Best Study Material for CLAT Exam
CLAT Exam > CLAT Notes > Current Affairs: Daily, Weekly & Monthly > UPSC Daily Current Affairs- January 12, 2022
UPSC Daily Current Affairs- January 12, 2022 | Current Affairs: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - CLAT PDF Download
GS-I
World Hindi Day

Context
- World Hindi Day (WHD) is celebrated every year on 10th January to promote the Hindi language all around the world.
- This year (2022) on the occasion UNESCO's World Heritage Centre (WHC) has agreed to publish Hindi descriptions of India's world heritage sites on WHC website.
- WHC was established in 1992 to coordinate all matters related to World Heritage. The Centre organises the annual sessions of the World Heritage Committee and its Bureau, and provides advice to States Parties in the preparation of site nominations.
About World Hindi Day
- It was first celebrated in 2006 to commemorate the anniversary of the first World Hindi Conference which was held in Nagpur on 10th January, 1975. It is different from Hindi Divas(National Hindi Day).
- It is also celebrated by Indian embassies located in various parts of the world.
- The World Hindi Secretariat building was inaugurated in Mauritius in 2018.
About National Hindi Day
- Hindi, written in the Devanagari script, was adopted as the official language of the Republic of India on 14th September, 1949. Therefore Hindi Divas is celebrated on 14th September every year.
- Kaka Kalelkar, Maithili Sharan Gupta, Hazari Prasad Dwivedi, Seth Govindadas made important contributions to make Hindi the official language.
- Hindi is also an eighth schedule language.
- Article 351 pertains to ‘Directive for development of the Hindi language’.
Government Initiatives to Promote Hindi
- The Central Hindi Directorate was established in 1960 by the Government of India under the Ministry of Education.
- Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) has established ‘Hindi Chairs’ in various foreign universities/institutions abroad.
- LILA-Rajbhasha (Learn Indian Languages through Artificial Intelligence) is a multimedia based intelligent self-tutoring application for learning Hindi.
- E-Saral Hindi Vakya Kosh and E-Mahashabdkosh Mobile App, both initiatives of the Department of Official Language, aim to harness information technology for the growth of Hindi.
- Rajbhasha Gaurav Puraskar and Rajbhasha Kirti Puraskar recognise contributions to Hindi.
GS-II
Hate speech in the time of free speech
Context
- The growing incidence of hate speeches, especially those targeting minorities, in combination with the judicial ambiguity has provided an opportunity to chart legislative reforms.
Current legal provisions to deal with hate speech
- Not defined in legal framework: Hate speech is neither defined in the Indian legal framework nor can it be easily reduced to a standard definition due to the myriad forms it can take.
- The Supreme Court, in Pravasi Bhalai Sangathan v. Union of India (2014), described hate speech as “an effort to marginalise individuals based on their membership in a group” and one that “seeks to delegitimise group members in the eyes of the majority, reducing their social standing and acceptance within society.”
- The Indian Penal Code illegalises speeches that are intended to promote enmity or prejudice the maintenance of harmony between different classes.
- Specifically, sections of the IPC, such as 153A, which penalises promotion of enmity between different groups;
- 153B, which punishes imputations, assertions prejudicial to national integration;
- 505, which punishes rumours and news intended to promote communal enmity, and
- 295A, which criminalises insults to the religious beliefs of a class by words with deliberate or malicious intention.
- Summing up various legal principles, in Amish Devgan v. Union of India (2020), the Supreme Court held that “hate speech has no redeeming or legitimate purpose other than hatred towards a particular group”.
- Lack of established legal standard: Divergent decisions from constitutional courts expose the lack of established legal standards in defining hate speech, especially those propagated via the digital medium.
Suggestions
- The Law Commission of India, in its 267th report, recommended the insertion of two new provisions to criminalise and punish the propagation of hate speech.
- The 189th Report of the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Home Affairs, in 2015, recommended the incorporation of separate and specific provisions in the Information Technology Act to deal with online hate speech.
- Specialised legislation for social media: Much of the existing penal provisions deal with hate speech belong to the pre-Internet era.
- The need of the hour is specialised legislation that will govern hate speech propagated via the Internet and, especially, social media.
- Recognise hate speech as reasonable restriction to free speech: Taking cue from best international standards, it is important that specific and durable legislative provisions that combat hate speech, especially that which is propagated online and through social media.
- Ultimately, this would be possible only when hate speech is recognised as a reasonable restriction to free speech.
Conclusion
- It is important that specific and durable legislative provisions be enacted to combat hate speech.
Mullaperiyar Dam Issue
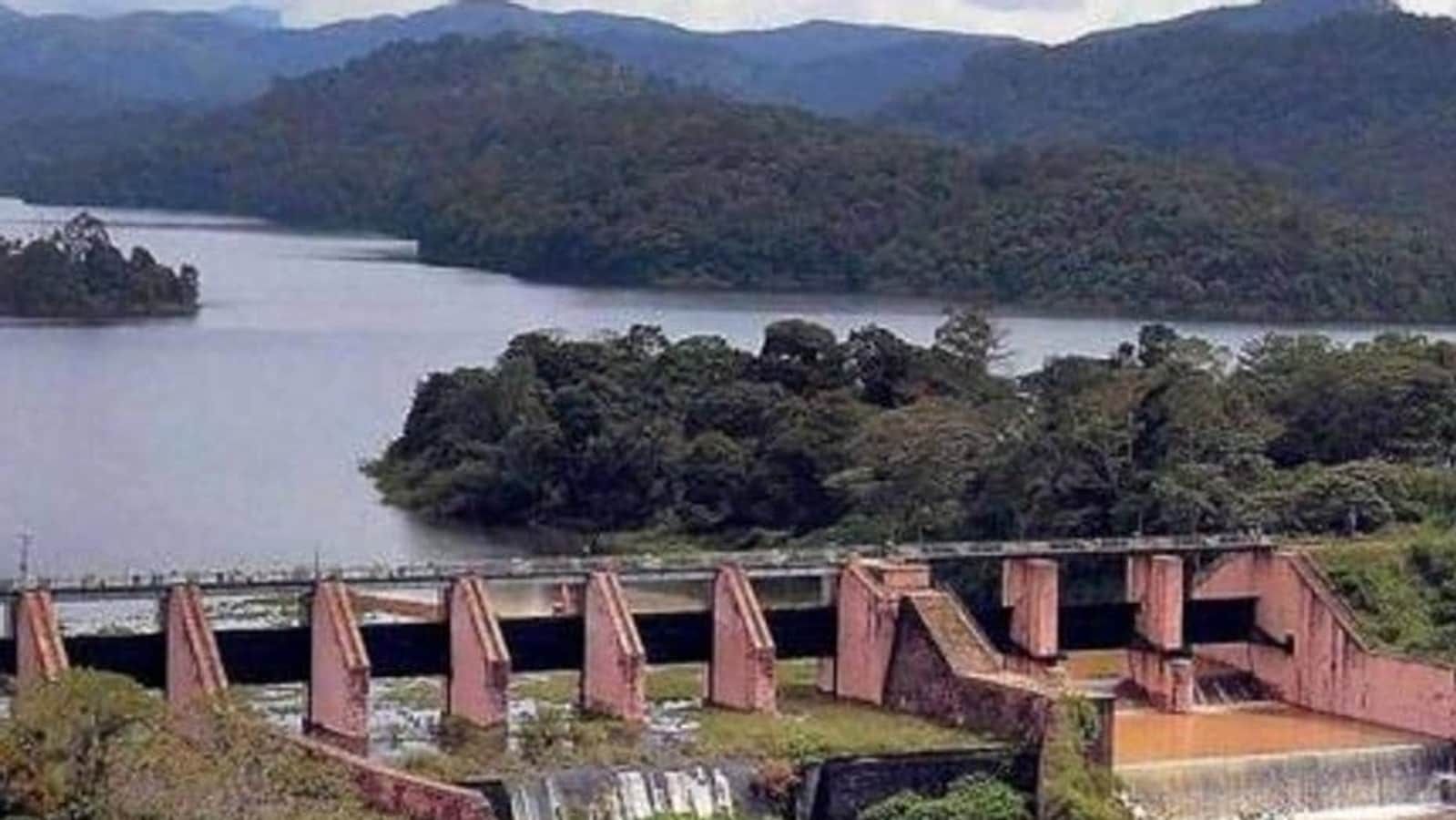

Context
- The Supreme Court has told Tamil Nadu and Kerala that it was not there to “administer the dam” when a supervisory committee was already in place to examine the issue of safety of the Mullaperiyar Dam and the management of its water level.
About Mullaperiyar Dam
- It is a masonry gravity dam on the Periyar River in Kerala.
- It is located on the Cardamom Hills of the Western Ghats in Thekkady, Idukki District.
- It was constructed between 1887 and 1895 by John Pennycuick (who was born in Pune) and also reached in an agreement to divert water eastwards to the Madras Presidency area.
- It has a height of 53.6 m (176 ft) from the foundation, and a length of 365.7 m (1,200 ft).
Operational issue
- The dam is located in Kerala but is operated and maintained by Tamil Nadu.
- The catchment area of the Mullaperiyar Dam itself lies entirely in Kerala and thus not an inter-State river.
- In November 2014, the water level hit 142 feet for first time in 35 years.
- The reservoir again hit the maximum limit of 142 feet in August 2018, following incessant rains in the state of Kerala.
- Indeed, the tendency to store water to almost the full level of reservoirs is becoming a norm among water managers across States.
The dispute: Control and safety of the dam
- Supreme court judgment came in February 2006, has allowed Tamil Nadu to raise the level of the dam to 152 ft (46 m) after strengthening it.
- Responding to it, the Mullaperiyar dam was declared an ‘endangered’ scheduled dam by the Kerala Government under the disputed Kerala Irrigation and Water Conservation (Amendment) Act, 2006.
- For Tamil Nadu, the Mullaperiyar dam and the diverted Periyar waters act as a lifeline for Theni, Madurai, Sivaganga, Dindigul and Ramnad districts.
- Tamil Nadu has insisted on exercising the unfettered colonial rights to control the dam and its waters, based on the 1886 lease agreement.
Rule of Curve issue
- A rule curve or rule level specifies the storage or empty space to be maintained in a reservoir during different times of the year.
- It decides the fluctuating storage levels in a reservoir.
- The gate opening schedule of a dam is based on the rule curve. It is part of the “core safety” mechanism in a dam.
- The TN government often blames Kerala for delaying the finalization of the rule curve.
Central Vista Project
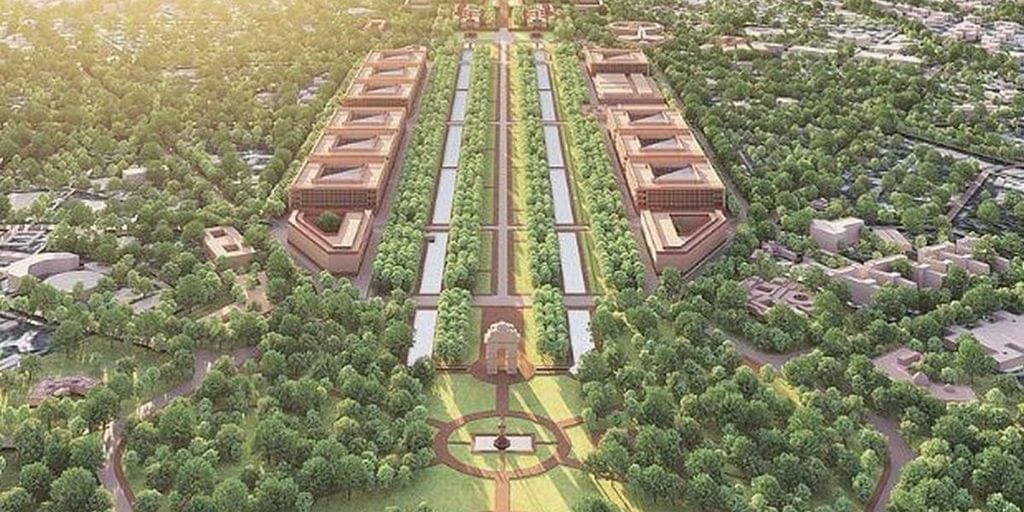

Context
- The redevelopment of central vista avenue in New Delhi, where the Republic Day parade is scheduled to be held, has been delayed by a couple of days due to heavy rainfall.
About Central Vista Project
- The project aims to renovate and redevelop 86 acres of land in Lutyens’s Delhi.
- In this, the landmark structures of the government, including Parliament House, Rashtrapati Bhavan, India Gate, North Block and South Block, etc. stand.
- This dream project of redeveloping the nation’s administrative heart was announced by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs back in September 13, 2019.
- This project has three main parts:
- New parliament building
- New secretariat complex to bring all the central govt ministries in one place
- Development of the Rajghat and the area around it
- This project will involve demolition of some non-heritage buildings in the area, and construction of new buildings in place of them.
Why need this Project?
- The most significant aspect of the project is the construction of a new parliament building. There are several reasons for needing a new building.
- Due to increased population, which has almost quadrupled since independence, there is a need to increase the number of Lok Sabha constituencies through delimitation.
- Similarly, the central hall of the parliament used to hold joint sessions, actually does not have enough seats for the MPs of both houses.
- During joint sessions, temporary chairs are placed on the aisles so that all the members can sit.
- This is certainly not a dignified scene for the parliament of the largest democracy in the world.
- The infrastructure of the parliament was also antiqued, as they were added at various times as and when required.
- Due to these reasons, a pressing need was felt to construct a new parliament building.
Significance of the project
- Modernising parliament’s facilities: The new Parliament building will be India’s first purpose-designed parliament, equipped with state-of-the-art infrastructure to meet all needs of an expanded parliament.
- Improving productivity and efficiency: All ministries of the government will be consolidated in one place and will be served by highly energy-efficient and sustainable infrastructure.
- Strengthening cultural and recreational facilities: The National Museum will be relocated and conceptualized to present the rich heritage and achievements of the nation.
- Providing modern and secure infrastructure: A modern, secure, and appropriately equipped executive enclave is proposed to house executive offices and facilities.
- Providing residential facilities for the PM: Modern and secure residential facilities for the vice president and the PM are proposed to the north of North Block and south of South Block respectively.
- Cultural significance: The overall objective of works planned on the Central Vista is to ensure environmental sustainability, restore the vista’s architectural character, protect its heritage buildings, expand and improve public space, and to extend its axis.
GS-III
Man-Portable Anti-Tank Guided Missile (MPATGM)
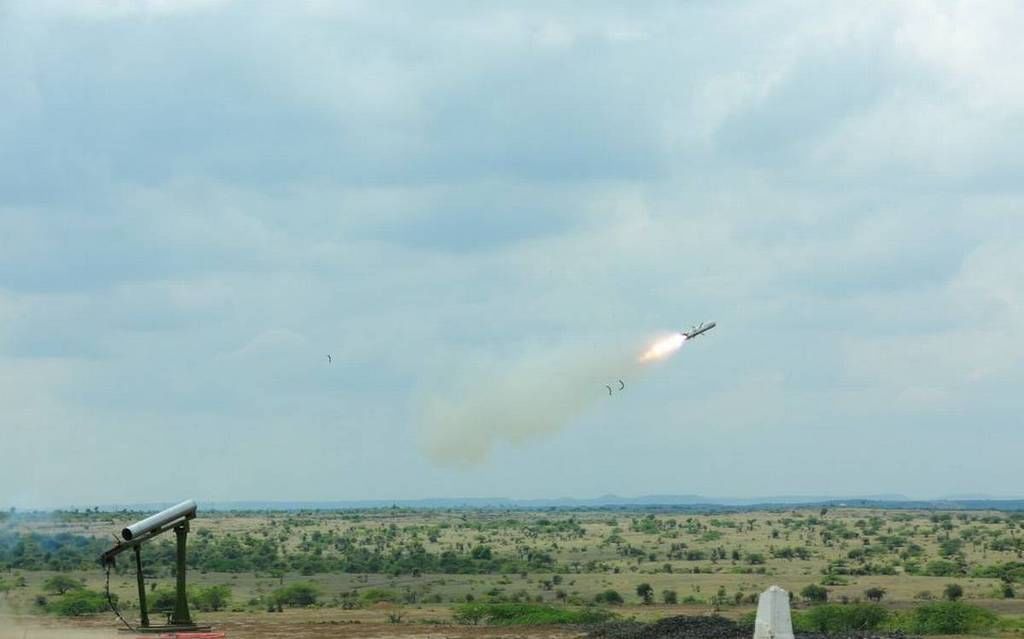

Context
- Recently, Defense Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully flight tested the final deliverable configuration of Man-Portable Anti-Tank Guided Missile (MPATGM).
About (MPATGM)
- It is an indigenously developed low weight, fire and forgets missile.
- The missile is incorporated with state-of-the-art Miniaturized Infrared Imaging Seeker (IIS) along with advanced avionics.
- It is a passive weapon guidance system that uses the infrared light emission from a target to track and follow it.
- Missiles that use infrared seeking are often referred to as "heat-seekers" since infrared is radiated strongly by hot bodies.
Significance of (MPATGM)
- The successful trial of the missile is a major boost for the government's 'Atma Nirbhar Bharat' (self-reliant India) campaign.
- The missile is being developed to strengthen the combat capabilities of the Indian Army.
 |
Download the notes
UPSC Daily Current Affairs- January 12, 2022
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
India improves position in Henley Passport Index, 2021

Context
- India now ranks at 83rd position in the Henley Passport Index, climbing seven places from 90th rank last year.
About Henley Passport Index
- The Henley & Partners publishes the ranking and the Index of the world’s passports according to the number of destinations their holders can access without a prior visa.
- It was launched in 2005.
- The ranking is based on data from the IATA (International Air Transport Association), a trade association of some 290 airlines, including all major carriers.
- The index includes 199 different passports and 227 different travel destinations.
- The data are updated in real time as and when visa policy changes come into effect.
India’s performance this year
- India is ranked at 83rd position and shares the rank with Sao Tome and Principe in Central Africa, behind Rwanda and Uganda.
- It now has visa-free access to 60 destinations worldwide with Oman and Armenia being the latest additions.
- It has added 35 more destinations since 2006.
Global performance
- Japan and Singapore has topped the list.
- The US and the UK passports regained some of their previous strength after falling all the way to eighth place in 2020.
- The passport of the Maldives is the most powerful in South Asia (58th) enabling visa-free entry to 88 countries.
- In South Asia, Bangladesh (103rd) is ahead of Pakistan (108th) and Nepal (105th).
- Afghanistan undoubtedly stands at the last rank.
BrahMos advanced variant test fired
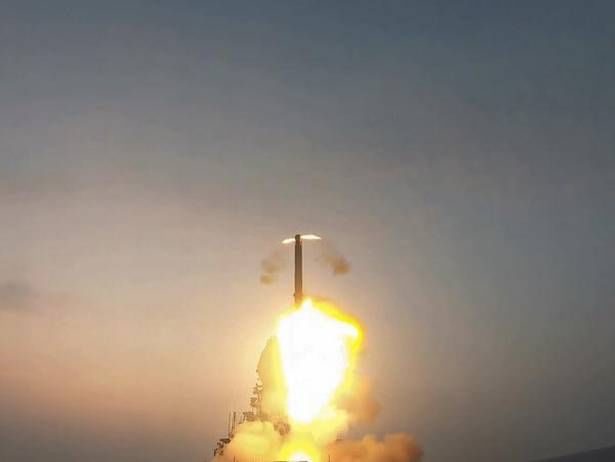

Context
- An extended range sea-to-sea variant of the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile was successfully test-fired by India from the Indian Navy’s newly commissioned INS Visakhapatnam.
About the missile
- BrahMos: deployed by the Navy on its warships first in 2005, has the capability to hit sea-based targets beyond radar horizon.
- It is capable of carrying a warhead of 300 kilograms (both conventional as well as nuclear).
- Specifications: This version of the missile has been designed to launch either in a vertical or a horizontal mode from moving/stationary assets to target both land and sea targets.
- The missiles, fired at a speed of 2.8 Mach or nearly three times the speed of sound, significantly increase the capability of the ships in engaging long-range targets.
- India-Russia synergy: BrahMos missiles are designed and developed by BrahMos Aerospace, a joint venture company set up by Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO) and Mashinostroyenia of Russia.
- Originally introduced in 2001, variations of these supersonic missiles can be launched from submarines, ships, aircraft, and land platforms.
- The range of the missile: was originally capped at 290 km as per obligations of the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR).
- Following India’s entry into the club in 2016, officials said the range would be extended to 450 km and to 600km at a later stage.
- INS Visakhapatnam: with a displacement of 7,400 Tonnes, is the first of four ingeniously designed and built Project-15B class stealth guided missile destroyers and was commissioned in 2021.
Grime-eating bacteria to restore classical art

Context
- The role of microorganisms has been recognised in protecting the artistic heritage of humanity since the 1980s when the bacteria Desulfovibrio Bulgaria was used.
- Earlier Art restorers have usually employed chemical agents and, more recently laser techniques, to remove dirt, oil, glue, or pollutants from monuments, stoneworks, and paintings.
About Grime-eating bacteria to restore classical art
- The researchers first used the bacteria Desulfovibrio Vulgaris to clean a marble monument at the Cave Hill Cemetery in Louisville, US.
- Desulfovibrio Vulgaris is a Gram-negative, anaerobic, non-spore-forming, curved rod-shaped bacteria, that can be found in soil, animal intestines and faeces, and fresh and saltwater
- It went on to meet several artworks, including, in 2013, the Allegoria Della Morte — the Allegory of Death — at the English Cemetery in Florence.
Other bacteria used
- Pseudomonas stutzeri has been trusted to clean a range of monuments, as well as the stones of historic bridges and granite slabs of chapels in Spain.
- This strain of bacteria was used for the bio-restoration of frescoes in the 17th century Church of Santos Juanes in Valencia, Spain, and murals of the Camposanto Monumentale di Pisa in Italy
- Recently P. stutzeri was used to clean the 14th-century Triumph of Death fresco at the Campo Santo. The cemetery was bombed during World War II.
- Pseudomonas stutzeri is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, motile, single polar-flagellated, soil bacterium that was first isolated from human spinal fluid and is widely distributed in the environment.
Significance for India
- Bio-restoration can save many of India’s monuments.
- In 2014, a paper published by researchers from Thapar Institute of Engineering and Technology, Patiala, and Curtin University in Perth, Australia, noted that calcifying bacteria could be used for remediation of stones and cultural heritage monuments, including the Taj Mahal.
The document UPSC Daily Current Affairs- January 12, 2022 | Current Affairs: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - CLAT is a part of the CLAT Course Current Affairs: Daily, Weekly & Monthly.
All you need of CLAT at this link: CLAT
|
962 docs|674 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- January 12, 2022 - Current Affairs: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - CLAT
| 1. What is the significance of GS-I in the UPSC exam? |  |
| 2. What does GS-II focus on in the UPSC exam? |  |
Ans. GS-II, or General Studies Paper-II, is a paper in the UPSC exam that assesses the candidate's knowledge and understanding of Governance, Constitution, Polity, Social Justice, and International Relations.
| 3. What topics are covered in GS-III for the UPSC exam? |  |
Ans. GS-III, or General Studies Paper-III, is a paper in the UPSC exam that covers topics such as Technology, Economic Development, Biodiversity, Environment, Security, and Disaster Management.
| 4. How can one prepare for the UPSC exam effectively? |  |
Ans. To prepare effectively for the UPSC exam, candidates should focus on comprehensive reading of newspapers, NCERT books, and relevant reference books. They should also solve previous years' question papers, practice answer writing, and join a reliable coaching institute if necessary.
| 5. What is the role of current affairs in the UPSC exam? |  |
Ans. Current affairs play a crucial role in the UPSC exam as questions related to recent events, government policies, international relations, and socio-economic developments are often asked. Candidates should stay updated with current affairs through newspapers, magazines, and online sources to perform well in the exam.
Related Searches





















