UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 21st January 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Science and Technology
Understanding HMPV - A Well-Known but Recently Spotlighted Virus
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
In light of recent respiratory disease outbreaks, including the Covid-19 pandemic, there is heightened awareness and concern regarding Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV). This has underscored the importance of science-based communication and effective public health responses.
- HMPV was first identified in 2001 and has been circulating among humans for decades.
- Recent media attention has brought HMPV into focus, although current cases are within expected seasonal ranges.
Additional Details
- Transmission: HMPV spreads through respiratory droplets, contact with contaminated surfaces, and direct physical interaction, such as handshakes.
- Symptoms: Symptoms typically manifest between 3-6 days post-infection and may include nasal congestion, sneezing, cough, breathlessness, fever, and sore throat. Severe cases are rare but can impact infants, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems.
- Prevention: Key preventive measures include wearing masks, practicing hand hygiene, avoiding touching the face, and steering clear of crowded places, particularly for vulnerable populations.
- Treatment: Management focuses on alleviating symptoms through hydration, rest, warm fluids, and the use of paracetamol for fever. Monitoring for severe respiratory symptoms is essential, especially in high-risk groups.
India's healthcare system is equipped to manage HMPV through RT-PCR testing, although testing is typically unnecessary for mild cases. Surveillance by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) indicates that HMPV accounted for approximately 3% of Influenza-Like Illness (ILI) and Severe Acute Respiratory Illness (SARI) cases this season. There are currently no indications of mutations in the virus, and its seasonal trends are being monitored actively.
Key Comparisons - HMPV vs. SARS-CoV-2
- Differences: HMPV is a well-studied virus that has been known for decades, contrasting sharply with the novel SARS-CoV-2, which emerged in 2019.
- Virus Families: HMPV belongs to the Pneumoviridae family, while SARS-CoV-2 is part of the Coronaviridae family, showcasing fundamentally different characteristics and epidemiology.
- Severity: Generally, HMPV causes milder illnesses with few long-term effects, unlike the more severe implications associated with SARS-CoV-2.
Lessons from the Pandemic
- Government Action: Proactive surveillance and response measures by health authorities enhance public confidence in managing outbreaks.
- Preparedness Goals: Recommendations from NITI Aayog emphasize the need for pandemic readiness through investments in research and development of vaccines and the strengthening of emergency response mechanisms.
- Environmental Considerations: Air pollution exacerbates respiratory illnesses, underscoring the need for a national, multi-sectoral response to public health challenges.
In conclusion, while the presence of HMPV in India is noteworthy, it does not warrant panic due to its well-understood nature and manageable impact. Continued proactive communication, robust surveillance, and addressing environmental factors like air pollution are essential for safeguarding public health.
GS3/Science and Technology
Surgical Tele-Robotic System
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?The SSI Mantra, India's first indigenous surgical tele-robotic system, has successfully completed two intricate heart surgeries. Notably, the surgeries were carried out with the patient located in Jaipur while the operating surgeon was in Gurgaon, highlighting the system's advanced capabilities.
- First-of-its-kind tele-robotic surgical system developed in India.
- Approved by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO) for safety and efficacy.
- Facilitates complex surgeries like Totally Endoscopic Coronary Artery Bypass (TECAB).
Additional Details
- Advantages:The system offers several benefits including:
- Reduced operation time
- Enhanced precision in surgical procedures
- Minimal trauma to the body, resulting in less incision and blood loss
- Shorter recovery time for patients
- Lower chances of infection
- Challenges:Key challenges include:
- Latency time affecting real-time operations
- Ensuring reliable connectivity during procedures
- Anticipating and managing potential medical and technical issues
- Higher costs associated with capital and operational expenditures
- Availability is primarily in metro and tier-1 cities, limiting accessibility.
The introduction of the SSI Mantra marks a significant advancement in surgical technology in India, with the potential to transform how complex surgeries are conducted, making them safer and more efficient.
GS2/Governance
SVAMITVA Scheme
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced that the distribution of property cards under the SVAMITVA scheme, once completed across all villages in the country, is expected to generate economic activities valued at over Rs 100 lakh crore. This announcement was made during an event where more than 65 lakh property cards were distributed to property owners in over 50,000 villages via video conferencing.
- The SVAMITVA scheme aims to provide a 'record of rights' to homeowners in rural areas.
- Launched on April 24, 2020, on National Panchayati Raj Day, it utilizes advanced technology for surveying properties.
- The scheme involves the use of drones to create GIS-based maps for each village.
Additional Details
- Benefits of SVAMITVA: The property cards allow rural households to leverage their property as a financial asset, enabling them to secure loans and access other financial services. This increases the liquidity of land parcels in the market and enhances financial credit availability in villages.
- Property Tax Determination: The scheme facilitates the calculation of property tax, which directly benefits Gram Panchayats in states authorized to collect such taxes.
- The initiative also contributes to the development of precise land records for rural planning, supporting taxation, issuance of construction permits, and the elimination of encroachments.
In summary, the SVAMITVA scheme not only provides essential property rights to rural residents but also serves as a catalyst for economic growth and better governance in village areas.
GS2/Polity
UGC Regulations vs State University Laws: A Constitutional Dispute
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?There is a significant conflict between the University Grants Commission (UGC) and various State governments concerning the appointment of Vice Chancellors (VCs) in State universities. This dispute has gained attention due to its implications for governance and academic administration in several states.
- The UGC's 2018 regulations require a UGC nominee in VC search committees, leading to tensions with State laws.
- Leadership vacancies in universities are causing administrative paralysis and affecting academic functions.
- Conflicting Supreme Court judgments have resulted in legal ambiguities regarding the authority of UGC regulations versus State laws.
Additional Details
- Core Issue: The primary concern is whether UGC Regulations can override State University Acts, which have their own provisions for appointing VCs.
- UGC's Position: The UGC argues that including its nominee in VC search committees ensures uniform academic standards across the nation.
- State's Argument: States like Tamil Nadu contend that UGC's imposition undermines their autonomy in university governance.
- Legal Complexity: The Supreme Court's conflicting rulings have created uncertainty, with some decisions affirming UGC regulations as mandatory and others treating them as advisory.
- Constitutional Considerations: Article 254(1) of the Constitution suggests that Central laws take precedence over State laws, but this primarily addresses plenary laws, not delegated legislation like UGC regulations.
In conclusion, the ongoing dispute between UGC regulations and State University Acts highlights broader issues of federalism and the relationship between Central and State authorities. Resolving this conflict requires judicial clarity and a collaborative approach to ensure effective governance in India's higher education system.
GS3/Economy
Contract Farming in India
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?India has significantly increased its exports of French Fries, largely due to the implementation of contract farming, which facilitates direct procurement of potatoes from farmers by companies, strengthening the relationship between growers and buyers.
- Contract farming involves an agreement between farmers and buyers regarding the production and marketing of agricultural products.
- Farmers benefit from financial stability and improved access to resources, while they face certain risks and challenges.
Additional Details
- Definition of Contract Farming: A formal agreement between farmers (producers) and buyers that outlines the terms for production and marketing, including pricing, quantity, quality, and delivery schedules.
- Advantages for Farmers:
- Access to financial support, services, and credit, leading to better production and management skills.
- Secure markets and potential access to new markets.
- Reduced price-related risks and more stable income for better planning.
- Introduction of new technologies in farming practices.
- Concerns for Farmers:
- Loss of flexibility to sell to other buyers if market prices rise.
- Possibility of delayed payments and late delivery of necessary inputs.
- Risk of becoming indebted due to loans from buyers.
- Environmental impacts from monoculture practices.
- Unequal bargaining power between farmers and buyers.
Overall, while contract farming presents several opportunities for farmers in India, it also raises critical concerns that need to be addressed to ensure fair practices and sustainability in agriculture.
GS3/Economy
Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARC)
Source: Business Standard
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has recently modified its guidelines concerning Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs), easing the norms related to the settlement of dues between ARCs and borrowers. This change is significant as it impacts the handling of non-performing assets (NPAs) within the banking sector.
- ARCs play a crucial role in acquiring and restructuring NPAs from banks.
- The regulation of ARCs is governed by the SARFAESI Act, 2002 and overseen by the RBI.
- Recent RBI guidelines aim to facilitate better recovery processes for ARCs.
Additional Details
- Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs): These specialized financial institutions are tasked with acquiring non-performing assets from banks and financial institutions, helping them recover or restructure these loans. This process allows banks to strengthen their balance sheets and concentrate on productive lending.
- Regulatory Framework: ARCs operate under the Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act, 2002, which empowers them to take possession of secured assets from defaulters without needing court intervention.
- Objectives of ARCs:
- Resolution of Stressed Assets: Aiding banks in recovering bad debts.
- Financial Stability: Enhancing the overall health of the banking sector by minimizing NPAs.
- Resource Allocation: Allowing banks to focus on productive lending by offloading non-performing loans.
- Functions of ARCs:
- Acquisition of NPAs: Purchase of bad loans from banks at discounted prices.
- Restructuring and Recovery: Implementing measures such as asset liquidation or settlement to recover dues.
- Issuance of Security Receipts (SRs): Funding their operations by issuing SRs to qualified institutional buyers (QIBs).
In summary, the recent changes in RBI guidelines signify a progressive step towards enhancing the operational efficiency of ARCs, which is critical for improving the financial health of banks and ensuring stability in the economy.
GS2/Polity
 |
Download the notes
UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 21st January 2025
|
Download as PDF |
RG Kar Rape Case: Not A Rarest Of Rare Case
Source: Indian Express
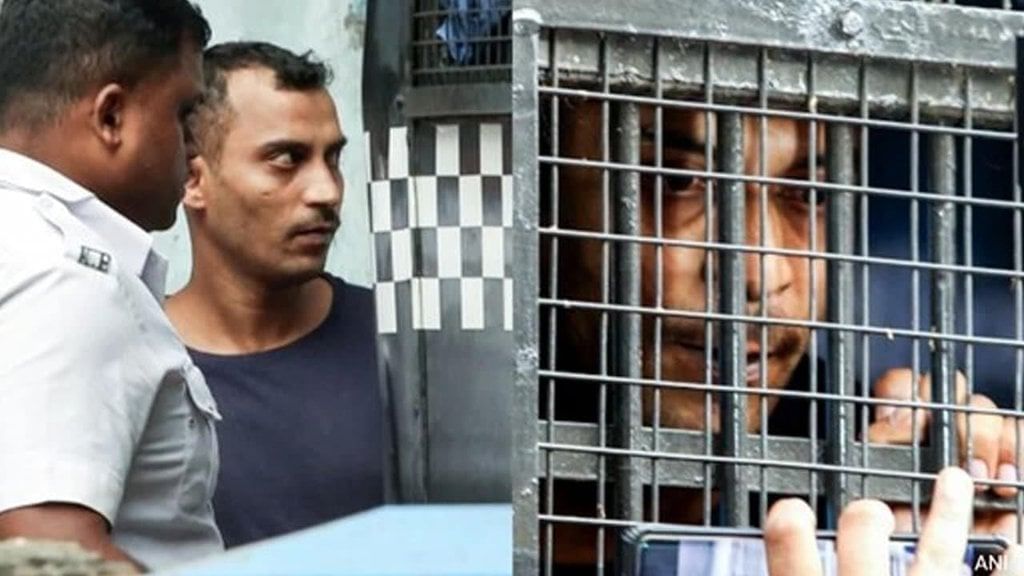 Why in News?
Why in News?Sanjoy Roy, convicted of raping and murdering a doctor at RG Kar Medical College in Kolkata, received a life imprisonment sentence from a sessions court. Despite the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) advocating for the death penalty amid public outrage, the court maintained the Supreme Court's principle that the death penalty should only be applied in the "rarest of rare" cases, taking into account both aggravating and mitigating circumstances as established in the Bachan Singh v. State of Punjab (1980) judgment.
- The court emphasized the importance of considering both aggravating and mitigating factors in sentencing.
- Sanjoy Roy's case was deemed not to meet the threshold for the death penalty as per established legal principles.
Additional Details
- Death Penalty - Rarest of Rare Test: The Supreme Court's ruling in 1980 stipulated that the death penalty is reserved for cases where there is no possibility of reform, though it did not set explicit standards for these determinations.
- Aggravating Circumstances: These include premeditated acts, exceptional depravity, and targeting of public servants, among others.
- Mitigating Circumstances: Instances such as the offender's age, mental impairment, or emotional disturbance are considered to potentially lessen the severity of the punishment.
- Recent cases have refined the understanding of these circumstances, with courts increasingly recognizing young age as a potential mitigating factor.
The evolving nature of judicial interpretation regarding mitigating and aggravating factors highlights inconsistencies, particularly relating to how age is considered in sentencing. Courts are urged to balance the nature of the crime with the offender's circumstances and potential for rehabilitation to ensure a fair sentencing process. The necessity for a separate sentencing trial post-conviction has been reinforced to allow for a thorough consideration of all relevant factors.
GS1/History & Culture
Kalaripayattu: Kerala's Ancient Martial Art Form
Source: Times Now
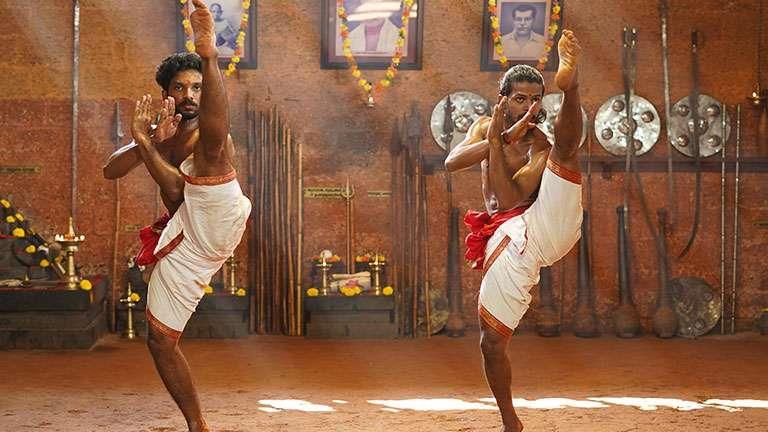 Why in News?
Why in News?Kalaripayattu, the traditional martial art of Kerala, has garnered attention as it faces controversy regarding its inclusion in the upcoming 38th National Games, set to begin on January 28 in Uttarakhand.
- Kalaripayattu is one of the oldest and most scientific martial art forms globally, focusing on mind and body coordination.
- The art form originated in Kerala and is taught in traditional gymnasiums called Kalari.
- It is believed that the warrior sage Parasurama established Kalaripayattu.
Additional Details
- Four Stages of Kalaripayattu:
- Maippayattu: This is the body conditioning phase, where individuals prepare physically for combat. Progression to the next phase requires mastering this stage.
- Kolthari: In this stage, practitioners learn attack and self-defense techniques using wooden weapons, including short and long sticks.
- Angathari: After overcoming the fear of wooden weapons, students move on to using sharp metal objects in this third stage.
- Verumkai: This final stage emphasizes bare-hand fighting techniques, where students study body anatomy to understand vulnerable points for striking.
- The main ethnic styles of Kalaripayattu practiced in northern Kerala, particularly in the Malabar region, include Vattenthirippu, Arappukkai, and Pillathangi.
- Kalaripayattu is thought to have influenced martial arts in China, particularly at the Shaolin Temple, thanks to Bodhidharma, who brought it there in the 5th century AD.
In summary, Kalaripayattu not only represents a rich cultural heritage of Kerala but also highlights the ongoing discussions about its role in contemporary sporting events.
GS3/Science and Technology
Midges Identified in Andaman and Nicobar Islands
Source: Deccan Herald
Why in News?
Researchers from the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) have discovered 23 species of blood-sucking flies, known as midges, in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Notably, 13 of these species have been recorded for the first time in India, highlighting the region's biodiversity and the importance of entomological studies.
- A total of 23 midge species were identified, with 13 new to India.
- These insects are significant vectors for various diseases affecting livestock.
- Five species are known to transmit the bluetongue disease virus.
Additional Details
- Midges: These tiny insects, closely related to mosquitoes but resembling flies, belong to the Culicoides genus and are locally referred to as bhusi files.
- Feeding Habits: Midges primarily feed on the blood of livestock, including sheep, goats, and cattle, as well as wild animals like deer.
- The bluetongue disease, transmitted by some midge species, can be fatal to livestock, presenting symptoms such as fever, facial swelling, excessive salivation, and a characteristic blue discoloration of the tongue.
- Despite 17 of the identified species being known to bite humans, there have been no reports of disease transmission to humans.
- The study conducted between 2022 and 2023 expanded the Indian Culicoides fauna to a total of 93 valid species.
- Global Significance: Midges are gaining attention for their role as vectors, impacting not just livestock but also wildlife and humans, transmitting nearly 60 viruses, 40 protozoans, and 24 filarial nematodes.
This research emphasizes the ecological importance of midges and their potential impact on livestock health and agricultural economies. Continued study and monitoring are essential to manage and mitigate the risks associated with these vectors.
GS2/International Relations
India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC)
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
Former US President Joe Biden recently underscored the potential realization of the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) in light of the Israel-Hamas ceasefire. This initiative is expected to significantly enhance trade and connectivity across multiple regions.
- The IMEC is a comprehensive connectivity project aimed at developing infrastructure linking India, the Arabian Peninsula, the Mediterranean region, and Europe.
- It was officially announced in 2023 during the G20 meeting in New Delhi, following a memorandum of understanding (MoU) signed between the European Union and seven countries, including India, the US, Saudi Arabia, UAE, France, Germany, and Italy.
Additional Details
- Project Overview:The IMEC will consist of two main corridors:
- Eastern Corridor: Connecting India to the Arabian Gulf.
- Northern Corridor: Linking the Gulf with Europe.
- The corridor will feature a cost-effective railway network, complemented by road and maritime routes. This includes:
- A shipping route connecting Mumbai and Mundra (Gujarat) to the UAE.
- A rail network linking the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Jordan to the Israeli port of Haifa, extending to the Mediterranean.
- Plans to connect by sea to the port of Piraeus in Greece, facilitating access to Europe.
- The corridor will also involve laying down networks for:
- Electricity grids
- Optical fiber cables for digital connectivity
- Pipelines for transporting hydrogen gas
- The IMEC aims to:
- Increase efficiency and reduce costs.
- Secure regional supply chains and enhance trade accessibility.
- Boost economic cooperation, generate jobs, and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
- Support for the project will come from the Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII), a US-led initiative designed to address infrastructure gaps in developing countries.
The IMEC represents a strategic initiative that could reshape trade dynamics and foster economic growth across regions, while also promoting infrastructure development and cooperation.
|
39 videos|4560 docs|976 tests
|






























