UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 15th October 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/Polity
Right to Unionise
Source: The Hindu

Why in news?
The ongoing protests by Samsung India workers in Sriperumbudur, Tamil Nadu, are centered around their fundamental right to establish a registered trade union, aiming to negotiate better employment conditions. Since September 9, 2024, these workers have been on strike, demanding recognition for their newly formed union and an increase in wages.
Right to Form Trade Unions: Constitutional Protection
- The Supreme Court, in the landmark 1989 case B. Singh vs Union of India, affirmed that the right to form associations or unions is a fundamental right under Article 19(1)(c) of the Indian Constitution.
- Restrictions on this right, as per Article 19(4), can only be enforced if they are necessary for maintaining public order, morality, sovereignty, or the integrity of India, and such restrictions must be rational and not arbitrary.
- The court emphasized that trade unions are vital for expressing workers' grievances, and the State has a duty to register unions, allowing workers a platform for collective representation.
- Registration under the Trade Unions Act, 1926 provides legal immunity for unions against civil and criminal actions.
- Section 4 of the Act allows even seven members to apply for registration, requiring the Registrar to ensure compliance with the Act’s rules.
- The Madras High Court, in Rangaswami vs Registrar of Trade Unions, stated that the Trade Unions Act's purpose is to facilitate collective bargaining.
Collective Bargaining: Definition and Importance
- Collective bargaining, as defined by the International Labour Organization (ILO) in the 1981 Collective Bargaining Convention, refers to negotiations between employees and employers to determine working conditions and terms of employment.
- Some labor law scholars view collective bargaining as a balance of power between workers and employers, while others recognize it as a fundamental right of workers.
- In India, collective bargaining is recognized under the Industrial Disputes Act of 1947.
- If collective bargaining fails, the State may involve a conciliation officer, and if necessary, escalate the matter to a labor court or industrial tribunal.
- The Industrial Disputes Act identifies refusal to engage in good faith bargaining as an unfair labor practice.
Historical Evolution of Collective Bargaining
- Collective bargaining has its origins in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, particularly among coal miners advocating for basic working conditions.
- The practice gained recognition following the Great Depression and World War II, evolving alongside the establishment of democratic governance globally.
- In India, early instances of collective bargaining were seen during the 1918 Ahmedabad Mills strike, led by Mahatma Gandhi, which involved forming a committee of arbitrators to resolve wage disputes.
Judicial Recognition of Collective Bargaining in India
- The Indian Supreme Court has consistently recognized the importance of collective bargaining for achieving social justice.
- In the Karnal Leather Karmchari vs Liberty Footwear Company case, the court highlighted its significance in contemporary industrial relations.
- In Ram Prasad Vishwakarma vs The Chairman, Industrial Tribunal, the court noted that prior to collective bargaining, workers faced significant disadvantages.
Right to Strike: Legal Recognition with Restrictions
- The right to strike is legally recognized under the Industrial Disputes Act of 1947, albeit with certain conditions.
- The Supreme Court views strikes as a demonstration of workers' rights, which can take various forms like 'go-slow', 'sit-in-work', and 'work-to-rule'.
- This right is acknowledged in most democratic countries and is considered by the ILO as a natural extension of the right to organize.
- However, the Industrial Disputes Act does not consider the right to strike as absolute, with Section 22 outlining specific conditions for a valid strike.
- These conditions include mandatory pre-notification to the employer at least six weeks in advance and prohibitions on strikes during conciliation or within seven days following such proceedings.
- The Supreme Court has ruled that while the right to form associations is guaranteed, unions must operate in accordance with industrial law.
Demand for the Recognition of the Newly Formed Samsung India Workers’ Union (SIWU)
- The primary issue at hand is the workers' demand for recognition of their newly formed Samsung India Workers’ Union (SIWU), affiliated with the Centre of Indian Trade Unions (CITU).
- CITU is a left-oriented labor organization linked to the Communist Party of India (Marxist).
- Samsung's management has resisted this demand, arguing against the notion of a union involving external leaders in collective bargaining.
- Experts note that Section 6(e) of the Trade Unions Act, 1926 permits honorary or temporary members to serve as union office-bearers, allowing for external assistance.
- Samsung's management also contested SIWU’s registration on the grounds of trademark infringement regarding the use of 'Samsung' in the union's name.
- Section 29(5) of the Trade Marks Act, 1999, prohibits the use of a registered trademark in a business name; however, trade unions are not classified as business entities but as organizations formed to regulate relations between workers and employers.
- U.S. courts have recognized the concept of 'nominative fair use', allowing enough use of a company's distinguishing features to reasonably associate a union with the company, which could apply in Samsung's situation.
Salary and Working Conditions Concerns
- Many protesting workers have expressed dissatisfaction over not receiving wage increases despite Samsung India’s profitability.
- Workers have also raised issues regarding excessively long working hours, often exceeding their nine-hour shifts, with many required to remain standing for most of their shifts.
GS2/International Relations
India-Canada Diplomatic Escalation Over Nijjar Killing Case
Source: The Hindu
Why in news?
India has expelled six Canadian diplomats, including Acting High Commissioner Stewart Wheeler, and has withdrawn its own diplomats from Canada due to security concerns. This move follows Canada's identification of these Indian diplomats as "persons of interest" in the investigation into the killing of Khalistan separatist Hardeep Singh Nijjar in 2023.
Allegations by Canadian Police Against Indian Government
- Diplomatic relations between India and Canada were established in 1947.
- The relationship was elevated to a strategic partnership during PM Modi's visit to Canada in 2015.
Commercial Relations
- Bilateral Trade Relation
- India was Canada's 10th largest trading partner.
- India's total exports to Canada reached US$ 4.10 billion in 2022-23, up from US$ 3.76 billion in 2021-22.
- India's imports from Canada totaled US$ 4.05 billion in 2022-23, increasing from US$ 3.13 billion in 2021-22.
- CEPA/EPTA Negotiations
- In March 2022, both countries agreed to re-launch Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) negotiations.
- They also decided to pursue an Early Progress Trade Agreement (EPTA) for mutual commercial benefits.
- Trade discussions were halted in September 2023 amid the diplomatic conflict over Nijjar's killing.
- Nuclear Cooperation
- Canada's assistance to India in nuclear technology began in 1956 but soured after India's Smiling Buddha nuclear test in 1974.
- Canada was instrumental in establishing CIRUS, India's first research reactor.
- Nuclear cooperation was restored in June 2010 with the signing of a Nuclear Cooperation Agreement (NCA) with Canada.
- People-to-People Relations
- Canada is home to a significant Indian diaspora of 1.6 million people (PIOs and NRIs), making up over 4% of its total population.
- In Canadian politics, the current House of Commons includes 22 Members of Parliament of Indian-origin.
- Separatist Khalistani Groups
- Canada has been perceived as a refuge for Khalistani separatist groups, which New Delhi believes is due to the Liberal Party's electoral strategy.
- Sikh diaspora members are represented in the Trudeau government, with some linked to pro-Khalistan factions.
- Jagmeet "Jimmy" Dhaliwal, whose party supports Trudeau's minority government, is viewed with skepticism by Indian officials.
- Last year, India protested Canada allowing a Khalistani secessionist referendum in the Sikh community.
- Concerns remain regarding Canada's slow response to anti-India activities within its borders.
- A significant controversy arose in June 2023 when a social media video featured a parade float depicting the assassination of former PM Indira Gandhi.
- The float was seen as a celebration of her assassination, organized by pro-Khalistani supporters prior to the anniversary of 'Operation Bluestar'.
- Other tensions include attacks on Indian-origin individuals and Canadian comments regarding India’s farmer protests.
- Death of Khalistan Tiger Force Chief
- Hardeep Singh Nijjar, a wanted figure in India, was killed in a targeted shooting in June 2023.
- The National Investigation Agency (NIA) had previously announced a reward of Rs 10 lakh for information on Nijjar, who was accused of plotting to kill a Hindu priest in Punjab.
- Nijjar was shot outside a gurdwara in Surrey, Canada.
- Issue Raised on the Sidelines of G20 Summit
- During the G20 Summit in Delhi on September 10, discussions between Canadian PM Trudeau and PM Modi addressed Khalistani extremism.
- Trudeau raised concerns about foreign interference in Nijjar's murder and sought India's cooperation in the investigation.
- Conversely, PM Modi expressed worries regarding ongoing anti-India activities by extremist groups in Canada.
- PM Trudeau Raises the Issue in Canadian Parliament
- On September 18, 2023, PM Trudeau informed Parliament that Canada was actively investigating credible allegations linking Indian agents to Nijjar's murder.
- India rejected Trudeau's claims as unfounded.
- This led to a tit-for-tat expulsion of diplomats, with both countries dismissing each other's top intelligence officials.
- India’s Response and Diplomatic Withdrawal
- India announced the withdrawal of its diplomats citing safety concerns, accusing Trudeau's government of failing to ensure their protection.
- On the evening of October 14, India's Ministry of External Affairs summoned Canadian diplomats and communicated the decision to expel six of their diplomats.
- This decision came after Ottawa identified India's High Commissioner and other diplomats as 'persons of interest' in the investigation related to Nijjar's murder.
- Long-standing Tensions in India-Canada Relations
- India has criticized Trudeau's positions on several matters, including his support for farmer protests and perceived leniency toward Khalistani separatists.
- India has accused Canada of providing refuge to extremists and neglecting extradition requests for individuals involved in crimes against India.
- Canada’s Position and Evidence
- The Acting High Commissioner of Canada stated that credible evidence had been presented linking Indian agents to Nijjar's murder, urging India to cooperate in the investigation.
- The Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP) accused Indian government agents of collaborating with the Lawrence Bishnoi gang to instigate terror activities in Canada.
- Lawrence Bishnoi, a gangster imprisoned in India, is suspected of being involved in the recent killing of former MLA Baba Siddiqui.
- Canadian authorities allege that Bishnoi's criminal network is active in Canada and has been used by the Indian government to target dissidents.
GS2/International Relations
Inter-Parliamentary Union
Source: New Indian Express

Why in News?
Recently, the Lok Sabha Speaker, leading an Indian Parliamentary Delegation at the 149th Assembly of the Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU) in Geneva, emphasized the importance of multilateralism in his address.
About
- The Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU) is an international organization of parliaments that was founded in 1889 in Paris with the aim of promoting representative democracy and fostering world peace.
- It facilitates parliamentary diplomacy and empowers parliaments and their members to advocate for peace, democracy, and sustainable development globally.
- As the first multilateral political organization worldwide, the IPU encourages cooperation and dialogue among all nations.
Members
- The IPU comprises 180 member parliaments and 15 associate members.
- It works to strengthen democracy and to make parliaments more youthful, gender-balanced, and diverse.
- The organization also defends the human rights of parliamentarians through a specialized committee consisting of members from various countries.
- In 1921, the IPU moved its headquarters to Geneva.
Funding
- The IPU is primarily financed by its members using public funds.
Structure
- IPU Assembly: The principal statutory body that articulates the IPU's views on political matters. It gathers parliamentarians to examine international issues and propose actions.
- Governing Council: The plenary policymaking body of the IPU, consisting of three representatives from each member parliament. The President of the IPU also serves as the ex-officio President of the Governing Council, which sets the annual program and budget.
- Executive Committees: A 17-member body responsible for the administration of the IPU, providing advice to the Governing Council. The members are elected for four-year terms, with the IPU President serving as an ex-officio member and President of the committee.
- Standing Committees: Three standing committees established by the Governing Council to support the Assembly in its functions.
GS2/Governance
What is UNICEF?
Source: UNICEF

Why in News?
Recently, the United Nations International Children’s Fund (UNICEF) has stated that Indian suppliers rank as the third largest contributor to the organization’s health and nutrition support for children across the globe.
About UNICEF:
- UNICEF, which stands for the United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund, was founded in 1946 in response to the challenges faced by children after World War II.
- The organization’s primary objective is to assist children and young people whose lives and futures are jeopardized, irrespective of their country's involvement in the war.
- UNICEF operates in more than 190 countries and territories, dedicated to safeguarding the rights of every child.
Funding:
- UNICEF's initiatives are financed entirely through voluntary contributions from millions of individuals worldwide, along with support from government bodies, civil organizations, and the private sector.
Awards:
- In recognition of its efforts, UNICEF was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1965.
- It received the Indira Gandhi Prize in 1989 for its contributions to child welfare.
- UNICEF was also honored with the Princess of Asturias Award in 2006.
Important Reports:
- The organization publishes significant reports, including "The State of the World’s Children," which assesses the challenges and conditions affecting children globally.
Global Initiatives:
- In 2012, UNICEF collaborated with Save the Children and the United Nations Global Compact to formulate the Children's Rights and Business Principles, which serve as guidelines for corporate social responsibility regarding children's rights.
- UNICEF's Data Must Speak Initiative (DMS) aims to help countries leverage existing data to enhance access to education and improve overall learning outcomes for children.
Headquarters:
- UNICEF is headquartered in New York City, which serves as the central hub for its global operations.
GS3/Environment
What are Biopolymers?
Source: News Medical

Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister inaugurated India’s first Demonstration Facility for Biopolymers in Pune.
About Biopolymers:
- Biopolymers are materials derived from biological sources such as fats, vegetable oils, sugars, resins, and proteins.
- They possess more intricate structures compared to synthetic polymers, resulting in higher biological activity in living organisms (in vivo).
- Biopolymers are biodegradable, which means they can break down naturally through microbial action in soil, unlike synthetic polymers that contribute to environmental pollution when incinerated.
Characteristics
- Biopolymers are capable of influencing the life processes of living organisms and are considered environmentally friendly.
- They decompose through processes such as oxidation (reaction with oxygen), hydrolysis (decomposition with water), or enzymatic action.
- Some biopolymers are compostable and exhibit unique chemical properties on their surfaces.
- Examples include polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid, and poly-3-hydroxybutyrate, which can exhibit plastic-like properties.
Benefits:
- These polymers can help lower atmospheric carbon dioxide levels and reduce carbon emissions.
- The biodegradation of biopolymers releases carbon dioxide, which can then be reabsorbed by crops grown as substitutes, promoting a sustainable cycle.
GS3/Economy
Nobel Prize in Economics 2024
Source: The Hindu
Why in news?
The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences has awarded the Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel for 2024 to three economists based in the United States: Daron Acemoglu, Simon Johnson, and James A. Robinson. Their research addresses a crucial question that has puzzled economists for many years: Why do some nations achieve wealth while others struggle with poverty? The focus of their work is on the influence of societal institutions on economic success, examining how the rules governing behavior can create significant wealth disparities among countries.
Key Contributions of the 2024 Laureates of the Nobel Prize in Economics:
- Classifying Institutions:
- Two main categories of institutions are identified:
- Inclusive Institutions:
- These involve democratic governance, a robust rule of law, and the safeguarding of property rights.
- Such frameworks foster a stable environment, encouraging individuals to invest and contribute to society.
- Extractive Institutions:
- These systems centralize power among a select few, often characterized by authoritarian governance and insufficient legal protections.
- In these contexts, individuals face considerable risks of asset confiscation, diminishing their motivation for long-term investments.
- Significance of This Classification:
- The type of institutional framework significantly influences individual incentives within an economy.
- In nations with inclusive institutions, people are more inclined to invest in their futures, fostering innovation and contributing to overall economic growth.
- Conversely, extractive systems, lacking security and opportunity, often lead to stagnation or economic decline.
Historical Events Shaping Institutions and Economies:
- Colonial Legacy:
- A vital contribution of the Nobel laureates is their analysis of how historical events, especially European colonization, have influenced contemporary economic outcomes.
- They argue that the political and economic structures established by colonizers have enduring effects on a nation's prosperity.
- Significance of This Examination:
- The researchers discovered a robust correlation between the mortality rates experienced by colonizers in various regions and the type of institutions they set up.
- In regions where colonizers faced high mortality due to diseases or conflicts, extractive institutions were more likely to emerge, focusing on immediate resource exploitation.
- Conversely, in areas where colonizers could settle safely, inclusive institutions tended to develop, benefiting both the colonizers and the local populace.
Case Studies of India and China:
- Diverging Paths - Relationship Between Political Systems and Economic Success:
- The economic paths of India and China illustrate the complex relationship between institutions and prosperity.
- India, with its democratic framework and inclusive institutions, has experienced relatively slow economic growth compared to China, which has thrived under a more authoritarian regime.
- The Future Outlook:
- Despite these differences, some experts believe India may still unlock its economic potential in the decades to come, as it continues to enhance its institutions.
- In contrast, China's future economic growth might be at risk due to its lack of inclusive frameworks, hinting at possible shifts in global economic dynamics.
Current Trends of the Democracies Around the World and the Need for Reform:
- Declining State of Democracies:
- The health of democracies is essential for ensuring governance that serves a wide array of citizens.
- However, there is a concerning trend of weakening institutions and a rising inclination towards authoritarianism worldwide.
- The Need for Reform:
- Effective governance, accountability, and broad participation are vital for creating an environment conducive to economic growth and social stability.
- This underscores the critical importance of inclusive institutions.
Significance of the 2024 Nobel Prize in Economics:
- The ongoing discourse surrounding the relationship between institutions and economic development continues to be crucial for both policymakers and scholars.
- The insights gained from this research will be significant in tackling disparities and fostering sustainable growth for future generations.
GS3/Science and Technology
What is Haber-Bosch Process?
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
A hundred million tonnes of nitrogen are now removed from the atmosphere and converted into fertilizer via the Haber-Bosch process, adding 165 million tonnes of reactive nitrogen to the soil.
About Haber-Bosch Process:
- The Haber-Bosch process is a method that fixes nitrogen from the atmosphere by combining it with hydrogen to produce Ammonia (NH3).
- This ammonia is crucial for the production of plant fertilizers.
- Developed in the early 20th century by Fritz Haber, it was later industrialized by Carl Bosch.
- Many scientists regard it as one of the most significant technological advancements of the 20th century.
- This process enabled the mass production of fertilizers, fundamentally transforming agricultural practices.
- It was also the first industrial chemical process that employed high pressure for a chemical reaction.
How does the Haber-Bosch Process Work
- The process combines nitrogen from the air with hydrogen under extremely high pressures and moderately high temperatures.
- A catalyst primarily made from iron facilitates the reaction, allowing it to occur at lower temperatures than would typically be feasible.
- Ammonia is removed from the reaction mixture immediately after it forms, which helps maintain an equilibrium that favors the production of more ammonia.
- In general, lower temperatures and higher pressures result in a greater yield of ammonia in the final mixture.
GS2/International Relations
 |
Download the notes
UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 15th October 2024
|
Download as PDF |
What is THAAD Missile System?
Source: BBC
Why in News?
As Israel intensifies its military operation against Hezbollah militants in Lebanon, the United States announced it will deploy a missile defence system, the Terminal High Altitude Area Defence (THAAD) battery, to Israel.
About THAAD Missile System
- THAAD is a sophisticated missile defense system designed to intercept and neutralize short-, medium-, and intermediate-range ballistic missiles during their terminal phase of flight.
- The system employs a "hit to kill" strategy, which involves destroying incoming missiles as they descend towards their target area.
- Utilizing kinetic energy, THAAD effectively neutralizes threats, including incoming nuclear warheads.
- Targeting capabilities are impressive, with the system able to engage targets at distances ranging from 150 to 200 kilometers (approximately 93 to 124 miles).
Development of THAAD
- THAAD was developed by the United States in response to the challenges posed by Iraq's Scud missile attacks during the Persian Gulf War in 1991.
- In 2008, an early missile warning radar was deployed to Israel as part of the THAAD system, enhancing Israel's defense capabilities.
- Subsequent deployments occurred in 2012 and 2019, further solidifying Israel's position as a formidable military power in the region.
GS1/Geography
Key Facts about Jordan Valley
Source: Nature
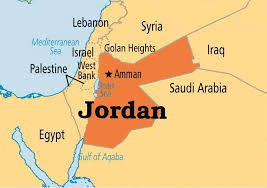
Why in news?
The Shiite militia group, the Islamic Resistance in Iraq, has recently taken responsibility for two drone attacks targeting Israeli locations in the Jordan Valley.
About Jordan Valley:
- The Jordan Valley is a significant rift valley located in the Middle East, specifically in southwestern Asia.
- This valley is a part of the East African Rift System and spans approximately 105 kilometers in length, stretching from the Sea of Galilee in the north to the Dead Sea in the south.
- Geographically, it runs along the Jordan River, marking Jordan's western border with Israel and the West Bank.
- It constitutes over one-fifth of Jordan’s territory, with the lowest point being the Dead Sea, which descends more than 1,400 feet (430 meters) below sea level, making it the lowest natural location on Earth.
- The width of the valley is roughly 6 miles (10 kilometers), although there are areas where it narrows significantly.
- Despite being sparsely populated, the valley is home to several communities, with the city of Jericho in the West Bank being one of the most notable.
- Religiously, the Jordan Valley holds great significance for Christianity, Judaism, and Islam, marking it as a site of immense cultural and spiritual importance.
Recent Developments:
- Drone strikes attributed to the Islamic Resistance in Iraq have heightened tensions in the region.
- The attacks specifically targeted Israeli sites, indicating a potential escalation in conflict.
GS3/Science and Technology
MAHA-EV Mission
Source: AIR
Why in news?
The Anusandhan National Research Foundation has unveiled the Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas - Electric Vehicle (MAHA-EV) Mission.
About MAHA-EV Mission:
- The MAHA-EV Mission is designed to foster the development of essential electric vehicle (EV) technologies.
- Its primary goal is to lessen reliance on imports, encourage domestic innovation, and establish India as a leader in the global EV market.
- This initiative is part of the ANRF's broader Advancement in High-Impact Areas (MAHA) program, which aims to stimulate collaborative efforts across various institutions and disciplines to address significant scientific challenges.
- The mission aspires to expedite technological progress in critical sectors vital for national growth, enhancing India's standing globally in the EV arena.
- It focuses on three major technology verticals:
- Tropical EV Batteries and Battery Cells
- Power Electronics, Machines, and Drives (PEMD)
- Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure
Significance:
- The mission will improve domestic capabilities in designing and developing key EV components.
- It aims to boost India's competitiveness, transforming the country into a central hub for EV component innovation and development.
- By facilitating the transition to electric mobility, the MAHA-EV Mission is expected to contribute significantly to a more sustainable and eco-friendly future.
GS3/Environment
What are Darwin’s Finches?
Source: Science| AAAS

Why in News?
In recent research, biologists have uncovered a significant link between ecology and the process of speciation in Darwin's finches, the renowned birds of the Galapagos Islands.
Overview of Darwin's Finches:
- Darwin's finches, named after the famous naturalist Charles Darwin, are a group of small land birds.
- This group consists of 15 distinct species, with 14 species found in the Galapagos Islands and 1 species on Cocos Island.
- These birds are considered monophyletic, meaning they share a common ancestor that migrated to the Galapagos from Central or South America.
- After their arrival in the Galapagos, the descendants of this ancestor also spread to Cocos Island.
Physical Characteristics:
- While Darwin’s finches are generally similar in shape, size, and coloration, there are notable differences among species.
- Key distinguishing features include variations in diet, habitat preferences, and the size and shape of their beaks.
Diversity of Beak Adaptations:
- These finches are particularly famous for their diverse beak forms, which have evolved to suit different food sources available in their environment.
- Their beaks are adapted for consuming a variety of foods, including seeds, fruits, invertebrates, and even blood.
- This remarkable variation in beak shapes and sizes enables each species to occupy unique ecological niches across the islands.
Adaptive Radiation:
- Darwin's finches serve as a classic example of adaptive radiation, a process where groups of organisms evolve into different species that are each tailored to specific ecological conditions.
|
39 videos|4551 docs|974 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 15th October 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the Right to Unionise in India? |  |
| 2. What are the key issues in the India-Canada diplomatic escalation over the Nijjar killing case? |  |
| 3. What is the role of the Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU)? |  |
| 4. What is UNICEF and what are its main objectives? |  |
| 5. How does UNICEF receive its funding? |  |

































