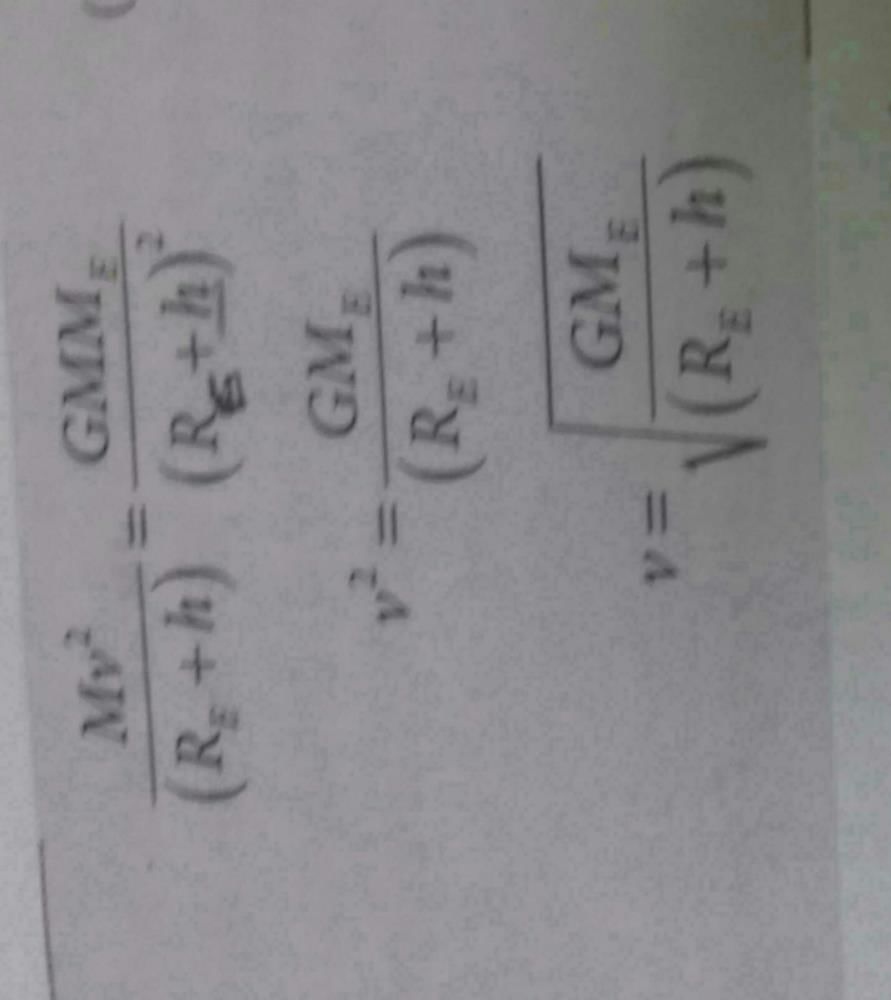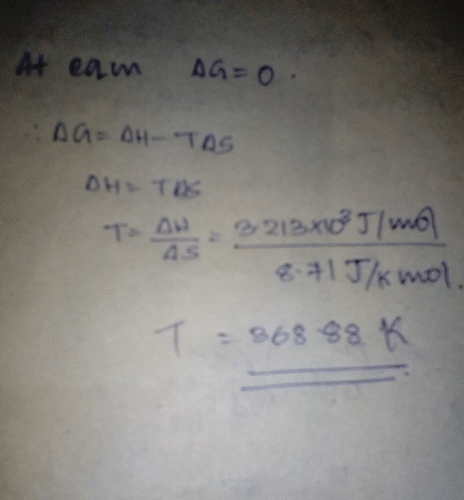All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of September Week 2 for NEET Exam
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The value of escape velocity on earth when the body is thrown making an angle of 45o with the horizontal is
- A:
11.2 x 21/4 km/s
- B:
22.4 km/s
- C:
11.2 x 21/2 km/s
- D:
11.2 km/s
The answer is d.
The value of escape velocity on earth when the body is thrown making an angle of 45o with the horizontal is
11.2 x 21/4 km/s
22.4 km/s
11.2 x 21/2 km/s
11.2 km/s
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Escape velocity does not depend on the angle of projection. Escape velocity will remain the same.
Hence, escape velocity is 11.2km/s .
Hence, escape velocity is 11.2km/s .
In meiosis, the daughter cells are not similar to the parent because of- a)Crossing over
- b)Synapsis
- c)Both 1 and 2 above
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In meiosis, the daughter cells are not similar to the parent because of
a)
Crossing over
b)
Synapsis
c)
Both 1 and 2 above
d)
None of the above
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Meiosis is basically an extended and complex version of mitosis. The term “Reductional division” gives this process the underlying definition, a sequence of events that results in reduction of the total number of chromosomes (from a diploid state of 46 to a haploid state of 23; in general, from ‘2n’ to ‘n’).
However, in the initial steps of meiosis, there is an eventful period wherein the previously duplicated chromosomes (in the S-Phase or Synthesis phase of cell cycle) exchange a part of their respective genetic material, a process termed as Recombination through crossing over (of the genetic material). The further steps are the same as in mitosis, but because of the exchange, the daughter chromosomes will have a different identity than their parents.
Crossing over may result in- a)Addition of genetic material
- b)Deletion of genetic material
- c)Exchange of genetic material
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Crossing over may result in
a)
Addition of genetic material
b)
Deletion of genetic material
c)
Exchange of genetic material
d)
All of the above
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Crossing over is the exchange of genes between two chromosomes, resulting in non-identical chromatids that comprise the genetic material of gametes. This process occurs during Prophase I of Meiosis, just prior to chromosome alignment and splitting of the cell.
Meiosis results in
- a)Production of gametes
- b)Reduction in Chromosome number
- c)Introduction of variation
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Meiosis results in
a)
Production of gametes
b)
Reduction in Chromosome number
c)
Introduction of variation
d)
All of the above
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
As previously mentioned, the first round of nuclear division that occurs during the formation of gametes is called meiosis I. It is also known as the reduction division because it results in cells that have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
What does the term escape speed of a planet mean?- a)the minimum speed of an object to reach a height equal to the radius of the planet
- b)cannot be defined
- c)the minimum speed required for an object to reach infinity
- d)the maximum speed required for an object to reach infinity
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What does the term escape speed of a planet mean?
a)
the minimum speed of an object to reach a height equal to the radius of the planet
b)
cannot be defined
c)
the minimum speed required for an object to reach infinity
d)
the maximum speed required for an object to reach infinity
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Escape velocity is the minimum velocity with which the body has to be projected vertically upwards from the surface of the earth so that it crosses the gravitational field of earth and never returns back on its own.
Match List I and List II, and select the correct answer.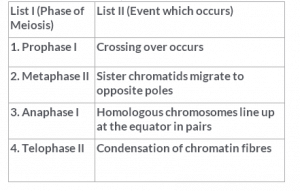
- a)1, 2 and 3 are correct.
- b)1 and 3 are correct.
- c)2 and 4 are correct.
- d)Only 1 is correct.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Match List I and List II, and select the correct answer.

a)
1, 2 and 3 are correct.
b)
1 and 3 are correct.
c)
2 and 4 are correct.
d)
Only 1 is correct.

|
Trisha Vashisht answered |
Correct Answer :- d
Explanation : Genetic variation comes from crossing over, which may occur during prophase I of meiosis.
In prophase I of meiosis, the replicated homologous pair of chromosomes comes together in the process called synapsis, and sections of the chromosomes are exchanged.
Standard entropies of X2, Y2 and XY3 are given below the reaction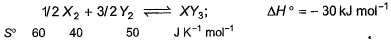 Q. At what temperature, reaction would be in equilibrium?
Q. At what temperature, reaction would be in equilibrium? - a)500 K
- b)750 K
- c)1000 K
- d)1250 K
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Standard entropies of X2, Y2 and XY3 are given below the reaction
Q. At what temperature, reaction would be in equilibrium?
a)
500 K
b)
750 K
c)
1000 K
d)
1250 K
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
1/2X2 + 3/2Y2 ⟶XY3,
ΔH= −30 kJ
ΔSreaction = ∑ΔSproduct−∑ΔSreactant
X2 + 3Y2 → 2XY3
ΔH=−60 kJ
ΔSreaction = 2×50−3×40−1×60 =100−120−60=−80 JK−1mol−1
ΔG=ΔH−TΔS=0
ΔH=TΔS
1000×(−60)=−80×T
T=750 K
ΔH= −30 kJ
ΔSreaction = ∑ΔSproduct−∑ΔSreactant
X2 + 3Y2 → 2XY3
ΔH=−60 kJ
ΔSreaction = 2×50−3×40−1×60 =100−120−60=−80 JK−1mol−1
ΔG=ΔH−TΔS=0
ΔH=TΔS
1000×(−60)=−80×T
T=750 K
An unmanned space probe is to the thrown with such a velocity that it does not return to earth. It should be thrown with- a)velocity ≥ (2GM/ R)1/2
- b)a great velocity but nothing more can be said
- c)velocity >(2GM)1/2/ R necessarily
- d)only the velocity = (2GM)1/2/R
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An unmanned space probe is to the thrown with such a velocity that it does not return to earth. It should be thrown with
a)
velocity ≥ (2GM/ R)1/2
b)
a great velocity but nothing more can be said
c)
velocity >(2GM)1/2/ R necessarily
d)
only the velocity = (2GM)1/2/R
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
It should be thrown with a velocity greater than or equal to escape velocity of the planet only then it will not return to Earth
Escape Velocity = √(2GM/R) = (2GM/R)1/2
Hence A is the correct answer.
Escape Velocity = √(2GM/R) = (2GM/R)1/2
Hence A is the correct answer.
The escape velocity for the moon is nearly- a)11.2km/s
- b)2.4km/s
- c)24km/s
- d)10km/s
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The escape velocity for the moon is nearly
a)
11.2km/s
b)
2.4km/s
c)
24km/s
d)
10km/s
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
About 11.2 km/s
In common usage, the initial point is on the surface of a planet or moon. On the surface of the Earth, the escape velocity is about 11.2 km/s, which is approximately 33 times the speed of sound (Mach 33) and several times the muzzle velocity of a rifle bullet (up to 1.7 km/s).
Synapsis occurs in which of the following stages of meiosis?- a)Diakinesis
- b)Pachytene
- c)Leptotene
- d)Zygotene
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Synapsis occurs in which of the following stages of meiosis?
a)
Diakinesis
b)
Pachytene
c)
Leptotene
d)
Zygotene
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Most of the events that function to differentiate meiosis from mitosis occur in Prophase I
Homologous chromosomes form bivalents (or tetrads) and crossing over occurs between non-sister chromatids
Prophase I is divided into 5 distinctive sub-stages:
1. Leptotene – The chromosomes begin to condense and are attached to the nuclear membrane via their telomeres
2. Zygotene – Synapsis begins with a synaptonemal complex forming between homologous chromosomes
3. Pachytene – Crossing over of genetic material occurs between non-sister chromatids
4. Diplotene – Synapsis ends with disappearance of synaptonemal complex; homologous pairs remain attached at chiasmata
5. Diakinesis – Chromosomes become fully condensed and nuclear membrane disintegrates prior to metaphase I
Synaptonemal complex is observed during cell division in- a)Meiotic prophase
- b)Mitotic prophase
- c)Meiotic metaphase
- d)Mitotic telophase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Synaptonemal complex is observed during cell division in
a)
Meiotic prophase
b)
Mitotic prophase
c)
Meiotic metaphase
d)
Mitotic telophase

|
Imk Pathsala answered |
The formation of tetrad is a special characteristic of Prophase 1 of meiosis 1.
The homologous pair aligns with each other and gets ready for crossing over.
So, the correct option is 'Meiotic Prophase'.
The homologous pair aligns with each other and gets ready for crossing over.
So, the correct option is 'Meiotic Prophase'.
When synapsis is complete all along the chromosome, the cell is said to have entered a stage called- a)Diakinesis
- b)Zygotene
- c)Diplotene
- d)Pachytene
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When synapsis is complete all along the chromosome, the cell is said to have entered a stage called
a)
Diakinesis
b)
Zygotene
c)
Diplotene
d)
Pachytene
|
|
Surbhi Dasgupta answered |
Pachytene Stage in Meiosis
The process of meiosis is divided into several stages, one of which is the Pachytene stage. This stage occurs during the first meiotic division or meiosis I. During this stage, homologous chromosomes pair up and form structures called bivalents or tetrads. The Pachytene stage is characterized by the following events:
Synapsis
During the Pachytene stage, homologous chromosomes pair up and form structures called bivalents or tetrads. This process is called synapsis. The synaptonemal complex plays a crucial role in this process. The complex is composed of proteins that hold the homologous chromosomes together.
Crossing over
Crossing over occurs during the Pachytene stage. It is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. This process results in the creation of new combinations of genes, which contributes to genetic diversity.
Chiasmata formation
During the Pachytene stage, the homologous chromosomes that have paired up undergo crossing over. This process results in the formation of chiasmata, which are visible under a microscope. Chiasmata are the points where the homologous chromosomes crisscross and exchange genetic material.
Conclusion
When synapsis is complete all along the chromosome, the cell is said to have entered a stage called Pachytene. During this stage, homologous chromosomes pair up and form bivalents or tetrads. Synapsis, crossing over, and chiasmata formation occur during this stage. The Pachytene stage is an essential process in meiosis as it contributes to the genetic diversity of offspring.
The process of meiosis is divided into several stages, one of which is the Pachytene stage. This stage occurs during the first meiotic division or meiosis I. During this stage, homologous chromosomes pair up and form structures called bivalents or tetrads. The Pachytene stage is characterized by the following events:
Synapsis
During the Pachytene stage, homologous chromosomes pair up and form structures called bivalents or tetrads. This process is called synapsis. The synaptonemal complex plays a crucial role in this process. The complex is composed of proteins that hold the homologous chromosomes together.
Crossing over
Crossing over occurs during the Pachytene stage. It is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. This process results in the creation of new combinations of genes, which contributes to genetic diversity.
Chiasmata formation
During the Pachytene stage, the homologous chromosomes that have paired up undergo crossing over. This process results in the formation of chiasmata, which are visible under a microscope. Chiasmata are the points where the homologous chromosomes crisscross and exchange genetic material.
Conclusion
When synapsis is complete all along the chromosome, the cell is said to have entered a stage called Pachytene. During this stage, homologous chromosomes pair up and form bivalents or tetrads. Synapsis, crossing over, and chiasmata formation occur during this stage. The Pachytene stage is an essential process in meiosis as it contributes to the genetic diversity of offspring.
The gravitational potential due to the gravitational force on the earth is defined as the- a)potential energy multiplied by the mass of the object
- b)potential energy of the mass placed at that point
- c)numerically equal to the potential energy
- d)potential energy of a unit mass at that point.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The gravitational potential due to the gravitational force on the earth is defined as the
a)
potential energy multiplied by the mass of the object
b)
potential energy of the mass placed at that point
c)
numerically equal to the potential energy
d)
potential energy of a unit mass at that point.
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
Gravitational Potential
Gravitational Potential is dened as the potential energy of a particle of unit mass at that point due to the gravitational force exerted byearth. Gravitational potential energy of a unit mass is known as gravitational potential.
Gravitational Potential is:- a)negative, scalar quantity , unit JKg-1
- b)positive, vector quantity , unit JKg-1
- c)positive, scalar quantity , unit JKg-1
- d)negative, vector quantity , unit JKg-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Gravitational Potential is:
a)
negative, scalar quantity , unit JKg-1
b)
positive, vector quantity , unit JKg-1
c)
positive, scalar quantity , unit JKg-1
d)
negative, vector quantity , unit JKg-1

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
Gravitational potential (radial fields) at a point in a radial field is the work done per unit mass against the field, in bringing a small mass from infinite distance to the point. Since gravitational fields are attractive and the potential at infinite distance is zero, all points within the field have negative values of potential. Gravitational potential is a scalar quantity with SI unit J kg^-1. The symbol used is mostly V but sometimes or Vr or V(r). A radial gravitational field is one in which the field strength has the same magnitude at all points at a given distance from the center.
Which reaction, with the following values of ΔH and ΔS at 400 K is spontaneous and endothermic?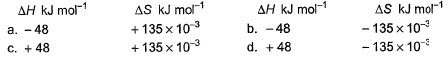
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which reaction, with the following values of ΔH and ΔS at 400 K is spontaneous and endothermic?
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Om Desai answered |
∆G = ∆H - T∆S
For opt (c), ∆G = 48000 - 400(135)
= 48000 - 54000
= -6000
∆G is -ve
Therefore reaction is spontaneous.
For opt (c), ∆G = 48000 - 400(135)
= 48000 - 54000
= -6000
∆G is -ve
Therefore reaction is spontaneous.
When a satellite moves in a circular orbit, the _______acceleration is provided by the gravitational attraction of the earth- a)tangential
- b)centrifugal
- c)centripetal
- d)fictitious
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When a satellite moves in a circular orbit, the _______acceleration is provided by the gravitational attraction of the earth
a)
tangential
b)
centrifugal
c)
centripetal
d)
fictitious
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
When any body or particle moves in circular orbit centripetal force acts on it and to move the object centripetal acceleration is necessary. So, when a satellite moves in circular orbit the centripetal acceleration is provided by the gravitational attraction of the earth.
The value of log10 K for a reaction, A 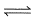 B is (Given, ΔH°298 = - 54.07 kJ mol-1;ΔS°298 = + 10 JK-1 mol-1; R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1 2.303 x 8.314 x 298 = 5705) [IITJEE2007]
B is (Given, ΔH°298 = - 54.07 kJ mol-1;ΔS°298 = + 10 JK-1 mol-1; R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1 2.303 x 8.314 x 298 = 5705) [IITJEE2007]- a)5
- b)10
- c)95
- d)100
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of log10 K for a reaction, A 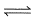 B is (Given, ΔH°298 = - 54.07 kJ mol-1;
B is (Given, ΔH°298 = - 54.07 kJ mol-1;
ΔS°298 = + 10 JK-1 mol-1; R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1 2.303 x 8.314 x 298 = 5705)
[IITJEE2007]
a)
5
b)
10
c)
95
d)
100
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
∆G° = ∆H° - T∆S°
= -54070 - 298 10
= -57050
∆G° = -2.303 RT log10k
-57050 = -2.303 8.314 298 log10k
57050 = 5705 log10k
log10k = 10
= -54070 - 298 10
= -57050
∆G° = -2.303 RT log10k
-57050 = -2.303 8.314 298 log10k
57050 = 5705 log10k
log10k = 10
An earth satellite is moved from one stable circular orbit to a farther stable circular orbit. which one of following quantity increases- a)gravitational potential energy
- b)centripetal acceleration
- c)gravitationl force
- d)linear orbital speed
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An earth satellite is moved from one stable circular orbit to a farther stable circular orbit. which one of following quantity increases
a)
gravitational potential energy
b)
centripetal acceleration
c)
gravitationl force
d)
linear orbital speed
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
We know that gravitational potential is negative in sign and its magnitude decreases when distance from the massive attracting object increases, hence when considered with sign we can say that gravitational potential increases with increases in distance.
Escape velocity is:- a)The minimum velocity with which the body has to be projected vertically upwards from the surface of the earth so that it crosses the gravitational field of earth and never returns back on its own.
- b)The minimum velocity with which the body has to be projected vertically upwards from the surface of the earth so that it crosses the gravitational field of earth and returns back
- c)The maximum velocity with which the body has to be projected vertically upwards from the surface of the earth so that it crosses the gravitational field of earth and returns back.
- d)The maximum velocity with which the body has to be projected vertically upwards from the surface of the earth so that it crosses the gravitational field of earth and never returns back on its own
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Escape velocity is:
a)
The minimum velocity with which the body has to be projected vertically upwards from the surface of the earth so that it crosses the gravitational field of earth and never returns back on its own.
b)
The minimum velocity with which the body has to be projected vertically upwards from the surface of the earth so that it crosses the gravitational field of earth and returns back
c)
The maximum velocity with which the body has to be projected vertically upwards from the surface of the earth so that it crosses the gravitational field of earth and returns back.
d)
The maximum velocity with which the body has to be projected vertically upwards from the surface of the earth so that it crosses the gravitational field of earth and never returns back on its own
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Escape velocity is the minimum velocity with which the body has to be projected vertically upwards from the surface of the earth so that it crosses the gravitational field of earth and never returns back on its own.
What could be the maximum value for gravitational potential energy?- a)1
- b)zero
- c)infinity
- d)1000
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What could be the maximum value for gravitational potential energy?
a)
1
b)
zero
c)
infinity
d)
1000
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
As, U=−Gm1m2/r,
it can be used to describe the potential energy in a system of point charges (or radially symmetric spheres) as a function of their separation distance r, then the maximum value is zero at infinite separation.
Hence, its maximum value is zero at infinity.
it can be used to describe the potential energy in a system of point charges (or radially symmetric spheres) as a function of their separation distance r, then the maximum value is zero at infinite separation.
Hence, its maximum value is zero at infinity.
Passage IIFor oxidation of iron at 298 K, 4 Fe (s) + 3 O2(g) → 2 Fe2O3(s)
ΔS° = - 549.4 JK-1 mol-1 and ΔH ° = - 1648 . 0 kJ mol-1 Q. Select the correct alternate.- a)This reaction is spontaneous
- b)ΔS° (surrounding) > 0
- c)ΔS° (total) > 0
- d)All of these are correct statements
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage II
For oxidation of iron at 298 K, 4 Fe (s) + 3 O2(g) → 2 Fe2O3(s)
ΔS° = - 549.4 JK-1 mol-1 and ΔH ° = - 1648 . 0 kJ mol-1
ΔS° = - 549.4 JK-1 mol-1 and ΔH ° = - 1648 . 0 kJ mol-1
Q. Select the correct alternate.
a)
This reaction is spontaneous
b)
ΔS° (surrounding) > 0
c)
ΔS° (total) > 0
d)
All of these are correct statements

|
Deepaklal T S answered |
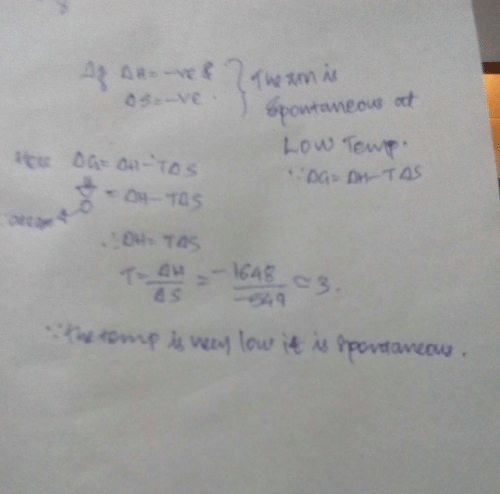
Which of the following is the correct sequence for a meiotic cell cycle?
S → G1 → G2 → M → S
G1 → S → G2 → M → G1
G2 → G1 → S → M → G2
G1 → G2 → S → M → G2- a)A
- b)B
- c)C
- d)D
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the correct sequence for a meiotic cell cycle?
S → G1 → G2 → M → S
G1 → S → G2 → M → G1
G2 → G1 → S → M → G2
G1 → G2 → S → M → G2
S → G1 → G2 → M → S
G1 → S → G2 → M → G1
G2 → G1 → S → M → G2
G1 → G2 → S → M → G2
a)
A
b)
B
c)
C
d)
D
|
|
Sagar Singh answered |
Interphase, Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I, Cytokinesis, Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II, Cytokinesis
The energy required to be spent by a satellite of mass m and speed v and orbital radius r in completing a circular orbit once round the earth of mass M is- a)GMm/r
- b)2GMm/r
- c)GMm/2r
- d)zero
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The energy required to be spent by a satellite of mass m and speed v and orbital radius r in completing a circular orbit once round the earth of mass M is
a)
GMm/r
b)
2GMm/r
c)
GMm/2r
d)
zero
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
As the satellite is bounded by earth's gravitational field and has some velocity, it would completely revolve around the circular orbit without any external energy required.
Velocity of geostationary satellite with respect to earth is- a)10 ms-1
- b)15 ms-1
- c)zero
- d)1 ms-1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Velocity of geostationary satellite with respect to earth is
a)
10 ms-1
b)
15 ms-1
c)
zero
d)
1 ms-1
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Because geostationary satellite ( completes it's rotation in about 24hrs).and it's rotation cycle is same as that of Earth .thus it's velocity is zero with respect to earth
Cross-like configurations when non-sister chromatids of a bivalent come in contact during the first meiotic division are- a)Chiasmata
- b)Chromomeres
- c)Bivalents
- d)Centromeres
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cross-like configurations when non-sister chromatids of a bivalent come in contact during the first meiotic division are
a)
Chiasmata
b)
Chromomeres
c)
Bivalents
d)
Centromeres
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Chiasmata) is the point of contact, the physical link, between two (non-sister) chromatids belonging to homologous chromosomes. At a given chiasma, an exchange of genetic material can occur between both chromatids, what is called a chromosomal crossover, but this is much more frequent during meiosis than mitosis.
Direction (Q. No. 9) This sectionis based on statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the code given below.Q. Statement I :Every endothermic reaction is spontaneous if TΔS > ΔH.Statement II : Sign of ΔG is the true criterion for deciding spontaneity of a reaction.- a)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
- b)Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
- c)Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- d)Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. No. 9) This sectionis based on statement I and Statement II. Select the correct answer from the code given below.
Q.
Statement I :Every endothermic reaction is spontaneous if TΔS > ΔH.
Statement II : Sign of ΔG is the true criterion for deciding spontaneity of a reaction.
a)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I
b)
Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is not the correct explanation of Statement I
c)
Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
d)
Statement II is correct but Statement I is incorrect

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Statement I: Every endothermic reaction is spontaneous if TΔS > ΔH.
Endothermic reactions have a positive ΔH (heat absorbed). For spontaneity, we use the Gibbs free energy equation:
ΔG=ΔH−TΔS\Delta G = \Delta H - T\Delta SΔG=ΔH−TΔS For a process to be spontaneous, ΔG<0\Delta G < 0ΔG<0. If TΔS>ΔHT\Delta S > \Delta HTΔS>ΔH, then ΔG\Delta GΔG becomes negative, indicating spontaneity. Hence, Statement I is correct.
ΔG=ΔH−TΔS\Delta G = \Delta H - T\Delta SΔG=ΔH−TΔS For a process to be spontaneous, ΔG<0\Delta G < 0ΔG<0. If TΔS>ΔHT\Delta S > \Delta HTΔS>ΔH, then ΔG\Delta GΔG becomes negative, indicating spontaneity. Hence, Statement I is correct.
Statement II: Sign of ΔG is the true criterion for deciding spontaneity of a reaction.
This is a fundamental thermodynamic principle. The sign of ΔG\Delta GΔG indeed determines whether a reaction is spontaneous (ΔG<0\Delta G < 0ΔG<0) or non-spontaneous (ΔG>0\Delta G > 0ΔG>0). Hence, Statement II is also correct.
Correct Answer: Since both statements are correct and the second statement explains the first, the correct option is:
A: Both Statement I and Statement II are correct and Statement II is the correct explanation of Statement I.
During meiosis, crossover occurs between- a)Non-sister chromatids of non-homologous chromosomes
- b)Sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes
- c)Sister chromatids of non-homologous chromosomes
- d)Non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
During meiosis, crossover occurs between
a)
Non-sister chromatids of non-homologous chromosomes
b)
Sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes
c)
Sister chromatids of non-homologous chromosomes
d)
Non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes

|
Shibashish Das answered |
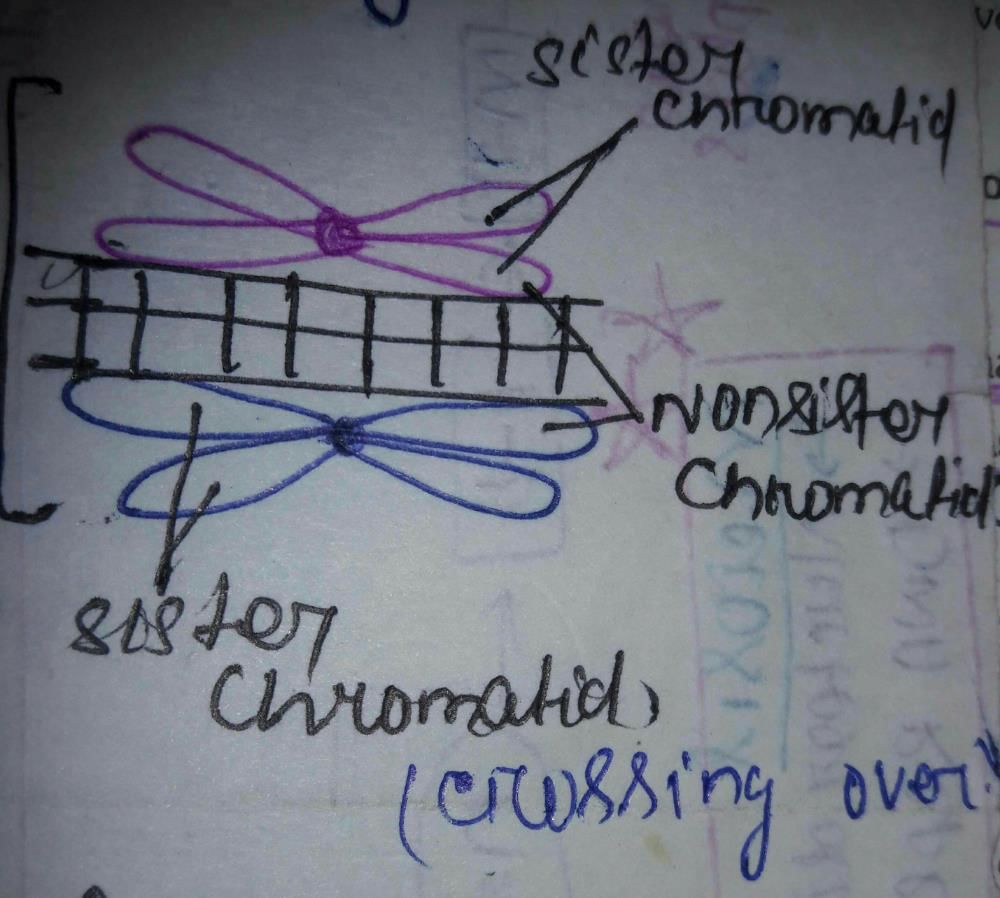
What is gravitational potential?- a)It is defined as the work done in taking a unit mass from one point to that point
- b)It is defined as the work done in taking a unit mass from infinity to that point
- c)It is defined as the energy spent in taking a unit mass from infinity to that point.
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is gravitational potential?
a)
It is defined as the work done in taking a unit mass from one point to that point
b)
It is defined as the work done in taking a unit mass from infinity to that point
c)
It is defined as the energy spent in taking a unit mass from infinity to that point.
d)
none

|
Pranavi Chavan answered |
The concept of Gravitational Potential:
The gravitational potential at a point is dened as the work done in bringing the unit mass from innity to that point without acceleration.
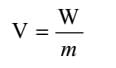
Gravitational potential is a scalar quantity. It is denoted by V. Its S.I. unit is J kg^-1 . Its c.g.s. unit is erg g^-1


Dimensions of gravitational potential are [M^0 L^2 T^-2 ].
Weight is- a)The force with which an object is pushed towards the centre of the Earth
- b)The force with which an object is pulled towards the centre of the Earth
- c)The force with which an object is pulled towards the centre of the Sun.
- d)The energy with which an object is pulled towards the centre of the Earth
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Weight is
a)
The force with which an object is pushed towards the centre of the Earth
b)
The force with which an object is pulled towards the centre of the Earth
c)
The force with which an object is pulled towards the centre of the Sun.
d)
The energy with which an object is pulled towards the centre of the Earth
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
Weight is a force caused by gravity. The weight of an object is the gravitational force between the object and the Earth. The more mass the object has the greater its weight will be. Weight is a force, so it's measured in newtons.
Direction (Q. Nos. 10 and 11) This section contains 2 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.Q. Which of the following statements is/are true?- a)The entropy of a substance increases on going from the liquid to the vapour state at any temperature
- b)An exothermic reaction will always be spontaneous
- c)Reactions with a positive (ΔH° and ΔS°) can never be product favoured
- d)If ΔG° for a reaction is negative, the reaction will have an equilibrium constant i greater than one
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 10 and 11) This section contains 2 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THANT ONE is correct.
Q. Which of the following statements is/are true?
a)
The entropy of a substance increases on going from the liquid to the vapour state at any temperature
b)
An exothermic reaction will always be spontaneous
c)
Reactions with a positive (ΔH° and ΔS°) can never be product favoured
d)
If ΔG° for a reaction is negative, the reaction will have an equilibrium constant i greater than one
|
|
Pallabi Rane answered |
The entropy of a substance increases on going from the liquid to the vapour state at any temperature. It is true. As randomness increases, entropy also increases.
∆G = ∆H - T∆S. So for spontaneous reaction, all 3(T, ∆H and ∆S) are needed.
An exothermic reaction will always be spontaneous. THis is false
Reactions with a positive (ΔH° and ΔS°) can never be product favoured. False, for a larger value of T, ∆G might be negative.
If ΔG° for a reaction is negative, the reaction will have an equilibrium constant greater than one. True, for ΔG° less than 0, reaction is spontaneous and so, ith=s eqm constant will have value greater than 1.
∆G = ∆H - T∆S. So for spontaneous reaction, all 3(T, ∆H and ∆S) are needed.
An exothermic reaction will always be spontaneous. THis is false
Reactions with a positive (ΔH° and ΔS°) can never be product favoured. False, for a larger value of T, ∆G might be negative.
If ΔG° for a reaction is negative, the reaction will have an equilibrium constant greater than one. True, for ΔG° less than 0, reaction is spontaneous and so, ith=s eqm constant will have value greater than 1.
Calculate the Gibbs free energy for the reaction of conversion of ATP into ADP at 293 Kelvin the change in enthalpy is 19.07 Kcal and the change in entropy is 90 cal per Kelvin.- a)7.3 cal
- b)-5.3 Kcal
- c)7.3 Kcal
- d) -7.3 Kcal
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the Gibbs free energy for the reaction of conversion of ATP into ADP at 293 Kelvin the change in enthalpy is 19.07 Kcal and the change in entropy is 90 cal per Kelvin.
a)
7.3 cal
b)
-5.3 Kcal
c)
7.3 Kcal
d)
-7.3 Kcal
|
|
Krithika Ahuja answered |
Calculation of Gibbs Free Energy for the Conversion of ATP into ADP:
- Given data:
- Change in enthalpy (ΔH) = 19.07 kcal
- Change in entropy (ΔS) = 90 cal/K
- Temperature (T) = 293 K
Formula to calculate Gibbs Free Energy (ΔG):
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
Calculation:
ΔG = 19.07 kcal - (293 K * 90 cal/K)
ΔG = 19.07 kcal - 26370 cal
ΔG = -26350 cal
ΔG = -26.35 kcal (Converting cal to kcal)
Therefore, the Gibbs free energy for the conversion of ATP into ADP at 293 K is -26.35 kcal. Since the options are in Kcal, the answer is -26.35 Kcal, which is closest to -7.3 Kcal (rounded to one decimal place). So, the correct answer is option 'D' (-7.3 Kcal).
A body is projected with velocity ‘v’ from a planet with escape velocity ‘ve‘ .What will happen if v < ve
- a)Body will leave the planets atmosphere and never come back
- b)Will reach certain height and orbit around planet or fall back on the planet
- c)Will reach certain height and orbit around planet
- d)Fall back on the planet
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A body is projected with velocity ‘v’ from a planet with escape velocity ‘ve‘ .What will happen if v < ve
a)
Body will leave the planets atmosphere and never come back
b)
Will reach certain height and orbit around planet or fall back on the planet
c)
Will reach certain height and orbit around planet
d)
Fall back on the planet
|
|
Akash Chakraborty answered |
Please provide the complete question. Without the full question and additional information, we cannot provide a meaningful answer.
The energy required to be spent by a satellite of mass m and speed v and orbital radius r in completing a circular orbit once round the earth of mass M is- a)GMm/r
- b)2GMm/r
- c)GMm/2r
- d)zero
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The energy required to be spent by a satellite of mass m and speed v and orbital radius r in completing a circular orbit once round the earth of mass M is
a)
GMm/r
b)
2GMm/r
c)
GMm/2r
d)
zero

|
Shakir Parvej answered |
too easy dear the satellite is in a conservative field in a equipotential surface so no need of energy
Earth attracts a body with a force equal to its- a)weight
- b)area
- c)volume
- d)pollution
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Earth attracts a body with a force equal to its
a)
weight
b)
area
c)
volume
d)
pollution
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Weight is a consequence of the universal law of gravitation: any two objects, because of their masses, attract each other with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
ΔHvap = 30 kJ mol-1 and ΔSvap = 75 J mol-1 K-1. Thus, temperature of vapour at one atmosphere is[IIT JEE 2004]- a)400 K
- b)350 K
- c)298 K
- d)250 K
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
ΔHvap = 30 kJ mol-1 and ΔSvap = 75 J mol-1 K-1. Thus, temperature of vapour at one atmosphere is
[IIT JEE 2004]
a)
400 K
b)
350 K
c)
298 K
d)
250 K
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
∆HVap = 30kJ/mol and ∆S = 75 J/K
∆G = ∆H - T∆S
At eqm, ∆G = 0
Therefore, ∆H = T∆S
Or T = 30×103/75 = 400 K
∆G = ∆H - T∆S
At eqm, ∆G = 0
Therefore, ∆H = T∆S
Or T = 30×103/75 = 400 K
If for the cell, Zn(s) + Cu2+(ag)  Cu(s) + Zn2+ (ag)entropy change ΔS° is 96.5 JK-1 mol-1, then temperature coefficient of the emf of a cell is
Cu(s) + Zn2+ (ag)entropy change ΔS° is 96.5 JK-1 mol-1, then temperature coefficient of the emf of a cell is- a)5 x 10-4 VK-1
- b)1 x 10-3 VK-1
- c)2 x 10-3 VK-1
- d)9.65 x 104 VK-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If for the cell, Zn(s) + Cu2+(ag) 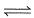 Cu(s) + Zn2+ (ag)entropy change ΔS° is 96.5 JK-1 mol-1, then temperature coefficient of the emf of a cell is
Cu(s) + Zn2+ (ag)entropy change ΔS° is 96.5 JK-1 mol-1, then temperature coefficient of the emf of a cell is
a)
5 x 10-4 VK-1
b)
1 x 10-3 VK-1
c)
2 x 10-3 VK-1
d)
9.65 x 104 VK-1
|
|
Amrita Choudhary answered |
ΔG=ΔH−nFT(dE/dT)P
and ΔG=ΔH−TΔS
∴ΔS/nF=(dE/dT)P
or
96.5/2×96500=(dE/dT)P
∴(dEcell/dT)P
=1×10−3 / 2
=5×10−4VK−1
and ΔG=ΔH−TΔS
∴ΔS/nF=(dE/dT)P
or
96.5/2×96500=(dE/dT)P
∴(dEcell/dT)P
=1×10−3 / 2
=5×10−4VK−1
When HCI(g)and NH3(g)come in contact, they react producing a white cloud of solid NH4CI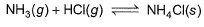 For this,
For this,- a)
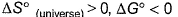
- b)
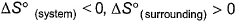
- c)
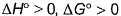
- d)

Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
When HCI(g)and NH3(g)come in contact, they react producing a white cloud of solid NH4CI
For this,
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Upasana Roy answered |
According to me, correct options are b and d.
For a reversible reaction, ∆S°(Universe) will be zero. ∆S°(Universe) is greater than zero for an irreversible reaction. SInce the randomness decreases, ∆S°(system) becomes less than zero and ∆S°(surrounding) becomes more than zero. BOth becomes equal with sign opposite and thus for reversible reaction, ∆S°(universe) = ∆S°(System) + ∆S°(surrounding) = 0
For a reversible reaction, ∆S°(Universe) will be zero. ∆S°(Universe) is greater than zero for an irreversible reaction. SInce the randomness decreases, ∆S°(system) becomes less than zero and ∆S°(surrounding) becomes more than zero. BOth becomes equal with sign opposite and thus for reversible reaction, ∆S°(universe) = ∆S°(System) + ∆S°(surrounding) = 0
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-14) This section contains 2 paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d).Passage lSulphur undergoes a phase transition between 80 and 110°C
S(rhombic) 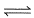 S (monoclinic); ΔH° = 3.213 kJ mol-1; ΔS° = 8.71 JK-1 mol-1 Q. Select the correct alternate(s).
S (monoclinic); ΔH° = 3.213 kJ mol-1; ΔS° = 8.71 JK-1 mol-1 Q. Select the correct alternate(s).- a)At 80°C SR is as stable as SM
- b)At 80°C SR is less stable than SM
- c)At 110°C SR is more stable than SM
- d)At 110°C SR is less stable than SM
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 11-14) This section contains 2 paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d).
Passage l
Sulphur undergoes a phase transition between 80 and 110°C
S(rhombic)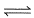 S (monoclinic); ΔH° = 3.213 kJ mol-1; ΔS° = 8.71 JK-1 mol-1
S (monoclinic); ΔH° = 3.213 kJ mol-1; ΔS° = 8.71 JK-1 mol-1
S(rhombic)
Q. Select the correct alternate(s).
a)
At 80°C SR is as stable as SM
b)
At 80°C SR is less stable than SM
c)
At 110°C SR is more stable than SM
d)
At 110°C SR is less stable than SM
|
|
Ameya Choudhury answered |
We have ∆G = ∆H - T∆S
For spontaneous reaction ∆G<0 and vice versa,
∆G at 80° C:-
3213 - (80+273)8.73 = 141.9 kJ mol-1
As it comes positive, the conversion of rhombic and monoclinic is non- spontaneous at 80° C.In other words, rhombic is more stable than monoclinic at this temperature.
∆G at 110° C:-
3213 - (110+273)8.73 = -119.1 kJ mol-1
As it comes positive, the conversion of rhombic and monoclinic is spontaneous at 110° C.In other words, rhombic is less stable than monoclinic at this temperature.
For spontaneous reaction ∆G<0 and vice versa,
∆G at 80° C:-
3213 - (80+273)8.73 = 141.9 kJ mol-1
As it comes positive, the conversion of rhombic and monoclinic is non- spontaneous at 80° C.In other words, rhombic is more stable than monoclinic at this temperature.
∆G at 110° C:-
3213 - (110+273)8.73 = -119.1 kJ mol-1
As it comes positive, the conversion of rhombic and monoclinic is spontaneous at 110° C.In other words, rhombic is less stable than monoclinic at this temperature.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1- 8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. For the given reaction, 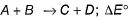 = - 1.3818 kcal at 300 K. Thus equilibrium constant is
= - 1.3818 kcal at 300 K. Thus equilibrium constant is- a)1
- b)0
- c)0.1
- d)100
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1- 8) This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. For the given reaction, 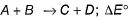 = - 1.3818 kcal at 300 K. Thus equilibrium constant is
= - 1.3818 kcal at 300 K. Thus equilibrium constant is
a)
1
b)
0
c)
0.1
d)
100
|
|
Aaryaa Sharma answered |
Since the reaction is not reversible, equilibrium constant is zero.
Chapter doubts & questions for September Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of September Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily


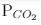 = 0.0030 atm.
= 0.0030 atm.