UPSC Daily Current Affairs- January 8, 2022 | Current Affairs: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - CLAT PDF Download
GS-I
Maya Civilisation

Context
- The Maya civilization may have had access to nearly 500 edible plants, many of which were highly resistant to drought as per the new study.
About Maya civilization
- The Maya civilization originated in the Yucatan Peninsula.
- The Yucatán Peninsula is a northeastern projection of Central America, lying between the Gulf of Mexico to the west and north and the Caribbean Sea to the east.
- It flourished between 600 and 800 AD.
Features of Maya civilization
- Known for its monumental architecture and an advanced understanding of mathematics and astronomy.
- They also developed a system of hieroglyphic writing and highly sophisticated calendrical and astronomical systems.
- They practised mainly slash-and-burn agriculture, but they used advanced techniques of irrigation and terracing.
- As early as 1500 BCE the Maya had settled in villages and had developed an agriculture based on the cultivation of corn (maize), beans, and squash; by 600 CE cassava (sweet manioc) was also grown.
- They built great stone buildings and pyramid temples and worked with gold and copper.
- They began to build ceremonial centres, and by 200 CE these had developed into cities containing temples, pyramids, palaces, courts for playing ball, and plazas.
Collapse
- The 800 and 950 AD period is called the collapse of the Classic Maya civilisations.
Reasons for collapse
- Past evidence: The Maya people faced starvation because of their dependence on drought-sensitive crops such as corn, beans and squash.
- Recent study: It examined the drought tolerance of the 497 indigenous food plants of the Maya lowlands under three different scenarios: Short-duration, medium-duration and extreme drought.
- These plants have also been identified through paleoethnobotany, a branch of science dealing with behavioural and ecological interactions between past humans and plants.
- Researchers found that Under extreme drought conditions, stems such as hearts of palm and cactus pads would remain available for multiple year’s.
- The Maya people could have turned to chaya and cassava to meet their carbohydrates and protein needs
- Chaya, a shrub whose leaves are high in protein, iron, potassium and calcium, could have also been available.
- They believe that social and economic upheaval likely played a role.
- Climate change is already hampering food security.
- For instance, studies suggest it has negatively affected the yield of maize and wheat in low-latitude areas.
GS-II
Target Olympic Podium Scheme (TOPS)

Context
- The Union Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports (MYAS) has approved the inclusion of Alpine Skiing athlete Mohammad Arif Khan in the Target Olympic Podium Scheme (TOPS) Core group.
About Target Olympic Podium Scheme
- In order to improve India’s performance at the Olympics and Paralympics, the MYAS started the Target Olympic Podium Scheme (TOPS) in September 2014.
- It includes foreign training, international competition, equipment, and coaching camp besides a monthly stipend of Rs. 50,000/- for each athlete.
- It was particularly launched for India’s Olympic medal dream, at the 2016 (Rio) and 2020 (Tokyo) Olympics.
About Target Olympic Podium Scheme Function
- The Mission Olympic Cell is a dedicated body created to assist the athletes who are selected under the TOP Scheme.
- The MOC is under the Chairmanship of the Director-General, Sports Authority of India (DG, SAI).
- The idea of the MOC is to debate, discuss and decide the processes and methods so that the athlete receives the best assistance.
- The MOC also focuses on the selection, exclusion, and retention of athletes, coaches, training institutes that can receive TOPS assistance.
‘One District One Product’ scheme

Context
- The Food Processing Ministry had inked an agreement with NAFED for developing 10 brands as the One District One Product brands under the Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro food processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme.
- Of this, six brands have been launched recently.
- The six brands include Amrit Phal (developed under the ODOP concept for Gurugram, Haryana), Cori Gold (developed for coriander powder which is the identified ODOP for Kota, Rajasthan), Kashmiri Mantra, Madhu Mantra (developed under the ODOP concept for honey from Saharanpur, Uttar Pradesh), Somdana (developed under the ODOP concept of millets from Thane, Maharashtra), and Whole Wheat Cookies of Dilli Bakes (developed under the bakery ODOP concept for Delhi).
- All the products will be available at NAFED Bazaars, E-commerce platforms, and prominent retail stores across India.
About the Pradhan Mantri Formalisation of Micro food processing Enterprises (PMFME) Scheme
- Launched in 2020, the scheme will be implemented for five years until 2024-25.
- It is for the Unorganized Sector on All India basis.
Objectives of Scheme
- Increase in access to finance by micro food processing units.
- Increase in revenues of target enterprises.
- Enhanced compliance with food quality and safety standards.
- Strengthening capacities of support systems.
- Transition from the unorganized sector to the formal sector.
- Special focus on women entrepreneurs and Aspirational districts.
- Encourage Waste to Wealth activities.
- Focus on minor forest produce in Tribal Districts.
Salient features
- Centrally Sponsored Expenditure to be shared by Government of India and States at 60:40.
- 2,00,000 micro-enterprises are to be assisted with credit linked subsidy. Micro enterprises will get credit linked subsidy at 35 per cent of the eligible project cost with ceiling of Rs. 10 lakh.
- Beneficiary contribution will be minimum 10 per cent and balance from loan. Seed capital will be given to SHGs (Rs. four lakh per SHG) for loan to members for working capital and small tools.
- Cluster approach.
- Focus on perishables.
Benefits of the scheme
- Nearly eight lakh micro-enterprises will benefit through access to information, better exposure and formalization.
- It will enable them to formalize, grow and become competitive.
- The project is likely to generate nine lakh skilled and semi-skilled jobs.
- Scheme envisages increased access to credit by existing micro food processing entrepreneurs, women entrepreneurs and entrepreneurs in the Aspirational Districts.
- Better integration with organized markets.
- Increased access to common services like sorting, grading, processing, packaging, storage etc.
Why do we need this scheme?
- There are about 25 lakh unregistered food processing enterprises which constitute 98% of the sector and are unorganized and informal. Nearly 66 % of these units are located in rural areas and about 80% of them are family-based enterprises.
- This sector faces a number of challenges including the inability to access credit, high cost of institutional credit, lack of access to modern technology, inability to integrate with the food supply chain and compliance with the health &safety standards.
- Strengthening this segment will lead to reduction in wastage, creation of off-farm job opportunities and aid in achieving the overarching Government objective of doubling farmers’ income.
3rd National Water Awards

Context
- Uttar Pradesh has been awarded the first prize in Third National Water Awards-2020 in the best state category, followed by Rajasthan and Tamil Nadu.
About the Awards
- The first National Water Award was launched by the Ministry of Jal Shakti in 2018.
- It was instituted to recognize and encourage exemplary work and efforts made by States, Districts, individuals and organizations across the country in attaining the government’s vision of a Jal Samridh Bharat.
Objectives of Scheme
- To encourage the stakeholders to adopt a holistic approach towards water resources management in the country.
- To create awareness among the people about the importance of water and attempt to motivate them to adopt the best water usage practices.
- Because water is fundamental to life.
- India has more than 18% of the world’s population, it has only 4% of the world's renewable water resources.
Categories
- Ministry of Jal Shakti is giving 57 awards to States, Organizations, Individuals etc. in 11 different categories -
- Best State, Best District, Best Village Panchayat, Best Urban Local Body, Best Media (Print & Electronic), Best School, Best Institution/RWA/Religious organization for Campus usage, Best Industry, Best NGO, Best Water User Association, and Best Industry for CSR Activity.
- Some of these categories have sub-categories for different zones of the country.
Reciprocal Access Agreement (RAA)
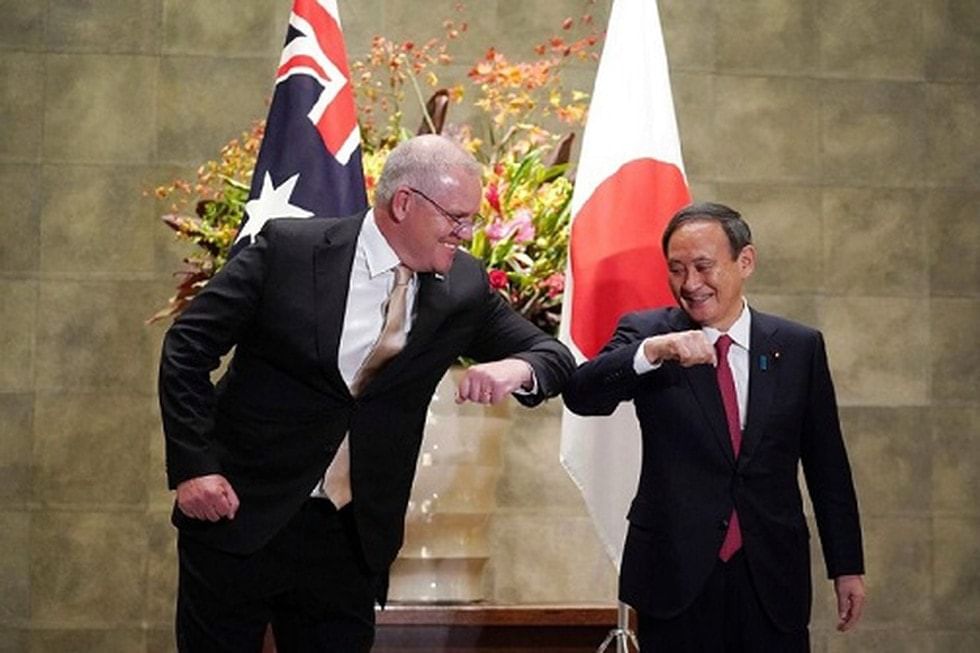

Context
- Reciprocal Access Agreement (RAA) signals that middle powers are willing to play a more active role in the Indo-Pacific.
About Reciprocal Access Agreement (RAA)
- The RAA is a bilateral defence and security pact between the governments of Australia and of Japan that provides for shared military training and military operations.
- It establishes streamlined arrangements to support the deployment of defence forces more quickly and with less administration.
- The pact was signed because of concerns that the Chinese Communist Party was exhibiting increased belligerence especially over the South China Sea region, including militarization of disputed features, and dangerous coercive use of coast guard vessels.
- On 6 January 2022, at a virtual summit, the Japanese Prime Minister and Australian Prime Minister formally signed the RAA.
- The Reciprocal Access Agreement (RAA), the defence treaty between Australia and Japan, apart from its strategic significance for Asia and the Indo-Pacific.
Significance of Reciprocal Access Agreement (RAA)
- Changing dynamics
- It fortifies trends that are part of the changing security architecture in the region.
- Moving away from supremacy of US
- It marks the move away from a US-centric outlook towards a greater focus on bilateral ties and regional groupings.
- Japan’s increasing role
- It is also a sign that Japan is willing to play a more proactive role in the region.
- For Japan, this marks an even greater shift, of a piece with the recent evolution in its outlook and global image. Thus far, Japan’s only major defence ally had been the US.
- Recently, both Vietnam and the Philippines have looked to Tokyo to provide a bulwark against Beijing, signalling a greater acceptance of Japan’s role as a strategic player. And Tokyo is now expanding its ties further: Reports suggest it will seek RAA-like agreements with the UK and France as well.
- Australia’s efforts
- It has been enabled, among other factors, by Australia’s willingness to stand up to China on the question of a free and open Indo-Pacific and rules-based global order, despite their deep economic ties.
Importance to India
- Countering Chinese Influence: Recent stand-offs on the Indo-China Border and the reluctance of Russia to step in and build pressure is forcing India to look for alternatives.
- Post-COVID Diplomacy: The disruption across the world and non-transparent systems of China pose an opportunity for India to take lead and become the World's Manufacturing Hub.
- India can leverage its expertise in the vaccine and pharma industry to increase its soft power.
- Further, Japan and the US want to shift their manufacturing companies out of China in order to curb its imperialistic behaviour.
- Net Security Provider in the Indian Ocean: India under the SAGAR initiative wants to become a net security provider in the Indian Ocean.
- Multipolar World: India has supported a rule-based multipolar world and such actions by Asian countries can help it in achieving its ambition of becoming a regional superpower.
Conclusion
- The Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (or the Quad, with India, Japan, Australia and the US), the AUKUS, and now the RAA between Japan and Australia — two treaty allies of the US — all point towards a more empowered and committed regional strategic network.
- India, for its part, has done much to expand bilateral, trilateral and regional cooperation in the security domain — it has “2+2” ministerial dialogues with both Tokyo and Canberra.
- India must step up this engagement, as well as reach out to other players in the region.
GS-III
Sea Dragon 22 Exercise
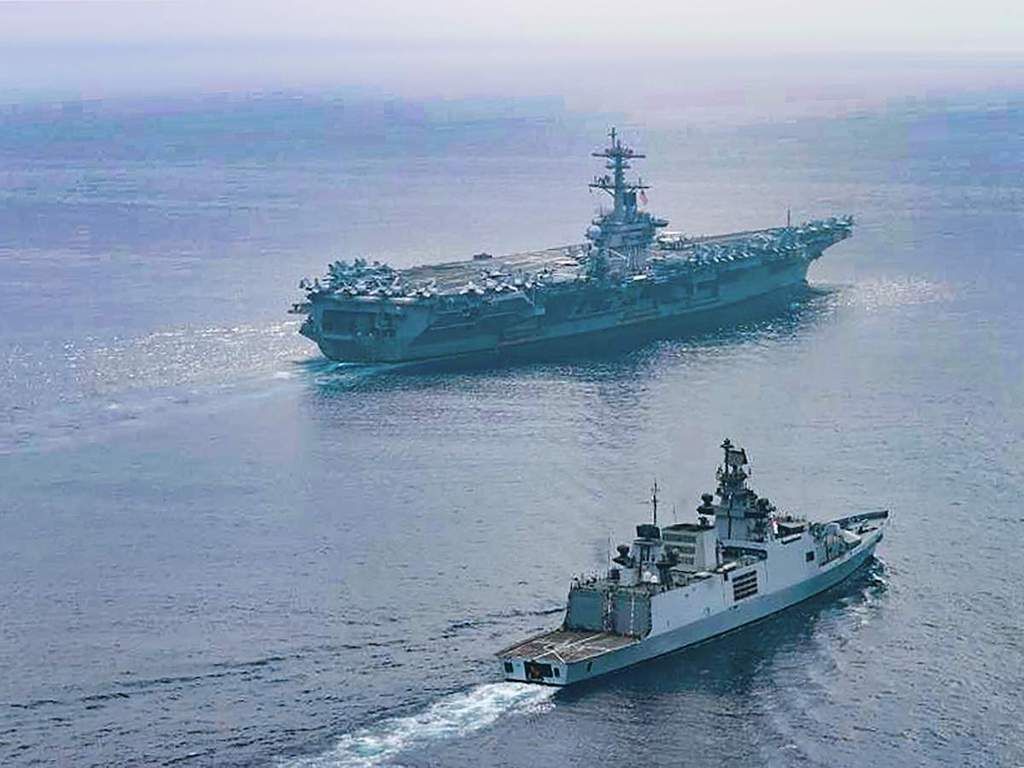

Context
- India and five other nations begin anti-submarine exercise Sea Dragon 22 in the Pacific Ocean.
- It is being held at Andersen Air Force Base in Guam in the Western Pacific and it includes contingents from India, the US, Australia, Canada, Japan and South Korea.
- India, Japan, Australia and America are also part of the Quad and also participate in the Malabar exercise.
About the exercise
- Sea Dragon is an annual US-led multinational exercise designed to practice and discuss Anti-submarine warfare tactics to operate together in response to traditional and non-traditional maritime security challenges in the Indo-Pacific region.
- It will involve more than 270 hours of in-flight training and activities ranging from tracking simulated targets to tracking a US Navy submarine.
- Each event will be graded and the nation scoring the highest total points will receive the coveted Dragon Belt award, which the Royal Canadian Air Force won in 2021.
Significance
- It will strengthen cooperation and deepen mutual understanding among the participating navies and air forces.
- They will be able to improve tactical skills.
Omisure: India’s first RT-PCR kit to identify Omicron strain
Context
- Omisure — India’s first home-grown testing kit has recently received approval from the Drugs Controller General of India.
About Omisure
- Omisure is an omicron detecting RT-PCR kit developed by the Mumbai-based Tata Medical and Diagnostics Ltd (TATA MD) in partnership with the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR).
- It can differentiate the omicron strain of the novel coronavirus from the delta, alpha and the other variants in under four hours.
- It can diagnose this variant in a single step.
How does it work?
- This new kit can identify the Omicron variant by targeting two regions of the S or the spike gene.
- This gene codes for the spike protein, which helps the novel coronavirus enter and infect human cells.
- The S, the Enveloped (E), and Nucleocapsid (N) genes are some of the targets of conventional RT-PCR tests.
- When it detects these genes, a patient sample is labelled positive. As omicron bears heavy mutations in the S gene, the RT-PCR can sometimes miss it.
- The absence of S gene likely indicates omicron’s presence.
- This is called S gene dropout or S gene target failure — and is one of the targets of Omisure.
How does Omisure compare with gene sequencing?
- Gene sequencing reads the order of nucleotides, which are the building blocks of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
- Despite being considered the gold standard, sequencing has a few limitations.
- It is slow, expensive and complicated. It is a multi-step process.
- It begins with extracting the virus’ RNA from patient samples, converting it into DNA, amplifying or multiplying it through RT-PCR before finally sending it for gene sequencing.
- This entire process can take as many as three days.
What are the First Advance Estimates of GDP?

Context
- The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has released the First Advance Estimates (FAE) for the current financial year (2021-22 or FY22).
About GDP
- GDP measures the monetary value of all goods and services produced within the domestic boundaries of a country within a timeframe (generally, a year).
- It is slightly different from the other commonly used statistic for national income — the GNP.
- The Gross National Product (GNP) measures the monetary value of all goods and services by the people and companies of a country regardless of where this value was created.
What are the First Advance Estimates of GDP?
- The FAE, which were first introduced in 2016-17, are typically published at the end of the first week of January.
- They are the “first” official estimates of how GDP is expected to grow in that financial year.
- But they are also the “advance” estimates because they are published long before the financial year (April to March) is over.
- It is important to note that even though the FAE are published soon after the end of the third quarter (October, November, December), they do not include the formal Q3 GDP data.
- Q3 data is published at the end of February as part of the Second Advance Estimates (SAE).
GDP estimates for FY22
- According to MoSPI, India’s GDP will grow by 9.2 per cent in 2020-21.
- Last financial year, FY21, the GDP had contracted by 7.3%.
Significance of FAE
- Budgetary calculations: Since the SAE will be published next month, the main significance of FAE lies in the fact that they are the GDP estimates that the Union Finance Ministry uses to decide the next financial year’s budget allocations.
- Basis for nominal GDP: From the Budget-making perspective, it is important to note what has happened to nominal GDP — both absolute level and its growth rate. That’s because nominal GDP is the actual observed variable.
|
1349 docs|788 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- January 8, 2022 - Current Affairs: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - CLAT
| 1. What is the significance of GS-I in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 2. What are the key topics covered in GS-II for the UPSC exam? |  |
| 3. How can I stay updated with the daily current affairs for the UPSC exam? |  |
| 4. What does UPSC stand for and what is its role in the examination process? |  |
| 5. How can I effectively prepare for the UPSC examination? |  |
















