Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Question Answers - Life Processes
Q1. Define nutrition. What are the different modes of nutrition?
Ans: Nutrition is the process by which living organisms obtain and use food for growth and health. There are three main modes of nutrition:

- Autotrophic Nutrition: Organisms create their own food using water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight through processes like photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
- Heterotrophic Nutrition: Organisms consume organic matter from other sources. This includes:
- Herbivores: eat plants.
- Carnivores: eat animals.
- Omnivores: eat both plants and animals.
- Detritivores: feed on dead organic matter.
- Saprotrophs: act as decomposers.
These modes of nutrition help organisms acquire the essential nutrients and energy needed for survival and growth in various environments.
Q2. What is the mode of nutrition in fungi?
Ans: Saprophytic nutrition is the primary mode of nutrition in fungi.

Q3. Name the pigment, which can absorb solar energy.
Ans: (i) The pigment that can absorb solar energy is called chlorophyll.
(ii) It is found in the chloroplasts of plant cells and is essential for photosynthesis.
(iii) Chlorophyll absorbs light in the blue and red parts of the spectrum and reflects green light, giving plants their characteristic colour. This ability has practical applications in fields such as solar energy production.
Q4. Name the two stages in photosynthesis.
Ans: The two stages in photosynthesis are:
- Light reaction
- Dark reaction
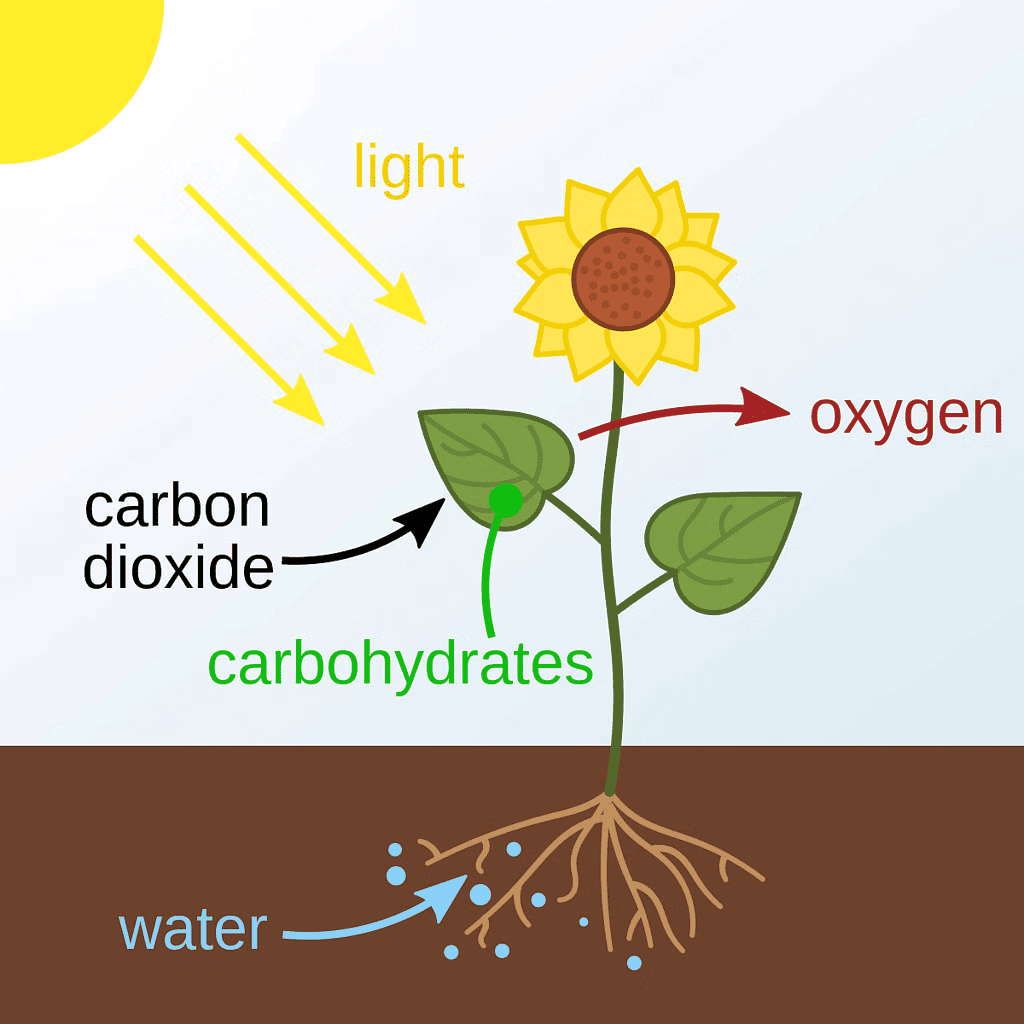 Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Q5. Name the factors, that affect Photosynthesis.
Ans: The factors that affect photosynthesis include:
- Light - Essential for the process to occur.
- Water - A critical raw material.
- Temperature - Influences the rate of photosynthesis.
- Humidity - Affects transpiration and gas exchange.
- Age of the leaf - Older leaves may be less efficient.
- Carbon dioxide - Necessary for the production of glucose.
Q6. Define a Herbivore and a Carnivore.
Ans: Herbivore: Animals that feed exclusively on plants are known as herbivores.
Carnivore: Animals that consume only flesh are referred to as carnivores.
Q7. How does Amoeba engulf its food?
Ans: Amoeba engulfs its food by extending pseudopodia. This process is known as phagocytosis.
- The amoeba stretches its membrane to form temporary arms called pseudopodia.
- These extensions surround the food particle.
- Once engulfed, the food is enclosed in a food vacuole.
- The amoeba then digests the food within this vacuole.
Q8. Name the parts of the digestive system of a grasshopper.
Ans: The parts of the digestive system of a grasshopper are the Mouth, Salivary glands, Esophagus, Crop, Gizzard, Stomach, Intestines, Rectum, and Anus.
Q9. What are the functions of the liver and the pancreas?
Ans: The liver and pancreas play crucial roles in digestion and metabolism:
Liver functions:
- Secretes bile, which includes bile pigments and salts.
- Bile is stored in the gall bladder until needed in the duodenum.
- Helps in emulsifying fats in food.
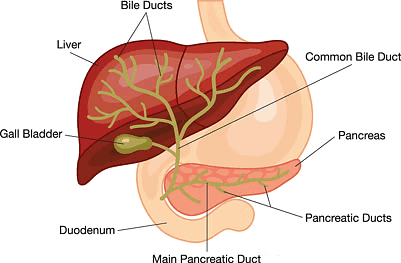
Pancreas functions:
- Located parallel to and beneath the stomach.
- Secretes digestive enzymes and hormones, including insulin and glucagon.
- Enzymes like trypsin digest proteins, while pancreatic amylase breaks down starch.
Both bile and pancreatic juice enter the duodenum through a common duct.
Q10. Define Breathing.
Ans: Breathing is a vital process for all organisms. It involves:
- Inhaling oxygen from the environment.
- The inhaled oxygen diffusing into the blood.
- Exhaling carbon dioxide, which has diffused from the blood into the alveoli.
This exchange of gases is essential for maintaining life.
Q11. How is respiration different from breathing?
Ans: 
Q12. In which kind of respiration is more energy released?
Ans: Aerobic respiration releases more energy compared to other types of respiration. This is due to the fact that most cells in the body depend on aerobic processes to produce the energy they require for normal functioning.
Q13. Which part of the roots is involved in the exchange of respiratory gases?
Ans: Root hair is the part of the roots that plays a key role in the exchange of respiratory gases.

Q14. What are
(i) stomata
(ii) lenticels
Ans: (i) Stomata are small openings on the surface of leaves that help control the exchange of gases, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide, as well as transpiration (the loss of water vapour).
(ii) Lenticels are raised pores found in the bark of woody plants. They facilitate gas exchange between the atmosphere and the plant's internal tissues.
Q15. Give two points of differences between respiration in plants and respiration in animals.
Ans: Respiration in plants differs from respiration in animals in two main ways:
- Gas transport: Plants have minimal transport of gases between different parts, whereas animals actively transport gases throughout their bodies.
- Respiration rate: Plant respiration occurs at a much slower rate than that of animals.
Q16. Name the respiratory organs of
(i) fish
(ii) mosquito
(iii) earthworm
(iv) dog
Ans: The respiratory organs of:
(i) fish – gills
(ii) mosquito–tracheoles
(iii) earthworm–skin
(iv) dog – lungs.
Q17. From where do the following take in oxygen?
(i) prawn
(ii) rat
Ans: (i) Prawns take in oxygen that is dissolved in water through their gills.
(ii) Rats breathe in oxygen from the atmosphere using their lungs.
Q18. State the function of epiglottis.
Ans: The epiglottis serves several important functions:
- It prevents food from entering the trachea.
- This flap of tissue is located in the throat and stops food and liquids from entering the windpipe and lungs during swallowing.
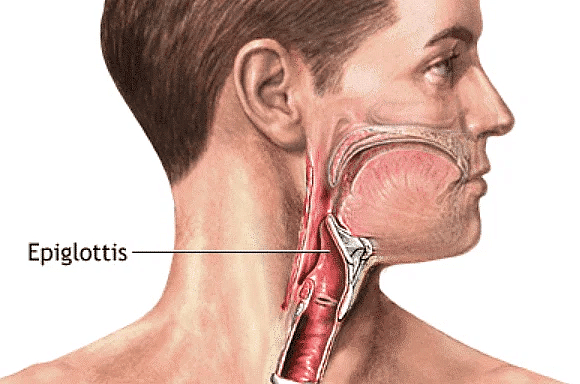
- It closes over the opening of the windpipe (the glottis) and directs food towards the oesophagus.
- Additionally, it helps in producing certain sounds during speech by adjusting the shape of the vocal tract.
Q19. Define Photolysis.
Ans: The term photolysis is derived from Greek, where photo means light and lysis means to break apart. It refers to the process of breaking down substances using light energy.
Specifically, photolysis involves:
- The breakdown of water molecules in the chloroplasts of plants when exposed to light.
- Generation of oxygen gas as a by-product of this process.
Q20. What are the living organisms that cannot make their food called?
Ans: The living organisms that cannot make their own food are called heterotrophs.
Q21. What are Chemotrophs?
Ans: Chemotrophs are organisms that do not need light to survive. Instead, they produce their own food using inorganic substances. They obtain energy from the oxidation of simple inorganic compounds, such as:
- Iron
- Sulphur
An example of a chemotroph is the bacterium Nitrosomonas.
Q22. What is Compensation Point?
Ans:
The compensation point is the specific level of light at which the rate of photosynthesis equals the rate of respiration. At this point:
- The absorption of CO2 by photosynthesis matches the release of CO2 through respiration.
- The uptake of O2 by respiration equals the O2 released by photosynthesis.
- This condition typically occurs in the early morning and late evening.
Q23. Other than chlorophyll, which another pigment is necessary for photosynthesis?
Ans: Carotenoids are essential pigments for photosynthesis, aside from chlorophyll. They are:
- Yellow, orange, red, or brown pigments.
- Responsible for absorbing sunlight.
- Assist in transferring energy to chlorophyll.
While carotenoids do not directly perform photosynthesis, they play a crucial role in the process.
Q24. Where does digestion begin?
Ans:
Digestion begins in the mouth. When we eat: 
- Our teeth break food into smaller pieces.
- This food mixes with saliva.
- Saliva contains enzymes that convert complex carbohydrates into simpler sugars.
Q25. What is the name given to the process of using the absorbed food for producing energy?
Ans: The process of using absorbed food to produce energy is called cellular respiration.
Q26. What happens to the visible light of the Sun when it falls on chlorophyll?
Ans: Visible light from the Sun includes seven colours: violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange, and red.
Chlorophyll interacts with this light as follows:
- It primarily absorbs blue, violet, red, and orange light.
- It does not absorb green light.
The reflection of green light is why plants appear green.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Question Answers - Life Processes
| 1. What are the main life processes in living organisms? |  |
| 2. How do plants carry out the process of photosynthesis? |  |
| 3. What is the role of respiration in living organisms? |  |
| 4. How do organisms excrete waste products? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of reproduction in life processes? |  |






















