UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 12th October 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/International Relations
India calls for safety of UN peacekeepers in Lebanon
Source: Indian Express

Why in News?
India expressed concern over the deteriorating security conditions in West Asia following an incident where two UN peacekeepers sustained injuries near the Lebanon-Israel border. This incident took place when an Israeli tank targeted a UN observation tower, marking a significant escalation in tensions after Israel requested the UN peacekeeping force, UNIFIL, to withdraw from areas near Hezbollah rocket launch sites, a request that was ultimately rejected by the UN.
- UNIFIL has operated in southern Lebanon since 1978, with its observational mandate being enhanced in 2006 after the Israel-Hezbollah conflict.
UN Peacekeeping
The UN Charter assigns the primary responsibility for maintaining international peace and security to the Security Council. To fulfill this role, the Council can establish a UN peace operation.
Peacekeeping Mandates
UN peace operations are deployed based on mandates from the United Nations Security Council, which vary according to the situation and the specific challenges presented by the conflict. Depending on their mandate, peace operations may be required to:
- Prevent the outbreak of conflict or its spillover across borders.
- Stabilize situations after a ceasefire.
- Assist in the implementation of comprehensive peace agreements.
- Guide states or territories through transitions to stable governance, grounded in democratic principles, good governance, and economic development.
Principles
- Consent of the parties: Peacekeeping operations require the consent of the conflicting parties; without it, they risk being drawn into the conflict and forced to take enforcement actions.
- Impartiality: Peacekeepers should act impartially with the conflicting parties but must not be neutral in executing their mandates.
- Non-use of force: Force should only be used in self-defense or when protecting the mandate.
Current Status
- India is one of the largest contributors of troops to UN peacekeeping efforts, with approximately 5,900 personnel currently deployed across 12 UN missions.
- India’s financial contribution to the peacekeeping budget is 0.16%.
Contribution So Far
- India has been involved in peacekeeping since 1950, initially providing medical personnel and troops to the UN Repatriation Commission in Korea.
- India has contributed around 275,000 troops to various peacekeeping missions and has seen 159 Indian Army soldiers lose their lives in these missions.
Joint Training of U.N. Peacekeepers from African Countries
- In 2016, India and the U.S. initiated an annual program for joint training of U.N. peacekeepers from African nations.
Centre for United Nations Peacekeeping (CUNPK)
- The Indian Army established the CUNPK in New Delhi to provide training for peacekeeping operations, training over 12,000 troops annually.
Women Deployment
- India has deployed Female Engagement Teams in the United Nations Organization Stabilization Mission in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the United Nations Interim Security Force for Abyei, representing the second-largest contingent of women after Liberia.
- Additionally, India has sent Women Military Police to the United Nations Disengagement Observer Force and has women staff officers and military observers in various missions.
Other Contributions
- In August 2021, India collaborated with the UN to launch the UNITE AWARE platform, a technology initiative aimed at ensuring the safety and security of peacekeepers.
- India has proposed a 10-point plan to enhance accountability for those targeting UN peacekeepers and suggested establishing a memorial wall to honor fallen peacekeepers.
UNIFIL
The United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon (UNIFIL) is an international peacekeeping mission comprising over 10,000 civilian and military personnel from 50 countries. Its primary task is to prevent violations along the 121-km "Blue Line" border separating Lebanon and Israel. Established by a UN resolution in 2006, UNIFIL is tasked with ensuring the area remains free of hostilities, including the presence of weapons or combatants.
However, UNIFIL has faced criticism from the U.S. and Israel for its perceived ineffectiveness in preventing Hezbollah from amassing and firing rockets. Although armed, peacekeepers can only use force when their safety or that of civilians is at immediate risk, and they must report violations to the UN Security Council.
Issue – Attack on UNIFIL
During its military operations in southern Lebanon, the Israeli army established positions near a UNIFIL base, utilizing these sites to engage Hezbollah targets, thereby increasing the risk to UN peacekeepers. Despite Israel's requests for UNIFIL to relocate, the UN force declined. Attacks on UN personnel are deemed illegal under international law, yet Hezbollah has been launching rockets from areas near UN positions for over a year, complicating the situation. Recently, Israeli tank fire struck a UN observation tower and the entrance of a bunker where peacekeepers were sheltering at a UNIFIL base in Naqoura, Lebanon.
GS2/International Relations
19th East Asia Summit
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
PM Modi attended the 19th East Asia Summit (EAS) on 11 October 2024 in Vientiane, Lao PDR. In his address, PM stressed ASEAN's central role in the Indo-Pacific regional architecture, in India’s Indo-Pacific Vision, and in Quad cooperation.
About
- The EAS serves as a platform for leaders from the Indo-Pacific region to discuss various political, security, and economic challenges.
- Established in 2005 by the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), the EAS is held annually.
- The inaugural EAS took place in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia in 2005.
Members
- Initially, the EAS included 16 countries from East Asia, Southeast Asia, South Asia, and Oceania.
- In 2011, the membership expanded to 18 countries, including Russia and the United States.
- Currently, the EAS forum includes 18 countries representing 54% of the world’s population and 58% of global GDP. The member countries are:
- Ten ASEAN member states: Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam
- Australia, China, Japan, India, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Russia, and the United States
- The EAS is the only leaders-led forum that includes the US, China, Russia, India, South Korea, and Australia.
- To join the EAS, countries must:
- Sign the ASEAN Treaty of Amity and Cooperation (TAC)
- Be a formal dialogue partner of ASEAN
- Establish substantial cooperative relationships with ASEAN
Six priority areas of regional cooperation within the framework of the EAS include:
- Environment and Energy
- Education
- Finance
- Global Health Issues and Pandemic Diseases
- Natural Disaster Management
- ASEAN Connectivity
India and EAS
- India has been a member of the EAS since its inception in 2005.
- During the 4th EAS in Thailand in 2009, leaders endorsed the revival of Nalanda University, a proposal first suggested by former President APJ Abdul Kalam in 2006.
Key highlights of the speech delivered by PM Modi
- Called for Peace and Stability in Eurasia and West Asia
- PM Modi urged the restoration of peace in conflict zones, highlighting their effects on the Global South.
- He emphasized that solutions should be achieved through diplomacy and dialogue rather than war.
- Emphasis on Development Over Expansionism
- In a subtle reference to China's assertiveness in the South China Sea, Modi stressed the need for a development-centric approach instead of expansionism.
- He reiterated the importance of a free, open, inclusive, and rules-based Indo-Pacific region to ensure peace and progress.
- Call for Compliance with UNCLOS
- Modi highlighted the necessity of maritime activities to adhere to the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), stressing freedom of navigation and airspace.
- He advocated for an effective Code of Conduct that does not restrict the foreign policies of regional nations.
- Addressing Global Conflicts and Terrorism
- Modi denounced ongoing conflicts such as the Israel-Hamas and the Russian-Ukraine wars.
- He reiterated that war is not a viable solution and emphasized respect for sovereignty and international law.
- He called for global collaboration to combat terrorism, particularly in cyber, maritime, and space domains.
- Support for ASEAN and Myanmar Engagement
- PM expressed India's support for ASEAN unity and centrality and endorsed ASEAN's approach regarding Myanmar.
- He reaffirmed India’s commitment to engage with Myanmar instead of isolating it in the peace process.
- Humanitarian Assistance and Quad Cooperation
- Modi mentioned India's humanitarian efforts, including Operation Sadbhav, in response to Typhoon Yagi.
- He reiterated India's commitment to its Act East Policy and Quad cooperation for a free and inclusive Indo-Pacific region.
GS1/Indian Society
International NGOs and the Perils of Outsourcing Development
Source: The Hindu
Why in news?
For many years, International NGOs (INGOs) have promoted donor-driven agendas that have frequently caused harm to local communities.
Case Study: Africa and Bolivia
- Tanzania and Kenya (Africa): In these regions, conservation initiatives led by INGOs, often funded by Western donors, resulted in the displacement of indigenous Maasai communities from their ancestral lands. While these projects were framed as conservation efforts, they overlooked local rights and livelihoods, inflicting social and economic harm on the Maasai.
- Bolivia (Cochabamba): The privatization of water resources, supported by INGOs and international donors, limited access to essential water services, leading to widespread public protests. This privatization was part of broader neoliberal reforms but was eventually reversed due to strong local resistance, highlighting the detrimental effects of donor-driven policies on vital public services.
What are the Historical roots of Gender Imbalance?
- Colonial Policies: British colonial land reforms in the 18th and 19th centuries particularly affected land-owning castes, exacerbating issues like female infanticide due to socio-economic factors tied to inheritance and property rights within the agrarian society.
- Post-Independence Malthusian Fears: After independence, Western fears of overpopulation influenced perceptions of India. INGOs, driven by these Malthusian concerns, advocated for population control measures.
- Note: These ideas stem from Thomas Malthus, an 18th-century British scholar. In his 1798 work, "An Essay on the Principle of Population," Malthus posited that population growth would outstrip food supply, resulting in widespread famine, disease, and societal collapse.
Role of INGOs in Worsening Gender Imbalance in India
- Population Control Focus: INGOs like the Ford Foundation, Rockefeller Foundation, and Population Council played a crucial role in introducing sex-determination technologies from the 1950s to the 1980s, channeling significant funding towards these initiatives while neglecting other public health needs.
- Influence in Institutions: INGOs integrated themselves within key Indian institutions such as AIIMS and the International Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS), steering research and policy towards population management. For instance, Sheldon Segal from the Population Council collaborated closely with the Indian Health Ministry to prioritize family planning over pressing health issues like tuberculosis and malaria.
- Promotion of Sex Selection: Under the influence of INGOs, medical professionals began endorsing sex-determination technologies like amniocentesis, claiming it was necessary to reduce "unnecessary fecundity."
Impact of Sex Determination Technology
- Introduction and Spread: Technologies like amniocentesis and ultrasound, originally designed to identify fetal abnormalities, were quickly repurposed for sex selection. This shift led to a dramatic increase in female foeticide, with census data showing a decline from 943 girls per 1,000 boys in 1951 to 927 girls per 1,000 boys by 1991. The most significant drop occurred between 1971 and 1991, coinciding with the proliferation of these technologies.
- Regional Variations: States with better access to sex-determination tests, such as Punjab and Haryana, saw the steepest declines in child sex ratios. By 2001, Punjab's ratio had fallen to 876 girls per 1,000 boys, while Haryana's dropped to 861.
- Missing Girls: A study published in 2006 in "The Lancet" estimated that sex-determination technologies led to the loss of approximately 10 million female births in India from 1980 to 2010, with around 500,000 female foetuses aborted each year during this time.
Way Forward
- Strengthen Legal Enforcement and Awareness: Implement stricter penalties for illegal sex determination practices and enhance public awareness to change societal norms that prioritize male children over female children, fostering gender equality at all levels.
- Focus on Holistic Public Health and Gender Policies: Redirect the efforts of INGOs and government initiatives towards comprehensive health programs that prioritize women's health, education, and economic empowerment, rather than concentrating solely on population control.
GS3/Economy
WTO Lowers Global Trade Growth Forecast Amid West Asia Conflict
Source: Mint

Why in News?
The World Trade Organization (WTO) has adjusted its forecast for global merchandise trade growth for 2025, reducing it from 3.3% to 3%. This change is attributed to escalating conflicts in West Asia, which have adversely affected vital shipping lanes, specifically the Red Sea corridor, and are anticipated to further disrupt global trade and energy prices.
Impact of the West Asia Conflict on Global Trade:
- The conflict in West Asia has intensified, particularly with military actions by Israel against the Iran-backed Hezbollah in Lebanon.
- Heightened tensions have resulted in violent incidents, including targeted explosions and the assassination of Hassan Nasrallah, a key Hezbollah leader.
- These developments raise concerns about the stability of trade in the area, essential for global petroleum production and shipping routes.
- The WTO has warned that the conflict might escalate, causing further disruptions in global shipping and driving up energy prices due to increased risk premiums.
- A disruption in energy supplies from West Asia could severely impact the economic growth of importing nations, thereby straining global trade.
Forecasts for Global Trade and GDP Growth:
- In response to these challenges, WTO economists predict that global merchandise trade growth will be 2.7% in 2024, followed by 3% in 2025.
- This represents a slight downward adjustment from previous forecasts, with global GDP growth also expected to stabilize at 2.7% for both years.
- These revisions follow an earlier forecast from April 2024 that estimated 2.6% growth in trade and GDP for 2024, and 3.3% trade growth with 2.7% GDP growth for 2025.
Regional Outlook - India, Vietnam, and Asia's Emerging Role:
- Despite the global trade slowdown, India and Vietnam are emerging as significant exporters.
- The WTO has noted their growing importance as "connecting economies," showcasing robust export growth in recent years.
- The recovery in Asian exports is driven by leading manufacturing nations, such as China, Singapore, and South Korea, which have been vital in revitalizing the region's trade through increasing demand for manufactured goods.
- However, some Asian economies, such as Japan, are expected to see stagnant export levels in 2024 after a decline in 2023.
- The WTO attributes Japan's trade difficulties to challenges within its export sectors, notably in machinery and technology industries.
Europe’s Drag on Global Trade Performance:
- In stark contrast to Asia’s growth, Europe continues to negatively impact global merchandise trade.
- The WTO has identified Europe as a burden on both imports and exports, with significant drops noted in sectors such as chemicals and automotive.
- Organic chemicals, which experienced a surge in demand during the pandemic for medicinal uses, are returning to pre-pandemic levels, leading to decreased trade activity.
- European imports have also declined, particularly affecting trade relations with other countries.
- This decline is attributed not only to geopolitical tensions but also to broader global economic trends, seen similarly in economies like the United States and South Korea.
Diverging Monetary Policies and Financial Volatility Risks:
- The WTO has cautioned that differing monetary policies among major economies could result in financial instability.
- As countries adopt varied approaches to interest rates and inflation management, there exists a risk of abrupt changes in exchange rates or capital movements, complicating debt servicing for less affluent nations.
- The WTO underscores that policymakers must navigate a delicate balance—excessive caution could lead to economic downturns, whereas aggressive policies might trigger inflation.
Fragmentation of Trade Flows Due to Geopolitical Tensions:
- Since the beginning of the Russia-Ukraine conflict, the WTO has observed increasing fragmentation in global trade flows.
- Trade routes and economic partnerships are becoming restructured along geopolitical lines, with nations forming new alliances and altering their import-export strategies.
- This fragmentation is expected to complicate the global trade landscape in the years ahead.
Conclusion:
- The WTO's reduced forecast for global trade growth highlights the multiple challenges confronting the global economy, from conflicts in West Asia to economic risks from diverging monetary policies.
- While countries like India and Vietnam show promise in the global trade arena, others, such as Japan and Europe, are likely to face tougher conditions.
- As the situation in West Asia and global financial uncertainties progress, these elements will influence the future of global trade and economic growth.
- Countries must adapt to these challenges by enhancing regional cooperation, promoting trade diversification, and strengthening supply chain resilience to navigate a more complex global trade environment.
GS3/Environment
Addressing Hunger and Malnutrition in India
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
India's challenges with hunger and malnutrition have been emphasized by its ranking in the 2024 Global Hunger Index (GHI), where it is positioned 105th out of 127 countries with a score of 27.3, placing it in the 'serious' category. Despite being one of the fastest-growing economies in the world, India continues to fall behind many of its South Asian neighbors, indicating a pressing need for effective solutions.
India's Performance Trends in the GHI
- The GHI is an annual report that measures and monitors hunger globally, regionally, and nationally, capturing various aspects of hunger over time.
- Established in 2006, the GHI was originally published by the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) and Welthungerhilfe, with Concern Worldwide joining as a co-publisher in 2007. After IFPRI's withdrawal in 2018, the GHI became a collaborative effort of Welthungerhilfe and Concern Worldwide.
- The GHI aims to:
- Raise awareness and understanding of hunger issues.
- Facilitate comparisons of hunger across countries and regions.
- Highlight areas with extreme hunger, necessitating urgent attention and intervention.
Highlights of the 19th GHI 2024:
- Theme: The theme for the 2024 GHI is "How gender justice can advance climate resilience and zero hunger."
- Global hunger statistics:
- The current GHI score is 8.3, reflecting a slight improvement from 2016's score of 18.8.
- 2.8 billion individuals are unable to afford a nutritious diet.
- Regional disparities in hunger:
- Sub-Saharan Africa experiences the highest rates of malnutrition and child mortality, exacerbated by ongoing conflicts in regions like Somalia and Sudan.
- South Asia, particularly countries like Afghanistan, India, and Pakistan, faces significant hunger challenges.
- Issues:
- Challenges in achieving Sustainable Development Goal 2 (Zero Hunger by 2030): The 2024 GHI indicates that 42 countries are facing alarming or serious levels of hunger, showing stagnation in progress despite previous advancements.
- Gender disparity: Women are disproportionately affected by food insecurity due to societal norms and violence that hinder their access to resources.
- Underlying causes of hunger include:
- Climate change and environmental degradation affecting food production and agricultural foundations.
- Armed conflicts leading to displacement and disruption of food systems, impacting agricultural practices.
- Lower-income nations facing debt challenges that divert funds from essential developmental priorities.
- Success stories amidst the crisis: Countries like Mozambique and Nepal have made notable improvements in their GHI scores since 2016, demonstrating that progress is achievable.
- A call to action: The GHI 2024 stresses the urgent necessity for coordinated efforts to tackle the overlapping crises of climate change, conflict, gender inequality, and economic instability, emphasizing support for vulnerable populations, especially women, in combating hunger.
India Specific Findings in the GHI 2024:
- Alarming child malnutrition rates: An estimated 35.5% of children under five are stunted, indicating chronic undernutrition, while 18.7% are wasted, showing acute malnutrition. These statistics reflect a severe lack of adequate nutrition during critical developmental stages, adversely affecting children's physical and cognitive growth. Additionally, around 13.7% of the overall population suffers from undernourishment, which remains a persistent concern.
- Child mortality rates: Though there has been some progress in reducing child mortality, with 2.9% of children dying before their fifth birthday, the overall hunger situation continues to be dire. The relationship between malnutrition and child mortality highlights the urgent need for immediate interventions.
India's Performance Trends in the GHI:
- Minimal improvement over the decade: India's GHI score has shown little progress, moving from 29.3 in 2016 to 27.3 in 2024. Although there have been improvements in certain areas such as child mortality rates, hunger remains a significant issue.
- India vs. neighbours: In comparison to neighboring countries like Sri Lanka, Nepal, and Bangladesh, which have fewer economic resources, India's GHI performance is particularly concerning, indicating that economic growth alone is not sufficient to enhance nutritional outcomes.
Addressing Hunger and Malnutrition in India:
- The necessity for comprehensive solutions: India's GHI score serves as a stark reminder that mere economic growth cannot eradicate hunger. A more holistic approach is needed to address the root causes of malnutrition.
- Effective policy interventions should focus on:
- Food security: Ensuring access to nutritious food for all populations is crucial.
- Healthcare access: Strengthening healthcare infrastructure can significantly improve maternal and child health outcomes.
- Maternal and child nutrition programs: Investing in targeted nutritional initiatives for mothers and children is essential for breaking the cycle of malnutrition.
- Some initiatives in India:
- National Food Security Act (NFSA)
- PM POSHAN Scheme
GS3/Environment
Baku and South Caucasus Region
Source: DTE
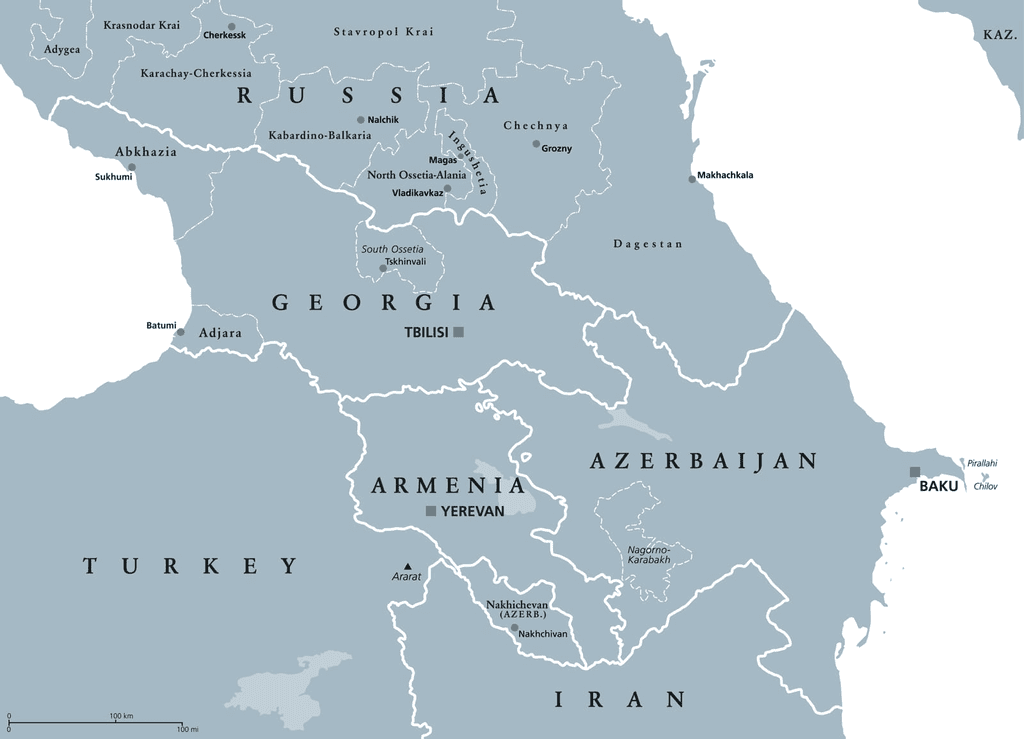
Why in news?
The 29th COP to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is set to commence on November 11, 2024, in the capital of Azerbaijan. As global leaders convene near the Caspian Sea, the South Caucasus region is confronted with significant climate challenges.
Key Areas at Risk:
- Regional/transboundary areas include:
- Northern Armenia and southern Georgia
- North-west Azerbaijan
- North-east Georgia (Alazani/Ganykh river basin)
- Within countries, the areas at risk are:
- Yerevan and Ararat Valley (Armenia)
- Lake Sevan
- Kura-Ara(k)s lowlands (Azerbaijan)
- Baku and Absheron peninsula
- Adjara and the Black Sea coast (Georgia)
- Tbilisi
- Mtskheta-Mtianeti, and Kakheti regions (Georgia)
- About South Caucasus Region (Transcaucasia):
- Location:
- Situated south of the Greater Caucasus Mountains, bordered by Russia (to the north), Turkey and Iran (to the south), and flanked by the Black Sea (to the west) and Caspian Sea (to the east).
- Countries:
- Includes Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia, along with disputed territories such as Nagorno-Karabakh (Artsakh), Abkhazia, and South Ossetia.
- Geographical Features:
- Lesser Caucasus Mountains rise up to 3,000 meters and feature ranges such as the Zangezur Range, Meskheti Range, and the Armenian Highlands.
- Seas:
- The region lies between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, with the Absheron Peninsula in Azerbaijan extending into the Caspian Sea, known for its rich oil deposits.
- Rivers and Lakes:
- Major rivers include the Kura River (flowing through Georgia and Azerbaijan) and the Aras River (flowing through Armenia and Azerbaijan). A key lake in the region is Lake Sevan (Armenia).
- Climate:
- The region experiences a continental climate with hot summers and cold winters, a subtropical climate along Georgia’s Black Sea coast, and a semi-arid to desert climate near the Caspian Sea, particularly in Azerbaijan.
- Natural Resources:
- This area is rich in oil and natural gas, especially in Azerbaijan, serving as a critical hub for energy pipelines, including the Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan pipeline.
- Geopolitical Importance:
- It serves as a strategic transit route for energy resources to Europe and is a region marked by geopolitical tensions due to conflicts in areas such as Nagorno-Karabakh, South Ossetia, and Abkhazia.
- Location:
GS3/Environment
 |
Download the notes
UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 12th October 2024
|
Download as PDF |
Hurricane Milton
Source: CNN
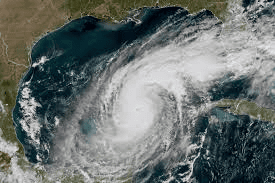
Why in News?
Hurricane Milton made landfall near Siesta Key, Florida, USA, resulting in severe rainfall, flooding, and strong winds that caused extensive damage and loss of life.
What is a Hurricane?
- A hurricane is a large and powerful cyclonic storm that forms over warm ocean waters.
- These storms primarily occur in the Atlantic Ocean, Gulf of Mexico, and the Caribbean Sea.
- Hurricanes typically form when sea surface temperatures exceed 26°C, which leads to evaporation that fuels the storm's intensification.
- Such storms usually develop during late summer and early fall, coinciding with the Atlantic hurricane season, which lasts from June to November.
Global Terminology:
- Typhoon: Refers to cyclonic storms in the Northwest Pacific Ocean.
- Cyclone: Refers to storms in the South Pacific and Indian Ocean.
- Hurricane: Specific to the North Atlantic, Central and Eastern North Pacific Oceans.
Hurricane Milton: Origin and Causes
- Hurricane Milton was a powerful storm that made landfall, causing widespread destruction.
- It reached Category 5 status with wind speeds of 285 km/h, ranking it among the strongest hurricanes documented.
- The storm originated in a region linked to warm ocean waters, which are conducive to hurricane development.Milton rapidly escalated from a Category 1 to a Category 5 hurricane within just 12 hours.
- This rapid intensification is uncommon; typically, hurricanes strengthen at a slower rate.
- The sea surface temperatures were notably high at 31°C, exceeding the usual requirements for hurricane formation, which enabled Milton to intensify swiftly.
- Unlike most hurricanes that generally move westward, Milton took an eastward trajectory, making landfall on the western coast of Florida—a rare path for hurricanes.
- Additionally, there was minimal wind shear, which usually hampers hurricane development, allowing Milton to strengthen unchecked.
GS1/History & Culture
Literature Nobel, 2024
Source: The Hindu

Why in News?
The 2024 Nobel Prize has been awarded to South Korean writer Han Kang for her “intense poetic prose that confronts historical traumas and exposes the fragility of human life.”
Who is Han Kang?
- Han Kang is a renowned South Korean author, born in 1970 in Gwangju, South Korea.
- She is celebrated for her poetic and experimental writing style that explores themes such as historical trauma, violence, grief, and the fragile nature of human life.
- Beginning her literary journey with poetry, she gained widespread recognition through her novels, which delve into complex human emotions and the impacts of societal and political frameworks.
Her Literary Works:
- The Vegetarian (2007): This novel, awarded the Man Booker International Prize in 2016, narrates the story of a woman who chooses to stop consuming meat, leading to extreme responses from her family. It explores themes of control, independence, and violence and was translated into English in 2015.
- Human Acts (2016): Set during the 1980 Gwangju Uprising, this novel recounts the massacre of protesting students by the South Korean military, giving a voice to historical victims through an experimental and visionary narrative style.
- The White Book (2017): This elegiac work is dedicated to a sibling who died shortly after birth. It meditates on grief through the lens of white objects, symbolizing loss and memory.
- Greek Lessons (2023): Originally published in Korean in 2011, the story follows a woman losing her ability to speak and her teacher facing blindness, exploring themes of loss, intimacy, and the relationship between language and identity.
- We Do Not Part (2025, forthcoming): This upcoming novel focuses on two women confronting a hidden massacre in Korean history from the 1940s, examining how trauma can be transformed into art.
Citation for Nobel Prize 2024
- The Swedish Academy’s official biography highlights her talent for crafting universal narratives through a poetic and radical imagination.
- Han Kang is recognized for addressing issues of patriarchy, violence, and historical injustices while exploring the connections between body and soul, as well as the living and the dead.
- The academy commends her as an innovator in contemporary prose, illustrating how literature can convey truth through her powerful and experimental narrative style.
Recent Nobel Prizes in Literature:
- 2023: Jon Fosse (Norway) for his innovative minimalistic plays and prose focused on the human condition.
- 2022: Annie Ernaux (France) for her courageous exploration of personal and collective memory.
- 2021: Abdulrazak Gurnah (Tanzania) for his compassionate depictions of colonialism and migration.
- 2020: Louise Gluck (USA) for her deeply personal poetry that resonates universally.
Rabindranath Tagore
- Won the Nobel Prize in 1913 for “Gitanjali,” becoming the first non-European laureate in Literature, recognized for his sensitive and spiritual poetry.
GS3/Environment
As the green patch spreads in Antarctica, here’s what is worrying scientists
Source: Indian Express

Why in News?
A recent study has discovered that the plant cover on the Antarctic Peninsula, which stretches toward South America, has increased by more than ten times in recent decades, driven by rising temperatures.
What has the study found?
- Vegetation on the Antarctic Peninsula has expanded 14 times from 1986 to 2021, growing from less than 1 square kilometer to nearly 12 square kilometers.
- Mosses and lichens are the predominant forms of this vegetation, with a 30% increase in greening observed between 2016 and 2021.
- This transformation is attributed to human-induced climate change, as evidenced by satellite data.
How quickly is Antarctica warming?
- Antarctica is experiencing warming at a rate twice that of the global average, with temperatures rising between 0.22°C and 0.32°C per decade, compared to the global average increase of 0.14°C to 0.18°C.
- The Antarctic Peninsula is warming five times faster than the global average and has seen a temperature rise of nearly 3°C since 1950.
- Record heatwaves have been reported, with temperatures soaring up to 28°C above normal in July 2023 and hitting 39°C above normal in March 2022.
Why should we worry about increased vegetation in Antarctica?
- Invasive Species: The rise in temperatures and vegetation disrupts the ecological balance, allowing non-native species to outcompete the native flora, such as mosses and lichens, which can lead to reduced biodiversity and changed habitats.
- Albedo Effect: More plant cover decreases the albedo effect, leading to higher absorption of solar energy and further warming, creating a feedback loop that encourages even more vegetation growth.
- Soil Formation: Increased plant life speeds up soil development by contributing organic matter, enhancing nutrient cycling, and creating a more favorable environment for non-native species, which raises the risk of invasives.
- Ice Loss and Sea-Level Rise: The combination of rising temperatures and the albedo effect results in greater ice melt, contributing to global sea-level rise and posing threats to coastal ecosystems and human settlements due to flooding and erosion.
Way forward:
- Strengthen climate action: Intensify global initiatives to lower greenhouse gas emissions, emphasizing renewable energy and sustainable practices to mitigate additional warming in Antarctica.
- Monitor ecosystems: Implement stricter biosecurity measures and enhanced monitoring systems to prevent the spread of invasive species that could disrupt Antarctica's delicate ecosystem.
- Promote global cooperation: Foster international collaboration in Antarctic research, focusing on understanding climate change impacts, protecting ecosystems, and developing adaptation strategies to minimize global sea-level rise and biodiversity loss.
GS3/Environment
Workplace carcinogens are increasingly a global problem
Source: DTE

Why in news?
Recent data indicates a worrying trend: cancer rates linked to workplace exposure to carcinogens in Central Europe and affluent Asian nations are nearing levels seen in Western Europe, Australia, and New Zealand. This rise highlights the growing relevance of occupational health concerns in these regions.
Carcinogens are associated with Occupational Cancer:
- Asbestos: A significant cause of lung cancer and mesothelioma, asbestos exposure remains the leading cause of occupational cancer fatalities.
- Benzene: Linked to leukemia and bladder cancer, benzene is commonly found in chemical industries, posing a major risk to workers.
- Silica: Associated with lung cancer, high levels of silica exposure predominantly occur in construction and mining sectors.
- Diesel Engine Exhaust: This is a known contributor to lung cancer and various respiratory disorders among workers exposed to diesel fumes.
- Secondhand Smoke: Workers in environments where smoking is prevalent face an elevated risk of developing lung cancer.
- Heavy Metals: Substances like arsenic, beryllium, cadmium, and chromium are linked to various cancers, including kidney and lung cancers.
Data Trends on Cancer from Workplace Exposure:
- Western Europe and Australasia: These regions have historically reported the highest mortality rates from cancers caused by workplace carcinogens, maintaining this trend for over thirty years.
- Southeast Asia: Countries such as Singapore, Japan, Brunei, and South Korea have experienced a threefold increase in cancer death rates from occupational exposure since 1990, correlating with the growth of their manufacturing sectors.
- Central Europe and East Asia: Death rates in Central Europe have doubled, while East Asia has seen a 2.5-fold increase since 1990, largely due to their extensive manufacturing economies lacking strict safety regulations.
International guidelines:
- World Health Organization (WHO): The WHO stresses the importance of primary prevention by minimizing exposure to carcinogens. They advocate for measures like banning asbestos and introducing alternatives to benzene, alongside comprehensive national cancer control initiatives that include occupational health standards.
- International Labour Organization (ILO):The ILO has set forth conventions and recommendations to mitigate occupational hazards from carcinogenic substances, which include:
- Replacing carcinogenic substances with safer alternatives.
- Creating lists of prohibited or strictly regulated carcinogens.
- Implementing medical monitoring and exposure assessments for workers.
Way forward:
- Strengthen Regulations and Enforcement: It is crucial to implement stricter health and safety regulations in workplaces, including banning or limiting known carcinogens like asbestos and benzene, while promoting safer alternatives.
- Enhance Awareness and Training: Comprehensive training programs should be developed for both workers and employers, focusing on the dangers of carcinogens, safe handling techniques, and the significance of regular health monitoring to prevent occupational cancers.
|
39 videos|4560 docs|976 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 12th October 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What actions has India taken to ensure the safety of UN peacekeepers in Lebanon? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the 19th East Asia Summit? |  |
| 3. How do international NGOs impact development efforts in developing countries? |  |
| 4. What factors contributed to the WTO lowering the global trade growth forecast? |  |
| 5. What are the implications of the green patch spreading in Antarctica for global climate change? |  |

































