NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 - Thermodynamics
Q11.1: A geyser heats water flowing at the rate of 3.0 liters per minute from 27°C to 77°C. If the geyser operates on a gas burner, what is the rate of consumption of the fuel if its heat of combustion is 4.0 × 104 J/g?
Ans: Volume of water heated = 3.0 litre per minute Mass of water heated, m = 3000g per minute Increase in temperature,
ΔT - 77°C - 27°C = 50°C
Specific heat of water, c = 4.2 Jg-1°C-1
amount of heat used, Q = mc ΔT
or
Rate of combustion of fuel
Q11.2: What amount of heat must be supplied to 2.0 × 10–2 kg of nitrogen (at room temperature) to raise its temperature by 45 °C at constant pressure? (Molecular mass of N2 = 28; R = 8.3 J mol–1 K–1.)
Ans: Here, mass of gas,
rise in temperature,
Heat required. Molecular mass, M = 28
Number of moles,
As nitrogen is a diatomic gas, molar specific heat at constant pressure is
As
∴
Q11.3: Explain why
(a) Two bodies at different temperatures T1 and T2, if brought in thermal contact, do not necessarily settle to the mean temperature (T1 + T2)/2.
(b) The coolant in a chemical or a nuclear plant (i.e., the liquid used to prevent the different parts of a plant from getting too hot) should have high specific heat.
(c) Air pressure in a car tyre increases during driving.
(d) The climate of a harbour town is more temperate than that of a town in a desert at the same latitude.
Ans: (a) In thermal contact, heat flows from the body at higher temperature to the body at lower temperature till temperatures become equal. The equilibrium temperature can be the mean temperature (T1 + T2 )/2 only when thermal capacities of the two bodies are equal.
(b) This is because heat absorbed by a substance is directly proportional to the specific heat of the substance.
(c) When car is driven, some work is being done on types in order to overcome dissipative forces of friction and air resistance etc. This work done is transformed into heat, due to which temperature of the car types increases.
(d) Water's high specific heat capacity allows it to absorb and release heat slowly, moderating temperature fluctuations in harbour towns. In contrast, desert towns, with their low specific heat surfaces like sand, experience more extreme temperature changes, leading to hotter days and colder nights, even at the same latitude.
Q11.4: A cylinder with a movable piston contains 3 moles of hydrogen at standard temperature and pressure. The walls of the cylinder are made of a heat insulator, and the piston is insulated by having a pile of sand on it. By what factor does the pressure of the gas increase if the gas is compressed to half its original volume?
Ans: Here the process is adiabatic compression and atm and for hydrogen (a diatomic gas) γ = 1.4.
⇒ P2 = (2)1.4 atm = 2.639 atm,
Q11.5: In changing the state of a gas adiabatically from an equilibrium state A to another equilibrium state B, an amount of work equal to 22.3 J is done on the system. If the gas is taken from state A to B via a process in which the net heat absorbed by the system is 9.35 cal, how much is the net work done by the system in the latter case? (Take 1 cal = 4.19 J)
Ans: Here, when the change is adiabatic,
If is change in internal energy of. the system, then
as
In the second case.
ΔW = ?
As + ΔW = ΔQ
ΔW = ΔQ - = 39.3 -22.3 - 17.0 J.
Q 11.6: Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other via a stopcock. A contains a gas at standard temperature and pressure. B is completely evacuated. The entire system is thermally insulated. The stopcock is suddenly opened. Answer the following:
(a) What is the final pressure of the gas in A and B?
(b) What is the change in internal energy of the gas?
(c) What is the change in the temperature of the gas?
(d) Do the intermediate states of the system (before settling to the final equilibrium state) lie on its P-V-T surface?
Ans: (a) Since the external temperature and initial temperature remain the same,
P2V2 = P1V1
But P1 = 1 atm, V1 = V, V2 = 2V and P2 - ?
(b) Since the temperature of the system remains unchanged, change in internal energy is zero.
(c) The system being thermally insulated, there is no change in temperature (because of free expansion)
(d) The expansion is a free expansion. Therefore, the intermediate states are non equilibrium states and the gas equation is not satisfied in these states. As a result, the gas can not return to an equilibrium state which lie on the P-V-T surface.
Q11.7: An electric heater supplies heat to a system at a rate of 100W. If system performs work at a rate of 75 joules per second. At what rate is the internal energy increasing?
Ans: According to law of conservation of energy
Total energy = work done + internal energy
ΔQ = ΔW + ΔU
Here,
Rate at which heat is supplied ΔQ = 100 W
Rate at which work is done ΔW = 75 Js-1
Rate of change of internal energy is ΔU
ΔU = ΔQ – ΔW
ΔU = 100 – 75
We get,
ΔU = 25 J s-1
Hence,
The internal energy of the system is increasing at a rate of 25 W.
Q11.8: A thermodynamic system is taken from an original state to an intermediate state by the linear process shown in Fig. Its volume is then reduced to the original value from E to F by an isobaric process. Calculate the total work done by the gas from D to E to F.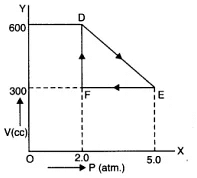 Ans: As is clear from Fig.
Ans: As is clear from Fig.
Change in pressure, ΔP = EF = 5.0 - 2-0 “ 3-0 atm = 3.0 * 105 Nm-2
Change in volume, ΔV=DF = 600 - 300 = 300 cc
= 300 * 10-6 m3
Work done by the gas from D to E to F = area of ΔDEF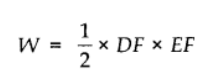
Old NCERT Solutions
Q1: A steam engine delivers 5.4×108 J of work per minute and services 3.6 × 109 J of heat per minute from its boiler. What is the efficiency of the engine? How much heat is wasted per minute?
Ans: Work done by the steam engine per minute, W = 5.4 × 108 J
Heat supplied from the boiler, H = 3.6 × 109 J
Heat energy wasted/ minute
= Heat energy, absorbed/minute - Useful work done/minute
Since ΔQ =
∴ Change in internal energy,
- 100 - 75 = 25 J/s.
Q2: A refrigerator is to maintain eatables kept inside at 9 °C, if room temperature is 36 °C. Calculate the coefficient of performance.
Ans: Here, T1 = 36°C = (36 + 273) K = 309 K
T2 = 9°C = (9 + 273) K = 282 K
Coefficient of performance,
|
96 videos|367 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 - Thermodynamics
| 1. What is the first law of thermodynamics and how does it apply to closed systems? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between isothermal and adiabatic processes in thermodynamics? |  |
| 3. How is the concept of entropy defined in thermodynamics? |  |
| 4. What are the different thermodynamic processes and their characteristics? |  |
| 5. How does the ideal gas law relate to thermodynamics? |  |






















