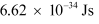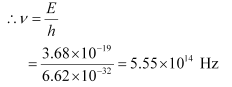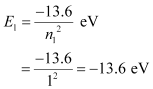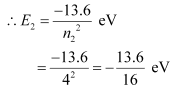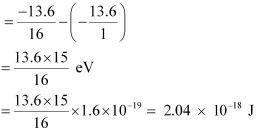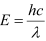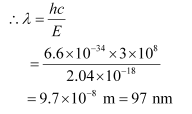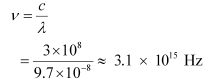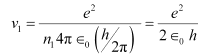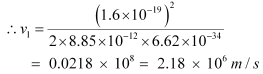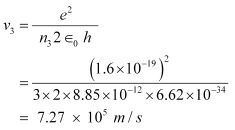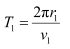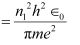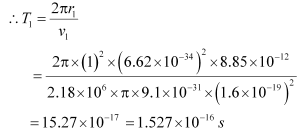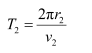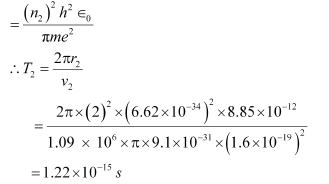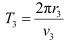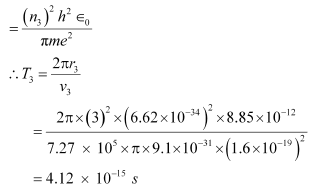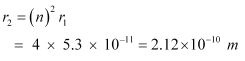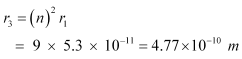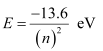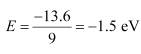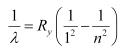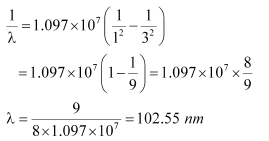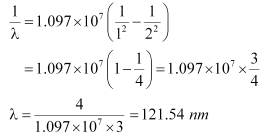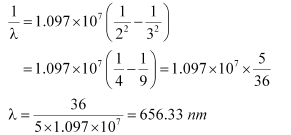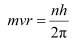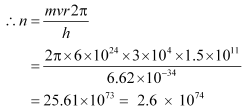Q12.1: Choose the correct alternative from the clues given at the end of the each statement:
(a) The size of the atom in Thomson’s model is .......... the atomic size in Rutherford’s model. (much greater than/no different from/much less than.
(b) In the ground state of .......... electrons are in stable equilibrium, while in .......... electrons always experience a net force.
(Thomson’s model/ Rutherford’s model.)
(c) A classical atom based on .......... is doomed to collapse.
(Thomson’s model/ Rutherford’s model.)
(d) An atom has a nearly continuous mass distribution in a .......... but has a highly non-uniform mass distribution in ..........
(Thomson’s model/ Rutherford’s model.)
(e) The positively charged part of the atom possesses most of the mass in .......... (Rutherford’s model/both the models.)
Ans: (a) The sizes of the atoms taken in Thomson’s model and Rutherford’s model have the same order of magnitude.
(b) In the ground state of Thomson’s model, the electrons are in stable equilibrium. However, in Rutherford’s model, the electrons always experience a net force.
(c) A classical atom based on Rutherford’s model is doomed to collapse.
(d) An atom has a nearly continuous mass distribution in Thomson’s model, but has a highly non-uniform mass distribution in Rutherford’s model.
(e) The positively charged part of the atom possesses most of the mass in both models.
Q12.2: Suppose you are given a chance to repeat the alpha-particle scattering experiment using a thin sheet of solid hydrogen in place of the gold foil. (Hydrogen is a solid at temperatures below 14 K.) What results do you expect?
Ans: In the alpha-particle scattering experiment, if a thin sheet of solid hydrogen is used in place of a gold foil, then the scattering angle would not be large enough. This is because the mass of hydrogen (1.67 × 10−27 kg) is less than the mass of incident α−particles (6.64 × 10−27 kg). Thus, the mass of the scattering particle is more than the target nucleus (hydrogen). As a result, the α−particles would not bounce back if solid hydrogen is used in the α-particle scattering experiment.
Q12.3: A difference of 2.3 eV separates two energy levels in an atom. What is the frequency of radiation emitted when the atom makes a transition from the upper level to the lower level?
Ans: Separation of two energy levels in an atom,
E = 2.3 eV
= 2.3 × 1.6 × 10−19
= 3.68 × 10−19 J
Let ν be the frequency of radiation emitted when the atom transits from the upper level to the lower level.
We have the relation for energy as:
E = hv
Where,
h = Planck’s constant


Hence, the frequency of the radiation is 5.6 × 1014 Hz.
Q12.4: The ground state energy of hydrogen atom is −13.6 eV. What are the kinetic and potential energies of the electron in this state?
Ans: Ground state energy of hydrogen atom, E = − 13.6 eV
This is the total energy of a hydrogen atom. Kinetic energy is equal to the negative of the total energy.
Kinetic energy = − E = − (− 13.6) = 13.6 eV
Potential energy is equal to the negative of two times of kinetic energy.
Potential energy = − 2 × (13.6) = − 27 .2 eV
Q12.5: A hydrogen atom initially in the ground level absorbs a photon, which excites it to the n = 4 level. Determine the wavelength and frequency of the photon.
Ans: For ground level, n1 = 1
Let E1 be the energy of this level. It is known that E1 is related with n1 as:

The atom is excited to a higher level, n2 = 4.
Let E2 be the energy of this level.

The amount of energy absorbed by the photon is given as:
E = E2 − E1

For a photon of wavelengthλ, the expression of energy is written as:

Where,
h = Planck’s constant = 6.6 × 10−34 Js
c = Speed of light = 3 × 108 m/s

And, frequency of a photon is given by the relation,

Hence, the wavelength of the photon is 97 nm while the frequency is 3.1 × 1015 Hz.
Q12.6: (a) Using the Bohr’s model calculate the speed of the electron in a hydrogen atom in the n = 1, 2, and 3 levels. (b) Calculate the orbital period in each of these levels.
Ans: (a) Let ν1 be the orbital speed of the electron in a hydrogen atom in the ground state level, n1 = 1. For charge (e) of an electron, ν1 is given by the relation,

Where,
e = 1.6 × 10−19 C
∈0 = Permittivity of free space = 8.85 × 10−12 N−1 C2 m−2
h = Planck’s constant = 6.62 × 10−34 Js

For level n2 = 2, we can write the relation for the corresponding orbital speed as:

And, for n3 = 3, we can write the relation for the corresponding orbital speed as:

Hence, the speed of the electron in a hydrogen atom in n = 1, n=2, and n=3 is 2.18 × 106 m/s, 1.09 × 106 m/s, 7.27 × 105 m/s respectively.
(b) Let T1 be the orbital period of the electron when it is in level n1 = 1.
Orbital period is related to orbital speed as:

Where,
r1 = Radius of the orbit

h = Planck’s constant = 6.62 × 10−34 Js
e = Charge on an electron = 1.6 × 10−19 C
∈0 = Permittivity of free space = 8.85 × 10−12 N−1 C2 m−2
m = Mass of an electron = 9.1 × 10−31 kg

For level n2 = 2, we can write the period as:

Where,
r2 = Radius of the electron in n2 = 2

And, for level n3 = 3, we can write the period as:

Where,
r3 = Radius of the electron in n3 = 3

Hence, the orbital period in each of these levels is 1.52 × 10−16 s, 1.22 × 10−15 s, and 4.12 × 10−15 s respectively.
Q12.7: The radius of the innermost electron orbit of a hydrogen atom is 5.3 ×10−11 m. What are the radii of the n = 2 and n =3 orbits?
Ans: The radius of the innermost orbit of a hydrogen atom, r1 = 5.3 × 10−11 m.
Let r2 be the radius of the orbit at n = 2. It is related to the radius of the innermost orbit as:

For n = 3, we can write the corresponding electron radius as:

Hence, the radii of an electron for n = 2 and n = 3 orbits are 2.12 × 10−10 m and 4.77 × 10−10 m respectively.
Q12.8: A 12.5 eV electron beam is used to bombard gaseous hydrogen at room temperature. What series of wavelengths will be emitted?
Ans: It is given that the energy of the electron beam used to bombard gaseous hydrogen at room temperature is 12.5 eV. Also, the energy of the gaseous hydrogen in its ground state at room temperature is −13.6 eV.
When gaseous hydrogen is bombarded with an electron beam, the energy of the gaseous hydrogen becomes −13.6 + 12.5 eV i.e., −1.1 eV.
Orbital energy is related to orbit level (n) as:


For n = 3,
This energy is approximately equal to the energy of gaseous hydrogen. It can be concluded that the electron has jumped from n = 1 to n = 3 level.
During its de-excitation, the electrons can jump from n = 3 to n = 1 directly, which forms a line of the Lyman series of the hydrogen spectrum.
We have the relation for wave number for Lyman series as:

Where,
Ry = Rydberg constant = 1.097 × 107 m−1
λ= Wavelength of radiation emitted by the transition of the electron
For n = 3, we can obtain λ as:

If the electron jumps from n = 2 to n = 1, then the wavelength of the radiation is given as:

If the transition takes place from n = 3 to n = 2, then the wavelength of the radiation is given as:

This radiation corresponds to the Balmer series of the hydrogen spectrum.
Hence, in the Lyman series, two wavelengths i.e., 102.5 nm and 121.5 nm are emitted. And in the Balmer series, one wavelength i.e., 656.33 nm is emitted.
Q12.9: In accordance with the Bohr’s model, find the quantum number that characterises the earth’s revolution around the sun in an orbit of radius 1.5 × 1011 m with orbital speed 3 × 104m/s. (Mass of earth = 6.0 × 1024 kg.)
Ans: Radius of the orbit of the Earth around the Sun, r = 1.5 × 1011 m
Orbital speed of the Earth, ν = 3 × 104 m/s
Mass of the Earth, m = 6.0 × 1024 kg
According to Bohr’s model, angular momentum is quantized and given as:

Where,
h = Planck’s constant = 6.62 × 10−34 Js
n = Quantum number

Hence, the quanta number that characterizes the Earth’s revolution is 2.6 × 1074.