UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 26th January 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-II
Health Ministry announces new treatment regimen for Leprosy
Subject: Governance
Why in News?
The Central government of India has given its approval for a new treatment regimen aimed at hastening the eradication of leprosy in the country.
- The move, based on the latest global scientific research and endorsed by the World Health Organization (WHO), seeks to transition from a two-drug regimen to a three-drug regimen for Pauci-Bacillary (PB) leprosy cases.
New Leprosy Treatment Regimen
- Objective: The primary goal is to halt the transmission of leprosy at the sub-national level by 2027, aligning with the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals, three years ahead of schedule.
- Transition from Two to Three Drugs: The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has approved a shift from the existing two-drug regimen for six months to a three-drug regimen for Pauci-Bacillary (PB) cases.
- Scientific Basis: This decision is grounded in the latest globally accepted scientific research studies and evidence-based practices.
- WHO Endorsement: The World Health Organization (WHO) has committed to supply the revised drug regimen starting April 1, 2025, signifying international recognition and support for this approach.
Key Implementation Steps
- Three-Drug Regimen: The WHO-recommended treatment regimen includes dapsone, rifampicin, and clofazimine, collectively referred to as MDT. MDT is highly effective in killing the pathogen and curing the patient.
- Advance Requisitions: All States and Union Territories are instructed to submit their requisitions for anti-leprosy drugs a full year in advance to ensure a smooth transition.
- Unified Implementation Date: The revised classification of leprosy and the treatment regimen for both Pauci-Bacillary (PB) and multi-bacillary (MB) cases in India will come into effect simultaneously on April 1, 2025.
Understanding Leprosy
- Leprosy Overview: Leprosy is a chronic infectious disease caused by the Mycobacterium leprae bacteria, primarily affecting the skin and peripheral nerves.
- Transmission: It spreads through droplets from the nose and mouth during close contact with untreated cases.
- Curability: Leprosy is curable with multi-drug therapy (MDT).
Distinction between PB and MB Cases
- PB Cases: These individuals have fewer visible bacteria and show no signs of advanced disease in biopsies.
- MB Cases: They have visible bacteria and may exhibit more advanced disease in biopsies.
Significance of the New Regimen
- Eradication Target: The adoption of this new treatment regimen is expected to accelerate India’s progress towards leprosy eradication by 2027, reinforcing the country’s commitment to combat this disease.
- Previous Funding: The WHO has been providing free MDT, initially funded by the Nippon Foundation and later through an agreement with Novartis. This regimen is known as ‘Uniform MDT,’ simplifying administration and manufacturing processes.
Source: The Hindu
Why India’s runaway Coaching Centres need Regulating?
Subject: Governance

Why in News?
The recent government guidelines on regulating the coaching industry have stirred debate and raised questions about the state of education in India.
- This article delves into the reasons behind the need for these guidelines and the potential impact on various stakeholders.
Coaching Chaos: What’s the Issue?
- Early Enrolment Scrapped: The government’s guidelines stipulate that students below 16 years of age should not be enrolled in coaching centers, restricting enrolment to post-secondary school (standard 10) examination.
- A Shift in Education: This rule has caused concern as coaching centers have evolved into an alternative education pathway. Students as young as 10-12 years old are prepared for highly competitive exams, such as engineering, medical, and civil service, with low success rates.
- Proliferation of Coaching Centers: Coaching centers are especially popular in states like Bihar, Rajasthan, Delhi, and Uttar Pradesh.
The Need for Regulation: Why?
- Rising Student Suicides: The alarming increase in student suicides, with 26 reported cases in Kota alone in 2023, underscores the immense pressure on schoolchildren.
- Government’s Concerns: The Department of Higher Education, under the Ministry of Education, expressed the need for regulations in light of issues like student suicides, fire incidents, inadequate facilities, and teaching methodologies.
- Emergence of ‘Dummy Schools’: The rise of ‘dummy schools’ linked to coaching centers, where physical attendance is not mandatory, has raised concerns. Parents often uproot their families and take loans to relocate to coaching hubs in pursuit of quality education.
Wider Implications: Who Else Will Be Affected?
- Ecosystem Impact: Coaching hubs like Kota have an entire ecosystem supporting institutes, students, and families, including middlemen, hostels, and hotels. All of these entities stand to lose out.
- Real Estate Implications: Families relocating to coaching hubs contribute to local real estate income. Regulation may impact this aspect.
- Impact on ‘Dummy Schools’: Dummy schools will face closure due to the new regulations.
Perspectives from the Coaching Centers
- Coaching Federation of India’s Response: The Coaching Federation of India (CFI), representing over 25,000 coaching institutes, may legally contest the minimum age requirement, seeking a reduction from 16 years to 12 years.
- Competitive Stress Concerns: Large coaching institutes express concerns that the regulations may intensify competitive stress among students, offering them less time for preparation.
- Regulatory Effectiveness: There is apprehension that the regulations may not effectively oversee smaller private coaching centers, making it challenging to monitor mom-and-pop establishments.
Education’s Dependent Dynamic
- Coaching Dependency: The guidelines shed light on the prevailing reliance on coaching institutes. They supplement students’ regular schooling and often require additional hours of study outside the classroom.
- Misleading Promises: The guidelines also highlight how institutes sometimes make misleading promises or guarantee high scores, emphasizing that ranks and marks have eclipsed holistic student development.
Conclusion
- The government’s new guidelines have ignited a critical discussion about the coaching industry and its role in the Indian education landscape.
- The regulations aim to address pressing concerns while acknowledging the evolving dynamics of education in the country.
Source: The Mint
Turkey’s parliament approves Sweden’s NATO membership
Subject: International Relations

Why in News?
Sweden’s attempt to join NATO cleared a major hurdle after Turkey’s parliament supported its membership.
- For a new country to join the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), all the existing members have to approve it.
- Turkey and Hungary had been opposing Sweden’s entry for almost the past two years.
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
- About
- Formed in 1949 with the signing of the Washington Treaty, NATO is a security alliance of 31 countries from North America and Europe.
- In April 2023, Finland joined the alliance as its 31st member.
- NATO’s fundamental goal is to safeguard the Allies’ freedom and security by political and military means.
- It is a system of collective defence where independent member states agree for mutual defence in case of any attack by external party.
- Article 5 of the Washington Treaty states that an attack against one Ally is an attack against all. This article forms the core of the Alliance, a promise of collective defense.
- Headquarter - Brussels, Belgium.
- Formed in 1949 with the signing of the Washington Treaty, NATO is a security alliance of 31 countries from North America and Europe.
- Functions
- Political
- NATO promotes democratic values and enables members to consult and cooperate on defence and security-related issues to solve problems, build trust and, in the long run, prevent conflict.
- Military
- NATO is committed to the peaceful resolution of disputes.
- If diplomatic efforts fail, it has the military power to undertake crisis-management operations.
- Political
News Summary: Turkey’s parliament approves Sweden’s NATO membership
- On January 23, Turkey's parliament voted to approve Sweden's membership bid to join NATO.
- The vote ended a 20-month delay that frustrated Turkey's Western allies.
Why does Sweden want to join NATO?
- Sweden has not fought a war in two centuries, staying neutral through the two World Wars and the Cold War.
- In recent years, while it joined the European Union and collaborated with NATO, it showed no intention of actually joining the military alliance.
- However, this neutrality had to be abandoned after Russia invaded Ukraine.
- With public opinion increasingly in favour of joining NATO, both Sweden and Finland applied for membership in 2022.
- While Finland’s bid was cleared, Sweden ran into stiff opposition from Turkey and Hungary.
Why was Turkey opposing Sweden’s bid?
- Support to Kurdish militant outfit
- Turkey had accused Sweden of going soft on groups it sees as terrorists, such as the Kurdish militant outfit.
- Quran-burning protests held in Sweden
- The government says that it is protected under freedom of speech laws. This further soured its relationship with Turkey.
- US agreeing to sell 40 F-16 fighter jets to Ankara
- Experts also linked Turkey’s support to Sweden with the US agreeing to sell 40 F-16 fighter jets to Ankara(capital of Turkey)
- While the US had not said the deal would depend on Turkey’s Sweden actions, the sale is expected to go through now.
What will Sweden bring to NATO?
- Once Sweden becomes a member, almost all of the Baltic Sea coastline, except that in Russia’s control, will become NATO territory.
- This will provide the alliance strategic bases close to Russia, make supply lines more streamlined, and make it easier to defend assets in the sea.
- Sweden’s military, though numerically small, is modern and experienced in past NATO missions. Importantly, it has advanced aircraft and submarine capabilities.
Source: The Hindu
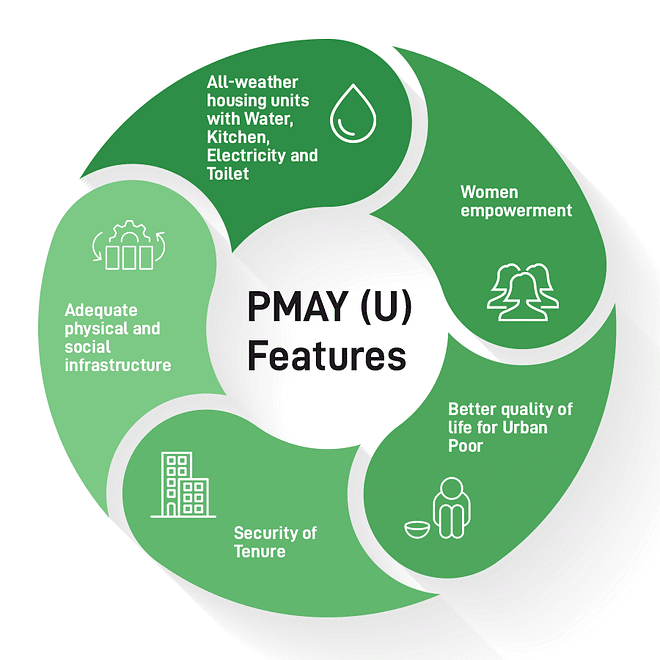
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban (PMAY-U)
Subject: Governance
Why in News?
More than 3,000 flats are likely to be allotted to slum dwellers by the Delhi Development Authority (DDA) under the PMAY-U.
About PMAY-U
- The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) launched the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban (PMAY-U) in 2015, as a flagship Mission of the Government of India.
- Objective: It addresses urban housing shortage among the Economically Weaker Section (EWS)/Low Income Group (LIG) category including the slum dwellers by ensuring a pucca house to eligible urban households.
- Coverage: The Mission covers the entire urban area consisting of Statutory Towns, Notified Planning Areas, Development Authorities, Special Area Development Authorities, Industrial Development Authorities or any such authority under State legislation which is entrusted with the functions of urban planning & regulations.
- Implementation period: The scheme was earlier from 25.06.2015 to 31.03.2022. Now it has been extended up to 31.12.2024, except Credit Linked Subsidy Scheme (CLSS) vertical, to complete all the houses sanctioned under the scheme.
Features
- PMAY-U adopts a demand-driven approach wherein the housing shortage is decided based on demand assessment by States/Union Territories (UTs).
- It is a demand driven scheme and GoI has not fixed any target for construction of houses.
Components of the scheme
- In-situ Slum Redevelopment (ISSR): Central Assistance of Rs. 1 lakh per house is admissible for all houses built for eligible slum dwellers under the component of ISSR using land as a Resource with the participation of private developers.
- Credit Linked Subsidy Scheme (CLSS): Beneficiaries are eligible for an interest subsidy of 6.5%, 4% and 3% on loan amounts up to Rs. 6 Lakh, Rs. 9 Lakh and Rs. 12 Lakh respectively.
- Affordable Housing in Partnership (AHP): Under AHP, Central Assistance of Rs. 1.5 Lakh per EWS house is provided by the Government of India.
- An affordable housing project can be a mix of houses for different categories but it will be eligible for Central Assistance, if at least 35% of the houses in the project are for the EWS category.
- Beneficiary-led Individual House Construction/ Enhancement (BLC-N/ BLC-E): Central Assistance up to Rs. 1.5 lakh per EWS house is provided to eligible families belonging to EWS categories for individual house construction/ enhancement.
- The Urban Local Bodies validate the information and building plan submitted by the beneficiary so that ownership of land and other details like economic status and eligibility can be ascertained.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
Operation Sarvashakti launched
Subject: Defense and Security

Why in News?
The Indian Army has initiated Operation Sarvashakti in the Rajouri-Poonch sector of Jammu and Kashmir to combat rising terrorist threats targeting security forces.
- This article explores Operation Sarpvinash, a similar military operation conducted in the same region over two decades ago, shedding light on its objectives, significance, and historical context.
Operation Sarvashakti: The Need for Action
- Escalating Threats: Recent years have witnessed three major terrorist attacks in the area, resulting in the loss of 20 soldiers.
- Foreign Terrorist Presence: The region is known for hosting foreign terrorists, making it a significant security concern.
- Enhancing Troop Presence: Operation Sarvashakti involves deploying additional troops to increase the density, thereby improving the chances of encounters with terrorists.
Reflecting on Operation Sarpvinash
- Counter-Insurgency in 2003: Operation Sarpvinash was conducted by Indian forces in response to the growing insurgency in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Extensive Troop Deployment: Over about three months, around 10,000 troops from the 15 Corps and 16 Corps participated in the operation.
- Aerial Support: Mi-17 helicopters facilitated troop transport to Hilkaka, a village seized by terrorists, while Lancer attack helicopters neutralized concrete bunkers built by infiltrators.
- Decisive Outcomes: The operation led to the elimination of nearly 100 terrorists, significant arms and ammunition seizures, including explosives, and the dismantling of 40-50 terrorist hideouts.
Origins of Operation Sarpvinash
- Post-Kargil War Scenario: With the Kargil war of 1999 fresh in memory and the aftermath of the December 2001 Parliament attack, Operation Parakram involved a substantial military mobilization along the Pakistan border.
- Preparation in 2003: Operation Sarpvinash preparations began after intelligence reports indicated the presence of over 300 foreign terrorists who had infiltrated the Line of Control (LoC) and established secure camps in Surankote and Hilkaka.
- Terrorist Control: These terrorists, affiliated with various Pakistan-based outfits, had created a demilitarized zone and asserted dominance, including the establishment of multiple hideouts and bunkers.
Strategic Significance
- Crucial Location: The areas south of Mendhar leading to the Pir Panjal range through Hilkaka offer the shortest infiltration route from across the LoC into the Kashmir valley.
- Infiltration Potential: Controlling this region provides a potential conduit for personnel during a Pakistani military operation and facilitates terrorist infiltration.
- Natural Cover: Dense forests and steep mountain slopes offer natural concealment, allowing terrorists to evade Indian forces during searches and engage them strategically.
Post-Sarpvinash Scenario
- Period of Peace: Following Operation Sarpvinash, the region experienced relative peace until 2017-18, despite ongoing terrorist incidents in the Kashmir valley.
- Recent Escalations: However, since 2021, this area has witnessed a resurgence of high-intensity attacks on security forces.
Source: Indian Express
Wandering albatrosses
Subject: Environment and Ecology

Why in News?
Wandering albatrosses are threatened with extinction and climate change could put their nesting sites at risk.
About Wandering albatrosses:
- It is the world’s largest flying bird, with a wingspan reaching an incredible 3.5 metres.
- These birds are oceanic nomads: they spend most of their 60 years of life at sea and only come to land to breed.
- These are found almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Their playground is the vast Southern Ocean— the region between the latitude of 60 degrees south and the continent of Antarctica.
- Marion Island and Prince Edward Island together support about half of the entire world’s wandering albatross breeding population.
- Habitat: They breed on several subantarctic islands, which are characterised by peat soils, tussock grass, sedges, mosses, and shrubs.
- Conservation status
- IUCN: Vulnerable
- Threats: The most likely cause is longline fishing, as they become hooked and will drown, as well as the ingestion of plastics, which kills both chicks and adults.
Source: Down to Earth
Vijay Raghavan Committee
Subject: Internal Security

Why in News?
AboutAn expert committee spearheaded by the former principal scientific advisor, Prof K Vijay Raghavan, has recently recommended a defence upgrade roadmap.
- The nine-member VijayRaghavan panel was set up by the government in 2023 to review the functioning of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- The government’s decision to review the functioning of DRDO comes against the backdrop of several of its projects suffering from huge delays.
- The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Defence, in its report had expressed concerns that 23 of its 55 mission mode projects could not be completed in time.
- A year before, in December 2022, the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG), in its report tabled in Parliament, had flagged that 119 (or 67%) of the 178 projects scrutinized by it had failed to adhere to their initially proposed timelines.
- The practice of seeking multiple extensions defeats the very purpose of projects taken under Mission Mode category.
- The CAG report had stated, adding these extensions were primarily sought due to factors like persistent alterations in design specifications, delays in completing user trials, and in placing supply orders.
- More focus on R&D: The DRDO should focus on its original goal of research and development for defence and refrain from involving itself in productization, production cycles, and product management, tasks that are more suitable for the private sector.
- Concentrate on few sectors only: There are numerous technologies that DRDO doesn’t necessarily need to get into. It asked, why should DRDO engage in drone development?
- Identify expertise: There is a necessity to identify expertise within India and internationally for various technologies.
- Creation of a separate department: Under the Defence Ministry, the Department of Defence Science, Technology, and Innovation can be created.
- This department is proposed to be headed by a technocrat.
- It will promote defence research and development in the academic and start-up ecosystem and also serve as the secretariat for the Defence Tech Council, chaired by the Prime Minister.
- Defence Tech Council: The committee recommended a top level body called the Defence Technology Council.
- Chaired by: Prime Minister of India, with the Defence Minister and the National Security Advisor as its Vice Presidents.
- Mandate: To determine the country’s defence technology roadmap and decide on major projects and their execution, a
- Executive committee: Chaired by the Chief of Defence Staff.
- The Principal Scientific Advisor, along with the three service chiefs and their vice chiefs, will also be its members.
- Furthermore, it will include representation from academia and industry, with two members from each sector.
Source: Indian Express
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|





















