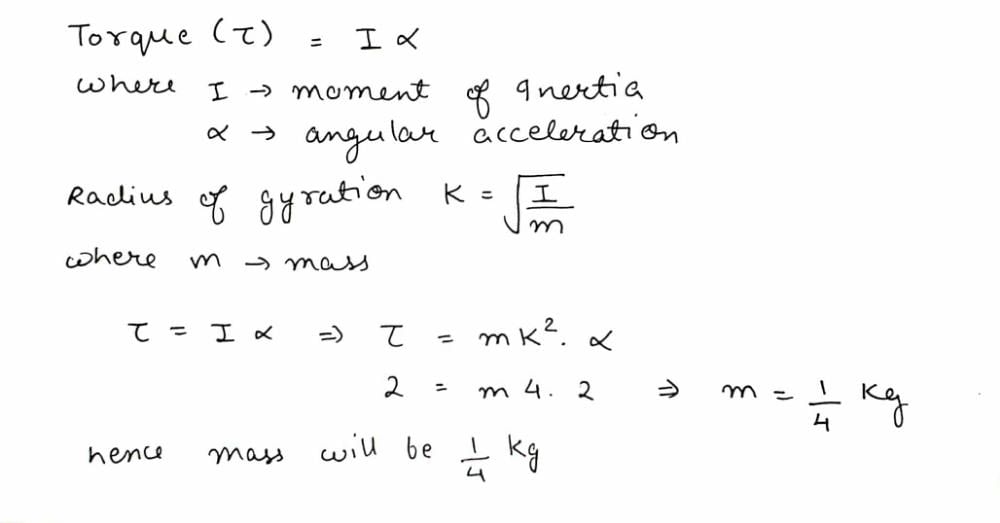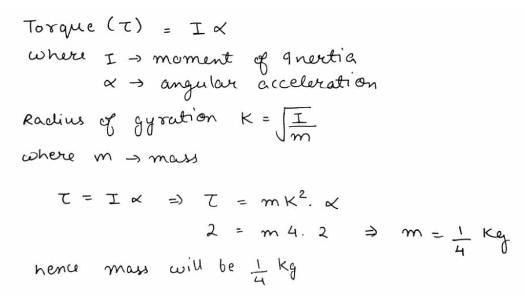All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of August Week 4 for NEET Exam
The number of amino acids found in proteins are- a)20
- b)21
- c)18
- d)16
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of amino acids found in proteins are
a)
20
b)
21
c)
18
d)
16
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Proteinogenic amino acids are amino acids that are incorporated biosynthetically into proteins during translation. ... Throughout known life, there are 22 genetically encoded (proteinogenic) amino acids, 20 in the standard genetic code and an additional 2 that can be incorporated by special translation mechanisms.
A right triangular plate ABC of mass m is free to rotate in the vertical plane about a fixed horizontal axis through A. It is supported by a string such that the side AB is horizontal. The reaction at the support A is : 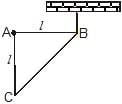
- a)
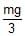
- b)
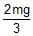
- c)
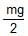
- d)mg
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A right triangular plate ABC of mass m is free to rotate in the vertical plane about a fixed horizontal axis through A. It is supported by a string such that the side AB is horizontal. The reaction at the support A is :
a)
b)
c)
d)
mg

|
Crafty Classes answered |
The distance of Centre Of Mass of the given right angled triangle is 2L/3 along BA and L/3 along AC from the point B.
Force of magnitude mg is acting downwards at its COM.
Moment balance around B gives:
mg(2L/3)−FA(L)=0
(Moment= × =rFsin(θ)=F(rsin(θ))=Fr⊥)
∴FA=2mg/3
Force of magnitude mg is acting downwards at its COM.
Moment balance around B gives:
mg(2L/3)−FA(L)=0
(Moment= × =rFsin(θ)=F(rsin(θ))=Fr⊥)
∴FA=2mg/3
The most abundant organic molecule present on earth is- a)Protein
- b)Lipid
- c)Steroids
- d)Cellulose
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The most abundant organic molecule present on earth is
a)
Protein
b)
Lipid
c)
Steroids
d)
Cellulose
|
|
Raghavendra Datta answered |
The most abundant organic molecule present on earth is cellulose.
What is Cellulose?
Cellulose is a complex carbohydrate that is found in the cell walls of plants. It is composed of repeating units of glucose molecules that are linked together to form long chains. These chains are then arranged in a way that gives cellulose its characteristic strength and rigidity.
Why is Cellulose Abundant on Earth?
Cellulose is abundant on earth for several reasons:
1. It is found in the cell walls of plants - Plants are the most abundant form of life on earth, and cellulose is a major component of their cell walls. This means that there is a huge amount of cellulose present on earth.
2. It is resistant to degradation - Unlike other organic molecules, cellulose is highly resistant to degradation by enzymes and other biological processes. This means that it can persist in the environment for a long time, contributing to its abundance.
3. It is a major component of biomass - Cellulose is a major component of the biomass of plants. When plants die and decompose, the cellulose in their cell walls is broken down into smaller molecules that can be used by other organisms. This means that there is a constant supply of cellulose being produced and broken down on earth.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, cellulose is the most abundant organic molecule present on earth due to its presence in the cell walls of plants, its resistance to degradation, and its role as a major component of biomass.
What is Cellulose?
Cellulose is a complex carbohydrate that is found in the cell walls of plants. It is composed of repeating units of glucose molecules that are linked together to form long chains. These chains are then arranged in a way that gives cellulose its characteristic strength and rigidity.
Why is Cellulose Abundant on Earth?
Cellulose is abundant on earth for several reasons:
1. It is found in the cell walls of plants - Plants are the most abundant form of life on earth, and cellulose is a major component of their cell walls. This means that there is a huge amount of cellulose present on earth.
2. It is resistant to degradation - Unlike other organic molecules, cellulose is highly resistant to degradation by enzymes and other biological processes. This means that it can persist in the environment for a long time, contributing to its abundance.
3. It is a major component of biomass - Cellulose is a major component of the biomass of plants. When plants die and decompose, the cellulose in their cell walls is broken down into smaller molecules that can be used by other organisms. This means that there is a constant supply of cellulose being produced and broken down on earth.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, cellulose is the most abundant organic molecule present on earth due to its presence in the cell walls of plants, its resistance to degradation, and its role as a major component of biomass.
A homogeneous cubical brick lies motionless on a rough inclined surface. The half of the brick which applies greater pressure on the plane is : 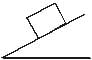
- a) Left half
- b)Right half
- c)Both applies equal pressure
- d)The answer depend upon coefficient of friction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A homogeneous cubical brick lies motionless on a rough inclined surface. The half of the brick which applies greater pressure on the plane is :
a)
Left half
b)
Right half
c)
Both applies equal pressure
d)
The answer depend upon coefficient of friction

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
As weight of the body (mg) acts along the left side i.e. mg sinx acts along flow of object.
mgcosx acts perpendicular to flow of the object.
The pressure of right half comes on left half hence left half has maximum pressure.
mgcosx acts perpendicular to flow of the object.
The pressure of right half comes on left half hence left half has maximum pressure.
A solid sphere and a hollow sphere of the same mass have the same moments of inertia about their respective diameters, the ratio of their radii is- a)(5)1/2 : (3)1/2
- b) (3)1/2 : (5)1/2
- c)3 : 2
- d)2 : 3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A solid sphere and a hollow sphere of the same mass have the same moments of inertia about their respective diameters, the ratio of their radii is
a)
(5)1/2 : (3)1/2
b)
(3)1/2 : (5)1/2
c)
3 : 2
d)
2 : 3
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
We know moment of inertia of solid sphere Is=2/5msRs2 and
moment of inertia of hollow sphere IH=2/3mHRH2 As per question Is=IH
Now,
2/5msRs2=2/3mHRH2
as the masses are equal the ratio of their radii will be
Rs2 /RH2 =2/3/2/5=√5/3=(5)1/2: (3)1/2
moment of inertia of hollow sphere IH=2/3mHRH2 As per question Is=IH
Now,
2/5msRs2=2/3mHRH2
as the masses are equal the ratio of their radii will be
Rs2 /RH2 =2/3/2/5=√5/3=(5)1/2: (3)1/2
Calculate the M.I. of a thin uniform ring about an axis tangent to the ring and in a plane of the ring, if its M.I. about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to plane is 4 kg m2.- a)12 kg m2
- b)3 kg m2
- c)6 kg m2
- d)9 kg m2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the M.I. of a thin uniform ring about an axis tangent to the ring and in a plane of the ring, if its M.I. about an axis passing through the centre and perpendicular to plane is 4 kg m2.
a)
12 kg m2
b)
3 kg m2
c)
6 kg m2
d)
9 kg m2
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
At tangent I =MR2/2 + MR2 --- (1)
MR2/2 = 4, MR2 = 8 then substitute in (1) you will get I = 12, this is for tangent perpendicular to plane then divide by 2 you will get tangent along the plane
MR2/2 = 4, MR2 = 8 then substitute in (1) you will get I = 12, this is for tangent perpendicular to plane then divide by 2 you will get tangent along the plane
The M.I. of a disc about its diameter is 2 units. Its M.I. about axis through a point on its rim and in the plane of the disc is- a)4 unit
- b)6 unit
- c)8 unit
- d)10 unit
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The M.I. of a disc about its diameter is 2 units. Its M.I. about axis through a point on its rim and in the plane of the disc is
a)
4 unit
b)
6 unit
c)
8 unit
d)
10 unit
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
We know that for a disc of mass m and radius r
MI of a disc about its diameter = mr2/4 = 2
And also MI about a point on its rim = mr2/4 + mr2
= 5mr2/4
= 5 x 2 = 10
MI of a disc about its diameter = mr2/4 = 2
And also MI about a point on its rim = mr2/4 + mr2
= 5mr2/4
= 5 x 2 = 10
From the following data, the heat of formation of Ca(OH)2(s) at 18°C is ………..kcal: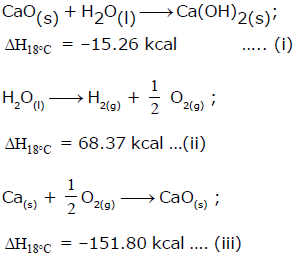
- a)-98.69
- b)-235.43
- c)194.91
- d) 98.69
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
From the following data, the heat of formation of Ca(OH)2(s) at 18°C is ………..kcal:
a)
-98.69
b)
-235.43
c)
194.91
d)
98.69

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
Ca(s) + O2(g) + H2(g) → Ca(OH)2 , ΔHf = ?
Desired equation = eq (iii) + eq(i) - eq (ii)
ΔHf = (−151.80)+(−15.26)−(−68.37)
ΔHf = (-151.80)+(-15.26)-(-68.37)
ΔHf = −235.43KCalmol−1
ΔHf = (-151.80)+(-15.26)-(-68.37)
ΔHf = −235.43KCalmol−1
The moment of inertia and rotational kinetic energy of a fly wheel are 20kg-m2 and 1000 joule respectively. Its angular frequency per minute would be -- a)600/π
- b)25/π2
- c)5/π
- d)300/π
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The moment of inertia and rotational kinetic energy of a fly wheel are 20kg-m2 and 1000 joule respectively. Its angular frequency per minute would be -
a)
600/π
b)
25/π2
c)
5/π
d)
300/π
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Rotational K.E. = ½ × moment of inertia × square of angular velocity = ½Iw2
An automobile engine develops 100H.P. when rotating at a speed of 1800 rad/min. The torque it delivers is- a)3.33 W-s
- b)200W-s
- c)248.7 W-s
- d)2487 W-s
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An automobile engine develops 100H.P. when rotating at a speed of 1800 rad/min. The torque it delivers is
a)
3.33 W-s
b)
200W-s
c)
248.7 W-s
d)
2487 W-s

|
Manish Aggarwal answered |
100 HP = 74570 W or 74.57 KW Now, P = 2*π*N*T/60 where, P is the power (in W), N is the operating speed of the engine (in r.p.m.) and T is the Torque (in N.m). Therefore, 74570 = 2*π*1800*T/60 i.e. T = 395.606 N.m
The reaction CH4(g) + Cl2(g) → CH3Cl(g) + HCl(g) has ΔH = -25 kCal.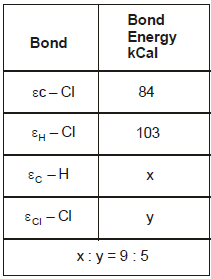 From the given data, what is the bond energy of Cl - Cl bond
From the given data, what is the bond energy of Cl - Cl bond- a)70 kCal
- b)80 kCal
- c) 67.75 kCal
- d) 57.75 kCal
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction CH4(g) + Cl2(g) → CH3Cl(g) + HCl(g) has ΔH = -25 kCal.
From the given data, what is the bond energy of Cl - Cl bond
a)
70 kCal
b)
80 kCal
c)
67.75 kCal
d)
57.75 kCal

|
Kamna Science Academy answered |
During bond breakage energy is absorbed and during bond formation it is released. From the reaction we can say that 1 C-H bond is broken 1 Cl-Cl bond is broken 1 c-cl bond is formed and 1 h-cl bond is formed. so using the sign conventions the equation becomes
x+y-84-103= -25 (∆H = -25)
5x=9y ..putting x=9/5y we get y = 57.75 kCal
x+y-84-103= -25 (∆H = -25)
5x=9y ..putting x=9/5y we get y = 57.75 kCal
NH3(g) + 3Cl2(g)  NCl3(g) + 3HCl(g) ; -ΔH1N2(g) + 3H2(g)
NCl3(g) + 3HCl(g) ; -ΔH1N2(g) + 3H2(g)  2NH3(g) ; ΔH2H2(g) + Cl2(g)
2NH3(g) ; ΔH2H2(g) + Cl2(g) 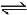 2HCl(g) ; ΔH3The heat of formation of NCl3 (g) in the terms of ΔH1, ΔH2 and ΔH3 is
2HCl(g) ; ΔH3The heat of formation of NCl3 (g) in the terms of ΔH1, ΔH2 and ΔH3 is- a)
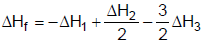
- b)
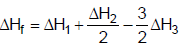
- c)
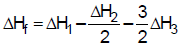
- d) None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
NH3(g) + 3Cl2(g) 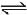 NCl3(g) + 3HCl(g) ; -ΔH1
NCl3(g) + 3HCl(g) ; -ΔH1
N2(g) + 3H2(g) 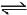 2NH3(g) ; ΔH2
2NH3(g) ; ΔH2
H2(g) + Cl2(g) 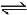 2HCl(g) ; ΔH3
2HCl(g) ; ΔH3
The heat of formation of NCl3 (g) in the terms of ΔH1, ΔH2 and ΔH3 is
a)
b)
c)
d)
None
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
The formation of NCl3 be like
½ N2 + 3/2Cl2 ⇋ NCl3
We can see that for this setup, we need to have eqn (ii) divided by 2, reversing eqn (iii) and multiplying it by 3/2 and then adding all these to equation (i).
So option a is correct.
½ N2 + 3/2Cl2 ⇋ NCl3
We can see that for this setup, we need to have eqn (ii) divided by 2, reversing eqn (iii) and multiplying it by 3/2 and then adding all these to equation (i).
So option a is correct.
The nucleotide chemical components are- a)Heterocyclic compounds, sugar and phosphate
- b)Sugar and Phosphate
- c)Heterocyclic compounds and sugar
- d)Phosphate and heterocyclic compounds
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The nucleotide chemical components are
a)
Heterocyclic compounds, sugar and phosphate
b)
Sugar and Phosphate
c)
Heterocyclic compounds and sugar
d)
Phosphate and heterocyclic compounds

|
Akshat Chavan answered |
The nucleotide has three chemically distinct components. One is a heterocyclic compound, the second is a monosaccharide and the third a phosphoric acid or phosphate.
How many kcal of heat is evolved by the complete neutralisation of one mole sulphuric acid with NaOH -- a)13.7 kcal
- b)27.4 kcal
- c)6.85 kcal
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many kcal of heat is evolved by the complete neutralisation of one mole sulphuric acid with NaOH -
a)
13.7 kcal
b)
27.4 kcal
c)
6.85 kcal
d)
None of the above
|
|
Om Desai answered |
For the reaction of 1 mole of H+ and OH-,we have 13.6 kcal energy released. In H2SO4, we have 2 moles of H+. So for its complete neutralisation, we need 2 moles of NaOH.
So in the end, 2 moles of H+ reacts with2 moles of OH- and 13.6 2 = 27.4 kcal energy is released.
So in the end, 2 moles of H+ reacts with2 moles of OH- and 13.6 2 = 27.4 kcal energy is released.
In the combustion of 4g. of CH4, 2.5 K cal of heat is liberated. The heat of combustion of CH4 is -- a) 20 K. cals
- b) 10 K. cals
- c) 2.5 K. cals
- d)5 K. cals
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the combustion of 4g. of CH4, 2.5 K cal of heat is liberated. The heat of combustion of CH4 is -
a)
20 K. cals
b)
10 K. cals
c)
2.5 K. cals
d)
5 K. cals
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Mol. wt. of methane =16gm
Heat liberated during the combustion of 4gm methane = 2.5kcal
Heat liberated during the combustion of 16gm methane = 2.5/4×16=10kcal
Hence the heat of combustion of methane is 10 kcal.
Heat liberated during the combustion of 4gm methane = 2.5kcal
Heat liberated during the combustion of 16gm methane = 2.5/4×16=10kcal
Hence the heat of combustion of methane is 10 kcal.
Three rings, each of mass P and radius Q are arranged as shown in the figure. The moment of inertia of the arrangement about YY' axis will be 
- a)
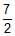 PQ2
PQ2 - b)
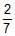 PQ2
PQ2 - c)
 PQ2
PQ2 - d)
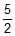 PQ2
PQ2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Three rings, each of mass P and radius Q are arranged as shown in the figure. The moment of inertia of the arrangement about YY' axis will be
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Lohit Matani answered |
For ring 1
(MOI)1 = MOI about diameter + PQ2
MOI about diameter = ½ PQ2
(MOI)1 = 3/2 PQ2
Similarly, (MOI)2 = 3/2 PQ2
(MOI)3 = ½ PQ2
Total MOI = 7/2 PQ2
(MOI)1 = MOI about diameter + PQ2
MOI about diameter = ½ PQ2
(MOI)1 = 3/2 PQ2
Similarly, (MOI)2 = 3/2 PQ2
(MOI)3 = ½ PQ2
Total MOI = 7/2 PQ2
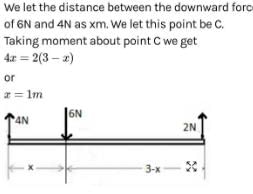
A weightless rod is acted on by upward parallel forces of 2N and 4N ends A and B respectively. The total length of the rod AB = 3m. To keep the rod in equilibrium a force of 6N should act in the following manner :- a)Downwards at any point between A and B.
- b) Downwards at mid point of AB.
- c)Downwards at a point C such that AC = 1m.
- d) Downwards at a point D such that BD = 1m.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A weightless rod is acted on by upward parallel forces of 2N and 4N ends A and B respectively. The total length of the rod AB = 3m. To keep the rod in equilibrium a force of 6N should act in the following manner :
a)
Downwards at any point between A and B.
b)
Downwards at mid point of AB.
c)
Downwards at a point C such that AC = 1m.
d)
Downwards at a point D such that BD = 1m.
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The moment of inertia of a body depends upon -- a) mass only
- b) angular velocity only
- c)distribution of particles only
- d)mass and distribution of mass about the axis
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The moment of inertia of a body depends upon -
a)
mass only
b)
angular velocity only
c)
distribution of particles only
d)
mass and distribution of mass about the axis
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
I = mr2, therefore it depends on body mass and its mass distribution.
A solution of 500 ml of 0.2 M KOH and 500 ml of 0.2 M HCl is mixed and stirred; the rise in temperature is T1. The experiment is repeated using 250 ml of each solution, the temperature raised is T2. Which of the following is true -- a)T1 = T2
- b)T1 = 2T2
- c)T1 = 4T2
- d)T2 = 9T1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A solution of 500 ml of 0.2 M KOH and 500 ml of 0.2 M HCl is mixed and stirred; the rise in temperature is T1. The experiment is repeated using 250 ml of each solution, the temperature raised is T2. Which of the following is true -
a)
T1 = T2
b)
T1 = 2T2
c)
T1 = 4T2
d)
T2 = 9T1
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
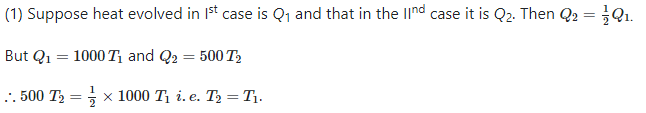
The energy currency of cell is—- a)GDP
- b)ATP
- c)ADP
- d)NAD
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The energy currency of cell is—
a)
GDP
b)
ATP
c)
ADP
d)
NAD
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
When the ATP converts to ADP, the ATP is said to be spent. he molecule is used like a battery within cells and allows the consumption of one of its phosphorous molecules.The energy currency used by all cells from bacteria to man is adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Which is the most abundant chemical for the living organisms?- a)Lipids
- b)Proteins
- c)Ions
- d)Water
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the most abundant chemical for the living organisms?
a)
Lipids
b)
Proteins
c)
Ions
d)
Water

|
Anand Jain answered |
Water is the most abundant chemical for the living organisms.
For which of the following change ΔH ≠ ΔE ?
a) H2(g) + I2(g) → 2HI (g)
b) HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O (l)
c) C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
d) N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
∆H = ∆U+∆ngRT
For ∆H not equal ∆U, ∆ng should not equal zero.
This happens only in option d, where ∆ng = -2
For ∆H not equal ∆U, ∆ng should not equal zero.
This happens only in option d, where ∆ng = -2
A wheel starting with angular velocity of 10 radian/sec acquires angular velocity of 100 radian/sec in 15 seconds. If moment of inertia is 10kg-m2, then applied torque (in newton-metre) is- a)900
- b)100
- c)90
- d)60
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A wheel starting with angular velocity of 10 radian/sec acquires angular velocity of 100 radian/sec in 15 seconds. If moment of inertia is 10kg-m2, then applied torque (in newton-metre) is
a)
900
b)
100
c)
90
d)
60
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
I(ωf - ωi)/t = τ
Hence, τ = 60
Hence, τ = 60
Consider the following statementsAssertion (A) : The moment of inertia of a rigid body reduces to its minimum value as compared to any other parallel axis when the axis of rotation passes through its centre of mass.Reason (R) : The weight of a rigid body always acts through its centre of mass in uniform gravitational field. Of these statements :- a)both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b) both A and R are true but R is not a correct explanation of A
- c)A is true but R is false
- d) A is false but R is true
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements
Assertion (A) : The moment of inertia of a rigid body reduces to its minimum value as compared to any other parallel axis when the axis of rotation passes through its centre of mass.
Reason (R) : The weight of a rigid body always acts through its centre of mass in uniform gravitational field. Of these statements :
a)
both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b)
both A and R are true but R is not a correct explanation of A
c)
A is true but R is false
d)
A is false but R is true
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Moment of inertia about its centroidal axis has a minimum value as the centroidal axis has mass evenly distributed around it thereby providing minimum resistance to rotation as compared to any other axis. Also the statement-2 is correct but is not the correct explanation for statement-1.
On applying a constant torque on a body- a) Linear velocity may be increases
- b)Angular velocity may be increases
- c)It will rotate with constant angular velocity
- d)It will move with constant velocity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
On applying a constant torque on a body
a)
Linear velocity may be increases
b)
Angular velocity may be increases
c)
It will rotate with constant angular velocity
d)
It will move with constant velocity
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
If a constant torque is applied it is possible that a positive angular acceleration gets generated which can generate a positive acceleration and hence increasing both velocity and angular velocity.
50.0 mL of 0.10 M HCl is mixed with 50.0 mL of 0.10 M NaOH. The solution temperature rises by 3.0°C Calculate the enthalpy of neutralization per mole of HCl. [take proper assumptions]- a)-2.5 × 102 kJ
- b)-1.3 × 102 kJ
- c)-8.4 × 101 kJ
- d)-6.3 × 101 kJ
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
50.0 mL of 0.10 M HCl is mixed with 50.0 mL of 0.10 M NaOH. The solution temperature rises by 3.0°C Calculate the enthalpy of neutralization per mole of HCl. [take proper assumptions]
a)
-2.5 × 102 kJ
b)
-1.3 × 102 kJ
c)
-8.4 × 101 kJ
d)
-6.3 × 101 kJ
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
No. of moles of HCl = 5 millimoles
No. of moles of NaOH = 5 millimoles
Mass of solution mixed = 50 gm+50 gm=100 gm
ΔH=−cmΔT(c=4.18 kJKg−1)
⇒ ΔH=−4.18×0.1×3
⇒ ΔH=−1.254 kJ (For 5 millimoles of water formed)
For 1 mole water = −1.254/5×10−3
=−2.5×102kJ
No. of moles of NaOH = 5 millimoles
Mass of solution mixed = 50 gm+50 gm=100 gm
ΔH=−cmΔT(c=4.18 kJKg−1)
⇒ ΔH=−4.18×0.1×3
⇒ ΔH=−1.254 kJ (For 5 millimoles of water formed)
For 1 mole water = −1.254/5×10−3
=−2.5×102kJ
(i) Cis - 2 - butene → trans - 2 - butene, ΔH1 (ii) Cis - 2 - butene → 1 - butene, ΔH2(iii) Trans - 2 - butene is more stable than cis - 2 - butene.(iv) Enthalpy of combustion of 1 - butene, ΔH = -649.8 kcal/mol(v) 9ΔH1 + 5 ΔH2 = 0(vi) Enthalpy of combustion of trans 2 - butene, ΔH = -647.0 kcal/molThe value of ΔH1 & ΔH2 in Kcal/mole are- a)-1.0, 1.8
- b)1.8, -1.0
- c)-5,9
- d)-2, 3, 6
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
(i) Cis - 2 - butene → trans - 2 - butene, ΔH1
(ii) Cis - 2 - butene → 1 - butene, ΔH2
(iii) Trans - 2 - butene is more stable than cis - 2 - butene.
(iv) Enthalpy of combustion of 1 - butene, ΔH = -649.8 kcal/mol
(v) 9ΔH1 + 5 ΔH2 = 0
(vi) Enthalpy of combustion of trans 2 - butene, ΔH = -647.0 kcal/mol
The value of ΔH1 & ΔH2 in Kcal/mole are
a)
-1.0, 1.8
b)
1.8, -1.0
c)
-5,9
d)
-2, 3, 6
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Trans-2-butene + 6O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 4H2O(l)
∆H = -647.0 kcal/mol ---(I)
1 - butene + 6O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 4H2O(l)
ΔH = -649.8 kcal/mol ---(II)
On (I)-(II)
Trans-2-butene → 1 - butene
ΔH = 2.7 kcal/mol
ΔH = (Hf)1-Butene - (Hf)trans-2-butene
= H2 - H1
H2 - H1 = 2.7 -----(A)
And 9ΔH1 + 5ΔH2 = 0 -----(B)
On solving eqn (A) and (B), we get
H1 = -1.0 and H2 = 1.8
∆H = -647.0 kcal/mol ---(I)
1 - butene + 6O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 4H2O(l)
ΔH = -649.8 kcal/mol ---(II)
On (I)-(II)
Trans-2-butene → 1 - butene
ΔH = 2.7 kcal/mol
ΔH = (Hf)1-Butene - (Hf)trans-2-butene
= H2 - H1
H2 - H1 = 2.7 -----(A)
And 9ΔH1 + 5ΔH2 = 0 -----(B)
On solving eqn (A) and (B), we get
H1 = -1.0 and H2 = 1.8
If x1, x2 and x3 are enthalpies of H - H, O = O and O - H bonds respectively, and x4 is the enthalpy of vaporisation of water, estimate the standard enthalpy of combustion of hydrogen- a)
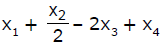
- b)
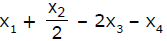
- c)
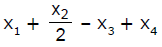
- d)
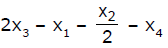
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If x1, x2 and x3 are enthalpies of H - H, O = O and O - H bonds respectively, and x4 is the enthalpy of vaporisation of water, estimate the standard enthalpy of combustion of hydrogen
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Combustion of hydrogen:
H2 + ½ O2→H2O (H−O−H)
As water contains two O−H bonds.
So, combustion enthalpy of hydrogen is:
ΔH= Bond energy of reactant − Bond energy of the product − Enthalpy of vaporization.
ΔH=x1+22−2x3−x4
H2 + ½ O2→H2O (H−O−H)
As water contains two O−H bonds.
So, combustion enthalpy of hydrogen is:
ΔH= Bond energy of reactant − Bond energy of the product − Enthalpy of vaporization.
ΔH=x1+22−2x3−x4
Which one of the following is fibrous protein?- a)Collagen
- b)Ribozymes
- c)Haemoglobin
- d)Hemicellulose
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is fibrous protein?
a)
Collagen
b)
Ribozymes
c)
Haemoglobin
d)
Hemicellulose

|
Shanaya Rane answered |
Collagen is a fibrous protein. It is the main structural protein in the extracellular space in thevarious connective tissues. It is the most abundant protein in mammals.
A polysaccharide present as storehouse of energy of plant tissues- a)Chitin
- b)Starch
- c)Hemi cellulose
- d)Cellulose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A polysaccharide present as storehouse of energy of plant tissues
a)
Chitin
b)
Starch
c)
Hemi cellulose
d)
Cellulose
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Polysaccharide
A polysaccharide is a large molecule made of many smaller monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars, like glucose. Special enzymes bind these small monomers together creating large sugar polymers, or polysaccharides. A polysaccharide is also called a glycan. A polysaccharide can be a homopolysaccharide, in which all the monosaccharides are the same, or a heteropolysaccharide in which the monosaccharides vary. Depending on which monosaccharides are connected, and which carbons in the monosaccharides connects, polysaccharides take on a variety of forms. A molecule with a straight chain of monosaccharides is called a linear polysaccharide, while a chain that has arms and turns is known as a branched polysaccharide.
Let IA and IB be moments of inertia of a body about two axes A and B respectively. The axis A passes through the centre of mass of the body but B does not.- a)IA < IB
- b) If IA < IB, the axes are parallel.
- c) If the axes are parallel, IA < IB
- d)If the axes are not parallel, IA ³ IB
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Let IA and IB be moments of inertia of a body about two axes A and B respectively. The axis A passes through the centre of mass of the body but B does not.
a)
IA < IB
b)
If IA < IB, the axes are parallel.
c)
If the axes are parallel, IA < IB
d)
If the axes are not parallel, IA ³ IB

|
EduRev Humanities answered |
If the axes are parallel, we use the formula:
Io = Icm + md2
For the first body the distance between the axis and the axis passing through C.O.M is 0
Therefore, Io = Icm + m(0)2 = lcm since it is mentioned in question
Whereas for the second body it is not passing through the C.O.M therefore, there is some distance between the axes, say 'd'
So, Io = Icm + md2
Io = Icm + md2
For the first body the distance between the axis and the axis passing through C.O.M is 0
Therefore, Io = Icm + m(0)2 = lcm since it is mentioned in question
Whereas for the second body it is not passing through the C.O.M therefore, there is some distance between the axes, say 'd'
So, Io = Icm + md2
One end of a uniform rod of mass m and length I is clamped. The rod lies on a smooth horizontal surface and rotates on it about the clamped end at a uniform angular velocity w. The force exerted by the clamp on the rod has a horizontal component- a)mw2l
- b)zero
- c) mg
- d)
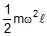
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One end of a uniform rod of mass m and length I is clamped. The rod lies on a smooth horizontal surface and rotates on it about the clamped end at a uniform angular velocity w. The force exerted by the clamp on the rod has a horizontal component
a)
mw2l
b)
zero
c)
mg
d)
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Consider a rod of length l and mass m rotating with an angular velocity of w
dF = dm l w2
dF = (m/l) dμ l w2
Integrating
F = ½mlw2
dF = dm l w2
dF = (m/l) dμ l w2
Integrating
F = ½mlw2
Which of the following carries the hereditary information from parents to progeny?- a)Nucleotides
- b)Nucleoside
- c)Nucleic acids
- d)Proteins
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following carries the hereditary information from parents to progeny?
a)
Nucleotides
b)
Nucleoside
c)
Nucleic acids
d)
Proteins
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Nucleic acid is the chemical name for the molecules RNA and DNA. The name comes from the fact that these molecules are acids – that is, they are good at donating protons and accepting electron pairs in chemical reactions – and the fact that they were first discovered in the nuclei of our cells.
The part of enzyme bound to the protein part by a covalent bond is called- a)Holoenzyme
- b)Cofactor
- c)Prosthetic group
- d)Apoenzyme
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The part of enzyme bound to the protein part by a covalent bond is called
a)
Holoenzyme
b)
Cofactor
c)
Prosthetic group
d)
Apoenzyme

|
Imk Pathsala answered |
A prosthetic group is a tightly covalently bound, specific non-polypeptide unit required for the biological function of some proteins. The prosthetic group may be organic (such as a vitamin, sugar, or lipid) or inorganic (such as a metal ion), but is not composed of amino acids.
In yeast, during fermentation the glycolysis pathway leads to- a)Production of glucose
- b)Production of oxygen
- c)Production of pyruvic acid
- d)Production of ethanol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In yeast, during fermentation the glycolysis pathway leads to
a)
Production of glucose
b)
Production of oxygen
c)
Production of pyruvic acid
d)
Production of ethanol

|
Jatin Chakraborty answered |
In yeast, during fermentation, the same pathway leads to the production of ethanol(alcohol).
A disc of radius 2m and mass 200kg is acted upon by a torque 100N-m. Its angular acceleration would be- a) 1 rad/sec2
- b)0.25 rad/sec2
- c)0.5 rad/sec2
- d)2 rad/sec2.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A disc of radius 2m and mass 200kg is acted upon by a torque 100N-m. Its angular acceleration would be
a)
1 rad/sec2
b)
0.25 rad/sec2
c)
0.5 rad/sec2
d)
2 rad/sec2.
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
F = ma
a = Wr
So, F = mwr
a = wr = acceleration
m = 200kg
F = 100 n-m, r = 2m, w = to be calculated
100 = 200 x w2
w = 0.25 rad/sec2
a = Wr
So, F = mwr
a = wr = acceleration
m = 200kg
F = 100 n-m, r = 2m, w = to be calculated
100 = 200 x w2
w = 0.25 rad/sec2
Two spheres of same mass and radius are in contact with each other. If the moment of inertia of a sphere about its diameter is I, then the moment of inertia of both the spheres about the tangent at their common point would be -- a)3I
- b)7I
- c)4I
- d)5I
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two spheres of same mass and radius are in contact with each other. If the moment of inertia of a sphere about its diameter is I, then the moment of inertia of both the spheres about the tangent at their common point would be -
a)
3I
b)
7I
c)
4I
d)
5I
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
The moment of inertia of a sphere about its diameter is given as,
I=2/5 MR2
The moment of inertia of the sphere about the tangent is given as,
I′=2/5MR2+MR2
I′=7/5MR2
The total moment of inertia of both spheres about the common tangent is given as,
It=2I′
It=2×7/5MR2
It=7I
I=2/5 MR2
The moment of inertia of the sphere about the tangent is given as,
I′=2/5MR2+MR2
I′=7/5MR2
The total moment of inertia of both spheres about the common tangent is given as,
It=2I′
It=2×7/5MR2
It=7I
. Select the correct order in the following :- a) 1 erg > 1 joule > 1 cal
- b)1 cal > 1 joule > 1 erg
- c) 1 erg > 1 cal > 1 joule
- d)1 joule > 1 cal > 1 erg
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
. Select the correct order in the following :
a)
1 erg > 1 joule > 1 cal
b)
1 cal > 1 joule > 1 erg
c)
1 erg > 1 cal > 1 joule
d)
1 joule > 1 cal > 1 erg
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
107 erg = 1 joule and 4.2 joules = 1 cal
Therefore 1 cal > 1 joule > 1 erg
Therefore 1 cal > 1 joule > 1 erg
The enthalpy of combustion of a substance -- a)is always positive
- b) is always negative
- c) can be either zero or greater than zero
- d)is unpredictable till calculations are done.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The enthalpy of combustion of a substance -
a)
is always positive
b)
is always negative
c)
can be either zero or greater than zero
d)
is unpredictable till calculations are done.

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
The reason behind is that combustion reactions are always exothermic. So the enthalpy of combustion is always less than zero.
A circular disc A of radius r is made from an iron plate of thickness t and another circular disc B of radius 4r is made from an iron plate of thickness t/4. The relation between the moments of inertia IA and IB is- a) IA > IB
- b)IA = IB
- c) IA < IB
- d) depends on the actual values of t and r.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A circular disc A of radius r is made from an iron plate of thickness t and another circular disc B of radius 4r is made from an iron plate of thickness t/4. The relation between the moments of inertia IA and IB is
a)
IA > IB
b)
IA = IB
c)
IA < IB
d)
depends on the actual values of t and r.
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
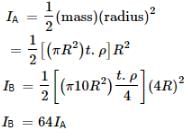
Proteins are made up of- a)Monomers
- b)Amino acids
- c)Homopolymers
- d)Nucleosides
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Proteins are made up of
a)
Monomers
b)
Amino acids
c)
Homopolymers
d)
Nucleosides
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Proteins are heteropolymers usually made of amino acids. While a nucleic acid like DNA or RNA is made of of only 4 types of nucleotide monomers, proteins are made of 20 types of monomers. Ans: (d) Proteins perform many physiological functions. ... Ans: (a) Glycogen is a homopolymer made of glucose units.
Moment of inertia of a thin semicircular disc (mass = M & radius = R) about an axis through point O and perpendicular to plane of disc, is given by : 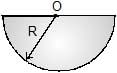
- a)
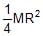
- b)
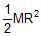
- c)
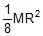
- d)MR2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Moment of inertia of a thin semicircular disc (mass = M & radius = R) about an axis through point O and perpendicular to plane of disc, is given by :
a)
b)
c)
d)
MR2
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Mass of semicircular disc = M
Suppose there is a circular disc of mass 2M, then
Moment of intertia of circular disc = ½ (2M)R2
Moment of intertia of circular disc = ½ (2M)R2 = MR2
=> So, Moment of intertia of semi-circular disc = ½ MR2
Suppose there is a circular disc of mass 2M, then
Moment of intertia of circular disc = ½ (2M)R2
Moment of intertia of circular disc = ½ (2M)R2 = MR2
=> So, Moment of intertia of semi-circular disc = ½ MR2
For the allotropic change represented by the equation C (graphite) → C (diamond), ΔH = 1.9 kJ. If 6 g of diamond and 6 g of graphite are separately burnt to yield CO2, the heat liberated in first case is- a) less than in the second case by 1.9 kJ
- b) more than in the second case by 11.4 kJ
- c) more than in the second case by 0.95 kJ
- d) less than in the second case by 11.4 kJ
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For the allotropic change represented by the equation C (graphite) → C (diamond), ΔH = 1.9 kJ. If 6 g of diamond and 6 g of graphite are separately burnt to yield CO2, the heat liberated in first case is
a)
less than in the second case by 1.9 kJ
b)
more than in the second case by 11.4 kJ
c)
more than in the second case by 0.95 kJ
d)
less than in the second case by 11.4 kJ
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
∆H given in the question is for one mole of C (g). If 6 gm of diamond and graphite are burnt in oxygen then the C (diamond) will first convert to graphite and then it will form CO2. While C (graphite) will directly form CO2. So due to the conversion of diamond into graphite, we will get extra heat. And since we have 6gm (0.5 mol) of diamond, so the heat released will be 0.5×1.9 kJ or 0.95 kJ more than the second case.
For the same total mass which of the following will have the largest moment of inertia about an axis passing through its centre of mass and perpendicular to the plane of the body- a)a disc of radius a
- b) a ring of radius a
- c)a square lamina of side 2a
- d) four rods forming a square of side 2a
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For the same total mass which of the following will have the largest moment of inertia about an axis passing through its centre of mass and perpendicular to the plane of the body
a)
a disc of radius a
b)
a ring of radius a
c)
a square lamina of side 2a
d)
four rods forming a square of side 2a

|
Lyrics Master answered |
Moment of inertia depends on distribution of mass around axis...the more the mass near the axis less the moment of inertia...four rods forming a square has less more moment of inertia because of less mass ner axis
A disc of metal is melted to recast in the form of a solid sphere. The moment of inertias about a vertical axis passing through the centre would -- a) decrease
- b)increase
- c) remains same
- d)nothing can be said
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A disc of metal is melted to recast in the form of a solid sphere. The moment of inertias about a vertical axis passing through the centre would -
a)
decrease
b)
increase
c)
remains same
d)
nothing can be said
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Moment of inertia will decrease, because
Id=1/2mr2 and Is=2/5mr2,
the radius of sphere formed on recasting the disc will also decrease.
Id=1/2mr2 and Is=2/5mr2,
the radius of sphere formed on recasting the disc will also decrease.
The enthalpy of neutralisation of HCl and NaOH is -57 kJ mol-1. The heat evolved at constant pressure (in kJ) when 0.5 mole of H2SO4 react with 0.75 mole of NaOH is equal to- a)57 ×
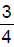
- b) 57 × 0.5
- c)57
- d) 57 × 0.25
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The enthalpy of neutralisation of HCl and NaOH is -57 kJ mol-1. The heat evolved at constant pressure (in kJ) when 0.5 mole of H2SO4 react with 0.75 mole of NaOH is equal to
a)
57 ×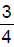
b)
57 × 0.5
c)
57
d)
57 × 0.25

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
-57 kJ of heat evolved when 1 mole of NaOH reacted with an acid.
We have 1 mole of H+ and 0.75 moles of OH-. So OH- iis limiting reagent. Or only 0.75 moles of OH- will be used. So for 1 mole of OH-, we have -57 kJ heat released. Therefore for 0.75 moles, we have ¾× -57 kJ heat released.
We have 1 mole of H+ and 0.75 moles of OH-. So OH- iis limiting reagent. Or only 0.75 moles of OH- will be used. So for 1 mole of OH-, we have -57 kJ heat released. Therefore for 0.75 moles, we have ¾× -57 kJ heat released.
A stone of mass 4kg is whirled in a horizontal circle of radius 1m and makes 2 rev/sec. The moment of inertia of the stone about the axis of rotation is- a) 64 kg × m2
- b) 4 kg × m2
- c)16 kg × m2
- d)1 kg × m2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A stone of mass 4kg is whirled in a horizontal circle of radius 1m and makes 2 rev/sec. The moment of inertia of the stone about the axis of rotation is
a)
64 kg × m2
b)
4 kg × m2
c)
16 kg × m2
d)
1 kg × m2
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
By using the Basic formula i.e I = MR^2
Where M = 4Kg , R = 1m
I = 4 x 1 ^2 = 4Kg/m^2
Chapter doubts & questions for August Week 4 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of August Week 4 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup