UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 26th December 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Economy
MoSPI Modifying CPI Base Year
Source: Business Today
Why in News?
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) is in the process of updating the Consumer Price Index (CPI) base year, which involves revising the CPI weights and baskets used for calculation.
- The CPI measures the average change in prices of a fixed basket of goods and services consumed by households.
- The MoSPI proposes to revise the CPI methodology, introducing a new base year of 2024.
- Inclusion of free items distributed under the Public Distribution System (PDS) is a significant change being considered.
- The revised CPI aims to reflect current consumption patterns and improve the accuracy of inflation measures.
Additional Details
- Consumer Price Index (CPI):The CPI tracks price changes for a fixed basket of goods, reflecting changes in the purchasing power of money over time. It includes various categories such as:
- Food and Beverages: Includes items like cereals, pulses, vegetables, milk, meat, and beverages.
- Housing: Accounts for rent or imputed rent for self-occupied houses.
- Clothing and Footwear: Covers costs of garments, footwear, and related items.
- Fuel and Light: Comprises LPG, kerosene, firewood, and electricity.
- Miscellaneous: Encompasses expenses related to education, healthcare, transport, communication, and recreation.
- Base Year: The current base year for CPI is 2012, with the new base year proposed to be 2024.
- Purpose of CPI: It serves multiple roles including tracking inflation, assisting in policy formulation by the RBI, and supporting wage and pension adjustments.
- Key Issues: The exclusion of free PDS items from CPI has raised concerns about the accuracy of inflation representation.
The ongoing discussions and proposed changes to the CPI methodology highlight the importance of accurately capturing consumer expenditure and inflation dynamics. Stakeholder feedback will play a critical role in shaping these revisions as India seeks to align its statistical practices with international standards.
GS2/Governance
Free Movement Regime (FMR) along the Myanmar Border
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?
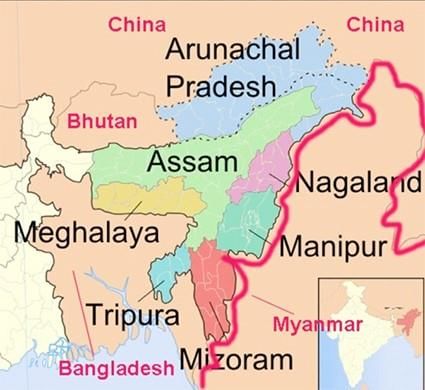
The Union Home Ministry has recently suspended the Free Movement Regime (FMR) along the Myanmar border, introducing a new protocol to regulate the movement of people living within a 10-kilometer radius on either side of the largely unfenced international border. This decision comes in the wake of security concerns and aims to maintain the demographic structure of the northeast region.
- The FMR, originally allowing movement up to 16 kilometers, has now been reduced to 10 kilometers.
- The Assam Rifles is responsible for guarding the 1,643-km border with Myanmar.
- The FMR facilitates cross-border movement for economic activities and family visits.
Additional Details
- Genesis of the FMR: The roots of the Free Movement Regime trace back to the late 19th century when both India and Myanmar were part of the British Empire. The arrangement continued post-independence with a bilateral agreement revised in 1967, and was formally established in 2018 under India's Act East Policy.
- New Protocol: Under the new guidelines, individuals entering India from Myanmar must report at designated border points, fill out a form, and undergo checks by the Assam Rifles and local authorities. A border pass will be issued, which must be returned upon departure within seven days.
- Violations of the movement conditions can lead to legal actions against offenders.
The implementation of these new regulations reflects the government's focus on enhancing internal security while continuing to allow some degree of cross-border movement, albeit under stricter controls.
GS3/Environment
Conservation Efforts for Red Pandas
Source: PIB
 Why in News?
Why in News?
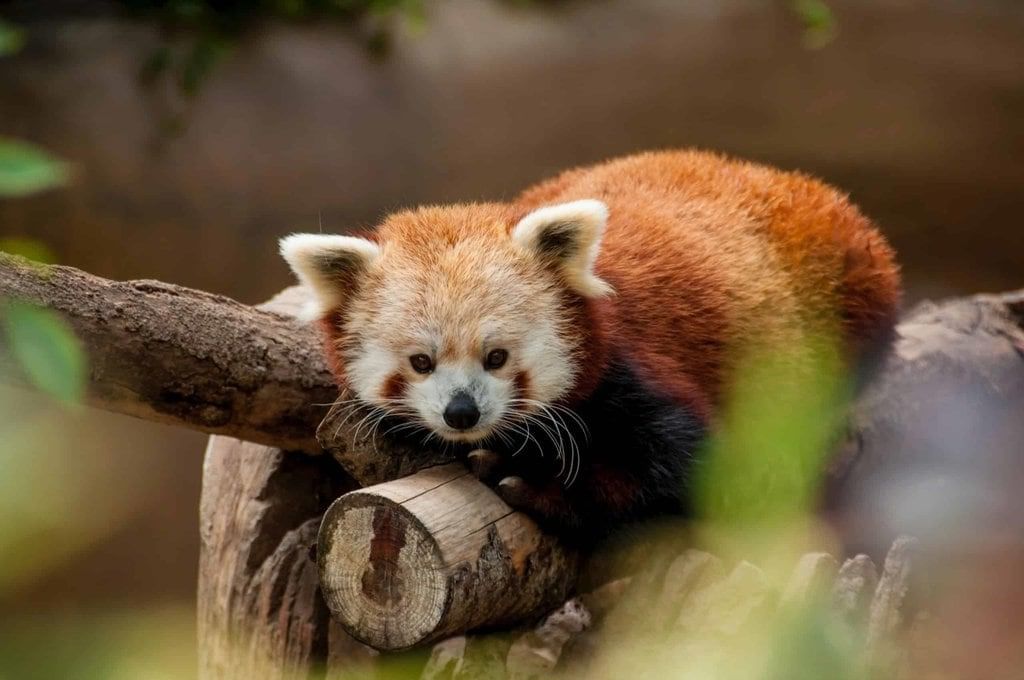
Two red pandas from the Rotterdam Zoo in the Netherlands are being relocated to the Padmaja Naidu Himalayan Zoological Park (PNZP) in Darjeeling, India, to support conservation breeding initiatives aimed at preserving this endangered species.
- Red pandas are classified as endangered on the IUCN Red List.
- They are primarily found in the Eastern Himalayas, especially in India, Nepal, Bhutan, and parts of China.
- The conservation breeding program at PNZP has been operational since 1986.
Additional Details
- Scientific Name: The red panda is scientifically known as Ailurus fulgens.
- Habitat: Red pandas thrive in mixed deciduous and conifer forests at altitudes of 2,200 to 4,800 meters, with a significant presence in bamboo-rich areas.
- Conservation Status: Red pandas are listed in CITES Appendix I and are protected under the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972 in India.
- Physical Characteristics: They are about the size of a house cat, renowned for their cute appearance and unique defensive posture.
- Ecological Role: They serve as an indicator species, reflecting the health of their forest ecosystems.
- Threats: The main threats to red pandas include habitat destruction due to deforestation and the loss of bamboo, their primary food source.
The relocation of Vishal and Koshi, the two red pandas, marks a significant step in global efforts to conserve this charming yet vulnerable species, contributing to their breeding success and overall survival in the wild.
GS3/Science and Technology
US FDA Approves Use of Weight Loss Drug for Sleep Apnoea
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The FDA has recently granted approval for Tirzepatide, known commercially as Zepbound, to be used in the treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA). This drug is advised to be used in conjunction with a low-calorie diet and increased physical activity for individuals suffering from moderate to severe OSA. This approval underscores the multifaceted applications of Tirzepatide beyond its initial use for managing type-2 diabetes and obesity, noting that fat accumulation around the neck can lead to muscle laxity in the throat, which is a contributing factor to OSA. Notably, this marks the first pharmacological option available for certain patients diagnosed with obstructive sleep apnoea.
- The FDA has approved Zepbound for treating moderate to severe OSA.
- This drug is linked to weight loss, which can alleviate symptoms of OSA.
- It is the first drug treatment specifically for patients with OSA.
Additional Details
- How Zepbound Works: Zepbound operates by activating receptors for hormones released by the intestine, such as glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), which help to reduce appetite and food intake.
- Types of Sleep Apnoea:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnoea (OSA): The most prevalent form, caused by a physical blockage of the airway.
- Central Sleep Apnoea: This occurs when the brain does not send correct signals to the muscles responsible for breathing.
- Complex Sleep Apnoea Syndrome: A combination of both obstructive and central sleep apnoea.
- Impact of Obesity: Obesity is a significant risk factor for OSA, as fat accumulation in the abdomen and neck can obstruct airways during sleep.
- Over 50% of patients with OSA are classified as obese, while 25% are considered overweight.
- Current Treatment Options: Common treatments include the use of positive airway pressure machines and lifestyle modifications, though prior to Zepbound, there were no specific drug therapies available for OSA.
The approval of Zepbound not only provides a new therapeutic option for those with OSA but also emphasizes the importance of weight management in addressing this condition. By potentially improving OSA symptoms through weight loss, Zepbound illustrates the interconnected nature of obesity and sleep disorders, paving the way for further research into its multifaceted benefits.
GS3/Environment
KEN-BETWA LINK PROJECT (KBLP) LAUNCHED
Source: PIB
Why in News?
The Ken-Betwa river-linking project was inaugurated by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in Khajuraho, Madhya Pradesh. This initiative aims to address the persistent water scarcity issues in the Bundelkhand region, which spans parts of both Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
- The KBLP is the first project under India’s National Perspective Plan for interlinking rivers, originally formulated in 1980.
- The project has a significant financial outlay of ₹45,000 crore.
- The KBLP will facilitate irrigation for over 10 lakh hectares and provide drinking water to approximately 62 lakh people.
Additional Details
- Project Objectives: The primary goal is to transfer water from the Ken River to the Betwa River, enhancing irrigation and drinking water supply while generating hydropower (103 MW) and solar power (27 MW).
- Components: The project includes the construction of the Daudhan Dam, a 77-meter-high dam, and a 221-kilometer canal connecting the two rivers.
- Phases of Implementation:
- Phase-I: Involves the construction of the Daudhan Dam complex, including various tunnels and powerhouses.
- Phase-II: Consists of the Lower Orr Dam, Bina Complex Project, and Kotha Barrage.
However, the project has raised concerns regarding its environmental and social impacts. The Central Empowered Committee (CEC) of the Supreme Court has scrutinized the wildlife clearance, questioning the project's economic viability and advocating for alternative irrigation methods before proceeding with such large-scale interventions.
Significant issues include:
- The inundation of approximately 98 square kilometers of Panna National Park and the felling of 2-3 million trees.
- The dam's location within the core area of a tiger reserve, raising concerns over its environmental implications.
- Potential adverse effects on wildlife, including the Gharial population in the Ken Gharial Sanctuary and vulture nesting sites.
GS2/International Relations
Strengthened India-Kuwait Relations and the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC)
Source: Business Standard
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The relationship between India and Kuwait has evolved into a strategic partnership, marked by Prime Minister Narendra Modi's significant visit, which is the second by an Indian Prime Minister since 1981. This visit underscores a robust commitment to enhancing trade, defense, and mutual cooperation.
- The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) was established as a political and economic alliance.
- The GCC is composed of six member states: Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
- India is the largest regional trading partner of the GCC, with substantial trade volumes and a significant Indian expatriate community.
Additional Details
- About the GCC: The GCC was formed in response to regional tensions arising from events like the Iranian Revolution (1979) and the Iran-Iraq War (1980-1988). Its primary objective is to promote political and economic collaboration among member states.
- Organizational Structure:
- Supreme Council: The highest authority, composed of the heads of state, making decisions through unanimous approval and rotating the presidency annually based on alphabetical order.
- Ministerial Council: Composed of foreign ministers or their representatives, this council proposes policies and implements Supreme Council decisions, meeting every three months.
- Secretariat General: Acts as the administrative arm, monitoring policy implementation and organizing meetings, headquartered in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
- India and the GCC:
- The GCC is India's largest regional trading bloc, with total bilateral trade reaching USD 161.59 billion in FY 2023-24.
- Indian exports to the GCC are valued at USD 56.3 billion, while imports amount to USD 105.3 billion.
- India ranks as the 3rd largest trading partner of the GCC and is the 2nd largest export destination.
- Approximately 8.9 million Indian expatriates live in GCC countries, contributing significantly to remittances, which are a vital income source for India.
This strategic partnership between India and Kuwait, along with the broader GCC relationship, highlights the importance of regional cooperation in trade, defense, and stability in the context of global dynamics.
GS3/Science and Technology
Imaging Active Hydrothermal Vents
Source: Financial Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
India's Deep Ocean Mission has made significant progress by successfully capturing high-resolution images of an active hydrothermal vent located 4,500 meters beneath the surface of the Indian Ocean. This achievement marks an important milestone in underwater exploration and research.
- Hydrothermal vents are underwater hot springs found near tectonic plate boundaries.
- These vents were first discovered in 1977 near the Galapagos Islands, Ecuador.
- Active hydrothermal vents expel superheated, mineral-rich water from beneath the Earth's crust.
- The discovery enhances India's capabilities in deep-sea mineral exploration and research.
Additional Details
- Formation: Cold seawater (approximately 2°C) seeps through fissures in the oceanic crust. This water comes into contact with hot magma, heating up to temperatures that can exceed 370°C. The resulting superheated water resurfaces as mineral-rich hydrothermal fluids, creating vents and plumes.
- Types of Hydrothermal Vents:
- Black Smokers: Emit particle-laden fluids predominantly composed of iron sulfides, forming distinctive black chimney-like structures.
- White Smokers: Release fluids rich in barium, calcium, and silicon, resulting in white chimneys.
- Significance of the Discovery for India:
- Mineral Exploration: This discovery enhances India's ability to explore and utilize deep-sea hydrothermal sulfide fields, crucial for securing valuable mineral resources.
- Support for Samudrayaan Mission: The findings bolster India's ambitious initiatives aimed at mineral extraction from the deep ocean.
- Microbial Research: Provides insights into chemosynthetic organisms and expands knowledge of deep-sea biology, with potential implications for biotechnology.
This landmark achievement not only advances India's research capabilities but also opens new avenues for exploration and understanding of the deep-sea ecosystems.
GS3/Science and Technology
Ocean Anoxic Event 1a (OAE 1a)
Source: Nature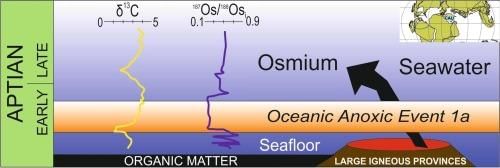 Why in News?
Why in News?
A recent study published in Science Advances has provided new insights into the timing and duration of Ocean Anoxic Event 1a (OAE 1a) by examining ancient rocks and fossils from Mount Ashibetsu, Japan.
- OAE 1a occurred during the Cretaceous Period (145–66 million years ago), when Earth's oceans experienced significant oxygen depletion.
- This event was triggered by massive volcanic eruptions that released substantial amounts of carbon dioxide (CO₂), leading to global warming and oxygen depletion in marine environments.
Additional Details
- Anoxic Marine Basins: These are water bodies, often in deep ocean regions, where oxygen levels are critically low or absent. They support specialized microbes and fungi, but most aerobic life forms cannot survive.
- Carbon Sequestration: Low oxygen levels slow the decomposition of organic matter, which aids in long-term carbon sequestration, helping to reduce atmospheric CO₂ levels. Examples include the Black Sea, Cariaco Basin (Caribbean Sea), and Orca Basin (Gulf of Mexico).
- Key Findings from the Recent Study: The study identified that OAE 1a began approximately 119.5 million years ago and lasted about 1.1 million years, indicating a prolonged recovery period for oceans following CO₂-driven warming and anoxia.
- The volcanic activity associated with this event is linked to the Ontong Java Nui complex, which contributed to the significant release of CO₂.
- Modern implications of these findings highlight parallels between ancient volcanic CO₂ emissions and current human-induced warming, suggesting that rapid modern warming could trigger similar ecological disruptions and potentially lead to a Holocene extinction event.
In summary, the research on OAE 1a underscores the profound impact of volcanic activity on oceanic conditions and marine life, drawing important lessons for current environmental challenges.
GS3/Science and Technology
Mitochondrial DNA Mutations and Age-Related Muscle Loss
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
A recent study published in Genome Research has highlighted the significant impact of deletion mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) on the loss of muscle mass associated with aging.
- Mitochondria are crucial organelles known as the "powerhouses" of the cell.
- Deletion mutations in mtDNA can lead to reduced mitochondrial efficiency and ATP production.
- Chimeric genes formed by these mutations disrupt mitochondrial function, contributing to muscle degradation.
- Older individuals show a marked increase in chimeric mitochondrial mRNA, linking mtDNA mutations to biological aging.
Additional Details
- Mitochondria: Membrane-bound organelles found in most eukaryotic cells, responsible for performing aerobic respiration, which converts glucose into ATP, the energy currency of cells, and produces carbon dioxide and water.
- Functions of Mitochondria: Beyond energy production, mitochondria regulate cell death through apoptosis and contain their own DNA, which is susceptible to mutations.
- Deletion Mutations: These mutations decrease the size and functionality of mtDNA, leading to a decline in ATP production as mutated mtDNA outcompetes healthy versions.
- Chimeric Genes: Formed by fusing different mitochondrial genes due to deletion mutations, these disrupt normal mtDNA expression and accelerate mitochondrial dysfunction.
- Age-Related Changes: Studies show that older adults exhibit a two-fold increase in chimeric mitochondrial mRNA, which correlates with biological aging.
- Biomarkers for Aging: mtDNA deletion mutations and chimeric mRNA are critical indicators of biological aging, which could inform therapies aimed at preventing or repairing mitochondrial mutations.
Understanding the role of mtDNA mutations in muscle loss with age could lead to therapeutic strategies that may help delay age-related muscle degeneration.
GS2/Governance
Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi Initiative
Source: New Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Union Minister of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions recently introduced the ‘Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi’ initiative on Good Governance Day, aimed at enhancing the governance capacity of local self-governments in India.
- This initiative is part of the larger ‘Prashasan Gaon Ki Aur’ campaign.
- It focuses on empowering Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) through training and resources.
- The program is being piloted in Odisha, Assam, Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Utilizes e-learning, AI chatbots, and mobile apps for effective service delivery.
Additional Details
- Objective: The initiative seeks to improve the capacity and skills of elected representatives and officials to ensure effective governance and participatory planning.
- Technology Integration: By leveraging modern technology, the initiative aims to close knowledge gaps and enhance service delivery at the grassroots level.
- Expected Outcomes: It is anticipated to create scalable models of citizen-centric governance that promote equitable and sustainable rural development.
- New Dashboard on iGOT Karmayogi Platform: A new dashboard has been introduced to empower ministries and departments, providing insights on user registrations and training progress.
- CPGRAMS Annual Report 2024: This report highlights the achievements of the Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System, including the resolution of over 25 lakh grievances annually.
The Viksit Panchayat Karmayogi initiative represents a significant step towards decentralizing governance and enhancing participatory decision-making, ultimately fostering better community engagement and development in rural areas.
|
39 videos|4357 docs|921 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 26th December 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of modifying the CPI base year in India? |  |
| 2. What is the Free Movement Regime (FMR) along the Myanmar border? |  |
| 3. What are the current conservation efforts for red pandas? |  |
| 4. How does the US FDA approval of a weight loss drug for sleep apnea impact public health? |  |
| 5. What is the purpose of the Ken-Betwa Link Project (KBLP)? |  |
|
39 videos|4357 docs|921 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|

















