UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 18th December 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Environment
Short Neck Clam Conservation Efforts
Source: ICAR
 Why in News?
Why in News?Recently, a significant conservation effort took place with the release of three million seeds of the short neck clam (Paphia malabarica) into Ashtamudi Lake, organized by the Vizhinjam Regional Centre of the Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI). This initiative aims to replenish the declining population of this economically important species.
Key Takeaways
- The short neck clam is a vital fishery resource in Ashtamudi Lake, Kerala.
- This species is fast-growing and reaches sexual maturity within its first year.
- It is the first fishery in India to receive certification from the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC).
- The clam's shells have various industrial uses, including in cement production and as a raw material for calcium carbide.
- Recent years have seen a drastic decline in clam populations, impacting local fishermen.
Additional Details
- Economic Importance: The short neck clam is a valuable resource, with around 80% of the harvested clams being exported to countries such as Vietnam, Malaysia, and Thailand.
- Environmental Challenges: The decline in clam populations is attributed to factors such as environmental pollution, the introduction of non-native species like the Charru mussel, and climate change effects, including altered salinity and water temperatures.
- The clam shells are not only sold for their meat but also serve as a mineral source for various industrial applications, including the production of slaked lime.
The release of clam seeds represents a critical step in addressing the decline of this species and supporting the livelihoods of thousands of fishermen dependent on clam fishing in the region.
GS3/Economy
Reasons for Potential Discontinuation of the Sovereign Gold Bond Scheme
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?The Sovereign Gold Bond (SGB) scheme, launched by the government, is under consideration for discontinuation due to a variety of economic factors. This scheme has been viewed as a safer and cost-effective alternative to holding physical gold, but recent developments have raised questions about its sustainability.
Key Takeaways
- The government is reassessing the utility of the SGB scheme amidst rising costs and competition from physical gold.
- There has been a marked decline in the issuance of SGBs, with only two tranches in the current financial year.
Additional Details
- What is the Sovereign Gold Bond scheme? The SGB scheme was launched on October 30, 2015, by the Government of India (GOI) with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) issuing the bonds. Its objectives include reducing reliance on gold imports and encouraging savings in paper form.
- Funding Mechanism: The bonds are issued under the sovereign guarantee of the government, ensuring security for both principal and interest payments.
- Targeted Beneficiaries: The scheme is aimed at various stakeholders, including individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs), trusts, universities, and charitable institutions.
- Concerns: The government has expressed concerns over the high cost of financing and the limited issuance of bonds, alongside increased competition from physical gold due to a reduction in import duties.
- Impact on Trade Deficit: High gold imports significantly contribute to India's trade deficit, with a record expenditure of $14.8 billion recorded in November 2024, affecting the value of the rupee.
- Smuggling Issues: The high import duties have led to a rise in smuggling, complicating market regulation and affecting government revenues.
The future of the SGB scheme will depend on how the government addresses these economic challenges, potentially looking towards enhancing liquidity and encouraging regular investments while balancing the interests of stakeholders.
GS1/Geography
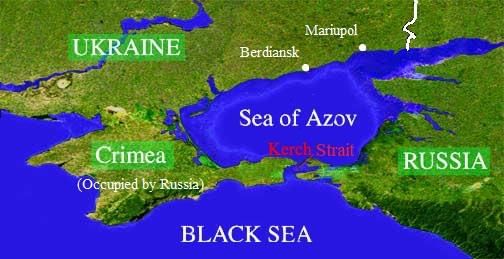
Kerch Strait
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?Recently, two Russian oil tankers were severely damaged in the Black Sea, leading to an oil spill. This incident occurred in the Kerch Strait, which serves as a crucial maritime passage separating Russia from Crimea, the Ukrainian peninsula that was unlawfully annexed by Moscow in 2014.
Key Takeaways
- The Kerch Strait is a narrow waterway in Eastern Europe connecting the Black Sea to the Sea of Azov.
- It is strategically important for the export of Russian grain, crude oil, fuel oil, and liquefied natural gas.
Additional Details
- Location: The strait divides the Kerch Peninsula of Crimea (part of the Russian-occupied territory) to the west from the Taman Peninsula of Russia's Krasnodar Krai to the east.
- Dimensions: The strait is approximately 35 kilometers long, with a width ranging from 3.1 kilometers to 15 kilometers. Its average depth is about 18 meters.
- Historical Significance:
- Ancient Names: Historically known as the Cimmerian Bosporus or Cimmerian Strait, named after the Cimmerians, a nomadic group.
- Roman Era: The Romans referred to it as the Strait of Cimmerian Bosphorus.
- World War II: The strait was a significant battlefield during World War II, marked by naval conflicts and strategic military operations.
- Modern Developments:
- Crimean Bridge: Completed in 2018, it stands as the longest bridge in Europe, measuring 19 kilometers (12 miles) and providing both road and rail connectivity.
- Conflict: The strait has been a focal point of conflict, especially post-Russia's annexation of Crimea in 2014, highlighted by the naval confrontation in 2018.
The ongoing situation in the Kerch Strait underscores its geopolitical significance and the environmental risks associated with maritime activities in this crucial passage.
GS2/Polity
The Introduction of 'One Nation, One Election' Bills and Parliamentary Procedures
Source: India Today
Why in News?The government has introduced two Bills regarding the concept of “One Nation, One Election” in the Lok Sabha, despite facing significant opposition from the INDIA bloc. The voting during the introduction showed 269 members in favor and 198 against the Bills. Union Home Minister Amit Shah and Law Minister Arjun Ram Meghwal assured that the Bills would be sent to a joint parliamentary committee for thorough examination.
Key Takeaways
- The introduction of the Bills aims to synchronize state and Lok Sabha elections.
- Strong opposition from major political parties raises concerns about federalism.
- The voting process during the introduction stage requires only a simple majority.
Additional Details
- Concept of "One Nation, One Election": This initiative envisions simultaneous elections for the Lok Sabha and state assemblies, meaning voters would cast ballots for both on the same day.
- Historical Context: The first general elections in India were held simultaneously in 1951, but subsequent changes have led to the current fragmented election cycle.
- After several premature dissolutions of the Lok Sabha, only four state assemblies have had concurrent elections with the Lok Sabha in the past two decades.
- Opposition's Concerns: Critics argue that this approach threatens the federal structure, questioning the implications if state governments were to fall when the central government collapses.
The introduction of these Bills marks a significant moment in Indian political discourse, highlighting the ongoing debate about the structure of elections and governance in the country. As discussions proceed, the implications of such a shift will likely be scrutinized in both legislative and public spheres.
GS3/Environment
Wroughton’s Free-tailed Bat Spotted in Delhi
Source: Hindustan Times
 Why in News?
Why in News?The recent sighting of Wroughton’s free-tailed bat at the Delhi Development Authority’s Yamuna Biodiversity Park has generated interest among conservationists and researchers alike. This rare species is significant for biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Key Takeaways
- Wroughton’s free-tailed bat is a highly rare species of molossid bat.
- It is characterized by its large size, prominent ears, and bicolored velvet fur.
- This species is known for its powerful flying capabilities.
- It primarily roosts in caves or dark, warm, and damp places.
- Its conservation status has evolved, with the current classification being Data Deficient by the IUCN.
Additional Details
- Habitat: Wroughton’s free-tailed bat typically roosts in moderate-sized colonies in caves or shaded, humid areas.
- Distribution: This bat is mainly found in the Western Ghats, with only one known breeding colony. Small colonies have also been noted in Jaintia Hills, Meghalaya, and an isolated individual was recorded in Cambodia.
- Conservation Status: It is classified as Data Deficient by the IUCN. Previously considered critically endangered due to a single known population in the Western Ghats, its status was updated to reflect the lack of comprehensive data.
- Ecological Significance: Wroughton’s free-tailed bat plays a vital role in regulating insect populations and aiding in plant pollination.
The sighting of Wroughton’s free-tailed bat emphasizes the importance of conservation efforts and habitat protection, as this species contributes significantly to its ecosystem.
GS2/Polity
In Today’s India, Can the Constitution Protect Individual Dignity?
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
The parliamentary discussions surrounding the Constitution have increasingly become partisan, with political parties accusing each other of undermining constitutional values. Amidst this contentious environment, it is crucial to examine the foundational principles of the Indian Constitution, the challenges it faces, and the steps needed to uphold its values.
Key Takeaways
- The Constitution is designed to protect individual rights and dignity.
- Equality before the law is a fundamental principle that ensures inclusivity.
- Checks and balances are essential to prevent the concentration of power.
- Political agency empowers citizens to participate actively in governance.
- Challenges include tensions between individual rights and group identities.
Additional Details
- Protection of Individual Rights: The Constitution enshrines fundamental rights, safeguarding freedoms such as speech, expression, and religion. These rights empower individuals and act as a safeguard against oppression.
- Equality Before the Law: This principle guarantees that all citizens, regardless of their background, receive equal protection and can participate in public life without discrimination.
- Checks and Balances: The separation of powers among the executive, legislative, and judicial branches is crucial for maintaining accountability and preventing the abuse of power.
- Limitation of Government Power: Clearly defined laws limit governmental authority, ensuring that power is exercised within legal bounds, crucial for preventing authoritarianism.
- Promotion of Political Agency: The Constitution encourages citizen participation in governance through mechanisms such as universal suffrage and free elections, reinforcing the role of individuals as political agents.
- Challenges to Constitutional Ideals: The reconciliation of individual rights with group identities poses significant challenges, especially with policies like caste-based reservations aimed at promoting social justice.
- Entrenchment of Identity-Based Politics: While the Constitution aims for a society free from ascriptive identities, political systems often exploit these divisions for electoral advantage.
- Subversion of Checks and Balances: There are concerns about the erosion of institutional autonomy and the judiciary’s role in policy-making, which blurs the separation of powers.
In conclusion, the Indian Constitution represents a vision of governance that transcends narrow party interests and aims to uphold the dignity and rights of all citizens. Addressing the existing paradoxes is essential for ensuring that the Constitution remains relevant and effective in safeguarding freedom, equality, and individual dignity in an evolving societal landscape.
GS3/Science and Technology
Science and Heritage Research Initiative (SHRI)
Source: Statetimes
 Why in News?
Why in News?The recent comments by the Union Minister of Science & Technology highlighted the potential benefits of integrating traditional knowledge with modern technological advancements, marking the five-year celebration of the Science and Heritage Research Initiative (SHRI).
Key Takeaways
- SHRI aims to foster collaboration among experts from various fields to address issues related to cultural heritage.
- The initiative focuses on promoting scientific research and development for the conservation of heritage objects.
Additional Details
- Objectives of SHRI:The initiative is designed to:
- Build capacity in human resources and encourage new researchers to engage in heritage research.
- Promote scientific R&D for conservation, including studies on material deterioration, preservation techniques, and restoration technologies.
- Safeguard knowledge, techniques, and practices recognized as integral to cultural heritage.
- Explore modern approaches and technologies to preserve the heritage and artworks of past civilizations.
- Encourage the application of archaeometric science across various fields.
- Support R&D activities in Tribal Arts for enhanced value addition.
- The initiative is set to be implemented nationwide, engaging diverse communities and stakeholders.
This initiative represents a significant step towards integrating traditional practices with contemporary scientific methods, potentially giving India a competitive edge in heritage conservation.
GS3/Environment
Moldova Signs International Solar Alliance (ISA) Framework Agreement
Source: ANI News
Why in News?
Moldova has recently made a significant commitment to renewable energy by officially signing the International Solar Alliance (ISA) Framework Agreement. This move reflects the country's dedication to promoting solar energy solutions and addressing climate change.
Key Takeaways
- Moldova's signing of the ISA Framework Agreement highlights its commitment to renewable energy.
- The ISA aims to promote solar energy solutions globally and combat climate change.
- The ISA's mission is driven by the 'Towards 1000' strategy, focusing on investment and energy access.
Additional Details
- International Solar Alliance (ISA): The ISA was established during COP21 in Paris in 2015 as a collaboration between India and France, with its headquarters in Gurugram, India.
- Goals of ISA: The ISA's mission includes mobilizing USD 1,000 billion in solar energy investments by 2030, providing energy access to 1,000 million people, and achieving the installation of 1,000 GW of solar energy capacity.
- ISA Assembly: This is the apex decision-making body that shapes policies and oversees the ISA's operations.
- Membership: Currently, the ISA comprises 104 member countries and 16 signatory countries.
- Key Initiatives:
- Scaling Solar Applications for Agricultural Use (SSAAU): A program aimed at increasing the availability of solar-powered water pumps to support agricultural practices.
- ISA CARES: This initiative focuses on providing innovative solar energy solutions for healthcare systems in low- and middle-income countries.
- Program on Solarizing Heating and Cooling Systems: This program addresses the growing demand for heating and cooling solutions across the commercial, industrial, and residential sectors through solar-based technologies.
- Global Solar Facility: Launched during COP27, this facility aims to catalyze solar investments in underserved regions, particularly in Africa.
The signing of the ISA Framework Agreement by Moldova marks a crucial step towards advancing renewable energy initiatives and highlights the importance of global collaboration in addressing climate change through solar energy.
GS2/Polity
National Investigation Agency
Source: Live Law
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Supreme Court has recently ruled that the powers of the National Investigation Agency (NIA) are not limited to investigating only the offences that are explicitly listed in the schedule of the NIA Act. This decision empowers the agency to probe non-scheduled offences that may be linked to its existing jurisdiction.
Key Takeaways
- The NIA was established under the National Investigation Agency Act in 2008 as a central counter-terrorism law enforcement body.
- It was formed in response to the 2008 Mumbai terror attacks to address the need for a dedicated agency to combat terrorism in India.
- The mandate of the NIA includes investigating serious offences affecting India’s sovereignty, security, and international relations.
- Recent amendments to the NIA Act have expanded its powers to include investigating certain offences committed by Indian citizens outside India.
Additional Details
- Establishment: The NIA was created following the realization of the need for a central agency to tackle terrorism after the 2008 Mumbai attacks.
- Areas of Investigation:The NIA investigates a wide range of offences, including those related to:
- Explosive substances
- Atomic energy and nuclear weapons
- Terrorist activities
- Hijacking
- Human trafficking
- Cyber terrorism
- Arms Act violations
- The NIA possesses the same powers as ordinary police officers when conducting investigations, including the authority to arrest individuals involved in scheduled offences.
- The administration of the NIA is headed by a Director-General, who has the same powers as a Director-General of Police.
- The NIA operates under the jurisdiction of the Union Ministry of Home Affairs, with its headquarters located in New Delhi.
The expansion of the NIA's investigative powers signifies a strengthened approach towards national security and the agency's role in addressing various forms of crime that pose a threat to India.
GS3/Economy
Inland Waterways in India
Source: Times of India
Why in News?The government has launched a significant policy initiative named ‘Jalvahak’ to enhance long-distance cargo transportation through inland waterways across National Waterways (NW) on rivers Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Barak. Despite having approximately 14,500 kilometers of navigable waterways, India's inland waterways currently account for only 2% of the country's modal mix, which is significantly lower than Bangladesh's 35% share.
Key Takeaways
- Inland waterways offer a cost-effective alternative for cargo transport, being 60% cheaper than road transport and 20-30% cheaper than rail.
- They contribute to environmental sustainability by emitting 10 times less carbon dioxide per ton-kilometer compared to road transport.
- Inland waterways can create job opportunities in sectors such as vessel operation, river conservancy, and tourism.
- They promote regional connectivity, particularly benefiting the northeastern states by linking them to the mainland.
Additional Details
- National Waterways Act of 2016: This act identifies 111 navigable water courses and designates them as national inland waterways.
- Fuel Efficiency: Research indicates that one liter of fuel can transport 24 tons of cargo for 1 km on roads, 85 km on railways, and 105 km on inland waterways, underscoring the fuel efficiency of this transport mode.
- Employment Generation: The development of inland waterways is expected to generate jobs in various fields including terminal management and tourism related to river cruises.
- However, challenges such as inadequate river depth, high siltation, and lack of modern terminals hinder operational efficiency.
In conclusion, while inland waterways in India present a promising avenue for economical and eco-friendly cargo transport, addressing the existing challenges is crucial for realizing their full potential. Initiatives like 'Jalvahak' are steps in the right direction to enhance this underutilized resource.
GS1/History & Culture
Carnatic Music: An Overview
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Supreme Court recently issued an interim order stating that musician T M Krishna should not be recognized as a recipient of theSangita Kalanidhi M S Subbulakshmi award and has prohibited him from presenting himself as such until a decision is made on an appeal challenging the award's grant to him. This order followed his receipt of the award from The Hindu during the Music Academy's 98th annual Conference and Concerts in Chennai.
Key Takeaways
- Carnatic music is a classical music tradition from Southern India.
- It has deep cultural and religious roots within the region.
- The tradition has evolved over centuries, influenced by various historical movements and composers.
Additional Details
- Origins and History: Carnatic music has ancient origins influenced by the Sama Veda, with temples playing a crucial role in its development, particularly through musical performances integral to rituals. The Bhakti movement (6th-17th centuries) significantly contributed to devotional music, while composers like Purandaradasa systematized Carnatic methods.
- The Trinity: In the 18th century, the Trinity of Carnatic music—Thyagaraja, Shama Shastri, and Muthuswami Dikshitar—emerged, compiling compositions that define the genre's repertoire.
- Key Concepts: - Raga: A melodic framework for improvisation and composition. - Tala: The rhythmic aspect of music, marked by mathematical precision. - Bhava: The expression of emotions and thoughts through music.
- Instruments: - Vocal: The human voice is the primary instrument. - Melody Instruments: Commonly used instruments include the Violin, Veena, Nadaswaram, and Flute. - Percussion Instruments: Essential rhythmic instruments include Mridangam, Ghatam, Kanjira, and Thavil.
- Performance Structure: - Kriti: A structured composition with a pallavi (refrain), anupallavi (second verse), and charanam (final verse). - Ragam Tanam Pallavi: A complex section showcasing improvisational skills. - Thillana: A rhythmic piece that concludes the performance.
- Notable Composers: - Purandaradasa, recognized as the father of Carnatic music. - The Trinity: Thyagaraja, Shama Shastri, and Muthuswami Dikshitar are pivotal figures in the genre.
Carnatic music remains a vital aspect of Southern Indian culture, reflecting its rich heritage through its complex structures and emotional depth. The recent legal developments surrounding T M Krishna highlight the ongoing discourse about recognition and representation within this traditional art form.
|
55 videos|5389 docs|1141 tests
|
















