Island
Select the correct answer from the following codes:
1. Along with the Northern plain, coastal plains also form one of the physiographic divisions of India.
2. Islands of India do not form part of physiographic divisions of India.
Mains Questions
1) What is physiography? What are the physiographic divisions of India? (250 words)
How to approach
- Intro- Define physiography and draw the map of India with the physical divisions.
- Body- Explain the divisions in detail separately.
- Conclusion- Two sentences about the significance of such geographical diversity.
|
263 videos|875 docs|232 tests
|
FAQs on Physical Geography of India - 2 - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the main geographical regions of India? |  |
| 2. What are the characteristics of the Indian Desert or Marusthali Region? |  |
| 3. What are the features of the Coastal Plains in India? |  |
| 4. What are the major islands of India? |  |
| 5. How do the geographical regions of India contribute to its overall diversity? |  |
















