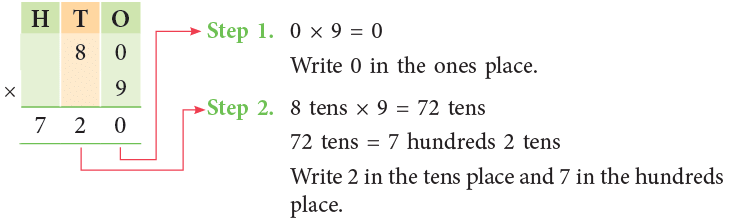Multiplication Class 3 Notes Maths
| Table of contents |

|
| Understanding Multiplication |

|
| Properties of Multiplication |

|
| Multiplication Tables |

|
| Multiplication by a Single Digit Number |

|
| Multiplication by a Two-Digit Number |

|
Understanding Multiplication
Multiplication is a quick way of adding the same number many times! For example, 3 x 4 means adding 3 four times (3 + 3 + 3 + 3), which equals 12. It’s like counting in groups, and it helps make math faster and easier!
Concept of Multiplication as Repeated Addition
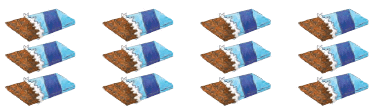
- Multiplication is a quicker way to find the total when you have the same number repeated multiple times. For example, if there are 4 groups of chocolates with 3 chocolates in each group, instead of adding 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 to get 12, you can multiply 4 by 3 to get 12 directly.
- This is written as 4 × 3 = 12, which means 4 groups of 3 or 3 groups of 4, showing that it doesn't matter which way you multiply (this is called the commutative property).
- So, adding four threes together gives you 12.
Terms Related to Multiplication
- Multiplicand: The number that is being repeated in multiplication.
- Multiplier: The number that tells how many times the multiplicand is repeated.
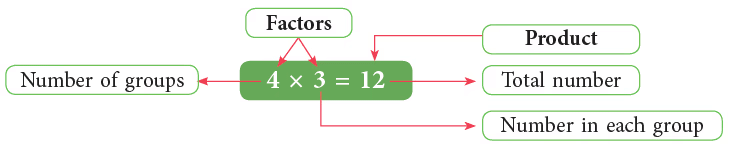
- Factors: The numbers that are being multiplied together.
- Product: The result of the multiplication. For example, in 3 × 4 = 12, 4 is the multiplier, 3 is the multiplicand, and 12 is the product.
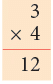
Properties of Multiplication
1. Property of one
Look and understand.
When 1 is a factor, the product is equal to the other factor.
2. Property of zero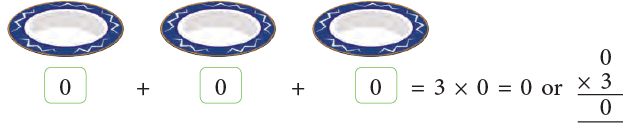
When 0 is a factor, the product is always 0.
Also, 0 × 3 = 3 × 0 = 0 or 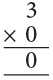
3. Order Property
Observe the different ways of arranging the dots as shown below: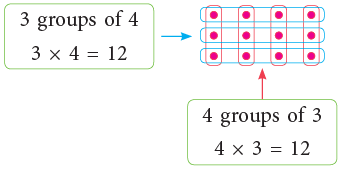 3 × 4 = 4 × 3 = 12
3 × 4 = 4 × 3 = 12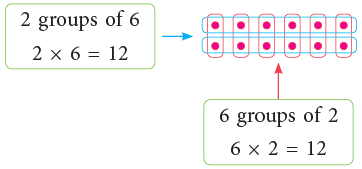 2 × 6 = 6 × 2 = 12
2 × 6 = 6 × 2 = 12
We observe that:
Changing the order of the two factors does not change the product.
The above property is called the commutative property of multiplication. We say multiplication is commutative.
We can show the commutative property using a number line as shown below: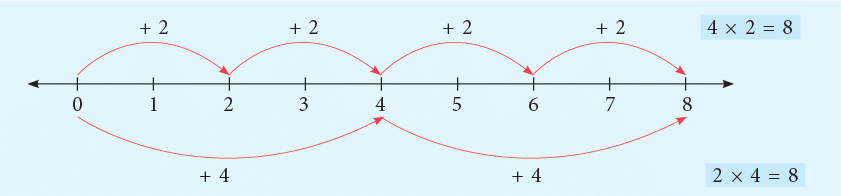
Multiplication Tables
You have learnt the multiplication tables up to 10 in your previous class. They are given here so that you may revise them.
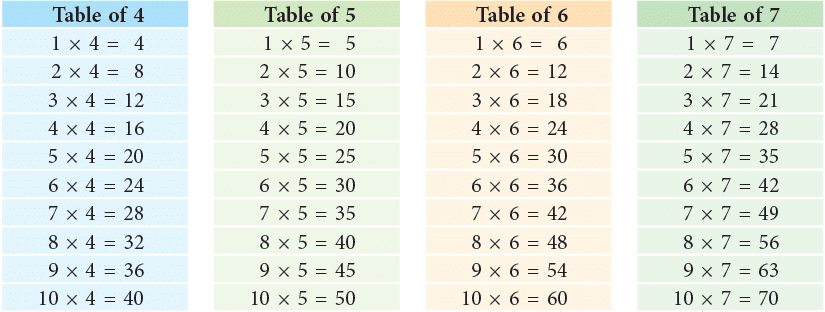
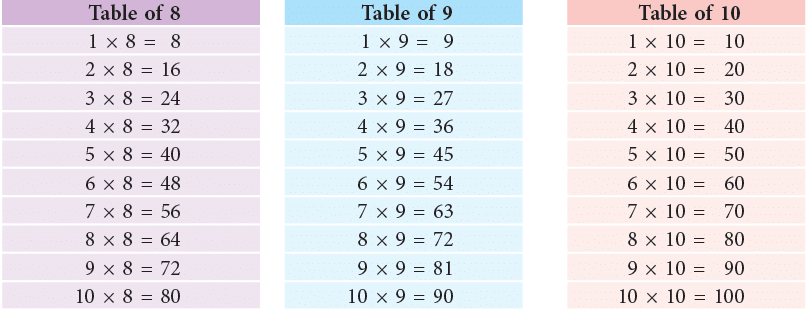
Multiplication Grid
You can find the products of 2 numbers with the help of a multiplication grid as shown here. The numbers along the top and side are factors. Suppose, you have to find 2 × 5.
Step 1: Find the row for 2 and the column for 5. Step 2: Locate the number in the square where the row and column meet. This number which is 10 gives the product of 2 and 5.
Step 2: Locate the number in the square where the row and column meet. This number which is 10 gives the product of 2 and 5.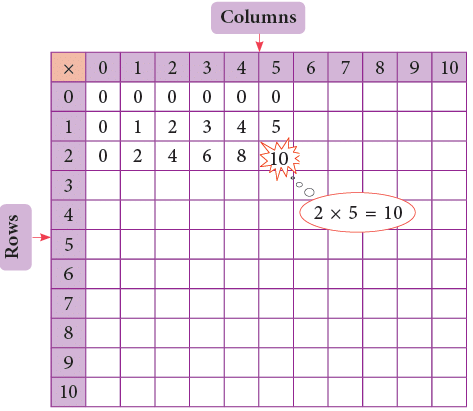
Skip Counting
Counting by 2s up to 20, we have 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20.
The counting by 2s means finding the products 2 × 1, 2 × 2, 2 × 3, … 2 × 10.
Multiples
The multiples of any counting number are obtained on multiplying this counting number by the counting numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, …
Thus, the multiples of 3 are 3 × 1, 3 × 2, 3 × 3, 3 × 4, …, that is, 3, 6, 9, 12, …
 |
Download the notes
Chapter Notes: Multiplication
|
Download as PDF |
Multiplication by a Single Digit Number
1. Without Carrying
Example 1: Multiply 43 by 2.
Thus, 43 × 2 = 86.
Example 2: Multiply 80 by 9.
Thus, 80 × 9 = 720.
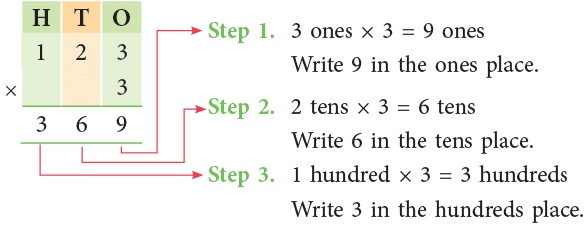
Example 3: Multiply 123 by 3.
Thus, 123 × 3 = 369.
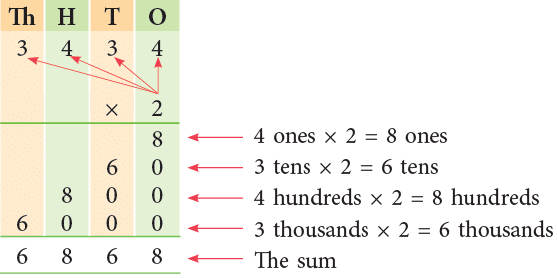
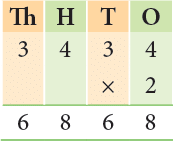
Example 4: Multiply 3434 by 2.
Thus, 3434 × 2 = 6868.
Think:
- 4 ones × 2 = 8 ones. Write 8 at ones place.
- 3 tens × 2 = 6 tens. Write 6 at tens place.
- 4 hundreds × 2 = 8 hundreds. Write 8 at hundreds place.
- 3 thousands × 2 = 6 thousands. Write 6 at thousands place.
Thus, 3434 × 2 = 6868.
2. Multiplication with Carrying
Example 5: Multiply 56 by 3.
Step 1: Multiply 6 ones by 3. 6 ones × 3 = 18 ones
= 1 ten 8 ones. Write 8 in the ones place and carry 1 to the tens place.
Step 2: Multiply 5 tens by 3. 5 tens × 3 = 15 tens
15 tens + 1 ten (carried over) = 16 tens Write 6 at tens place and 1 at hundreds place.
Thus, 56 × 3 = 168.
Example 6: Multiply 126 by 7.
Step 1: 6 ones × 7 = 42 ones = 4 tens 2 ones.
Write 2 in the ones place and carry 4 to the tens place.
Step 2: 2 tens × 7 = 14 tens
14 tens + 4 tens (carried over) = 18 tens
= 1 hundred 8 tens.
Write 8 in the tens place and carry 1 to the hundreds place.
Step 3: 1 hundred × 7 = 7 hundreds
7 hundreds + 1 hundred (carried over)
= 8 hundreds.
Write 8 in the hundreds place.
Thus, 126 × 7 = 882.
Example 7: Multiply 1252 by 6.
2 ones × 6 = 12 ones = 1 ten 2 ones
Write 2 in the ones place and carry 1 ten to the tens place.
5 tens × 6 + 1 ten (carried over) = 31 tens
= 3 hundreds 1 ten
Write 1 in the tens place and carry 3 hundreds to hundreds place.
(2 × 6) hundreds + 3 hundreds (carried over)
= 15 hundreds = 1 thousand 5 hundreds
Write 5 in the hundreds place and carry 1 thousand to the thousands place.
1 thousand × 6 + 1 thousand (carried over) = 7 thousands.
Write 7 in the thousands place.
Thus, 1252 × 6 = 7512.
3. Multiplying by 10, 100, 1000
(i) Look at these.
6 × 10 = 6 tens = 60
61 × 10 = 61 tens = 610
348 × 10 = 348 tens = 3480
Rule: When you multiply a number by 10, you simply write the number and put a zero. That is, you write a 0 after the numeral.
(ii) Look at these.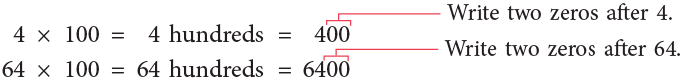
Rule: When you multiply a number by 100, you write two zeros after the numeral.
(iii) Look at these.
Rule: When you multiply a number by 1000, you write three zeros after the numeral.
4. Multiplying by Multiples of 10, i.e., 20, 30, 300, etc.
Observe the following:
(i) 8 × 20 = 8 × 2 tens
= 16 tens
= 160
Multiply 8 by 2. You get 16. Now write one zero to the right of product 16. You get 160.
(ii) 15 × 300 = 15 × 3 hundreds
= 45 hundreds
= 4500
Multiply 15 by 3. You get 45. Now write two zeros to the right of product 45 You get 4500.
Similarly, 4 × 20 = 80, 7 × 70 = 490, 9 × 600 = 5400, 30 × 300 = 9000.
We observe that,
To multiply a number by a multiple of 10, i.e., 20, 30, … 90, multiply the number by 2, 3, … 9 and put one zero to the right of the product.
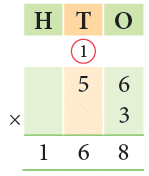
Multiplication by a Two-Digit Number
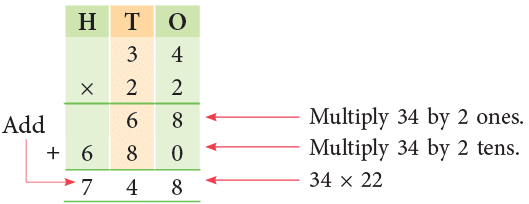
Example 9: There were 34 cartons with 22 apples in each carton. How many apples were there in all?
You have to think of equal groups as being put together, so you multiply 34 by 22.
Using the place value system, this can be done in a short way as under:
34 × 2 = 68
34 × 20 = 680
Thus, there were 748 apples in all.
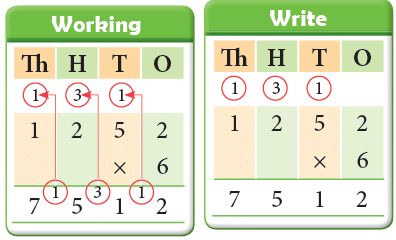
Example 10: Multiply:
(a) 423 by 14
(b) 237 by 25
Thus, 423 × 14 = 5922
(b) Similarly,
Thus, 237 × 25 = 5925.
Problems Based on Real Life Situations
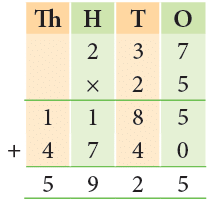
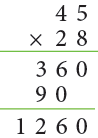
Example 11: Aman's stamp book has 45 pages and each page has 28 stamps. How many stamps does Aman have?
Total number of pages = 45
Number of stamps in each page = 28
Working:
∴ Total number of stamps = 45 × 28 = 1260 stamps.
|
42 videos|45 docs|56 tests
|
FAQs on Multiplication Class 3 Notes Maths
| 1. What are the basic properties of multiplication? |  |
| 2. How can I memorize multiplication tables from 11 to 20 effectively? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between multiplying by a single-digit number and a two-digit number? |  |
| 4. How can I practice multiplication by a two-digit number? |  |
| 5. Why is understanding multiplication important in daily life? |  |