Resources & Development Summary Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1
Resources
Everything available in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs, provided, it is technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally acceptable can be termed as ‘Resource’.
Classification of Resources
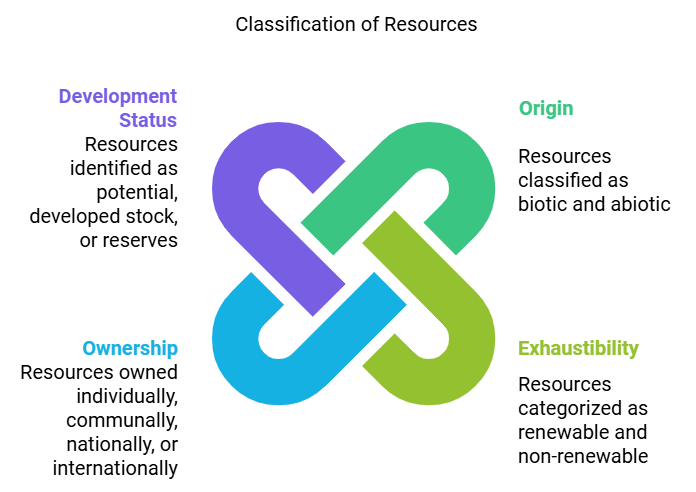
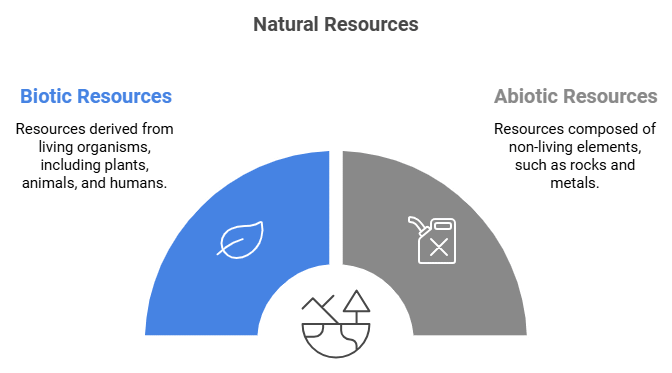
On the Basis of Origin
On the Basis of Exhaustibility
- Renewable Resources: The resources which can be renewed or reproduced by physical, chemical or mechanical processes are known as renewable resources. For example, solar and wind energy, water, forests and wildlife, etc.
- Non-Renewable Resources: The resources once consumed cannot be replaced are known as non-renewable resources. These resources take millions of years in their formation.For example: Oil, Coal etc.
On the Basis of Ownership
- Individual Resources: The resources owned privately by individuals are called Individual resources. For example: Plot, houses etc. owned by a person.
- Community Owned Resources: The resources which are accessible to all the members of the community. For example: Public parks, picnic spots owned by a community.
- National Resources: The resources which come under nation are known as National Resources. Technically, all the resources belong to the nation.
- International Resources: The resources lying beyond 200 kms of Exclusive Economic Zone in the oceans are called International Resources. No one can use these resources without the permission of international institutions.
On the Basis of the Status of Development
- Potential Resources: Resources which are found in a region, but have not been utilised. For example: the regions Rajasthan and Gujarat have enormous potential for the development of wind and solar energy.
- Developed Resources: Resources which are surveyed and their quality and quantity have been determined for utilisation.
- Stock: The resources that have been surveyed, but cannot be used due a lack of technology. For example: water is a compound of two inflammable gases; hydrogen and oxygen, which can be used as a rich source of energy but we don't have technical know-how to use them.
- Reserves: The resources that have been surveyed and we can use them with present technology but their use has not been started are known as Reserves. For example: the water in the dams, forests etc.
Development of Resources
- Resources are vital for human survival.
- It was believed that resources are free gifts of nature so, human beings used them indiscriminately and this has led to the following major problems:
- Depletion of resources for satisfying the greed of few individuals.
- Accumulation of resources in few hands which divides the society into rich and poor.
- Indiscriminate exploitation of resources has led to global ecological crises such as, global warming, ozone layer depletion, environmental pollution and land degradation.
- For a sustained quality of life and global peace, an equitable distribution of resources has become essential.
- For using resources judiciously, we need to adopt sustainable economic development.
- Sustainable economic development means development should take place without damaging the environment, and development in the present should not compromise with the needs of the future generations.
Resource Planning
Resource planning is a complex process which involves :
- Identification and inventory of resources across the regions of the country. This involves surveying, mapping and qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of the resources.
- Evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional set up for implementing resource development plans.
- Matching the resource development plans with overall national development plans.
Resource Planning in India
Resource planning in India is a comprehensive process aimed at efficiently utilizing the nation's resources for balanced development. It involves:
- Identifying and listing resources: This includes surveying, mapping, and measuring the quantity and quality of natural resources across different regions.
- Creating a planning system: Effective resource management requires the use of advanced technology, skilled workforce, and well-structured organizations.
- Aligning with national goals: Resource development must be in harmony with broader national development objectives to ensure sustainable and equitable growth.
Conservation of Resources
Resources are essential for sustainable development, but their over-consumption and mismanagement can lead to socio-economic and environmental challenges. Conservation is key to preventing depletion.
Historically, leaders like Gandhiji emphasized resource conservation, criticizing exploitative technologies and advocating for sustainable, localized production systems. He believed in using resources for everyone's needs, but not for greed, which was a primary cause of depletion.
Land Resources
Land is a natural resource of utmost importance.
- It supports natural vegetation, wild life, human life, economic activities, transport and communication systems.
- Land is present in limited size so we must use them effectively.
Land Resources in India
- About 43 percent of the land area is plain, which provides facilities for agriculture and industry.
- About 30 percent of the total surface area of the country are mountains which ensure perennial flow of some rivers and provide facilities for tourism and ecological aspects.
- About 27 per cent of the area of the country is the plateau region that possesses rich reserves of minerals, fossil fuels and forests.
Land Use Pattern in India
The use of land is determined by:
- Physical factors such as topography, climate, soil types
- Human factors such as population density, technological capability and culture and traditions etc.
Land use data, however, is available only for 93 per cent of the total geographical area because the land use reporting for most of the north-east states except Assam has not been done fully.
- Also, some areas of Jammu and Kashmir occupied by Pakistan and China have also not been surveyed.
Land Degradation and Conservation Measures
- Human activities such as deforestation, over grazing, mining and quarrying contributed in land degradation.
- Measures to control land degradation:
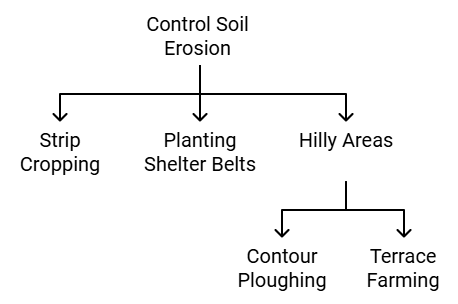
- Afforestation
- Planting of shelter belts of plants
- control on over grazing
- stabilisation of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes
- Proper management of waste lands
- control of mining activities
Soil as a Resource
- Soil is the most important renewable natural resource.
- It is the medium of plant growth and supports different types of living organisms on the earth.
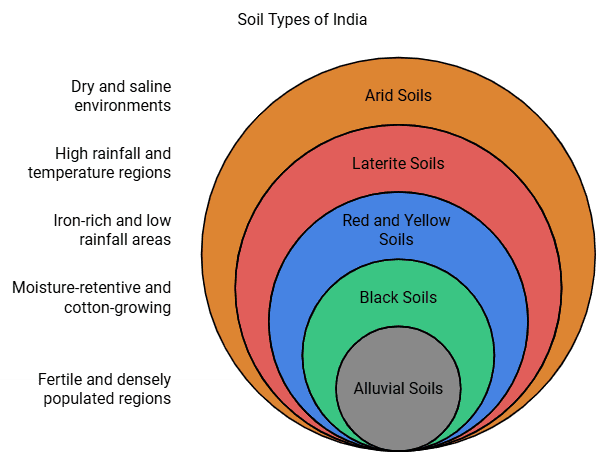
Classification of Soils
On the basis of the factors responsible for soil formation, colour, thickness, texture, age, chemical and physical properties, the soils of India can be classified in different types:
Soil Erosion and Soil Conservation
- Natural ways of Soil erosion: Wind, glaciers and water lead to soil erosion.
- Human activities: Deforestation, over-grazing, construction and mining etc., contributes in soil erosion.
- Measures to control Soil erosion:
For a more detailed explanation of the above topics, check out this video:
|
66 videos|614 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Resources & Development Summary Class 10 Social Science Chapter 1
| 1. What are the main types of resources discussed in the NCERT chapter on Resources & Development? |  |
| 2. How can resources be classified based on their availability? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of sustainable development in resource management? |  |
| 4. What role does technology play in resource development? |  |
| 5. How do human activities impact the distribution and availability of resources? |  |