Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Question Answers - Light - Reflection and Refraction
Q1: Draw the ray diagrams showing the image formation by a concave lens.
Ans:
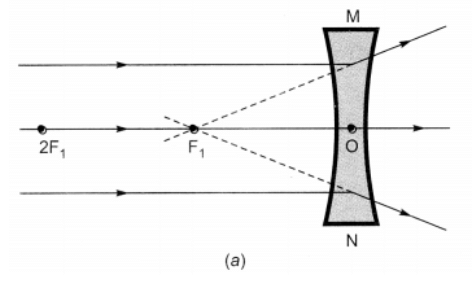
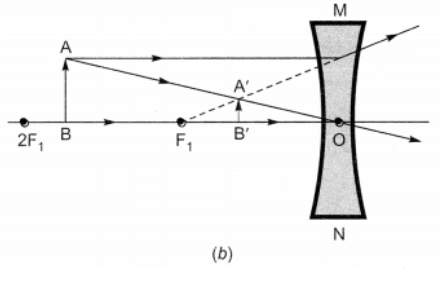 Nature, position and relative size of the image formed by a concave lens
Nature, position and relative size of the image formed by a concave lens
Q2: Write lens formula and define magnification.
Ans: Lens formula and magnification: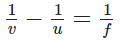 u = object distance
u = object distance
v = image distance
f = focal length
Magnification (m): Magnification is defined as the ratio of height of image and to height of the object.

h’ = height of image
h = height of object
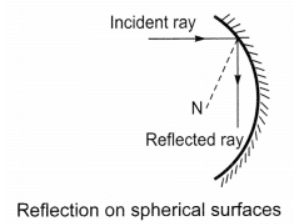
Q3: State laws of reflection.
Ans: Laws:
- The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- The incident ray, the normal to the mirror at the point of incidence and reflected ray, all lie in the same plane.
These laws of reflection are applicable to all types of reflecting surfaces including spherical surfaces.
Q4: Write four difference between real and virtual image.
Ans:
Real image:
- When rays of light after reflection meets at a point real image is formed.
- Real image can be obtained on screen.
- Real image is formed in front of mirror.
- Real image is always inverted.
Virtual image:
- When rays of light do not actually meet but appear to meet at a point after reflection, virtual image is formed.
- Virtual image cannot be obtained on screen.
- Virtual image is formed behind the mirror.
- Virtual image is always erect.
Q5: If the speed of light in vacuum is 3 × 108 ms-1, find the speed of light in a medium of absolute refractive index 1.5.
Ans:
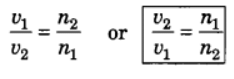
Here, v1 = 3 × 108 m/s, n1 = 1, n2 = 1.5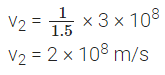
Q6: An object of height 6 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave lens of focal length 5 cm. Use lens formula to determine the position, size and nature of the image if the distance of the object from the lens is 10 cm.
Ans: h = 6 cm, f = -5 cm, u = -10 cm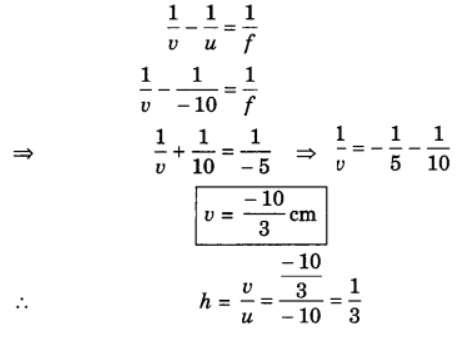
Image is diminished and erect.
Q7: Define refractive index and relative refractive index.
Ans:
1. Refractive index: The ratio of speed of light in vacuum (c) to the speed of light in any medium (v) is called refractive index of the medium. 2. Relative refractive index: The relative refractive index of a medium with respect to other medium is the ratio of the speed of light in the first medium with respect to the second medium.
2. Relative refractive index: The relative refractive index of a medium with respect to other medium is the ratio of the speed of light in the first medium with respect to the second medium.
Here, n21 = Relative refractive index of medium 2 with respect to medium 1 is Here, n12 = Relative refractive index of medium 1 with respect to medium 2.
Here, n12 = Relative refractive index of medium 1 with respect to medium 2.
Q8: Write some illustrations of refraction.
Ans: Some applications of refraction:
- Bottom of a tank or a pond containing water appears to be raised due to refraction.
- When a thick glass slab is placed over some printed matter the letters appear raised when viewed through the glass slab.
- When a pencil is partly immersed in water, it appears to be bent at the interface of air and water.
- A lemon kept in water in a glass tumbler appears to be bigger than its actual size, when viewed from the sides.
Q9: Name the type of mirror used in solar furnace. How is high temperature achieved by this device?
Ans: Concave mirror is used in solar furnace. The solar furnace is placed at the focus of the large concave reflector. The concave reflector focus the Sim’s heat rays on the furnace and a high temperature is achieved.
Q10: The absolute refractive indices of glass and water are 4/3 and 3/2 respectively. If the speed of light in glass is 2 × 108 ms-1, calculate the speed of light in (i) vacuum and (ii) water.
Ans:
Given, µg = 43 and µw = 32
Speed of light in glass = 2 × 108 ms-1
(i) Speed of light in vacuum, c = µg × vg = 4/3 × 2 × 108 = 2.67 × 108 ms-1
(ii) Speed of light in water,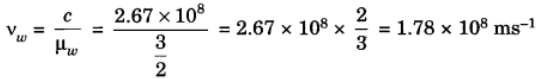
Q11: A convex lens of focal length 25 cm and a concave lens of focal length 10 cm are placed in closed contact with each other. Calculate the lens power of the combination.
Ans: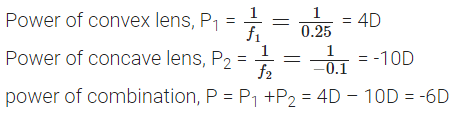
Q12: Define power of a lens. What is its unit? One student uses a lens of focal length 50 cm and another of -50 cm. What is the nature of the lens and its power used by each of them?
Ans: Power of a lens: The power of a lens is defined as reciprocal of its focal length.
P = 1/f
f = focal length (in metre)
The SI unit of power is ‘dioptre’. It is denoted by the letter D.
Here, f= 50 cm = 0.5 m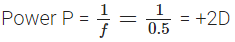
f = – 50 cm = -0.5 m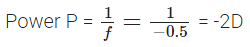
Q13: Define lens. What is difference between convex and concave lens?
Ans:
Lens: A transparent medium bound by two surfaces, of which one or both surfaces are spherical, forms a lens:
Convex lens: A lens having two spherical surfaces, bulging outwards is called a double convex lens or convex lens.
- It is thicker at the middle as compared to the edges.
- Convex lens converges light.
- Hence, convex lens are called converging lens.
Concave lens: A double concave lens is bounded by two spherical surfaces curved inwards.
- It is thicker at edges than in the middle.
- Concave lens is diverging in nature.
Q14: Write down the uses of concave and convex mirror.
Ans: Uses of mirrors:
1. Uses of concave mirrors:
- Concave mirrors are commonly used in torches, searchlights and vechicles headlights to get powerful beam of light.
- It is used in shaving mirrors to see large image of the face.
- Dentists use concave mirror to see large images of the teeth of patients.
- Large concave mirrors are used to concentrate sunlight to produce heat in solar furnace.
2. Uses of convex mirrors:
- Convex mirrors are used as rear-view (wing) mirrors in vehicles.
- Convex mirrors are used as street reflectors because they are able to spread light over a bigger area.
Q15: (i) “The refractive index of kerosene is 1.44.” What is meant by this statement?
(ii) A ray of light strikes a glass slab of an angle of incidence equal to 30°. Find the refractive index of glass such that the angle of refraction is 19.5°. (Take sin 19.5° = 1/3 and sin 30° = 1/2 )
Ans:
(i) Refractive index of any medium with respect to another indicated the extent to which binding of light takes place when it enters from the first medium to the given medium. The given value of refractive index also states that speed of light in kerosene is 1/1.44 times the speed of light in a vacuum.
(ii) Given, i = 30°, r = 19.5°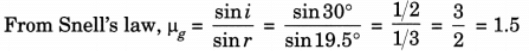
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Question Answers - Light - Reflection and Refraction
| 1. What is the difference between reflection and refraction of light? |  |
| 2. How does the angle of incidence affect the angle of reflection? |  |
| 3. Why does a pencil appear bent when partially immersed in water? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between regular reflection and diffuse reflection? |  |
| 5. How does the speed of light change when it passes from one medium to another? |  |
















