Reciprocal Recurrent Selection | Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Science Optional for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Recurrent Selection System |

|
| Reciprocal Recurrent Selection |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
The significance of overdominance in heterosis has prompted the proposal of a recurrent selection breeding system by Hull. This method aims to enhance heterosis by systematically selecting highly inbred lines, assumed to be homozygous at most loci, as testers. The process involves evaluating the progeny of numerous individuals crossed with the tester line, selecting the best-performing progeny, and intermating them. This cycle is repeated iteratively to potentially induce homozygosity for different alleles in the selected line compared to the inbred tester.
Recurrent Selection System
Initial Selection:
- A highly inbred line, presumed to be homozygous, is chosen as the tester.
- Numerous individuals are crossed with this tester, and their progeny undergo evaluation.
Successive Cycles:
- The best-performing progeny are selected and intermated to propagate the selected line.
- A substantial number of their progeny is then tested in crosses with the inbred tester, and the cycle repeats.
Objective:
- If heterosis is predominantly linked to overdominance, this process aims to drive the selected line towards homozygosity for different alleles than the inbred tester.
Reciprocal Recurrent Selection
Alternative Approach:
- Reciprocal recurrent selection is another system employed for a similar purpose.
- Representatives from two non-inbred strains are randomly selected, and their progeny are tested in crosses with each other.
Successive Iterations:
- Individuals from each strain producing the best cross progeny are then intermated to perpetuate their respective strains.
- Offspring from within-strain matings are progeny tested in crosses with the other strain, and the cycle is repeated.
The Schematic Representation of Reciprocal Recurrent Selection
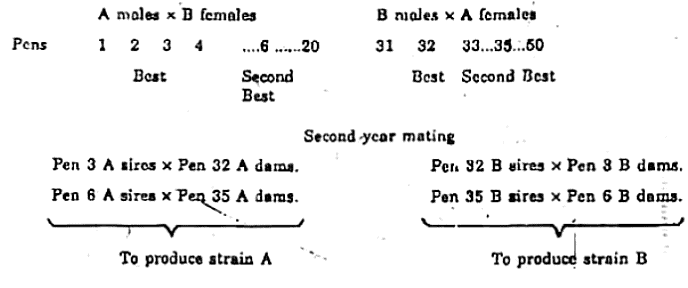
Thus, the selection is made for specific combining ability
Conclusion
Recurrent selection strategies, whether involving a single inbred tester or a reciprocal approach, are designed to exploit overdominance for maximizing heterosis. These methods aim to iteratively enhance genetic diversity and drive homozygosity for different alleles, contributing to improved performance in subsequent generations. Understanding and implementing these strategies can be instrumental in achieving progress in plant breeding programs.
FAQs on Reciprocal Recurrent Selection - Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Science Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is the recurrent selection system? |  |
| 2. What is reciprocal recurrent selection? |  |
| 3. How does the recurrent selection system work? |  |
| 4. What are the benefits of using reciprocal recurrent selection in plant breeding? |  |
| 5. Is reciprocal recurrent selection a widely used breeding method in agriculture? |  |




















