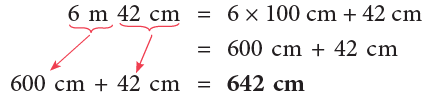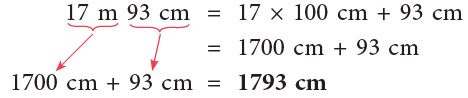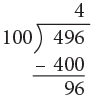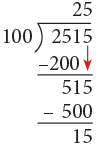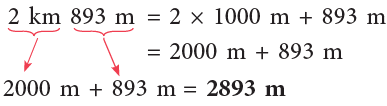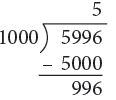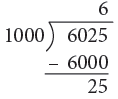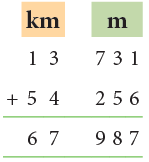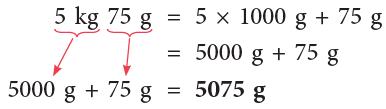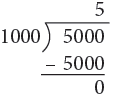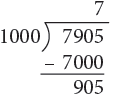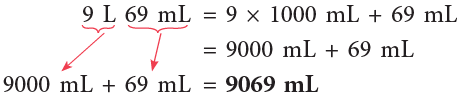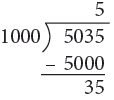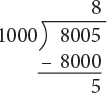Measurement Class 3 Notes Maths
Measuring Lengths
Do you wonder how in olden days people used to measure lengths? It’s interesting to know that parts of the body were used to measure lengths. Here are some of the units which were used.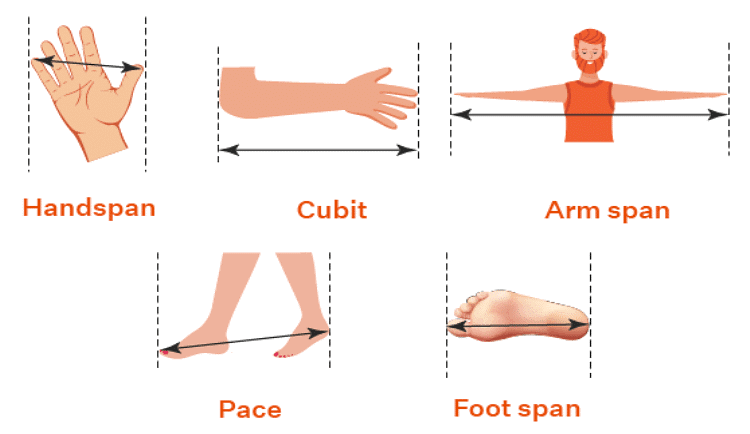 Even now you can see the old ladies in the house using these units for measuring lengths.
Even now you can see the old ladies in the house using these units for measuring lengths.
A hand span is the distance from the tip of the thumb to the tip of the little finger when the fingers are widespread.
A cubit is the distance from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger when the hand is outstretched.
Generally, no two persons have their fingers or hand spans or cubits equal.
So, when they measure a particular length they do not get the same measurement. The mathematicians, therefore, decided to have standard units of length.
In many parts of the world, the units named below are used. These were used in our country also until these were replaced by metric units after independence. Foot Scale
Foot Scale
Standard Units of Length
- Foot: 12 inches make one foot.
- Yard: 3 feet make 1 yard.
- Metre: The standard unit for measuring length today is the metre (written as "m").
- Kilometres (km) are used for longer distances, while centimetres (cm) are used for shorter lengths.
Tools for Measuring Lengths
For measuring lengths, we use:
- a metre rod,
- a measuring tape
- and a ruler.
A cloth merchant measures cloth by iron rod called the metre rod. Metre Rod
Metre Rod
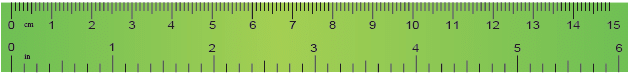 15 cm Ruler
15 cm Ruler
Here, the distance from the floor to a door knob is about 1 metre and the height of the plant is also about 1 metre.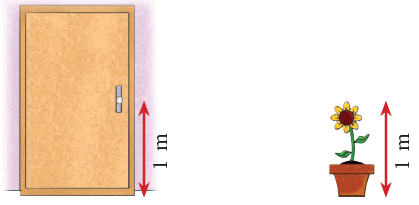 There are certain things such as the following that are more than a metre long.
There are certain things such as the following that are more than a metre long.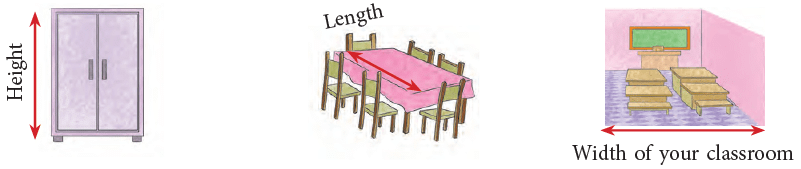 There are certain things like those shown below that are less than a metre long.
There are certain things like those shown below that are less than a metre long.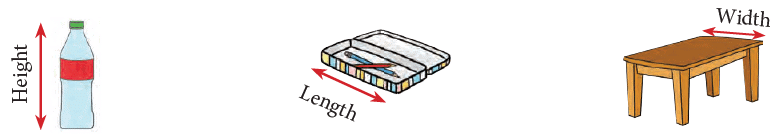
We use metres to measure long lengths and centimetres to measure short lengths.
Measurement of Length Using Centimetre Scale
Your finger is about 1 centimetre wide.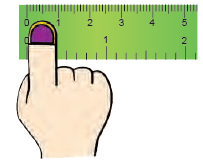 This will help you to estimate lengths in centimetres.
This will help you to estimate lengths in centimetres.
A 15 cm or 30 cm ruler is used to measure lengths in centimetres.
To measure the length of an object, say, a sharpener, line up one of the sharpener ends at the 0 mark of the ruler. The other end, touches the 2 cm mark of the ruler, so it is 2 cm long.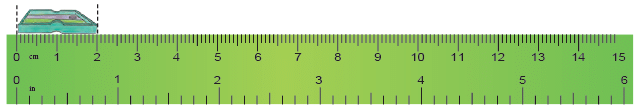 Similarly, we can measure the length of the following objects
Similarly, we can measure the length of the following objects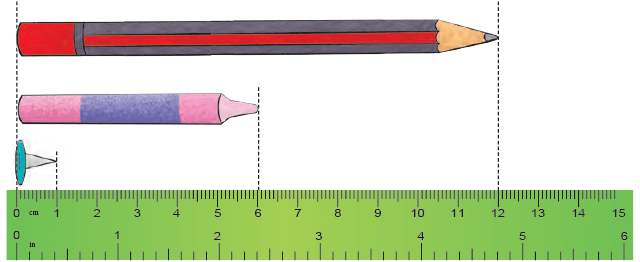
- The length of the pencil is 12 cm.
- The length of the crayon is 6 cm.
- The length of the board pin is 1 cm.

Long distances measured using kilometres that is represented by km.
Relation Between Kilometres, Metres and Centimetres
A metre is 100 times longer than 1 centimetre or we can say that 100 centimetres make 1 metre. A kilometre is 1000 times longer than 1 metre or we can say that 1000 metres make one kilometre.
100 centimetres = 1 metre
1000 metres = 1 kilometre
Conversion of Units of Length
1. Conversion of Metres to Centimetres
Rule: To convert metres to centimetres, we multiply the number of metres by 100.
Example 1: Convert 5 m and 16 m into cm.
5 m = 5 × 100 cm = 500 cm
16 m = 16 × 100 cm = 1600 cm
Example 2: Express the following in centimetres.
(a) 6 m 42 cm
(b) 17 m 93 cm
(a)
(b)
2. Conversion of Centimetres to Metres
Rule: To convert centimetres to metres, divide the number of centimetres by 100.
Example 3: Express the following lengths in metres.
(a) 496 cm
(b) 2516 cm
(a) 496 cm = 400 cm + 96 cm
= (400 ÷ 100) m + 96 cm
= 4 m + 96 cm
= 4 m 96 cm
Think:
(b) 2515 cm = 2500 cm + 15 cm
= (2500 ÷ 100) m + 15 cm
= 25 m + 15 cm
= 25 m 15 cm
Think:
3. Conversion of Kilometres to Metres
Rule: To convert kilometers to metres, multiply by 1000.
Example 4: Express the following in metres.
(a) 16 km
(b) 2 km 893 m
(a) 16 km = 16 × 1000 m = 16000 m
(b)
4. Conversion of Metres to Kilometres
Rule: To convert metres to kilometers, divide by 1000.
Example 5: Express the following in kilometres and metres.
(a) 5996 m
(b) 6025 m
(a) 5996 km = 5000 m + 996 m
= (5000 ÷ 1000) km + 996 m
= 5 km 996 m
Think:
(b) 6025 m = 6000 m + 25 m
= (6000 ÷ 1000) km + 25 m
= 6 km 25 m
Think:
Addition, Subtraction and Multiplication of Kilometres, Metres and Centimetres
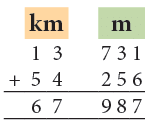
Example 6: Add 13 km 731 m and 54 km 256 m.
Working:
Think:
- 731 m + 256 m = 987 m
- 13 km + 54 km = 67 km
Thus, 13 km 731 m + 54 km 256 m = 67 km 987 m.
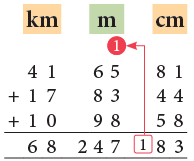
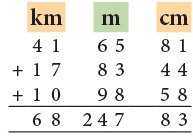
Example 7: Add:
41 km 65 m 81 cm, 17 km 83 m 44 cm and 10 km 98 m 58 cm
Working:
Think:
- 81 cm + 44 cm + 58 cm = 183 cm = 1 m 83 cm
Carry 1 m to the metres column.- 1 m + 65 m + 83 m + 98 m
= 247 m- 41 km + 17 km + 10 km = 68 km
Thus, the sum of 41 km 65 m 81 cm, 17 km 83 m 44 cm and 10 km 98 m 58 cm is 68 km 247 m and 83 cm.
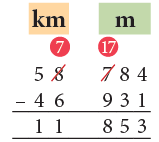
Example 8: Subtract 46 km 931 m from 58 km 784 m.
- We cannot subtract 931 from 784. So, we borrow 1 km from km column.
- Now, we have 1 km + 784 m = 1784 m. Subtracting 931 m from 1784 m, we get 853 m.
- Since from km column we have borrowed 1 km so we are left with (58 – 1) km = 57 km.
- Subtracting 46 km from 57 km, we get 11 km.
Edurev Tips: Carrying is done in the same manner as in the case of rupees and paise.
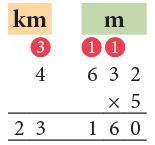
Example 9: Multiply 4 km 632 m by 5.
Think:
632 m × 5 = 3160 m = 3 km 160 m
Carry 3 to the km column.Thus, 4 km 632 m when multiplied by 5 gives the product as 23 km 160 m.
Measures of Weight (Kilograms and Grams)
Now that we have covered lengths, let's see how we can measure. In earlier times, people used to measure the weight of an object by comparing it to the weight of some other objects like a rock or a stone, and they would do it for many times till they weighed the entire amount of the good.
- We use the standard units to measure the weights of various objects around us. The standard unit of weight in the metric system is gram. You measure small weights in grams.
- Previously most of the countries including our country weighed things in pounds and ounces. These days most of the people use grams and kilograms.
- It can be verified by placing 1000 weights of 1 gram each on one side of the balance and a single weight of 1 kilogram on the other side.
1 kilogram = 1000 grams
You measure large weights in kilograms. For example, weight of an adult is measured in kilograms.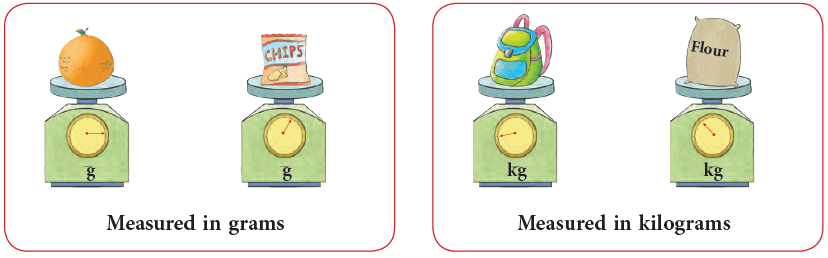 Familiarise yourself with the following standard weights.
Familiarise yourself with the following standard weights.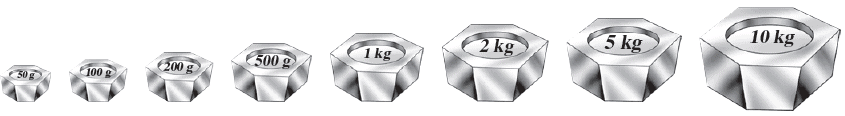
Relation Between Kilograms and Grams
1. Conversion of Kilograms to Grams
Rule: To convert kilograms to grams, multiply by 1000.
Example 10: Express the following in grams.
(a) 4 kg
(b) 5 kg 75 g
(a) 4 kg = 4 × 1000 g = 4000 g
(b)
Example 11: Express the following in kilograms and grams.
(a) 5000 g
(b) 7905 g
(a) 5000 g = (5000 ÷ 1000) kg = 5 kg
Think:
(b) 7905 g = 7000 g + 905 g
= (7000 ÷ 1000) kg + 905 g
= 7 kg 905 g
Think:
Addition, Subtraction and Multiplication of Kilograms and Grams
Addition, subtraction and multiplication of kilograms and grams is done in the same manner as you did in case of addition, subtraction and multiplication of kilometres, metres and centimetres.
Measures of Capacity (Litres and Millilitres)
The maximum amount of liquid that a container can hold is called its capacity.
Capacities are generally measured in litres (L) and millilitres (mL).
The amount of water, milk and other liquids that a bottle or any other container can hold is measured in litres, written in short as L. If you see at any bottle of liquid medicine or a juice tetrapack, you will find printed on it, its capacity in millilitre (mL).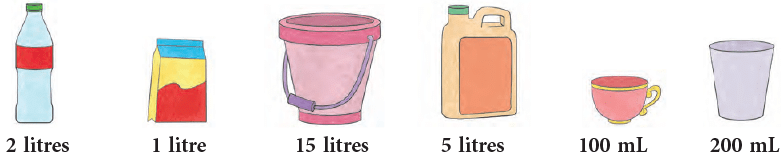 Milli means one-thousandth, that is one part out of 1000 parts. So, millilitre means one-thousandth of a litre.
Milli means one-thousandth, that is one part out of 1000 parts. So, millilitre means one-thousandth of a litre.
1 litre (L) = 1000 millilitre (mL)
A millilitre is a very small amount.
A teaspoon holds about 5 millilitres of liquid. A tablespoon holds about 10 millilitres of liquid.
A tablespoon holds about 10 millilitres of liquid. The litre jug is one container that can be used to measure capacity.
The litre jug is one container that can be used to measure capacity.
The standard sized containers used for measuring liquids are shown.
- First kind
(generally used for measuring milk):
- Second kind
(generally used for measuring petrol and oil):
Relation Between Litres and Millilitres
1. Conversion of Litres to Millilitres
Rule: To convert litres to millilitres, multiply by 1000.
Example 12: Express the following in millilitres.
(a) 15 litres
(b) 9 litres 69 millilitres
(a) 15 litre = 15 × 1000 mL = 15000 mL
(b)
2. Conversion of Millilitres to Litres
Rule: To convert millilitres to litres, divide by 1000.
Example 13: Convert the following to litres and millilitres.
(a) 6000 mL
(b) 5035 mL
(c) 8005 mL
(a) 6000 mL = (6000 ÷ 1000) L = 6 L
(b) 5035 mL
= 5000 mL + 35 mL = 5 L + 35 mL
= 5 L 35 mL
Think:
(c) 8005 mL = 8000 mL + 5 mL
= 8 L + 5 mL
= 8 L 5 mL
Addition, Subtraction and Multiplication of Litres and Millilitres
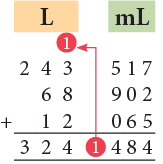
Example 14: Add 243 L 517 mL, 68 L 902 mL and 12 L 65 mL.
1. Add the millilitres.
517 mL + 902 mL + 65 mL = 1484 mL = 1 L + 484 mL
Carry 1 L to the litres column.
2. Add the litres.
1 L (carried over) + 243 L + 68 L + 12 L = 324 L
Thus, the sum of 243 L 517 mL, 68 L 902 mL and 12 L 65 mL is 324 L 484 mL.
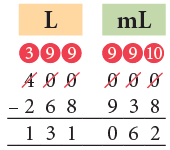
Example 15: Subtract 268 L 938 mL from 400 L.
We cannot subtract 938 mL from 0 mL.
So, we borrow 1 L from 400 L. 1 L = 1000 mL.
Then, subtract as shown.
Thus, 400 L – 268 L 938 mL = 131 L 62 mL.
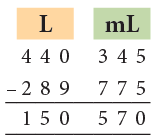
Example 16: Subtract 289 L 775 mL from 440 L 345 mL.
1. We cannot subtract 775 mL from 345 mL.
So, we borrow 1 L from 440 L.
Now, 1 L + 345 mL = 1000 mL + 345 mL = 1345 mL.
Then, 1345 mL – 775 mL = 570 mL.
2. 439 L – 289 L = 150 L
Thus, 440 L 345 mL – 289 L 775 mL = 150 L 570 mL.
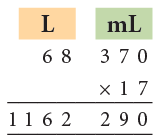
Example 17: Multiply 68 L 370 mL by 17.
1. 370 mL × 17 = 6290 mL. 6290 mL = 6 L 290 mL.
Write 290 mL under mL column and carry over 6 L to L column.
2. 68 L × 17 = 1156 L.
Then, 1156 L + 6 L = 1162 L.
Thus, the product is 1162 L 290 mL.
Problems Based on Real Life Situations
Example 18: Ravi bought 508 m cloth for dresses and 286 m cloth for shirts for his factory. How many metres of cloth in all did he buy altogether?
Total cloth bought = 508 m + 286 m
= 794 m
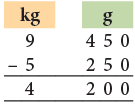
Example 19: The weight of a television set is 9 kg 450 g. It is 5 kg 250 g heavier than a table fan. What is the weight of the fan?
The weight of the fan = 9 kg 450 g – 5 kg 250 g
= 4 kg 200 g
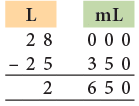
Example 20: Anil Kumar has 28 L milk. He sells 25 L 350 mL milk. How much milk is left with him?
Quantity of milk left = 28 L – 25 L 350 mL
= 2 L 650 mL
|
37 videos|72 docs|49 tests
|
FAQs on Measurement Class 3 Notes Maths
| 1. What tools are commonly used for measuring lengths accurately? |  |
| 2. How can I convert units of length from metres to centimetres? |  |
| 3. What is the relationship between kilograms and grams? |  |
| 4. How do I perform addition and subtraction of litres and millilitres? |  |
| 5. What is the process for multiplying lengths measured in kilometres, metres, and centimetres? |  |