UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 16th January 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Environment
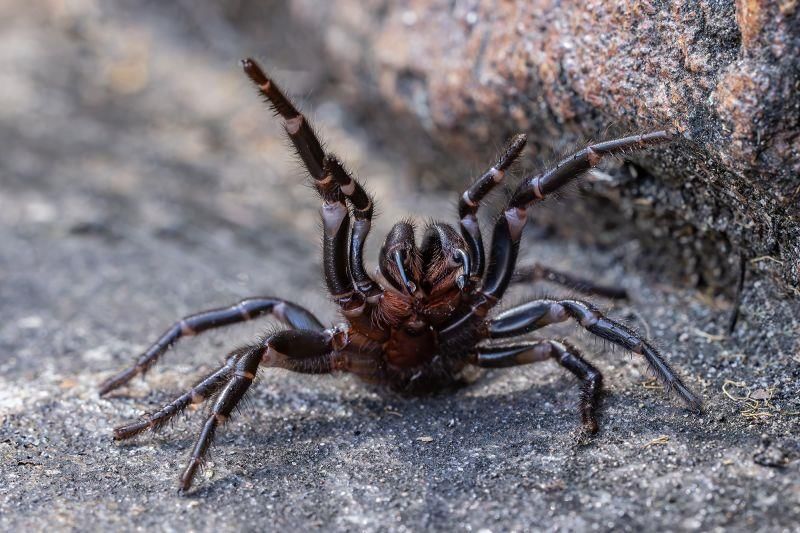
Sydney Funnel-Web Spider
Source: MSN
 Why in News?
Why in News?Recently, Australian scientists have identified a new, larger, and more venomous species of the Sydney funnel-web spider, named Atrax christenseni, also affectionately referred to as "Big Boy". This discovery highlights the ongoing research into the biodiversity of Australia and the potential dangers posed by its wildlife.
- The newly discovered species measures approximately 9 centimeters (3.54 inches) in length.
- It was first located in the early 2000s near Newcastle, Australia, which is about 170 km (105 miles) north of Sydney.
- Only male Sydney funnel-web spiders possess the potent venom responsible for human fatalities.
Additional Details
- Characteristics: This spider is characterized by its shiny, dark brown to black coloration, and features long, finger-like spinnerets at the end of its abdomen. Its venom glands are significantly larger, and it possesses longer fangs compared to other species.
- Habitat: Sydney funnel-web spiders thrive in bushy suburban areas, open and closed sclerophyll forests, and woodlands, typically found on south or east-facing slopes or in shaded gullies.
- Funnel-Web Spider Overview: Among the most dangerous arachnids globally, there are 36 described species of Australian funnel-web spiders categorized into three genera: Hadronyche, Atrax, and Illawarra. Their venoms contain over 40 different toxic proteins.
This discovery not only adds to the understanding of arachnid diversity in Australia but also emphasizes the need for awareness regarding the dangers posed by such species in their natural habitats.
GS2/Polity
What is Blood Money?
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The recent death sentence awarded by a Yemeni court to a nurse from Kerala, along with ongoing discussions and efforts regarding her acquittal and repatriation, has reignited interest in the concept of 'blood money' and its implications.
- Blood Money Definition: Also known as 'diya', blood money is a form of monetary compensation mandated under Islamic Sharia law.
- Application: It is primarily applicable in cases of unintentional murder and situations where the victim's family opts not to seek retribution.
- Community and State Rights: Even with reconciliation through blood money, the state retains the right to impose additional penalties.
Additional Details
- Concept of Diya: Under this system, a specified amount of money must be paid by the offender to the victim's family in cases of death resulting from a crime.
- Contextual Variations: In countries like Saudi Arabia, blood money is specifically mandated for traffic accident fatalities, with additional prison terms for perpetrators.
- India's Legal Stance: While India does not formally recognize blood money, it allows for 'plea bargaining' where the accused can negotiate terms with the prosecution.
- Plea Bargaining Limitations: This process is restricted to specific types of offenses and cannot be used for serious crimes such as murder or offenses against women or children.
In conclusion, while blood money serves as a means of compensating victims' families in certain cultures, its application varies significantly across different legal systems, with India focusing on plea bargaining as an alternative, albeit with more restrictions.
GS3/Science and Technology
Electrokinetic Mining: An Eco-Friendly Method for Rare Earth Element Extraction
Source: Economic Times
Why in News?
A research team has developed an innovative technique known as Electrokinetic Mining (EKM), which offers an environmentally friendly approach to extracting rare earth elements (REEs). This method addresses the limitations of conventional mining practices, particularly in the context of heavy rare earth elements (HREEs).
- Electrokinetic Mining utilizes electric fields to enhance the movement of metals and particles.
- Conventional mining methods for HREEs have significant environmental impacts and low efficiency.
- EKM reduces the need for harmful leaching agents and lowers energy consumption.
- The recovery rate of HREEs through EKM exceeds 95%, marking a significant advancement in sustainable mining.
Additional Details
- Electrokinetic Mining (EKM): This technique employs the application of direct or alternating electric fields to accelerate the movement of metals and other movable species, thus enabling more efficient extraction processes.
- Challenges of Conventional Mining: The traditional extraction of HREEs from ion-adsorption deposits, primarily in South China, has led to excessive use of ammonium-salt leaching agents, resulting in environmental degradation and inefficiency.
- EKM is designed to not only enhance recovery rates but also to promote sustainable practices by minimizing the environmental footprint of mining activities.
In summary, Electrokinetic Mining represents a groundbreaking shift in the extraction of rare earth elements, providing an eco-friendly solution that significantly reduces harmful practices while improving recovery rates and efficiency.
GS3/Economy
Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme 1.1
Source: PIB
Why in News?
The Union Minister for Steel and Heavy Industries has inaugurated the second phase of the Specialty Steel initiative, referred to as PLI Scheme 1.1.
- The PLI Scheme 1.1 aims to enhance domestic manufacturing of high-value steel.
- It seeks to reduce imports and improve India’s position in the global steel market.
- Five specialty steel categories are targeted under this scheme.
- The program covers production from FY 2025-26 to FY 2029-30 with a budget of ₹6,322 crore.
Additional Details
- Specialty Steel Categories:
- Coated/Plated Steel Products for appliances, construction, and automotive sectors.
- High Strength/Wear-Resistant Steel for infrastructure, mining, and heavy machinery.
- Specialty Rails for railways and metros.
- Alloy Steel Products and Steel Wires for industrial uses.
- Electrical Steel (CRGO and others): Cold-Rolled Grain-Oriented Steel, crucial for power transformers and electrical applications.
- Changes Introduced:
- Investment and capacity thresholds have been reduced significantly.
- For CRGO Steel:
- Investment threshold lowered to ₹3,000 crore; capacity threshold to 50,000 tonnes.
- This encourages CRGO production as a strategic priority under Atmanirbharta.
- Carry-forward provision allows excess production in one year to offset shortfalls in another.
- Companies focusing on capacity augmentation can now participate with thresholds reduced to 50% of the original requirements.
- Guidelines have been simplified to improve accessibility and encourage industry participation.
Bakc2Basics: PLI Schemes 1.0 and 2.0
- PLI Scheme 1.0:
- Launched in March 2020 to boost domestic manufacturing and reduce imports.
- Initially focused on three industries, later expanded to 14 sectors.
- Provided 1%-4% incentives on incremental sales with a ₹7,350 crore outlay for IT hardware.
- PLI Scheme 2.0:
- Launched in May 2023, focusing on laptops, tablets, servers, and PCs.
- Comes with a higher budget of ₹17,000 crore over a 6-year duration.
- Incentives include ~5% on incremental sales, targeting ₹2,430 crore in investments and $12–17 billion in exports by 2025–26.
GS2/International Relations
New US AI Export Rule Excludes India from Benefits of Closest Allies
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Joe Biden administration recently introduced a regulatory framework called the ‘Framework for Artificial Intelligence Diffusion’ just days before leaving office. This framework categorizes countries into three tiers regarding AI hardware export restrictions, significantly affecting India's position and access to advanced AI technologies.
- The framework classifies countries into three tiers based on their relationship with the US and the level of export restrictions imposed.
- India is placed in the second tier, which entails limitations on importing advanced AI chips.
- Major US allies in the first tier face minimal restrictions on AI hardware exports.
Additional Details
- Three-Tier Framework:The framework consists of three tiers:
- Tier 1: Comprises 18 close US allies such as Australia, Canada, Germany, Japan, and the UK, with minimal restrictions on computing power deployment.
- Tier 2: Encompasses most countries, including India, which is limited to importing approximately 50,000 advanced AI chips through 2027, potentially increasing with a US agreement.
- Tier 3: Contains countries of concern like Russia, China, North Korea, and Libya, facing severe restrictions on AI technology exports.
- Special Provisions for India and China: Both countries are included in a special review category called the General Validated End User, allowing authorized companies to use exported items for civilian and military purposes, barring nuclear applications.
- Impact on India's AI Development: While the immediate procurement plan for 10,000 GPUs under the IndiaAI Mission remains intact, long-term scaling may face challenges due to licensing uncertainties and trade negotiations.
This regulatory change aims to safeguard US technological leadership while addressing national security concerns. However, it raises significant questions about the future of AI development in India and its ability to compete on a global scale. The incoming Trump administration's stance on these restrictions could further influence India's approach to managing its AI ambitions.
GS3/Environment
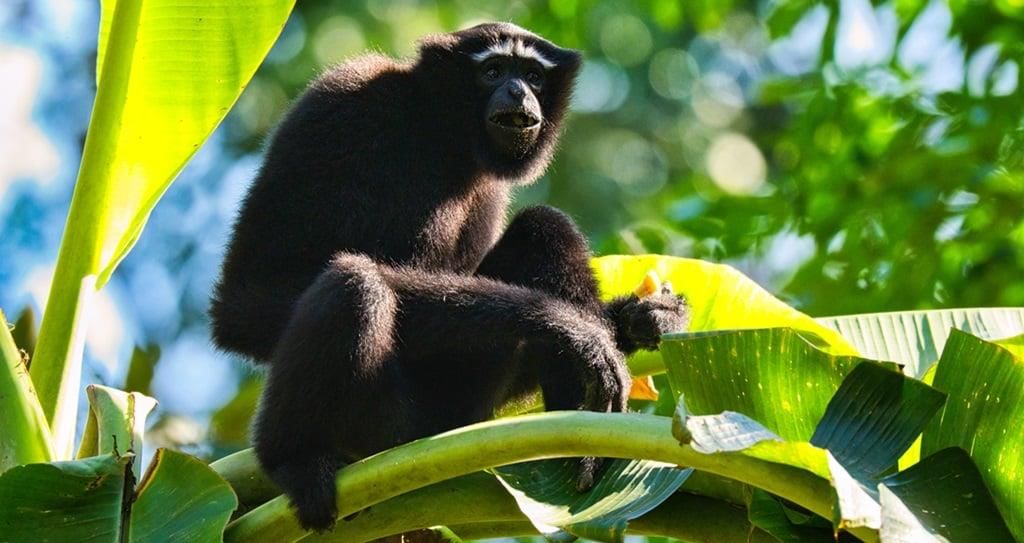
Centre Clears Exploratory Drilling in Hollongapar Gibbon Sanctuary
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?The approval for exploratory drilling for oil and gas has been granted within the eco-sensitive zone surrounding the Hollongapar Gibbon Wildlife Sanctuary, raising environmental concerns.
- The Hollongapar Gibbon Wildlife Sanctuary is a vital habitat for the hoolock gibbons.
- Established as a reserve forest in 1997 and renamed in 2004, it is located in Assam, India.
- The sanctuary features a diverse range of flora and fauna, making it ecologically significant.
Additional Details
- Hollongapar Gibbon Wildlife Sanctuary: Initially established in 1997, it was renamed in 2004, serving as the only habitat for hoolock gibbons in India. The sanctuary is situated in Assam, bordered by the Bhogdoi River.
- Biome Classification: The sanctuary's ecosystem includes plains alluvial semi-evergreen forests and patches of wet evergreen forests.
- Flora:
- Upper Canopy: Dominated by hollong trees (Dipterocarpus macrocarpus), Sam, Amari, Sopas, Bhelu, Udal, and Hingori.
- Middle Canopy: Features Nahar trees.
- Lower Canopy: Composed of evergreen shrubs and herbs.
- Fauna: The sanctuary is home to various primates including hoolock gibbons, Bengal slow loris, stump-tailed macaques, and more. Other mammals include Indian elephants, tigers, and leopards.
- Hoolock Gibbons: These are the smallest and fastest apes, residing in tropical and subtropical forests. They exhibit high intelligence and strong familial bonds. The population is estimated at around 12,000.
- Conservation Status: Both hoolock gibbon species are classified as Endangered and Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List and are protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
The recent decision regarding exploratory drilling poses a threat to the ecological balance of the sanctuary, which is crucial for the survival of its unique wildlife and plant species.
GS3/Science and Technology
Atomic Energy Commission (AEC)
Source: Economic Times
 Why in News?
Why in News?The government has recently re-constituted the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) to enhance its role in managing atomic energy initiatives in India.
- The AEC is the governing body of the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), established to oversee all atomic energy-related activities in India.
- It was officially formed on March 1, 1958, following a government resolution that highlighted the need for a dedicated commission.
- The AEC is chaired by the secretary to the government of India in the DAE.
Additional Details
- Department of Atomic Energy (DAE):Established on August 3, 1954, the DAE is responsible for the development and application of nuclear power technology, which includes:
- Exploration and processing of uranium resources and atomic minerals.
- Fabrication of nuclear fuel.
- Production of heavy water and operation of nuclear power plants.
- Nuclear fuel reprocessing and waste management.
- Additionally, the DAE conducts research in various fields such as fast reactors, fusion technologies, and advanced electronics.
- In non-power applications, it focuses on the use of isotopes and radiation technologies in healthcare, agriculture, industry, and environmental protection.
The reconstitution of the AEC signifies the government's commitment to advancing atomic energy in India, both for power generation and for various non-power applications, thereby ensuring its potential benefits are fully realized.
GS3/Science and Technology
Indian National Science Academy (INSA) - A Shift in Tradition
Source: Nature
 Why in News?
Why in News?This year, the Indian National Science Academy (INSA) made headlines by including prominent Indians who are not professional scientists in its annual list of Fellows, marking a significant departure from its traditional norms.
- INSA was founded in 1935 to promote science in India and leverage scientific knowledge for humanity and national welfare.
- The Academy initially operated as the National Institute of Sciences of India (NISI) and was established through collaborative efforts of various organizations.
- It has shifted its headquarters from Calcutta to Delhi since 1951.
Additional Details
- Objectives of INSA: The INSA aims to enhance scientific knowledge in India and ensure its practical application to national challenges.
- It coordinates efforts among different scientific bodies, institutions, and government departments to act as a representative body for scientists.
- INSA also provides a platform for scientists to engage with each other both nationally and internationally.
- The Academy recognizes outstanding contributions in science through awards, medals, and financial support for research initiatives.
- International Relations: It has established exchange programs with various overseas academies to encourage collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- In 1968, INSA was designated as the adhering organization in India to the International Council for Science (ICSU).
Overall, the INSA's decision to include non-scientists as Fellows reflects an evolving understanding of the value of diverse perspectives in the scientific community, aiming to address the need for greater diversity and inclusivity.
GS3/Science and Technology
 |
Download the notes
UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 16th January 2025
|
Download as PDF |
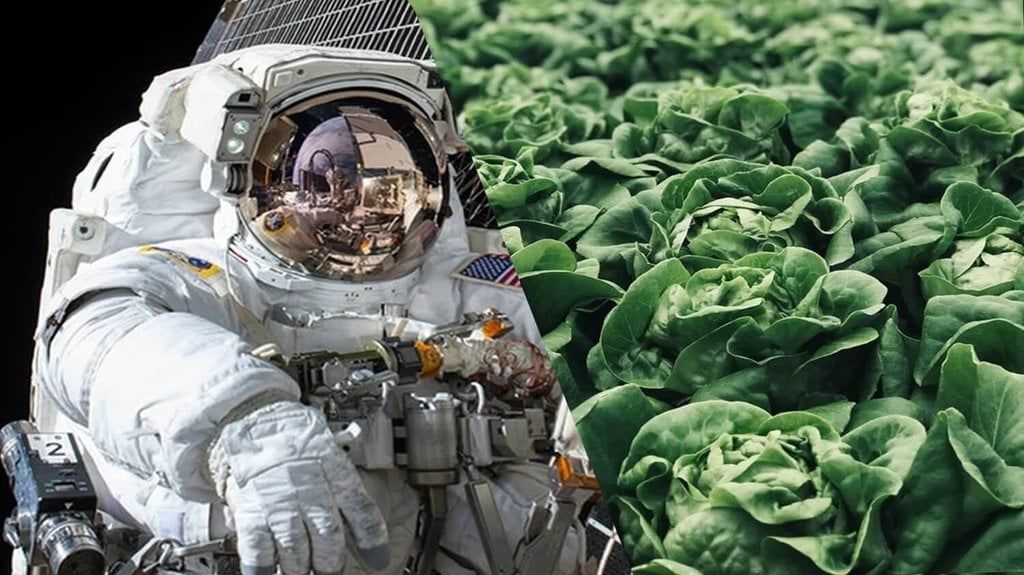
Growing Plants in Space: The Future of Sustenance Beyond Earth
Source: India Today
 Why in News?
Why in News?ISRO has made significant advancements by successfully germinating lobia seeds in space, a vital step in exploring the potential for sustainable food sources in extraterrestrial environments. This achievement is part of the Compact Research Module for Orbital Plant Studies (CROPS) and underscores the importance of developing agriculture in outer space for future missions to the Moon and Mars.
- Plants can serve as a renewable food source and aid in oxygen production during long space missions.
- ISRO's CROPS experiment has demonstrated the potential of growing crops in microgravity environments.
- Space farming presents unique challenges, such as water delivery and radiation exposure.
Additional Details
- Importance of Space Farming: Growing plants in space is essential for long-term sustainability as it provides fresh food, recycles resources, and supports astronauts' mental health.
- Challenges: The microgravity environment complicates root growth and water delivery, while radiation and temperature variations pose risks to plant development.
- Innovative Techniques: Various methods such as hydroponics and aeroponics are being utilized to facilitate plant growth without soil, optimizing resource use.
- ISRO's Experiment with Lobia: The CROPS module created Earth-like conditions using clay pellets and regulated light and temperature, successfully germinating seeds in space.
- Ideal Space Crops: Leafy greens, beans, root vegetables, grains, and fruits are considered suitable for cultivation due to their quick growth and nutritional value.
The successful germination of lobia seeds in ISRO's space module marks a pivotal advance in addressing the complexities of space agriculture. As humanity prepares for extended missions and the eventual colonization of other planets, innovations in space farming will be crucial in ensuring sustainability and self-sufficiency beyond Earth.
GS1/Indian Society
What is Kokborok Language?
Source: India Today NE
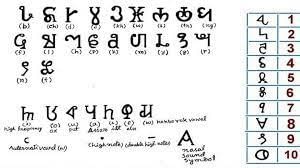 Why in News?
Why in News?The Twipra Student Federation (TSF), part of the North East Students Organisation (NESO), recently organized a protest in Agartala. The demonstration aimed to advocate for the adoption of the Roman script for the Kokborok language.
- Kokborok is a language spoken by the Borok people, also referred to as Tripuris.
- It is one of the official languages of Tripura, recognized since January 19, 1979.
- Kokborok belongs to the Sino-Tibetan language family, with historical roots dating back to at least the 1st century AD.
- The language's name is derived from 'Kok,' meaning 'verbal,' and 'Borok,' meaning 'people' or 'human.'
- According to the 2011 Census, there are 880,537 Kokborok speakers, representing 23.97% of Tripura's population.
Additional Details
- Historical Context: The Kokborok language's earliest known mention was as 'Kok-boro' in 1897/98 in a primer by Daulat Ahmed. The term 'Kokborok' was formalized in a grammar publication by Thakur Radhamohan Debbarma in 1900.
- Throughout history, British officials referred to the language as Tipperh, Tipura, or Tipra Language.
The push for the Roman script highlights ongoing efforts to promote and preserve the Kokborok language, reflecting its cultural significance among the Borok people of Tripura.
GS3/Economy
No, Legal Guarantee for MSP is Not a “Folly”
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
There is an ongoing heated discussion about whether farmers should be given a legal guarantee for Minimum Support Price (MSP). This debate raises questions about the feasibility of implementing such a guarantee within India's economic framework.
- The legal guarantee for MSP aims to protect farmers from market fluctuations.
- It addresses rural distress and ensures livelihood security for farmers.
- A guaranteed MSP supports national food security.
- Arguments against it include the risk of market distortions and unsustainable fiscal burdens.
Additional Details
- Protects Farmers from Market Fluctuations: Farmers often face volatile market prices due to surplus production, inadequate infrastructure, or global competition. A legal guarantee for MSP ensures a minimum income and shields them from sudden price crashes. Example: Crops like onions and tomatoes frequently see price collapses that leave farmers unable to cover costs.
- Addresses Rural Distress and Ensures Livelihood Security: A guaranteed MSP provides a reliable source of income, reducing poverty and addressing the rural distress that drives issues like farmer suicides. In drought-prone regions, assured MSP acts as a safety net against the dual impacts of climate change and market failures.
- Supports National Food Security: Incentivizing farmers through a guaranteed MSP ensures the continued production of essential crops, securing food for the nation and stabilizing food prices for consumers. Government procurement of rice and wheat at MSP forms the backbone of the Public Distribution System (PDS), ensuring affordable food for millions.
- Risk of Market Distortions: A legally enforced MSP could disrupt natural price discovery, discouraging private investment in agriculture and creating inefficiencies in the market. Guaranteed MSP could encourage overproduction of certain crops, leading to supply gluts and environmental degradation.
- Unsustainable Fiscal Burden: Implementing MSP for a wide range of crops would require massive public expenditure, diverting resources from other developmental priorities like healthcare and education.
- Mechanisms to Ensure MSP: To help farmers receive MSP without direct government purchases, options include widening the food basket under PDS, establishing targeted market intervention schemes, and implementing a Price Deficit Payment (PDP) system to compensate farmers when market prices fall below MSP.
The demand for a legally guaranteed MSP reflects an unwritten social contract between the Indian state and farmers. Breaching this contract could lead to further disenfranchisement of farmers facing challenges like climate change and global competition. Ultimately, a legal guarantee could alter market dynamics, ensuring that farmers are not solely dependent on volatile market conditions and might encourage more stable agricultural production and investment in rural areas.
In conclusion, while the concept of a legally guaranteed MSP holds promise for protecting farmers and ensuring food security, careful consideration of the economic implications and potential market distortions is essential for developing effective agricultural policies.
GS3/Environment
What is a Mud Volcano?
Source: MSN
 Why in News?
Why in News?A recent eruption of a mud volcano in the Caspian Sea led to the formation of a temporary 'ghost island' in early 2023, which unfortunately eroded away by the end of 2024.
- Mud volcanoes are small, cone-shaped formations made of mud and clay, typically less than a few meters tall.
- Their craters can erupt mud intermittently, continuously reshaping the cones.
- They can occur due to hot spring activity or in oil-field regions under compactional stress.
Additional Details
- Mud Volcano: A geological formation characterized by the eruption of mud, often mixed with gases like methane, creating a conical shape.
- Eruption Variants: Includes the porridge pot, which erodes rock chunks, and the paint pot, which is colored by minerals.
- Mud volcanoes are generally less hazardous than traditional volcanoes, as they emit warm mud and have a limited impact radius.
- However, large mud volcanoes can displace communities and damage infrastructure due to significant mud flow.
- Approximately 1,000 mud volcanoes have been identified across the globe in regions including southeastern Ukraine, Italy, Azerbaijan, Iran, and parts of the Americas.
Mud volcanoes, while fascinating geological features, pose unique challenges due to their potential to displace populations and disrupt ecosystems through mud floods.
|
39 videos|4770 docs|1028 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 16th January 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of the Sydney Funnel-Web Spider in its ecosystem? |  |
| 2. How is Blood Money defined in legal terms? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of Electrokinetic Mining for rare earth elements? |  |
| 4. What is the goal of the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme 1.1 in India? |  |
| 5. Why did the new US AI export rule exclude India from benefits granted to its closest allies? |  |