UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 19th December 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Environment
Sacred Groves
Source: DTE
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Supreme Court of India has instructed the Union Government to develop a comprehensive policy aimed at managing sacred groves throughout the country. This directive underscores the importance of these ecologically and culturally significant areas.
- Sacred groves are small patches of forests or natural vegetation protected by local communities.
- These areas hold religious and cultural significance, often dedicated to local deities.
- Sacred groves serve as biodiversity repositories, sheltering rare species.
Additional Details
- Sacred Groves: These are areas that prohibit hunting and deforestation, allowing only sustainable practices like honey collection and gathering deadwood.
- Geographical Distribution:Sacred groves are prevalent in regions such as:
- Western Ghats
- Himalayas
- Northeastern hill tracts
- Central India
- Regional Names:Various regions have unique names for sacred groves:
- Sarna in Bihar
- Dev Van in Himachal Pradesh
- Devarakadu in Karnataka
- Kavu and Sarpa Kavu in Kerala
- Devrai and Deorai in Maharashtra
- Law Kyntang and Asong Khosi in Meghalaya
- Oran in Rajasthan
- Example of Success: In Piplantri Village, Rajasthan, a notable initiative involves planting 111 trees for every girl child born, enhancing local income, reducing female foeticide, and empowering women’s self-help groups.
The Supreme Court's directive emphasizes the need for a structured approach to conserve these vital ecological and cultural sites, which play a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity and supporting local communities.
GS3/Science and Technology
Kisan Kavach
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
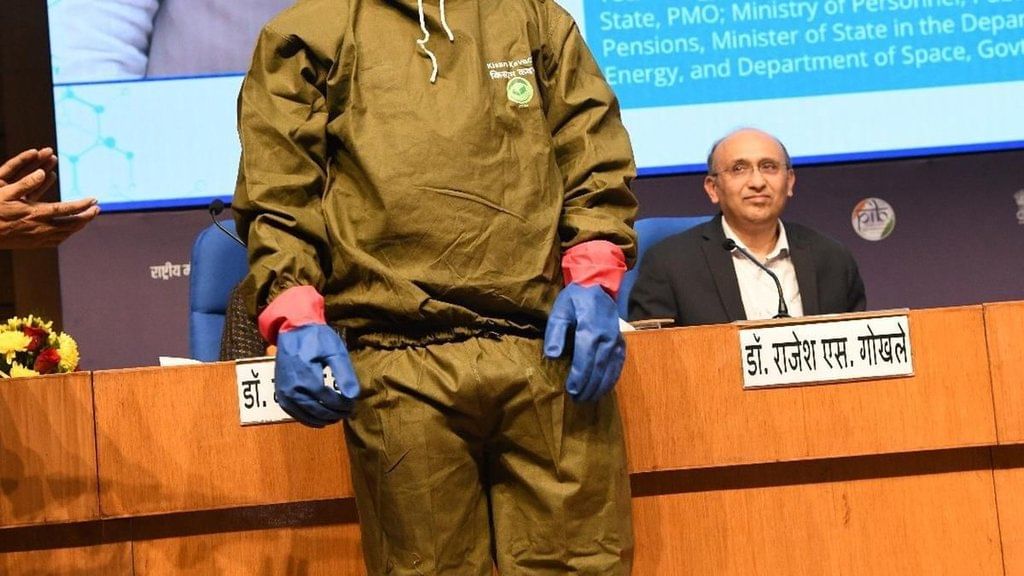
Why in News?Recently, the Union Minister of State (Independent Charge) for Science and Technology introduced the Kisan Kavach, a protective innovation aimed at safeguarding farmers from the adverse effects of pesticide exposure.
- Kisan Kavach is the first anti-pesticide bodysuit specifically designed for farmers.
- The suit protects farm laborers from absorbing harmful pesticides during application.
- Developed by the Biotechnology Research and Innovation Council (BRIC-inStem) in Bangalore, in collaboration with Sepio Health Pvt. Ltd.
Additional Details
- Design: The kit includes a trouser, pullover, and face-cover made from 'oxime fabric' that chemically breaks down common pesticides that may come into contact with the suit during spraying.
- Price: Each kit is priced at ₹4,000.
- Mechanism: The Kisan Kavach fabric employs nucleophilic mediated hydrolysis to deactivate pesticides upon contact, effectively reducing the risk of pesticide-induced toxicity.
- The suit is durable, maintaining its protective qualities across a wide temperature range, under UV exposure, and even after 150 washes.
This innovative solution aims to significantly improve the safety and health of farmers who are regularly exposed to harmful pesticides, ensuring a safer working environment in agriculture.
GS3/Economy
Comprehensive Telecom Development Plan
Source: PIB
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Comprehensive Telecom Development Plan (CTDP) aims to enhance mobile coverage and improve telecommunications infrastructure in India's North Eastern Region (NER), focusing on providing connectivity to uncovered villages and national highways. This initiative is part of the broader efforts under the Digital Bharat Nidhi (DBN) program.
- CTDP focuses on expanding mobile and broadband access in underserved areas.
- Digital Bharat Nidhi (DBN) replaces the Universal Service Obligation Fund (USOF) to better address connectivity in remote regions.
- Funding comes from a 5% Universal Service Levy on the Adjusted Gross Revenue (AGR) of telecom operators.
- CTDP has a statutory status established through amendments to the Indian Telegraph Act, now superseded by the Telecom Act, 2023.
Additional Details
- Mobile Coverage Expansion: The plan includes the installation of 2,619 mobile towers, providing coverage to 3,223 villages and 286 highway locations.
- 4G Connectivity: A significant goal is to achieve 4G saturation in remote villages to enhance digital access.
- Socio-Economic Support: The initiative aims to empower citizens through Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) for overall development.
- Digital Inclusion: Efforts are made to bridge the digital divide, ensuring equitable access to technology.
In conclusion, the Comprehensive Telecom Development Plan is a critical step towards improving telecommunications in India's North Eastern Region, with a focus on enhancing connectivity and supporting socio-economic development through digital inclusion.
GS2/Governance
Crime and Criminal Tracking Network and Systems (CCTNS)
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?Nearly 15 years after its inception, the Crime and Criminal Tracking Network and Systems (CCTNS) has successfully linked all 17,130 police stations across India. This initiative is critical for modernizing law enforcement and improving the overall efficiency of policing in the country.
- CCTNS was launched in 2009 and aims to enhance the efficiency of policing through technology.
- The system is integral to the implementation of three new criminal laws introduced on July 1.
Additional Details
- Objectives:
- To create a nationwide integrated platform for the investigation, detection, and prevention of crimes.
- To improve citizen services, such as the online registration of complaints and tracking of case statuses.
- Scope: The CCTNS aims to connect all police stations in India through a unified network, facilitating seamless information sharing regarding crimes and criminals among law enforcement agencies.
- Components:
- Core Application Software (CAS): Provides a standardized platform for data entry, retrieval, and sharing.
- National Database: A centralized repository containing criminal records, FIRs, and investigation reports.
- Integration with Other Systems: Connects with various databases, including Fingerprint Identification Systems, Vehicle Registration, and Passport Verification.
- Citizen-Centric Services:
- Online filing of complaints.
- Viewing the status of registered complaints and FIRs.
- Searching for missing persons or stolen vehicles.
- Integrated Criminal Justice System (ICJS): The CCTNS has evolved to integrate police data with other components of the criminal justice system, such as courts, prisons, prosecution, forensics, and fingerprints, leading to the development of the ICJS.
In conclusion, the CCTNS represents a significant step forward in the modernization of India's policing system, aiming to provide more effective crime management and enhanced services for citizens.
GS3/Environment
Hindu Kush Himalaya Faces Risks Amid Record Glacier Melting
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?The State of the Cryosphere 2024 report, presented at the UN Climate Change Conference in Baku, highlights alarming trends in glacier melting due to rising carbon emissions. It warns that global temperatures could rise by over 3°C by the end of the century, significantly impacting the Indian Himalayan Region and other areas.
- The cryosphere encompasses all frozen water on Earth, including snow, glaciers, ice caps, ice sheets, sea ice, and permafrost.
- Rising temperatures have been detrimental to the cryosphere, with the summer of 2023 marking the third consecutive year of reduced sea ice in Antarctica to below 2 million square kilometers.
- Continued warming could lead to the complete loss of Antarctic sea ice during summer months, exacerbating ice sheet melting.
- Exceeding the 1.5°C temperature rise could result in a sea level increase of over 10 meters in the coming centuries.
- Venezuela's last glacier, 'Humboldt,' has melted away, and Indonesia's 'Eternity Glacier' is expected to vanish within two years.
- Increased temperatures lead to a shift from solid to liquid precipitation, resulting in diminished seasonal snow even at higher elevations.
- Thawing permafrost is contributing to higher atmospheric CO2 concentrations.
Additional Details
- Impacts on the Hindu Kush Himalayan Region: The HKH region has experienced record-low snowfall during the winter of 2023-2024, which threatens food, energy, and water security across the area.
- The Indian Himalayan Region, which includes 13 states and Union Territories, could see a 50% loss of ice from High Mountain Asian glaciers with just a 2°C rise in global temperatures.
- This ice loss could lead to increased risks of catastrophic events, such as Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs), which have already become a reality in High Mountain Asia. The recent GLOF incident at South Lhonak Lake in Sikkim (October 2023) resulted in loss of life and significant infrastructure damage.
The ongoing challenges posed by climate change and glacier melting in the Hindu Kush Himalaya region underscore the urgent need for effective environmental policies and global cooperation to mitigate these effects.
GS2/International Relations
What is OPEC+?
Source: Reuters Why in News?
Why in News?
With the potential return of Donald Trump to the White House, OPEC+ delegates have expressed concerns regarding higher oil production levels in the United States. Trump's administration may prioritize deregulation in the energy sector, which could lead to increased oil output and further diminish OPEC+'s market share.
- OPEC+ is a coalition of oil-producing nations aimed at managing oil production and stabilizing prices.
- Formed in 2016, OPEC+ responds to the rising oil production from the United States, particularly shale oil.
Additional Details
- Formation and Purpose: OPEC+ consists of both OPEC members and non-OPEC oil-producing nations working together to stabilize global oil prices.
- OPEC Members: Founded in 1960, OPEC includes 12 member countries: Algeria, Angola, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Venezuela.
- Non-OPEC Members in OPEC+: The coalition also includes 10 non-OPEC members: Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Mexico, Oman, Russia, South Sudan, and Sudan.
- Global Influence: Together, OPEC+ countries produce about 40% of the world’s crude oil and control approximately 80% of proven oil reserves.
- Factors Influencing OPEC+ Oil Production Cuts:
- Rising US oil production impacts OPEC+'s market influence due to the shale boom.
- OPEC+ implements production cuts to maintain global price stability.
- Extended production cuts are necessary due to weak global demand, particularly in major economies.
- Implications of OPEC+ Policies:
- OPEC+'s market share has decreased from 55% in 2016 to 48% in 2024.
- While production cuts aim to stabilize prices, increasing US production complicates this goal.
- Production cuts help ensure economic stability for oil-producing economies.
Understanding OPEC+ and its dynamics is crucial for grasping the global oil market's complexities, especially in light of geopolitical changes and energy policies.
GS3/Environment
Strengthening the Roots of an Agri-Carbon Market
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?In India, it is crucial to review current carbon credit projects implemented by private organizations to ensure they are fair and function effectively. This review aims to enhance the sustainability and inclusivity of agricultural practices that contribute to carbon credit generation.
- Current carbon credit projects lack effective registration, leaving farmers without financial incentives.
- Inadequate communication and training hinder the adoption of sustainable practices among farmers.
- Exclusion of marginalized communities limits the socioeconomic benefits of carbon markets.
- Technological advancements can improve the measurement and verification processes in carbon farming.
Additional Details
- Collaborative Initiatives: NABARD, ICAR, and State Universities have identified five agricultural carbon credit projects in the Verra registry aimed at promoting sustainable agriculture.
- Carbon Farming Projects: More than 50 projects targeting 1.6 million hectares aim to generate 4.7 million carbon credits annually; however, none are registered, leaving farmers devoid of financial compensation.
- Challenges: Key challenges include a lack of communication (45% of farmers reported insufficient information), exclusion of marginalized groups (only 4% of participants are women), and inadequate financial incentives, as 28% of farmers stopped sustainable practices after two years.
- Technological Advancements: Improved measurement techniques through digital technologies can enhance monitoring and reporting essential for assessing soil carbon levels and GHG emissions.
To encourage farmers’ participation in carbon markets, it is vital to promote inclusive projects, offer guaranteed timely payments, and leverage technology for better efficiency. Strengthening these areas will not only enhance the viability of carbon markets but also ensure broader socioeconomic benefits for farming communities in India.
GS3/Environment
Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary
Source: New Indian
 Why in News?
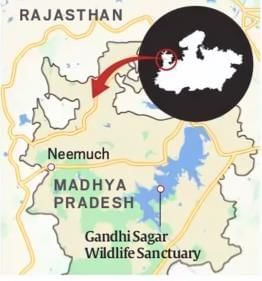
Why in News?Madhya Pradesh has announced plans to establish a suitable habitat for cheetahs within the Gandhi Sagar Wildlife Sanctuary, which spans an impressive 2,500 sq. km across the states of Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan.
- The sanctuary was declared in 1974, covering an area of 368 sq. km.
- It is located in northwestern Madhya Pradesh along the Madhya Pradesh-Rajasthan border.
- The Chambal River bisects the sanctuary into two distinct regions.
- It is recognized as an Important Bird and Biodiversity Area (IBA).
Additional Details
- Topography and Vegetation: The sanctuary features a diverse landscape including hills, plateaus, and the catchment area of the Gandhi Sagar Dam. The primary types of vegetation found here include:
- Northern tropical dry deciduous forest
- Northern tropical dry mixed deciduous forest
- Dry deciduous scrub
- Principal Tree Species: Key species include Khair, Salai, Kardhai, Dhawda, Tendu, and Palash.
- Fauna: The sanctuary is home to various species, such as:
- Herbivores: Chinkara, Nilgai, and Spotted Deer
- Carnivores: Indian Leopard, Striped Hyena, and Jackal
- Aquatic Species: Crocodiles, fish, otters, and turtles
- Historical and Cultural Importance: The sanctuary is notable for its historical and archaeological sites, including:
- Chaurasigarh
- Chaturbhujnath Temple
- Bhadkaji rock paintings
- Hinglajgarh Fort and Taxakeshwar Temple
The initiative to create a habitat for cheetahs highlights the commitment to wildlife preservation and biodiversity in India, while also addressing the challenges faced by existing fauna.
GS3/Science and Technology
Imaging Underwater Hot Spring Active with Microbial Life
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?Indian oceanographers have achieved a historic milestone by capturing an image of an active hydrothermal vent located at a depth of 4,500 meters in the Indian Ocean. This significant discovery, part of the Ministry of Earth Sciences' Rs 4,000-crore Deep Ocean Mission, holds great potential for mineral exploration.
- The Deep Ocean Mission (DOM) aims to explore deep ocean resources.
- Hydrothermal vents are hotspots for mineral-rich deposits and unique ecosystems.
- This discovery enhances India's role in deep-sea exploration and scientific research.
Additional Details
- Deep Ocean Mission (DOM): A comprehensive program focusing on exploring the deep ocean and developing technologies for resource utilization. The mission has an estimated budget of Rs. 4,077 crore over five years, divided into phases, with the first phase (2021-2024) allocating Rs. 2,823.4 crore.
- Components:The mission includes six main components:
- Manned submersible: Designed to carry three people to depths of 6,000 meters, equipped with scientific tools and sensors.
- Ocean climate change advisory services: Developing models to understand and predict climate variables.
- Deep-sea biodiversity: Studying deep-sea flora and fauna, including microbes, to promote sustainable use of bio-resources.
- Deep ocean survey and exploration: Identifying sites for multi-metal hydrothermal sulfide mineralization in the Indian Ocean.
- Energy and freshwater: Exploring the ocean’s potential for energy and freshwater resources.
- Advanced marine station: Establishing a station dedicated to ocean biology.
- Hydrothermal Vents: These are underwater springs located near tectonic plate boundaries, formed when cold seawater (around 2°C) interacts with magma, resulting in superheated water (up to 370°C) that emerges as mineral-rich plumes.
The discovery of the hydrothermal vent not only confirms previous surveys but also paves the way for deeper understanding of marine ecosystems and the potential for mineral resources. The National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR) aims to further explore these vents using advanced sampling techniques, solidifying India's position as a leader in deep-sea exploration.
GS3/Science and Technology
Milkweed Fiber
Source: PIB
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Union Ministry of Textiles is promoting research and development into innovative natural fibers, particularly focusing on milkweed fiber, which is gaining attention for its potential sustainability benefits.
- Milkweed fiber is a seed fiber derived from the milkweed plant (Asclepias syriaca).
- This plant is commonly found in India, particularly in Rajasthan, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
- Milkweed fiber has unique properties, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
Additional Details
- Milkweed Plant: The milkweed plant belongs to the genus Asclepias in the family Asclepiadaceae and is often referred to as a stubborn weed. It produces a significant amount of milk sap in its leaves, stems, and pods.
- Properties of Milkweed Fiber: This fiber contains oily materials and lignin, a woody substance that contributes to its brittleness, making it unsuitable for traditional spinning. Additionally, its surface is hydrophobic and oleophobic due to natural waxes.
- Applications:
- Used in the paper industry.
- Serves as an insulative filling material.
- Incorporated in water-safety equipment like life jackets and belts.
- Effective in oil spill cleanup due to its ability to absorb oil while repelling water.
In conclusion, milkweed fiber represents a promising natural resource with multiple applications, particularly in sustainable industries. Its unique properties make it an important focus for ongoing research and development efforts.
GS1/History & Culture
Remembering Mirza Ghalib
Source: The Portrait
Why in News?A recent three-day event titled 'Remembering Ghalib' was organized by the Delhi government to celebrate the birth anniversary of the esteemed poet, Mirza Ghalib. This event, conceptualized by the acclaimed Kathak exponent, Padma Bhushan Uma Sharma, aimed to capture the essence of Ghalib's life and literary contributions for contemporary audiences.
- Mirza Ghalib (1797-1869) was a prominent Urdu and Persian poet, recognized as the last great poet of the Mughal era.
- Born as Mirza Asadullah Beg Khan on December 27, 1797, in Agra, India.
- Ghalib faced significant personal losses early in life, including the death of his father and uncle.
Additional Details
- Literary Contributions: Ghalib wrote extensively in Urdu and Persian, with his most celebrated work being Diwan-e-Ghalib, a collection of profound Urdu ghazals.
- Themes of His Poetry: His poetry often delved into themes of love, loss, and existential reflection, mirroring the socio-political climate of 19th-century India under British colonial rule.
- Financial Struggles: Throughout his life, Ghalib encountered financial hardships and depended on patrons for support.
- Recognition: Despite his challenges, he gained recognition and served as the poet laureate in the court of the last Mughal emperor, Bahadur Shah Zafar.
Mirza Ghalib remains a central figure in Urdu literature, and events like 'Remembering Ghalib' play a crucial role in preserving and promoting his legacy in contemporary culture.
|
39 videos|4287 docs|905 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 19th December 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are Sacred Groves and their significance in biodiversity conservation? |  |
| 2. What is Kisan Kavach and how does it benefit farmers? |  |
| 3. How does the Comprehensive Telecom Development Plan aim to improve communication in India? |  |
| 4. What is the Crime and Criminal Tracking Network and Systems (CCTNS)? |  |
| 5. What are the implications of glacier melting in the Hindu Kush Himalaya region? |  |
|
39 videos|4287 docs|905 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|

















