UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 15th December 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/Polity
Impeachment of South Korea's President Yoon Suk Yeol
Source: Times of India
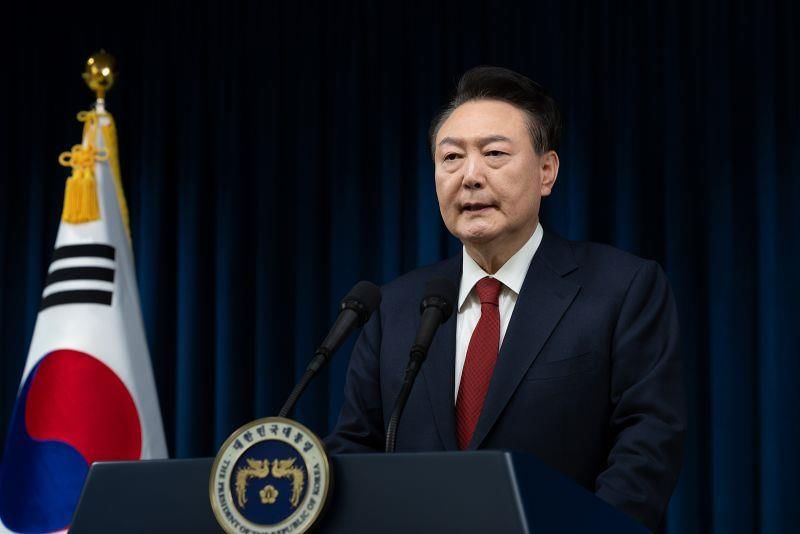 Why in News?
Why in News?
South Korean President Yoon Suk Yeol is in the spotlight following his impeachment by the opposition-led parliament. This decision came after his controversial attempt to impose martial law, a move that shocked the nation and raised questions about his governance and the state of democracy in South Korea.
- Yoon Suk Yeol faced political unrest and dissatisfaction during his presidency, leading to significant protests.
- The declaration of martial law was intended to address national security concerns but was perceived as a power grab.
- The impeachment process emphasized the importance of democratic principles and accountability in governance.
Additional Details
- Background of the Incident: Yoon's presidency was marred by public dissatisfaction driven by economic issues and allegations of power misuse, culminating in mass protests against his administration.
- Martial Law Declaration: On December 3, 2024, Yoon declared martial law to manage escalating unrest, allowing military deployment and suspension of civil rights, which critics viewed as unconstitutional.
- Aftermath: The public backlash was immediate, leading to significant protests and a swift repeal of martial law by the National Assembly, which included members from Yoon's own party.
- Impeachment Process: The National Assembly initiated impeachment proceedings based on Yoon's abuse of power and failure to protect constitutional rights, culminating in a Constitutional Court review.
- Significance of the Impeachment: This event reinforced South Korea's commitment to democratic norms, highlighting the resilience of its political institutions in the face of challenges.
- India’s Stance: India, maintaining a neutral position, emphasized the need for democratic governance and constitutional processes while continuing diplomatic engagements with South Korea.
The impeachment of President Yoon Suk Yeol represents a crucial moment in South Korea's political landscape, reflecting the nation's dedication to upholding democratic values even amid significant challenges. This incident illustrates the necessity for leaders to adhere to democratic principles to maintain public trust and international credibility.
GS3/Environment
Malwa Canal Project
Source: Hindustan Times
 Why in News?
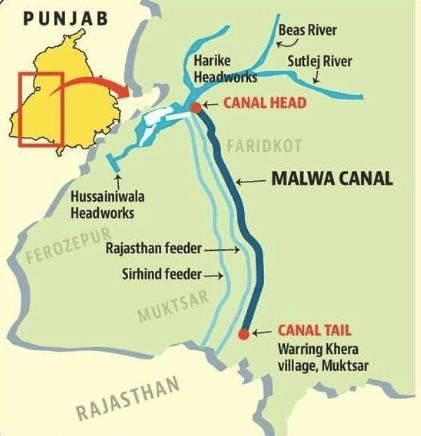
Why in News?The Malwa Canal Project is significant due to its projected impact on irrigation and water management in Punjab, India. Recently, it was announced that around 1.30 lakh trees and plants may be removed to facilitate the construction of this extensive canal system.
- The Malwa Canal is a planned irrigation project in Punjab, marking the first major canal construction in the state since independence.
- Estimated to cost Rs 2,300 crore, the canal will stretch 150 kilometers, beginning at Harike headworks on the Sutlej River.
- The project aims to serve the irrigation requirements of nearly 2 lakh acres in southern Punjab.
Additional Details
- Canal Specifications: The Malwa Canal will be approximately 150 km long, 50 feet wide, and 12.6 feet deep, designed to carry a flow of 2,000 cusecs of water.
- Location: It will flow from Ferozepur district to Warring Khera village in Muktsar district, running parallel to the Sirhind Feeder and Rajasthan Feeder canals.
- Environmental Impact: The construction is expected to result in the felling of 1.30 lakh trees, raising concerns about the ecological consequences of the project.
The Malwa Canal Project represents a major development in Punjab's irrigation infrastructure, but it also brings challenges related to environmental sustainability and resource management.
GS3/Environment
Sultanpur National Park
Source: Times of India
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Additional Chief Secretary (ACS) of Forest and Wildlife has requested the district administration to compile a report regarding illegal constructions surrounding Sultanpur National Park. This report will be submitted to the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change of India (MoEF & CC).
- Sultanpur National Park is located in the Gurgaon district of Haryana, approximately 46 km from Delhi.
- Recognized as a Ramsar site in 2021, it plays a crucial role as a habitat for numerous migratory bird species.
Additional Details
- Location: Sultanpur National Park, previously known as Sultanpur Bird Sanctuary, covers an area of 1.42 sq.km and features marshy lakes and floodplains. It includes a core area of 1.21 sq.km, primarily consisting of the Sultanpur Lake/Jheel.
- Hydrology: The Sultanpur Jheel is a seasonal freshwater wetland with varying water levels, mainly fed by the River Yamuna’s Gurgaon canal and runoff from nearby agricultural fields.
- Flora: The park's vegetation includes tropical and dry deciduous species like grasses, dhok, khair, tendu, jamun, neem, berberis, and various Acacia species.
- Fauna: Over 320 bird species have been recorded, making it an important wintering ground for migratory birds from regions like Russia, Turkey, Afghanistan, and Europe.
- Notable bird species include the Common Hoopoe, Purple Sunbird, Black Francolin, Little Cormorant, Indian Cormorant, Siberian Crane, and Greater Flamingo.
- Other seasonal migrants include the Common Teal, Common Greenshank, and Ruff, alongside resident wildlife such as Nilgai, Sambar, golden jackals, wild dogs, striped hyenas, Indian porcupine, and mongoose.
The park's ecological significance and biodiversity make it critical to monitor and address any illegal constructions that threaten its integrity.
GS3/Economy
India’s NPA Crisis
Source: Economic Times
 Why in News?
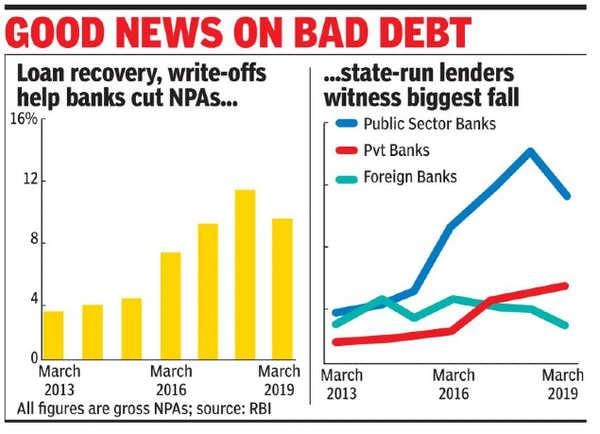
Why in News?India's banking sector is currently facing a significant challenge with a sharp rise in non-performing assets (NPAs). An RTI inquiry conducted by a prominent newspaper unveiled that as of March 2019, a staggering 43% of the total NPAs, amounting to ₹4.02 lakh crore, was owed by just 100 companies. This situation underscores systemic issues within the banking framework and highlights the concentration of bad loans among a select group of borrowers.
- The NPA crisis reflects deep-seated problems in India’s banking system.
- A few large companies account for a disproportionate share of total NPAs, indicating a lack of diversification in lending.
- Ongoing recovery efforts are crucial to restoring the health of the banking sector.
Additional Details
- Definition of Non-Performing Assets (NPAs): An NPA is a loan or advance for which the principal or interest payment has been overdue for more than 90 days. For banks, loans are considered assets since they generate interest income. When customers fail to make payments, these assets become "non-performing," meaning they no longer earn income for the bank.
- Classification of Assets:According to RBI guidelines, NPAs are categorized into:
- Substandard Assets: NPAs that have been overdue for less than or equal to 12 months.
- Doubtful Assets: Assets that have been in the substandard category for over 12 months.
- Loss Assets: Considered uncollectible and of such little value that they should not be maintained as bankable assets.
- NPA Provisioning: Banks must set aside a certain percentage of their loans as provisions. The standard provisioning rate ranges from 5% to 20%, depending on the business sector and the borrower’s repayment capacity. For NPAs, 100% provisioning is mandated under Basel-III norms.
- GNPA and NNPA:These metrics help assess the NPA situation:
- GNPA: Refers to the total gross NPAs of a bank in a given period.
- NNPA: This figure represents gross NPAs minus the provisions made by the bank, providing a clearer picture of the bank’s recoverable assets.
Impact on the Banking Sector
- As of March 2023, 51 of the top 100 companies still carried debts totaling ₹3.58 lakh crore, showing ongoing financial distress.
- Many of these defaulters are involved in critical sectors such as oil & gas, power generation, mining, and infrastructure.
- Recovery prospects are bleak, with 82 of the top 100 companies under bankruptcy, a third of which are facing liquidation.
- High-profile defaults, including Jet Airways and IL&FS subsidiaries, suggest minimal recovery for lenders.
- Limited funds available for lending may lead banks to raise interest rates, potentially stifling economic growth and increasing unemployment.
The concentration of bad loans among a few corporate giants raises significant concerns regarding governance and accountability within India's banking system. While efforts to recover these loans are ongoing, the NPA crisis highlights the urgent need for enhanced regulatory oversight and improved lending practices to avert similar crises in the future.
GS1/Indian Society
Konda Reddi Tribe
Source: The Hindu Why in News?
Why in News?
The Konda Reddi tribe is an intriguing example of a community that maintains its unique cultural identity while facing the pressures of modernity. Their traditional lifestyle and practices offer valuable insights into the balance between heritage and contemporary influences.
- The Konda Reddi is classified as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG).
- They inhabit the banks of the Godavari River in Andhra Pradesh.
- The tribe predominantly practices Folk Hinduism, focusing on local traditions and deities.
Additional Details
- Language: The Konda Reddi tribe speaks Telugu with a distinct accent.
- Family Structure: Their social organization is patriarchal and patrilocal, with monogamy being the norm, although polygamous arrangements exist. Various socially accepted marriage practices include negotiations, love matches, elopement, service, capture, and exchange.
- Political Organization: They have a social control institution known as Kula Panchayat, and each village is led by a hereditary headman called Pedda Kapu, who also serves as the village priest.
- Livelihood: The Konda Reddi primarily engage in shifting cultivation, relying on forest resources and cultivating jowar as their staple food. They also grow commercial crops like cashew, niger, chilli, and cotton through the Podu cultivation method.
- Architecture: Their houses are characterized by a unique circular architectural style, featuring mud walls and thatched roofs, reminiscent of the Bhunga architecture found in Gujarat’s Kachchh region.
The Konda Reddi tribe's rich cultural heritage and sustainable practices offer a glimpse into the complexities of preserving tradition in a rapidly changing world. Their deep connection to nature not only sustains their community but also serves as a vital lesson in ecological balance.
GS3/Science and Technology
Dulcibella camanchaca: A New Discovery in the Atacama Trench
Source: Economic Times
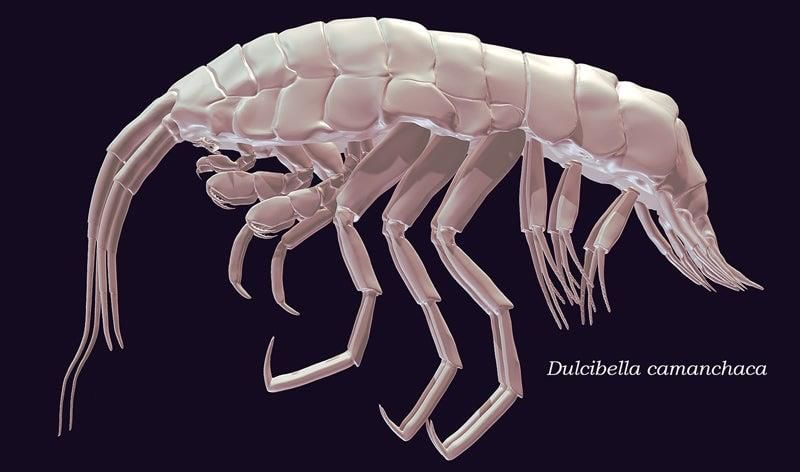 Why in News?
Why in News?Researchers from the University of Concepción in Chile and the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution in the US have made a remarkable discovery of a new predatory amphipod species, named Dulcibella camanchaca, in the Atacama Trench. This finding adds significant knowledge to the deep-sea biodiversity catalog.
- Dulcibella camanchaca: A newly identified predatory amphipod species.
- Habitat: Discovered at a depth of 7,902 meters in the Atacama Trench.
- Significance: It represents a new genus within the Eusiridae family.
- Physical Features: Measures just under 4 centimeters and possesses unique hunting appendages.
Additional Details
- Predatory Behavior: Unlike many scavenging amphipods, this species actively preys on other amphipods, playing a crucial role in the deep-sea food web.
- Unique Adaptations: Exhibits pale coloring, typical of deep-sea species, which helps it thrive in the darkness of its environment.
- Atacama Trench: This trench is located along the eastern South Pacific Ocean, plunging to depths over 8,000 meters and characterized by extreme pressure and darkness.
- Geographical Isolation: The Atacama Trench is one of the most isolated hadal regions, lying under eutrophic surface waters and featuring high sediment loads.
The discovery of Dulcibella camanchaca not only highlights the biodiversity present in extreme environments but also emphasizes the importance of ongoing research in deep-sea ecosystems.
GS2/Polity
Appointment of a Permanent Vice-Chancellor at TISS
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Tata Institute of Social Sciences (TISS) in Mumbai is preparing to appoint its first permanent Vice-Chancellor after a delay exceeding one year. The selection committee is set to conduct in-person interviews with ten shortlisted candidates for the position.
- TISS is Asia's oldest institute for professional social work education.
- It was founded in 1936 as the Sir Dorabji Tata Graduate School of Social Work.
- TISS was renamed in 1944 and became a deemed university in 1964.
- The institute offers a range of academic programs in the Social Sciences.
Additional Details
- Tata Institute of Social Sciences (TISS): TISS is a multi-campus, public-funded research university located in Mumbai, India, renowned for its focus on social sciences and its commitment to field activities.
- Academic Programs: The institute offers doctoral degrees in various fields, including Management, Labour Studies, Development Studies, and more.
- Historical Context: Since its inception, TISS has actively engaged in fieldwork, responding to significant national events such as the Partition of India and natural disasters like the Bhopal disaster and the Uttarakhand floods.
The upcoming appointment of a Vice-Chancellor marks a significant step for TISS, reinforcing its leadership as a premier institution in social sciences education and research.
GS3/Science and Technology
 |
Download the notes
UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 15th December 2024
|
Download as PDF |
ISRO's CE20 Cryogenic Engine Hot Test
Source: Times of India
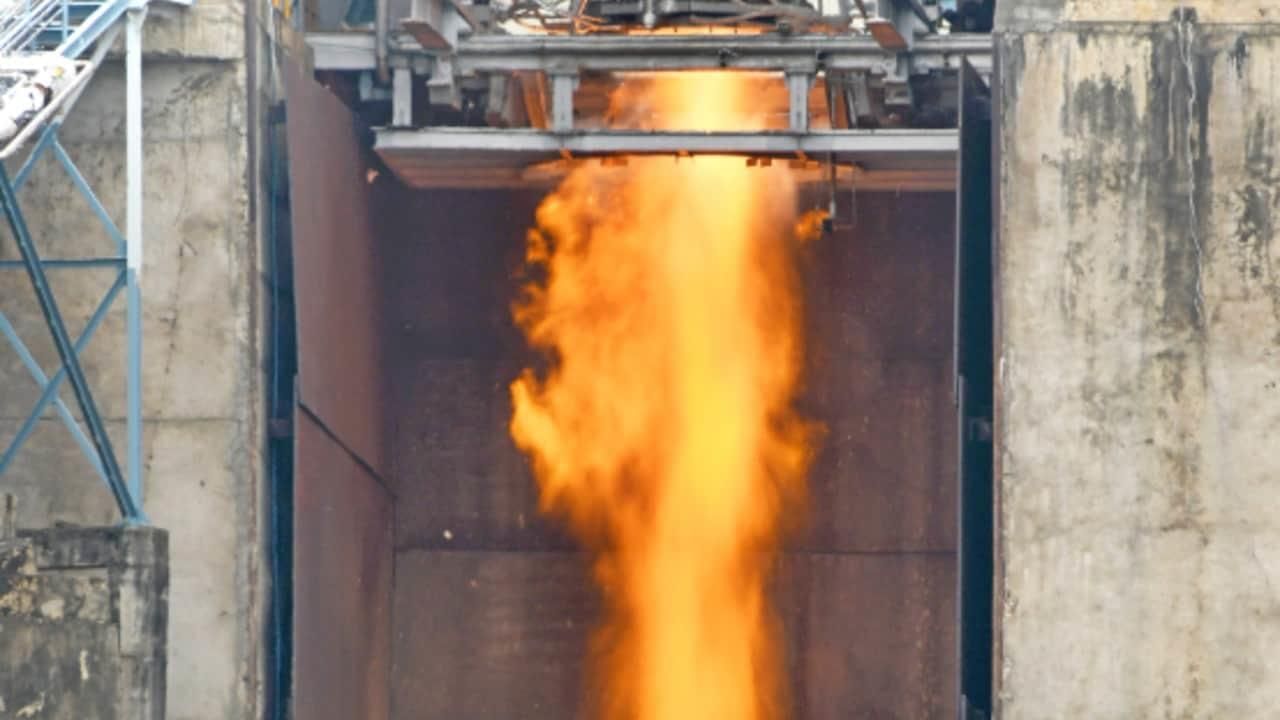 Why in News?
Why in News?The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully conducted a sea level hot test of its CE20 cryogenic engine, marking a significant milestone in India's indigenous space technology development.
- The CE20 engine is developed by ISRO's Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre.
- It powers the upper stage of the LVM3 launch vehicle, achieving a qualified thrust level of 19 tonnes.
- So far, the CE20 engine has successfully powered six LVM3 missions.
- It has been qualified for the Gaganyaan mission with a thrust level of 20 tonnes.
- Future enhancements aim for an uprated thrust level of 22 tonnes for the C32 stage.
- The engine features an innovative Nozzle Protection system to simplify testing processes.
Additional Details
- Key Achievements of the Test:
- Successful testing of an engine with a nozzle area ratio of 100.
- Evaluation of a multi-element igniter, activating only the first element.
- Confirmation of normal performance for both the engine and testing facility.
- The test represents a major advancement in ISRO's capability to address complex rocket propulsion challenges.
This successful test not only strengthens ISRO's engine development efforts but also paves the way for future missions, reinforcing India's position in space exploration.
GS2/International Relations
Syria after Assad’s Exit
Source: The Hindu Why in News?
Why in News?
Bashar al-Assad has fled to Russia with his family following the collapse of his regime after 24 years as Syria’s President. This significant political shift has brought a transitional government led by the Islamist militant group Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS) to power, raising concerns about the future governance of Syria.
- The Assad regime collapsed rapidly due to military, economic, and geopolitical factors.
- The current power structure in Syria includes multiple militant coalitions vying for control.
- Geopolitical interests of major powers like Turkey, Iran, and Russia are at play in the new political landscape.
- The future for Syria remains uncertain amid competing regional interests and ideological divides.
Additional Details
- Reasons Behind the Fall of the Assad Regime: The regime faced a crumbling economy, an 87% decline in GDP since 2011, and Western sanctions. These factors, combined with the demoralization of its soldiers and repeated Israeli airstrikes, led to its rapid decline.
- Current Power Structure: Syria is now divided among four main coalitions, with HTS emerging as a dominant force. HTS claims to respect Syria’s diversity despite its transnational jihadist affiliations.
- Geopolitical Stakes: Russia is focused on securing its naval and air bases in Syria, which are crucial for projecting military power. Iran’s interests in maintaining supply routes to Hezbollah have also been jeopardized.
- Turkey's Role: Turkey has reinforced its influence in Syria by supporting HTS and the Syrian National Army (SNA), marking a significant shift in regional power dynamics.
- Uncertain Future: Despite promises from HTS for inclusivity and rebuilding, the ideological and operational challenges make a peaceful transition unlikely. Historical parallels suggest that Syria may face prolonged instability without effective governance.
The transition in Syria following Assad’s exit presents both opportunities for change and significant challenges. The interplay of regional powers, local militias, and ideological factions will determine whether Syria can achieve stability or will descend into further chaos.
GS3/Environment
Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP)
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?The National Dam Safety Authority (NDSA) is expected to submit its final report on the Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Scheme (KLIS) soon, though it will not include the results of geo-technical tests.
- The Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project (KLIP) is a major irrigation initiative located in Telangana, India.
- It aims to provide water for both irrigation and drinking purposes across a vast area.
- KLIP is currently the world's largest multi-stage lift irrigation project.
Additional Details
- Project Overview: KLIP is designed to serve approximately 45 lakh acres across 20 of Telangana's 31 districts, including the urban areas of Hyderabad and Secunderabad.
- Geographical Significance: The project draws water from the Godavari River, specifically at the confluence of the Pranhita and Godavari rivers, which is formed by numerous smaller tributaries such as the Wardha, Painganga, and Wainganga rivers.
- Infrastructure: KLIP comprises 7 links and 28 packages that extend nearly 500 km (310 mi) through 13 districts, utilizing a canal network exceeding 1,800 km (1,100 mi).
- Water Allocation:The project is set to produce a total of 240 TMC of water, with allocations including:
- 169 TMC for irrigation
- 30 TMC for municipal water supply in Hyderabad
- 16 TMC for industrial uses
- 10 TMC for drinking water in nearby villages
- The remainder accounts for estimated evaporation loss.
In conclusion, the Kaleshwaram Lift Irrigation Project is a significant undertaking aimed at enhancing water availability for agriculture and domestic use in Telangana, reflecting a strategic approach to regional water management.
GS3/Economy
SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 Initiative
Source: Financial Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?Recently, the Minister of State for Heavy Industries and Steel provided crucial insights regarding the SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 initiative in the Rajya Sabha, highlighting its significance for the Indian manufacturing sector.
- The initiative is part of the Ministry of Heavy Industry & Public Enterprises' efforts to enhance competitiveness in the Indian Capital Goods Sector.
- SAMARTH Udyog engages key stakeholders including manufacturers, vendors, and customers.
- It aims to promote awareness of Industry 4.0 through experiential and demonstration centers established across India.
Additional Details
- SAMARTH Centres:Four Smart Advanced Manufacturing and Rapid Transformation (SAMARTH) Centres have been established:
- Centre for Industry 4.0 (C4i4) Lab, Pune
- IITD-AIA Foundation for Smart Manufacturing, IIT Delhi
- I-4.0 India @ IISc, Bengaluru
- Smart Manufacturing Demo & Development Cell, CMTI, Bengaluru
- The centres provide various forms of assistance to industries, especially MSMEs, through:
- Organizing awareness seminars and workshops on Industry 4.0.
- Training sessions to educate industries about Industry 4.0 technologies.
- Consultancy in areas such as IoT hardware, software development, and data analytics, along with incubation support for start-ups.
- Financial Assistance: It is important to note that no financial support is provided to industries, including MSMEs, for adopting Industry 4.0-enabled technologies under the SAMARTH initiative.
The SAMARTH Udyog Bharat 4.0 initiative represents a significant step towards modernizing and enhancing the capabilities of the Indian manufacturing sector, preparing it for the challenges and opportunities presented by Industry 4.0.
|
39 videos|4544 docs|971 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 15th December 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. क्या दक्षिण कोरिया के राष्ट्रपति युन सुक येओल को महाभियोग का सामना करना पड़ सकता है? |  |
| 2. मालवा नहर परियोजना का मुख्य उद्देश्य क्या है? |  |
| 3. कोंडा रेड्डी जनजाति के बारे में कुछ जानकारी दें। |  |
| 4. भारत की NPA संकट का मुख्य कारण क्या है? |  |
| 5. ISRO के CE20 क्रायोजेनिक इंजन का महत्व क्या है? |  |

































