UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 2nd December 2024 | Current Affairs: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - CLAT PDF Download
GS3/Science and Technology
What India’s AI Safety Institute could do?
Source:The Hindu
Why in news?
In October, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) held discussions with industry leaders and experts about establishing an AI Safety Institute as part of the IndiaAI Mission.
Core Objectives and Focus Areas for the AI Safety Institute
- Setting Standards for AI Safety: The AISI aims to create frameworks, guidelines, and standards for the safe implementation of AI technologies. This initiative is designed to encourage innovation while prioritizing safety without functioning as a regulatory body.
- Enhancing Domestic Capacity: The focus will be on strengthening local capabilities in AI safety. This will leverage India's unique strengths and address specific challenges in the deployment of AI technologies.
- Promoting Multi-Stakeholder Collaboration: It is essential to involve various stakeholders, including government entities, industry leaders, academic institutions, and civil society, to ensure a comprehensive approach to AI safety that incorporates diverse viewpoints.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: The AISI will work on developing tools for assessing and mitigating risks associated with AI technologies, particularly concerning issues like bias, discrimination, and social exclusion.
- Global Engagement: By becoming part of international networks, such as the Bletchley Process, the AISI will engage in global discussions on AI safety, advocating for the concerns of developing countries and contributing to a more inclusive governance framework.
Organizational Structure for Scalability and Independence
- Independence from Regulatory Bodies: The AISI should function independently from rulemaking and enforcement bodies to maintain its focus on research, testing, and standardization rather than regulatory compliance.
- Collaboration with Academic Institutions: Positioning the AISI within academic settings, such as IITs, can provide the institute with independence while utilizing existing research capabilities and expertise.
- Scalable Framework: The organizational design should be adaptable to evolving technologies and the growing demand for oversight in AI safety.
- Technical Research Focus: Prioritizing research and development of local AI safety tools that address the specific challenges faced by India while aligning with global standards is essential.
Strategies for Engaging Stakeholders in AI Safety Governance
- Building Strong Partnerships: The AISI should actively pursue partnerships with key stakeholders across government, industry, academia, and civil society, both nationally and internationally, to promote collaboration on AI safety initiatives.
- Engaging in Global Dialogues: Participation in international discussions about AI governance will position India as a leader in global dialogues on AI safety, facilitating knowledge exchange and the sharing of best practices.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities through outreach programs can enhance awareness of AI-related risks and promote inclusive participation in the development of AI governance policies.
- Establishing Voluntary Compliance Tools: Creating voluntary compliance toolkits can assist industries in adopting best practices for AI safety without imposing stringent regulatory requirements that might hinder innovation.
- Continuous Feedback Mechanisms: Implementing ongoing feedback systems from stakeholders will help ensure that the AISI remains responsive to new challenges in AI technology and governance.
Mains PYQ:
What are the main socio-economic implications arising out of the development of IT industries in major cities of India? (UPSC IAS/2021)
GS3/Science and Technology
What is a Solar Storm?
Source:NASA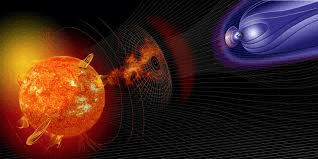
Why in News?
Scientists have uncovered evidence of an immense solar storm that struck Earth around 664–663 BCE.
About Solar Storm:
- A solar storm refers to a sudden eruption of particles, energy, magnetic fields, and material ejected into the solar system by the Sun.
What causes a solar storm?
- The Sun’s complex magnetic fields become twisted as it rotates, with the equator spinning faster than the poles.
- Solar storms usually start when these contorted magnetic fields become so stressed that they snap and reconnect, a process known as magnetic reconnection, releasing vast amounts of energy.
- These intense eruptions can produce various phenomena, including:
- A bright flash of light termed a solar flare.
- A radiation storm, which is a burst of solar particles sent into space at high velocities.
- A massive cloud of solar material known as a coronal mass ejection.
Effects on Earth:
- When a solar storm is directed towards Earth, it can lead to significant disturbances in the planet’s magnetic field, termed a geomagnetic storm.
- Such storms can result in various effects, including:
- Radio blackouts.
- Power outages.
- Stunning auroras that illuminate the night sky.
- Although solar storms do not directly harm humans on Earth, our planet’s magnetic field and atmosphere serve as protective barriers against the most severe impacts of these storms.
GS3/Environment
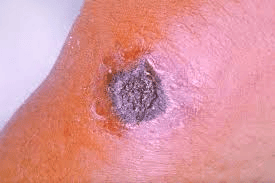
What is Anthrax?
Source: Deccan Herald
Why in News?
A female elephant died due to suspected anthrax at the Bandipur Tiger Reserve recently.
About Anthrax:
- Anthrax is a rare but serious disease caused by the spore-forming bacterium, Bacillus anthracis.
- This bacterium is naturally present in soil worldwide and typically affects livestock and wild animals.
- It produces spores capable of surviving in the environment for many years.
Transmission
- Livestock and wild animals can contract anthrax by inhaling, ingesting, or drinking contaminated soil, plants, or water.
- Humans are usually infected through direct contact with infected animals or contaminated animal products.
- Infection can also occur via contaminated food, water, or soil.
- Although anthrax does not spread from person to person, skin lesions may be contagious through contact.
- Human infections primarily affect the skin, gastrointestinal system, or lungs.
Symptoms:
Depending on the infection route, symptoms can include:
- Chest pain and difficulty breathing.
- Fever accompanied by excessive sweating.
- Headaches or muscle pain.
- Itchy blisters or bumps on the skin.
- Skin ulcers with a characteristic black center.
- Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and bloody diarrhea.
- Swollen lymph nodes.
Treatment
Effective treatment for anthrax involves antibiotics
.Common antibiotics used include:
- Doxycycline
- Amoxicillin
- Ciprofloxacin
- Vaccination against anthrax is recommended solely for individuals at risk, such as those working in areas where anthrax is prevalent.
GS1/History & Culture
Ajmer Sharif Dargah - A Spiritual and Cultural Jewel of Rajasthan
Source:Indian Express
Why in news?
Recently, an Ajmer court has accepted a petition that requests a survey of the Ajmer Sharif Dargah, the shrine of Sufi saint Khwaja Moinuddin Chishti. The petition claims that the dargah was constructed on the remnants of demolished Hindu and Jain temples.
Background – Origin of the city
- Ajmer, initially known as Ajaymeru, served as the capital of the Chauhan Rajputs, who governed parts of modern-day Rajasthan, Haryana, Delhi, and Uttar Pradesh from the 7th to the 12th centuries CE.
- The city was founded by Ajaydeva during the mid-12th century.
The Ghurid Invasion and Decline
- In 1192, Ajmer was invaded by Muhammad of Ghor, leading to the defeat of Prithviraj Chauhan in the Second Battle of Tarain.
- The Ghurid forces reportedly destroyed temples and plundered the city, as noted by Har Bilas Sarda in his work "Ajmer: Historical and Descriptive" (1911).
- Sarda’s writings are referenced in the court petition regarding the dargah’s location over demolished temples, though he does not assert that a temple was specifically destroyed to construct the shrine.
- The city experienced a decline for nearly 400 years, only to be revitalized during the reign of Mughal Emperor Akbar (1556-1605).
Establishment of Ajmer Sharif Dargah
- The mausoleum of Khwaja Moinuddin Chishti was built in the late 15th century.
- According to Sarda, the burial site included a cellar that previously contained an image of Mahadeva, cared for by a Brahman family.
Initial Burial and Early Neglect
- Khwaja Moinuddin Chishti was buried in 1236 at the location where he lived, but initially, no mausoleum was constructed, leading to a lapse in his memory for over two centuries.
Construction by the Khaljis (1460s)
- Sultan Mahmud Khan Khalji of Malwa, along with his son Ghiyasuddin, built the first stone mausoleum and the grand Buland Darwaza.
- This gateway, featuring three-storied chatrees, is believed to have utilized materials from a demolished Jain temple.
Expansion under the Mughals
- In 1532, the current white marble dome was constructed during the reign of Humayun.
- Akbar's reverence for Chishti saints led to extensive developments in Ajmer, including the construction of the Akbari Masjid in the 1570s.
- Jahangir enhanced the shrine by adding a gold railing around the saint's tomb in 1616, with further expansions occurring under Shah Jahan.
Architectural marvel
- The Dargah complex is an impressive example of Indo-Islamic architecture, featuring a white marble shrine embellished with intricate silver and gold decorations.
- The Nizam Gate, donated by the Nizam of Hyderabad in the 19th century, signifies the saint’s broad reverence.
- The Dargah reflects Mughal architectural styles, with contributions spanning from Humayun to Shah Jahan.
Key Features of the Complex
- The saint’s grave is enclosed within a silver railing and surrounded by a marble screen.
- A prayer room, constructed by Chimni Begum, Shah Jahan's daughter, provides a tranquil area exclusively for women.
Universal Appeal of Ajmer Sharif Dargah
- Recognized as one of India’s holiest Muslim shrines, Ajmer Sharif attracts individuals from various faiths, symbolizing religious tolerance and syncretism.
- Visitors include devotees from diverse backgrounds, alongside Bollywood celebrities, who come to seek blessings and spiritual comfort.
The Urs Festival
- The six-day Urs festival commemorating the death anniversary of Khwaja Moinuddin Chishti is the most significant event at the shrine.
- This festival features qawwali performances, special prayers, and offerings of chaddars at the tomb, drawing thousands of devotees from around the world to celebrate spirituality and devotion.
Early Life of Khwaja Moinuddin Chishti
- Khwaja Moinuddin Chishti was born in 1141 in Sistan (Persia). After being orphaned at 14, he began his spiritual journey following an encounter with the mystic Ibrahim Qandozi.
- He pursued studies in various fields, including theology, philosophy, and ethics, at seminaries in Bukhara and Samarkand.
Spiritual Mentorship and Travels
- Moinuddin met his mentor, Khwaja Usman Harooni, in Herath (Afghanistan) and was initiated into the Chishti order.
- He accepted Qutbuddin Bakhtiyar Kaki as his first disciple and traveled to Multan, where he learned Sanskrit and interacted with Hindu scholars.
- From Multan, he journeyed to Lahore, Delhi, and ultimately settled in Ajmer in 1191.
Life in Ajmer and Legacy
- Upon settling in Ajmer, Moinuddin established a modest home that became a refuge for the poor and needy.
- His acts of generosity and selflessness earned him the title Gharib Nawaz, meaning "Friend of the Poor," solidifying his status as a compassionate spiritual figure.
The Chishti Order in India
- The Chishti Sufi order, which Moinuddin Chishti followed, along with later saints like Hazrat Nizamuddin Auliya, incorporated local practices that were often viewed as heretical by orthodox Islam.
- Sufism, a mystical branch of Islam, emerged between the 7th and 10th centuries as a counter-response to orthodoxy and materialism, emphasizing tolerance and spiritual devotion.
- Chishti saints preached themes of acceptance and inclusivity, highlighting devotion as the path to achieving spiritual enlightenment.
GS3/Environment
Madhav National Park
Source:Telegraph India
Why in News?
In a significant step towards conservation, the National Tiger Conservation Authority has given preliminary approval to designate Madhav National Park in Shivapuri district as a tiger reserve.
About Madhav National Park:
- Location:
- Madhav National Park is located in Madhya Pradesh.
- The park is positioned on the northern edge of the Central Highlands of India, part of the Upper Vindhyan Hills, characterized by a mix of plateaus and valleys.
- Lakes:
- The park features two significant lakes: Sakhya Sagar and Madhav Sagar, which are vital for aquatic biodiversity and serve as essential resources for terrestrial wildlife.
- Rivers:
- The northern area contains a drainage pattern that directs towards the north and northeast, contributing to the Amarnadi river catchment.
- The park also encompasses the catchment area of the Sind river, which flows along its eastern boundary.
- Geology:
- The eastern section of the park is composed of sedimentary rocks from the Vindhyan system, primarily consisting of sandstone, shale, and limestone.
- Vegetation:
- The forests in Madhav National Park are classified as Northern tropical dry deciduous mixed forests and Dry Thorn Forests, typical of Northwestern Madhya Pradesh.
- Flora:
- The park is home to various plant species including Kardhai, Salai, Dhaora, and Khair.
- The understory is predominantly made up of Ber, Makor, and Karonda, with Jamun and Mahua found along the nullahs (small watercourses).
- Fauna:
- The park hosts a variety of wildlife, including Nilgai, Chinkara, and various deer species such as Chital, Sambar, and Barking Deer.
- Predators like Leopard, Wolf, Jackal, Fox, and Wild Dog are also part of the park's ecosystem.
GS3/Environment
Red-breasted Flycatcher
Source:The Hindu
Why in News?
Recently, the Red-Breasted Flycatcher, a migratory bird from Eastern Europe, was spotted at Ameenpur Lake in Hyderabad, seeking refuge from the severe winter.
About Red-breasted Flycatcher:
- Scientific Name: Ficedula parva
- This bird is classified as a small passerine, measuring between 11 to 12 cm in length.
- It belongs to the Old World Flycatcher family.
- The Red-breasted Flycatcher is occasionally seen feeding on figs from trees such as banyan and peepal in urban gardens.
Appearance:
- Males are characterized by a striking reddish-orange throat that extends to the upper breast.
- Females, in contrast, have an overall brown coloration.
- This species can be easily identified by the structure of their toes, which are arranged with three pointing forward and one backward, allowing for efficient clinging to branches.
Migration Behavior:
- The Red-breasted Flycatcher migrates to South Asia during winter months to escape harsh weather conditions.
- In South Asia, they thrive in moderate temperatures and find an ample food supply.
Breeding Habits:
- This species breeds from spring to summer in deciduous mixed forests across Eastern Europe and Central Asia.
- During the winter months, typically from September to March, they migrate to diverse habitats such as forests, woodlands, orchards, parks, and roadside trees throughout the Indian Subcontinent.
- In peninsular India, they can be observed during the winter season from October to March.
Conservation Status:
- The Red-breasted Flycatcher is classified as "Least Concern" by the IUCN, indicating a stable population.
GS3/Defence & Security
Vadhavan Port
Source:The Hindu Business Line

Why in news?
The Vadhavan greenfield port, currently being constructed near Dahanu in Maharashtra, is expected to significantly enhance India's container trade capacity upon its completion.
Overview of Vadhavan Port:
- The Vadhavan Port is set to be an all-weather, deep-draft major port located in the Palghar District.
- This project is being executed by Vadhavan Port Project Limited (VPPL), a special purpose vehicle (SPV) established by the Jawaharlal Nehru Port Authority (JNPA) and the Maharashtra Maritime Board (MMB), with respective shareholdings of 74% and 26%.
- The total estimated cost of the project, which includes land acquisition, is approximately 76,220 Crore INR.
- It is scheduled for completion by the year 2034 and is projected to rank among the top 10 ports globally.
Infrastructure and Facilities:
- The port will feature nine container terminals, each measuring 1000 meters in length, in addition to four multipurpose berths (including a coastal berth), four liquid cargo berths, a Ro-Ro berth, and a berth for the Coast Guard.
- By 2029, the first four terminals are expected to be operational, with the remaining five terminals to be completed by 2034.
Capacity and Economic Impact:
- The project aims to create a total capacity of 298 million metric tons (MMT) per annum, which includes approximately 23.2 million TEUs (twenty-foot equivalent units) designated for container handling.
- The port is anticipated to facilitate export-import trade through key trade corridors, including the India Middle East Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEC) and the International North South Transportation Corridor (INSTC).
- Overall, the Vadhavan Port is expected to be a transformative initiative for India's maritime trade landscape.
GS3/Economy
 |
Download the notes
UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 2nd December 2024
|
Download as PDF |
North Eastern Tea Association (NETA)
Source:The Hindu
Why in news?
The North Eastern Tea Association (NETA) has requested the Ministry of Commerce and Industry to allow tea producers to market their products through both private sales and public auction systems. This follows a gazette notification issued on February 26, 2024, which mandates that all dust teas must be sold via public auctions.
About
- NETA is an association representing tea producers, with its headquarters located in Golaghat, Upper Assam.
- It was established in 1981.
- The association is a significant part of the Joint Forum and the Consultative Committee of Plantation Associations (CCPA), specifically within the Assam Valley branch.
- NETA's primary goal is to advocate for its members' interests and bolster the tea industry in Assam.
Structural Mandate
- NETA has a robust presence in Golaghat, Assam.
- It plays a crucial role in representing tea producers and is pivotal for the advancement of Assam’s tea industry.
- NETA advocates for enhancements within the tea sector, offers policy suggestions, and guides the development of the tea industry.
Powers and Functions
- Advisory Role: NETA provides expert opinions and guidance to both the Assam government and its members regarding issues affecting the tea industry.
- Policy Advocacy: The association encourages changes in governmental policies to benefit the tea sector, such as proposing the relocation of the Tea Board of India's headquarters to Guwahati.
- Industry Growth: NETA promotes the production of high-quality tea and counsels growers on improving tea quality to attract international buyers.
- Small Tea Grower Representation: The association advocates for changes to the definition of Small Tea Growers, suggesting that those owning up to 50.6 hectares of land should be recognized as small growers.
- Government Relations: NETA offers recommendations to the government aimed at enhancing and expanding the tea industry in Assam.
GS2/Polity
SC Mandates Prior Sanction to Prosecute Public Servants under PMLA
Source:Indian Express

Why in news?
The Supreme Court, in its ruling on November 6, has established for the first time that the Enforcement Directorate (ED) must obtain prior sanction to prosecute public servants on charges of money laundering.
About Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002:
The Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), 2002 was enacted in January 2003. The Act aims to combat money laundering in India and has three primary objectives:
- To prevent and control money laundering.
- To confiscate and seize properties obtained from laundered money.
- To address any other issues related to money laundering in India.
Section 3 of the Act defines the offence of money laundering. The Act has been amended by the Prevention of Money Laundering (Amendment) Act, 2009 and the Prevention of Money Laundering (Amendment) Act, 2012.
Major Provisions of the Act:
- The Act requires banking companies, financial institutions, and intermediaries to verify and maintain records of the identity of all clients and all transactions.
- PMLA authorizes the Directorate of Enforcement (ED) to investigate cases involving money laundering offences and to attach properties involved in such activities.
- ED, as a law enforcement and economic intelligence agency, was established to enforce economic laws and tackle economic crimes in India.
- The Act provides for the establishment of an Adjudicating Authority to exercise jurisdiction and authority to confirm property attachments or confiscations.
- It also sets up an Appellate Tribunal to handle appeals against orders from the Adjudicating Authority.
- PMLA allows the Central Government to enter into agreements with foreign governments to enforce PMLA provisions.
News Summary:
Delhi's former Chief Minister Arvind Kejriwal and Congress MP P. Chidambaram have requested relief in their respective trials, citing a recent ruling by the Supreme Court as a precedent. The Delhi High Court is yet to decide on Kejriwal's plea related to the excise policy scam, while Chidambaram’s trial in the Aircel-Maxis case was stayed on November 20.
Supreme Court Precedent (November 6, 2023):
The Supreme Court ruled that prior government sanction is now essential for prosecuting public servants if the alleged offences are connected to their official duties. This is grounded in Section 197 of the Criminal Procedure Code (CrPC).
Understanding the Legal Framework:
Prior Sanction Provision:
CrPC Section 197 states that courts cannot take cognizance of offences committed by public servants in their official capacity without prior government approval.
- Exceptions exist for serious offences such as sexual harassment, trafficking, or rape, where no sanction is required.
Landmark Case:
- In the case of Devinder Singh v. State of Punjab (2016), the Supreme Court clarified that this provision does not protect corrupt activities disguised as official duties.
Supreme Court’s Recent Decision:
- The Supreme Court upheld a 2019 ruling from the Telangana High Court, which reversed the trial court’s cognizance of charges against IAS officers Bibhu Prasad Acharya and Adityanath Das in a money laundering case tied to former Andhra Pradesh CM Jagan Mohan Reddy.
- PMLA's Section 65 aligns with CrPC Section 197, necessitating prior sanction for public servants.
- The connection between the alleged criminal acts and the accused's duties makes prior sanction necessary.
Application to Current Cases:
- Chidambaram argued that the trial court’s cognizance of charges against him by the ED violated this ruling, as no prior sanction was obtained.
- Kejriwal similarly challenged the ED's chargesheet in the liquor policy scam, noting that the CBI had obtained prior sanction for related allegations.
Impact of the Prior Sanction Requirement:
- Investigations under the PMLA remain valid, but trial courts cannot proceed with charges against public servants without prior sanction.
- Convictions may be overturned on appeal if it is shown that prior sanction was not secured.
- Public servants can raise this argument at any stage of the trial, even after a conviction (as established in P K Pradhan v. State of Sikkim, 2001).
Challenges to Prosecution:
- Prosecuting agencies may experience delays as they must obtain government approvals before proceeding with cases.
Significance of the Ruling:
- This provision aims to protect honest officials carrying out their duties from baseless prosecutions while ensuring accountability for misconduct.
- High-profile individuals are using this ruling to challenge the proceedings against them.
- The ruling establishes a significant precedent for cases involving public servants under the PMLA.
GS1/Indian Society
India’s cities, their non-communicable disease burden
Source: The Hindu

Why in news?
The recent cardiac arrest and subsequent death of a Bengaluru Metropolitan Transport Corporation (BMTC) bus driver while on duty has sparked conversations about worsening health outcomes in urban areas.
Primary Risk Factors Contributing to Rising NCD Burden:
- High-Stress Work Environments: Urban workers, particularly bus drivers, often experience high stress due to long hours, irregular schedules, and demanding job conditions. A BMTC study revealed that over 40% of employees aged 45-60 are at risk for cardiovascular diseases, worsened by continuous driving and unhealthy eating habits.
- Poor Nutrition and Lifestyle: Many workers lack access to nutritious food options and opportunities for physical activity, leading to increased obesity, hypertension, and diabetes rates. Alarming health conditions within the BMTC workforce are often linked to lifestyle choices made under stress.
- Lack of Health Insurance and Support: Many informal workers do not have health insurance or regular health screenings, delaying diagnosis and treatment of NCDs and increasing the risk of severe health events, such as heart attacks.
- Socioeconomic Marginalization: A significant number of urban residents live in slums or informal settlements, with limited access to healthcare. This socioeconomic status results in poorer health outcomes and a higher incidence of NCDs.
Strengthening Urban Health Systems:
- Improving Access to Primary Healthcare: Urban health systems should enhance access to primary healthcare services for marginalized communities by expanding facilities in underserved areas and ensuring affordability and cultural relevance.
- Implementing Regular Health Screenings: Regular health evaluations for high-risk groups, such as bus drivers, should be mandated to identify risk factors early and facilitate timely interventions.
- Integrating Health Services with Employment Policies: Employers should collaborate with health departments to create wellness programs, including stress management workshops and nutrition education tailored for their workforce.
- Community-Based Health Promotion: Local organizations can effectively educate communities about NCD risks and promote healthy lifestyles through workshops and outreach programs that directly engage residents.
Role of Public Awareness and Community Engagement:
- Raising Awareness About NCD Risks: Public campaigns can inform individuals about the importance of regular health screenings and lifestyle changes to mitigate NCD risks, empowering communities to take charge of their health.
- Encouraging Community Participation: Involving community members in health promotion activities fosters ownership over health outcomes. Community-led initiatives can effectively address local health issues by tailoring solutions to specific needs.
- Utilizing Technology for Monitoring Health: Digital tools can enable real-time monitoring of health metrics for at-risk populations, allowing for proactive management of conditions such as hypertension and diabetes.
- Creating Support Networks: Establishing networks among workers can provide emotional support and resource sharing for managing health issues collectively, especially beneficial for those in high-stress jobs.
Way Forward:
- Strengthen Urban Primary Healthcare: Enhance access to affordable and culturally relevant primary health services, implement regular screenings for high-risk groups, and integrate wellness programs with employment policies for vulnerable workers.
- Promote Community-Led Health Initiatives: Engage local organizations and residents to raise awareness about NCD risks, encourage healthy lifestyles, and utilize digital tools for real-time health monitoring and proactive care.
Mains PYQ:“Besides being a moral imperative of a Welfare State, primary health structure is a necessary precondition for sustainable development.” Analyse.
GS2/Governance
PM attends 59th All India Conference of Director Generals/Inspector Generals of Police
Source:PM India

Why in news?
PM Modi attended the 59th All India Conference of Director Generals/Inspector Generals of Police in Bhubaneswar on December 1. The conference, which lasted three days, was inaugurated by Home Minister Amit Shah on November 29. This event serves as a crucial platform for discussing issues related to national security, law enforcement strategies, and collaboration among various security and police agencies across India. The previous conference took place in Jaipur, Rajasthan in January 2023.
Key highlights of the speech delivered by PM Modi
About
- The three-day conference, running from November 29 to December 1, 2024, was conducted in a hybrid format in Bhubaneswar, Odisha.
- Attendees included the Union Home Minister, Principal Secretary to the Prime Minister, National Security Advisor, Ministers of State for Home, and the Union Home Secretary.
- Directors General of Police (DGsP) and Inspectors General of Police (IGsP) from all States and Union Territories were present physically, while over 750 officers participated virtually.
- This conference represents the culmination of extensive discussions involving police and intelligence officers from district, state, and national levels on various identified themes.
- Hosted by: Intelligence Bureau (IB).
Outcomes
- Best practices from different States and Union Territories were shared to facilitate mutual learning.
- In-depth discussions focused on existing and emerging challenges to national security, which included:
- Counter-terrorism
- Left-wing extremism
- Cybercrime
- Economic security
- Immigration
- Coastal security
- Narco-trafficking
- Deliberations also addressed:
- Emerging security concerns along the borders with Bangladesh and Myanmar
- Trends in urban policing and strategies to counter malicious narratives
- A review was conducted regarding the implementation of newly enacted major criminal laws and the security situation in the neighborhood.
Addressing Deepfakes and Digital Threats
- PM Modi highlighted the significance of leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) to combat deepfakes, which can negatively impact social and familial relationships.
- He proposed the formation of special teams to tackle digital fraud, emphasizing the importance of updating crime data and raising public awareness during events like parents-teachers meetings.
- The Prime Minister stressed the necessity of dismantling the narco-trafficking nexus and called for stringent actions from the top down.
- Previously, PM Modi had expressed concerns regarding 'digital arrests' and deepfakes in his Mann ki Baat address in November 2023.
Enhanced Police Engagement in Border Areas
- Police personnel stationed in border regions were instructed to spend nights in villages alongside senior officials to better understand local issues and foster community trust.
Utilizing Technology for Policing
- Modi advocated for the adoption of technology to alleviate the workload of police constables and suggested that police stations should serve as central hubs for resource distribution.
Combating Cyber Fraud and Crime
- The Prime Minister underscored the need for electronic updates of crime data and to enhance countermeasures against cyber-related crimes.
- According to the Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C), India reportedly lost around Rs 11,333 crore to cyber fraud by September 2024.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has established a high-level committee, and the I4C is collaborating with states and the private sector to address these issues.
- More than 6.69 lakh SIM cards and 1.32 lakh IMEIs linked to cyber crimes have been blocked, saving over Rs 3,431 crore through proactive measures by I4C.
Urban Policing and Emerging Security Concerns
- Modi proposed expanding successful urban policing initiatives to cover all 100 cities and advocated for the SMART policing approach, which stands for:
- Strategic
- Meticulous
- Adaptable
- Reliable
- Transparent
- PM Modi commemorated Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, recalling his "unparalleled contribution" to the Ministry of Home Affairs and urging the security establishment to honor his 150th birth anniversary by setting goals to improve police image and professionalism.
|
969 docs|678 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 2nd December 2024 - Current Affairs: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - CLAT
| 1. What are the main objectives of India’s AI Safety Institute? |  |
| 2. What are the potential impacts of a solar storm on Earth? |  |
| 3. How is anthrax transmitted and what are its symptoms? |  |
| 4. What makes the Ajmer Sharif Dargah significant in Rajasthan? |  |
| 5. What is the role of the North Eastern Tea Association (NETA) in the tea industry? |  |

































