Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Question Answers - Control and Coordination
Q1: What is a neuron?
Ans: A neuron is a nerve cell that is the basic building block of the nervous system. Neurons are specialized to transmit information throughout the body.
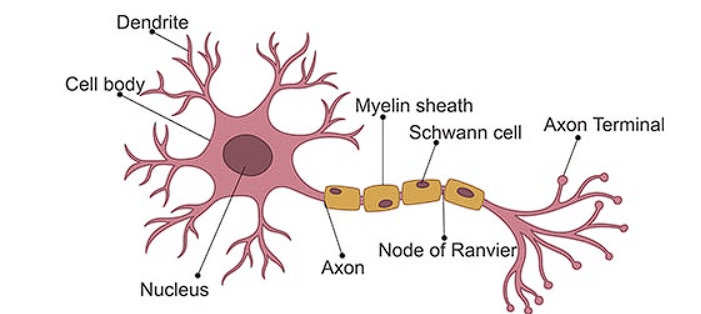
These highly specialized nerve cells are responsible for communicating information in both chemical and electrical forms. There are also several different types of neurons responsible for different tasks in the human body.
Q2: How does the feedback mechanism regulate the hormone action? Explain with the help of an example.
Ans: The presence or absence of a particular hormone can regulate its further formation with the help of a regulatory mechanism called the feedback mechanism.
Example: Hypothalamus regulates thyroxin levels in blood by secreting thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). If the thyroxine levels increase then the hypothalamus stops secreting TSH in order to reduce the production of thyroxine from the thyroid gland.
Low levels of thyroxin in blood again switch on the release of TSH from the hypothalamus to increase levels of thyroxin in blood.
Q3: Name any two types of tropism.
Ans: The two types of tropism are phototropism and geotropism.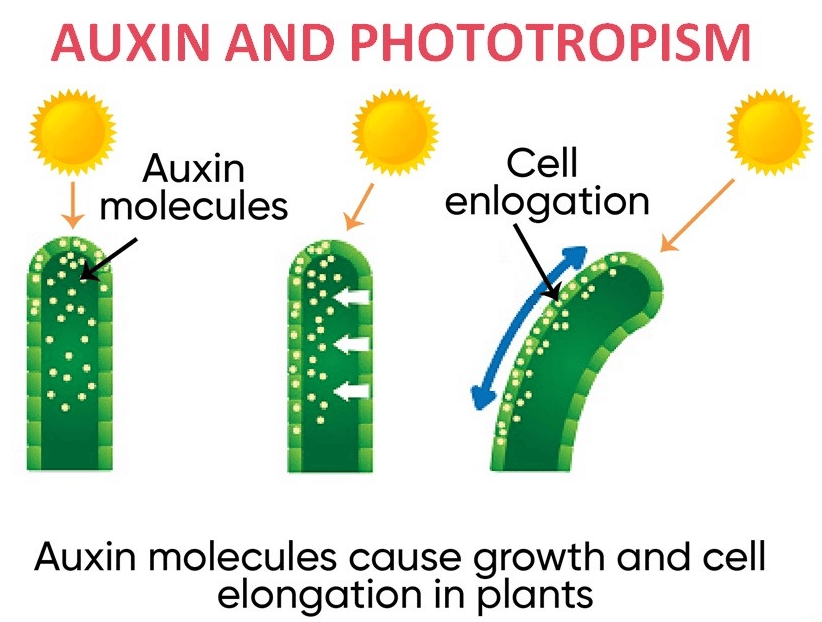
Q4: How do control and coordination take place in plants?
Ans: Plants have a unique mechanism of controlling and coordinating their various physiological and biological processes. Plants respond to light, touch, gravitational force, and other stimuli. Growth and movements in plants are regulated by both external and internal factors. The functions of control and coordination in plants are performed by chemical substances known as plant hormones or phytohormones.
Q5: Describe the central nervous system in human beings.
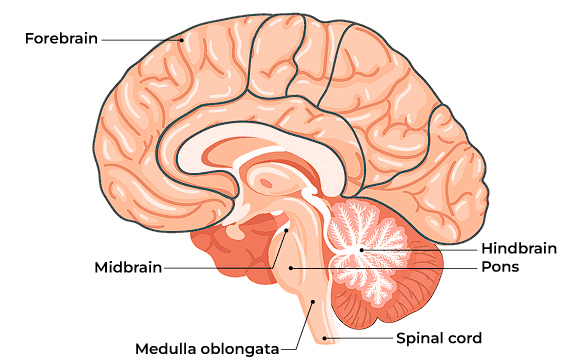
Ans: The central nervous system (CNS) in human beings consists of the brain and the spinal cord, which are the main coordinating centers of the body. They work together to receive, process, and integrate information from all parts of the body and generate appropriate responses.
1. The Brain
 Brain
Brain
The brain is the main control center of the CNS and is responsible for thinking, decision-making, and coordination of voluntary and involuntary actions. It is divided into three major parts:
a. Fore-brain: It is the main thinking part of the brain, responsible for sensory processing, decision-making, and voluntary actions.
Specialized Regions:
- Separate areas process inputs like hearing, sight, smell, and touch.
- Associative areas interpret sensory inputs by integrating them with stored information.
- The hunger center in the fore-brain regulates sensations like feeling full after eating.
- The motor areas control voluntary muscle movements.
b. Mid-brain: It controls involuntary actions like changes in pupil size and reflexes related to sight and hearing.
c. Hind-brain:
(i) Medulla: Controls involuntary actions such as heartbeat, blood pressure, salivation, and vomiting.
(ii) Cerebellum: Maintains posture, balance, and precision of voluntary actions, enabling activities like walking, riding a bicycle, and picking up objects.
2. The Spinal Cord
The spinal cord acts as a communication bridge between the brain and the rest of the body.
Functions:
- Reflex Actions: Reflex arcs are formed in the spinal cord, enabling quick responses to stimuli without involving the brain. For example, pulling your hand away from a hot object.
- Signal Transmission: It carries sensory signals from receptors to the brain and motor signals from the brain to muscles or glands.
Q6: Write the functions of any one part of the hindbrain.
Ans: The cerebellum is the part of the hindbrain that controls and coordinates the movements of our body and helps adjust posture. It functions even when the person is asleep.
Q7: Define reflex action with suitable examples.
Ans: When we suddenly withdraw our hands on pricking a pin, it is a reflex action. This type of sudden response to a stimulus is involuntary. A reflex action is defined as an unconscious and involuntary response of effectors to a stimulus. In reflex actions, a message from the receptors is relayed by sensory nerves to the spinal cord, which sends information for response via motor nerves to effectors. The pathway is called a reflex arc. The simplest type of reflex action is the knee-jerk reflex. In this case, while sitting with freely hanging legs, a strike below the kneecap kicks the leg forward. Other reflex actions are coughing, sneezing, yawning and blinking of eyes. 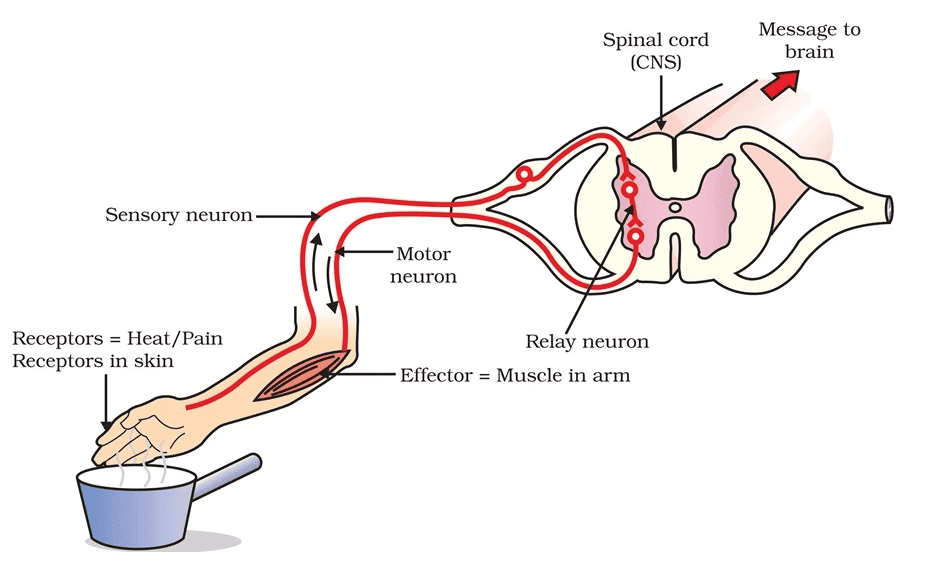 Q8: Name the hormones secreted by the thyroid and pancreas.
Q8: Name the hormones secreted by the thyroid and pancreas.
Ans: (i) Thyroid secretes thyroxin (ii) Pancreas secrete insulin and glucagon.
Q9: List the functions of testosterone and estrogen.
Ans: The functions of testosterone are the regulation of male accessory sex organs and secondary sexual characters like moustache, beard, and voice.
The functions of estrogen are the regulation of female accessory sex organs and secondary sexual characters like mammary glands, hair pattern and voice, and the maintenance of pregnancy.
Q10 : Discuss the role of adrenaline in the body's response to stress.
Ans: Adrenaline, secreted by the adrenal gland, prepares the body for a fight-or-flight response during stressful situations. It increases heart rate, dilates air passages, boosts blood flow to muscles, and raises blood sugar levels, ensuring that the body is ready to react quickly to danger.
Q11: Why is the flow of signals in a synapse from the axonal end of one neuron to the dendritic end of another neuron but not the reverse?
Ans: The information received by the dendrites of neurons present at receptors is transferred in the form of electrical impulses to the cell body, axon, and the nerve endings at the ends of the axon. At the axonal ends, chemicals are released between the junction of two neurons called synapses. The chemical diffuses towards the dendrite of the next neuron where it generates an electrical impulse again. So, the electrical signals change to chemical signals and again to electrical signals for the next neuron.
Since the chemicals Eire are released at the axonal ends and absent at the dendrite end, the signal travels from the axonal end to the dendritic end of another neuron but not the reverse i.e., the flow of electrical impulse is unidirectional only.
Q12: How does nervous tissue cause muscle action, and what role do special proteins play in muscle movement?
Ans: Nervous tissue causes muscle action by transmitting electrical impulses to muscle cells. When a nerve impulse reaches a muscle, it stimulates the muscle fibers to contract. This contraction is made possible by special proteins, such as actin and myosin, within the muscle cells. These proteins respond to the electrical impulses by changing their shape and rearranging themselves. This rearrangement shortens the muscle fibers, resulting in movement. The coordinated interaction of nervous tissue and muscle tissue allows for precise and effective muscle actions.Voluntary muscles, controlled consciously, and involuntary muscles, which operate without conscious thought, rely on this process for their function.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Question Answers - Control and Coordination
| 1. What is the role of the nervous system in control and coordination? |  |
| 2. How do hormones contribute to control and coordination in the body? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between the nervous system and the endocrine system in terms of control and coordination? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of reflex actions in the human body? |  |
| 5. How do plants coordinate their growth and responses to the environment? |  |

















