All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of October Week 3 for NEET Exam
Which of the following is not correct about the Krebs cycle?
- a)It starts with a six-carbon compound.
- b)It occurs in mitochondria.
- c)It is also called the citric acid cycle.
- d)The intermediate compound which links glycolysis with the Krebs cycle is malic acid.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not correct about the Krebs cycle?
a)
It starts with a six-carbon compound.
b)
It occurs in mitochondria.
c)
It is also called the citric acid cycle.
d)
The intermediate compound which links glycolysis with the Krebs cycle is malic acid.
|
|
Om Desai answered |
- Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle because this reaction starts with the six-carbon compound which is citric acid. It occurs in the mitochondrial matrix.
- Krebs cycle is a closed-loop cycle. And each loop of the cycle generates a molecule of ATP. This cycle consists of eight steps which include redox, dehydration, hydration, and decarboxylation reactions. It is an aerobic pathway because NADH is produced and the electrons released are used up in the next cycle which uses oxygen.
- The process of the cycle starts with the condensation of acetyl- CoA with oxaloacetate.
- This reaction is controlled by the amount of ATP present.
- If the ATP level increases then the rate of the reaction decreases and vice versa. After glycolysis, the pyruvate is then converted into acetyl CoA which enters the citric acid cycle.
- The Krebs cycle is the pathway that all organisms use to generate energy. The intermediate compound that links pyruvate to the Krebs cycle is Acetyl CoA.
- So, the answer is option (B) ‘the intermediate compound which links glycolysis with the Krebs cycle is malic acid’.
The TCA cycle is named after- a)Robert Emerson
- b)Melvin Calvin
- c)Embden
- d)Hans Krebs
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The TCA cycle is named after
a)
Robert Emerson
b)
Melvin Calvin
c)
Embden
d)
Hans Krebs
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta answered |
*Tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle is a series of enzyme-catalyzed chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to release the stored energy........ *It is a part of cellular respiration........ *It is also called as citric acid cycle or Krebs cycles which is named after it's discoverer Hans Krebs..... Thus, the correct answer is option 'D'.
Consider the following equilibrium in a closed container
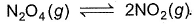 At a fixed temperature, the volume of a reaction container is halved. For this change, which of the following statements holds true regarding the equilibrium constant (Kp) and degree of dissociation (α) ?
At a fixed temperature, the volume of a reaction container is halved. For this change, which of the following statements holds true regarding the equilibrium constant (Kp) and degree of dissociation (α) ?- a)Neither Kp nor α change
- b)Both Kp and α change
- c)Kp changes but α does not change
- d)Kp does not change but α changes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following equilibrium in a closed container
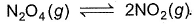
At a fixed temperature, the volume of a reaction container is halved. For this change, which of the following statements holds true regarding the equilibrium constant (Kp) and degree of dissociation (α) ?
a)
Neither Kp nor α change
b)
Both Kp and α change
c)
Kp changes but α does not change
d)
Kp does not change but α changes
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
We know that Kp depends only on Temperature. As the temp. remains constant , Kp also remains constant.
α depends on the concentration of the reactant
So as the volume of the reaction container is halved, α also changes
So option d is correct.
α depends on the concentration of the reactant
So as the volume of the reaction container is halved, α also changes
So option d is correct.
Most of the enzymes of the TCA cycle are present in- a)Intermembrane space of mitochondria
- b)Mitochondrial matrix
- c)Inner membrane of mitochondria
- d)Cytoplasm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most of the enzymes of the TCA cycle are present in
a)
Intermembrane space of mitochondria
b)
Mitochondrial matrix
c)
Inner membrane of mitochondria
d)
Cytoplasm
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Mitochondrial matrix.
In the mitochondrion, the matrix is the space within the inner membrane. ... The enzymes in the matrix facilitate reactions responsible for the production of ATP, such as the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, oxidation of pyruvate and the beta oxidation of fatty acids.
In the mitochondrion, the matrix is the space within the inner membrane. ... The enzymes in the matrix facilitate reactions responsible for the production of ATP, such as the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, oxidation of pyruvate and the beta oxidation of fatty acids.
An open-ended U-tube of uniform cross-sectional area contains water (density 1.0 gram/centimeter3) standing initially 20 centimeters from the bottom in each arm. An immiscible liquid of density 4.0 grams/centimeter3 is added to one arm until a layer 5 centimeters high forms, as shown in the figure above. What is the ratio h2/h1 of the heights of the liquid in the two arms ? 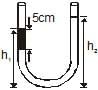
- a) 3/1
- b)5/2
- c)2/1
- d)3/2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An open-ended U-tube of uniform cross-sectional area contains water (density 1.0 gram/centimeter3) standing initially 20 centimeters from the bottom in each arm. An immiscible liquid of density 4.0 grams/centimeter3 is added to one arm until a layer 5 centimeters high forms, as shown in the figure above. What is the ratio h2/h1 of the heights of the liquid in the two arms ?
a)
3/1
b)
5/2
c)
2/1
d)
3/2

|
Ambition Institute answered |
5 × 4 × 10 + (h1 - 5) × 10 = h2 × 1 × 10
200 + 10h1 – 50 = 10h2
10h2 - 10h1 = 150
h2 - h1 = 15
h2 + h1 = 20 + 20 + 5 = 45
2h2 = 60
h2 = 30
h1 = 15
h2/h1 = 30/15
h2/h1 = 2/1
200 + 10h1 – 50 = 10h2
10h2 - 10h1 = 150
h2 - h1 = 15
h2 + h1 = 20 + 20 + 5 = 45
2h2 = 60
h2 = 30
h1 = 15
h2/h1 = 30/15
h2/h1 = 2/1
Mitochondria are called the powerhouses of the cell. Which of the following observations support this statement?- a)Mitochondria are found in almost all plant and animal cells.
- b)The enzymes of the Krebs cycle and the cytochromes are found in mitochondria.
- c)Mitochondria synthesise ATP.
- d)Mitochondria have a double membrane.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Mitochondria are called the powerhouses of the cell. Which of the following observations support this statement?
a)
Mitochondria are found in almost all plant and animal cells.
b)
The enzymes of the Krebs cycle and the cytochromes are found in mitochondria.
c)
Mitochondria synthesise ATP.
d)
Mitochondria have a double membrane.
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Mitochondria (singular - Mitochondrion) are known as the powerhouse of the cell because they are responsible for the release of energy from food ,i.e, cellular respiration. This energy is released in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of the cell.
While the cells release 2 ATP, mitochondria releases 34 ATP which adds up to 36 ATP. Since a major portion of the ATP is released by mitochondria, they are called the powerhouse of the cell.
Water is flowing in a tube of non-uniform radius. The ratio of the radii at entrance and exit ends of tube is 3 : 2. The ratio of the velocities of water entering in and exiting from the tube will be –- a)8 : 27
- b)4 : 9
- c) 1 : 1
- d) 9 : 4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is flowing in a tube of non-uniform radius. The ratio of the radii at entrance and exit ends of tube is 3 : 2. The ratio of the velocities of water entering in and exiting from the tube will be –
a)
8 : 27
b)
4 : 9
c)
1 : 1
d)
9 : 4
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
We know, for the fluid flowing through the non-uniform pipe the velocity of fluid is inversely proportional to the area of cross-section.
Hence, if v1, v2 are the velocities of entry and exit end of the pipe and a1, a2 are the area of cross-sections of entry and exit end of the pipe, then
v1/v2=a2/a1
⇒v1/v2=(r2)2/(r1)2
∴v1/v2=(2)2/(3)2=4/9
Hence, if v1, v2 are the velocities of entry and exit end of the pipe and a1, a2 are the area of cross-sections of entry and exit end of the pipe, then
v1/v2=a2/a1
⇒v1/v2=(r2)2/(r1)2
∴v1/v2=(2)2/(3)2=4/9
H2O (l)  H2O(s) ; ΔH = -qApplication of pressure on this equilibrium
H2O(s) ; ΔH = -qApplication of pressure on this equilibrium- a)cause formation of more ice
- b)cause fusion of ice
- c)has no effect
- d)lower the melting point
Correct answer is option 'B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
H2O (l)  H2O(s) ; ΔH = -q
H2O(s) ; ΔH = -q
 H2O(s) ; ΔH = -q
H2O(s) ; ΔH = -qApplication of pressure on this equilibrium
a)
cause formation of more ice
b)
cause fusion of ice
c)
has no effect
d)
lower the melting point
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The correct answers are Options B and D.
As we know that reaction is exothermic it means heat is released in the reaction so, if we apply pressure then reaction will proceed in backward direction but if there is gas phase equilibrium the reaction will shift in that direction in which less number of moles are present. If pressure increases then the ice will melt and ice gets more energy at low temp. To melt ,so it’s melting point decreases.
As we know that reaction is exothermic it means heat is released in the reaction so, if we apply pressure then reaction will proceed in backward direction but if there is gas phase equilibrium the reaction will shift in that direction in which less number of moles are present. If pressure increases then the ice will melt and ice gets more energy at low temp. To melt ,so it’s melting point decreases.
The area of cross-section of the wider tube shown in figure is 800 cm2. If a mass of 12 kg is placed on the massless piston, the difference in heights h in the level of water in the two tubes is : 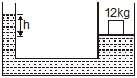
- a)10 cm
- b)6 cm
- c)15 cm
- d)2 cm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The area of cross-section of the wider tube shown in figure is 800 cm2. If a mass of 12 kg is placed on the massless piston, the difference in heights h in the level of water in the two tubes is :
a)
10 cm
b)
6 cm
c)
15 cm
d)
2 cm

|
EduRev JEE answered |
h × ρ × 10 = 120/800 × 10-4
h × ρ = 12/8 × 102
h × ρ = 150m
h × 1000 = 150m
h = 15cm
h × ρ = 12/8 × 102
h × ρ = 150m
h × 1000 = 150m
h = 15cm
We know that the relationship between Kc and Kp is Kp = Kc (RT)Δn
What would be the value of Δn for the reaction NH4Cl (s) ⇔ NH3 (g) + HCl (g)
a)1b)0.5c)1.5d)2Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The answer is d.
The relationship between Kp and Kc is
The relationship between Kp and Kc is
Kp = Kc (RT) ∆n
Where ∆n = (number of moles of gaseous products) – (number of moles of gaseous reactants)
For the reaction,
NH4C1(s) ⇆ NH3(g) + HCl(g)
∆n = 2 – 0 = 2
Water is flowing in a horizontal pipe ofnon-uniform cross - section. At the most contracted place of the pipe –- a)Velocity of water will be maximum and pressure minimum
- b)Pressure of water will be maximum and velocity minimum
- c)Both pressure and velocity of water will be maximum
- d)Both pressure and velocity of water will be
minimum
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is flowing in a horizontal pipe of
non-uniform cross - section. At the most contracted place of the pipe –
a)
Velocity of water will be maximum and pressure minimum
b)
Pressure of water will be maximum and velocity minimum
c)
Both pressure and velocity of water will be maximum
d)
Both pressure and velocity of water will be
minimum
minimum
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
Continuity equation states that, "For a non-viscous liquid and streamlined flow the volume flow rate (Area of cross section x velocity) is constant throughout the flow at any point".
According to this, Av = constant. So if at any point the cross-section area decreases then velocity of liquid at that point increases and vice-versa.
Bernoulli's equation states that, "For a streamlined and non-viscous flow the total energy (kinetic energy and pressure gradient) remains constant throughout the liquid.
According to this, kinetic energy + Pressure gradient = constant. So, if at any point the velocity increases the pressure at that point decreases and vice-versa.
At the most contracted place of the pipe area of cross section is minimum
⇒ velocity is maximum
⇒ pressure is minimum
According to this, Av = constant. So if at any point the cross-section area decreases then velocity of liquid at that point increases and vice-versa.
Bernoulli's equation states that, "For a streamlined and non-viscous flow the total energy (kinetic energy and pressure gradient) remains constant throughout the liquid.
According to this, kinetic energy + Pressure gradient = constant. So, if at any point the velocity increases the pressure at that point decreases and vice-versa.
At the most contracted place of the pipe area of cross section is minimum
⇒ velocity is maximum
⇒ pressure is minimum
In the following equilibrium AB  A+ + B-
A+ + B-
AB is 10% dissociated, when [AB] = 1MQ. What is per cent dissociation if 1 M AB is dissociated in the presence of 1 M A+? - a)5.2%
- b)6.0%
- c)1.1%
- d)10.0%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following equilibrium AB 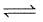 A+ + B-
A+ + B-
AB is 10% dissociated, when [AB] = 1M
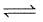 A+ + B-
A+ + B-AB is 10% dissociated, when [AB] = 1M
Q. What is per cent dissociation if 1 M AB is dissociated in the presence of 1 M A+?
a)
5.2%
b)
6.0%
c)
1.1%
d)
10.0%
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The correct answer is option C
Let initially
AB = 1M
AB = A+ + B-
⇒1 - 0.1
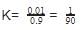
K should remain same
AB ⇌ A+ + B-
1-x
Let initially
AB = 1M
AB = A+ + B-
⇒1 - 0.1
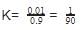
K should remain same
AB ⇌ A+ + B-
1-x
Pyruvic acid, the key product of glycolysis, can have many metabolic fates. Under aerobic conditions, it forms- a)CO2
- b)CO2+ H2O
- c)Lactic acid
- d)Acetyl CoA + CO2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Pyruvic acid, the key product of glycolysis, can have many metabolic fates. Under aerobic conditions, it forms
a)
CO2
b)
CO2+ H2O
c)
Lactic acid
d)
Acetyl CoA + CO2
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
Pyruvate, the product obtained through glycolysis, gets oxidised with the loss of its carboxy group as CO2, to give acetyl Co-A, under aerobic condition. This acetyl Co-A is further oxidised completely to CO2 + H2O in citric acid cycle. Other options are incorrect as Lactic acid is formed in muscles under anaerobic conditions. Ethanol and CO2 are products of anaerobic respiration in yeast cells. CO2 and H2O are final and complete reaction products released at the end of cellular respiration.
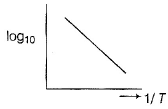
Variation of log Kp with temperature. 1/T is given by for the equilibrium.
NH4HS (s)  NH3(g) + H2S
NH3(g) + H2S
 Q. The equilibrium is displaced in forward side on
Q. The equilibrium is displaced in forward side on- a)increasing temperature and decreasing pressure
- b)increasing temperature and pressure both
- c)decreasing temperature and pressure both
- d)decreasing temperature and increasing pressure
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Variation of log Kp with temperature. 1/T is given by for the equilibrium.
NH4HS (s) NH3(g) + H2S
NH3(g) + H2S

NH4HS (s)
Q. The equilibrium is displaced in forward side on
a)
increasing temperature and decreasing pressure
b)
increasing temperature and pressure both
c)
decreasing temperature and pressure both
d)
decreasing temperature and increasing pressure

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
The correct answer is Option A.
When ammonia is added after equilibrium is established, the partial pressure of ammonia will increase.When the temperature of an endothermic reaction is increased, the equilibrium will shift in the forward direction so that the heat is absorbed which will nullify the effect of increased temperature. Hence, the partial pressure of ammonia will increase.When the volume of the flask is increased, the pressure will decrease.
When ammonia is added after equilibrium is established, the partial pressure of ammonia will increase.When the temperature of an endothermic reaction is increased, the equilibrium will shift in the forward direction so that the heat is absorbed which will nullify the effect of increased temperature. Hence, the partial pressure of ammonia will increase.When the volume of the flask is increased, the pressure will decrease.
Choose the correct statement.- a)There is a complete breakdown of glucose during fermentation.
- b)Pyruvate is formed in the mitochondrial matrix.
- c)During the conversion of succinyl CoA to succinic acid, a molecule of ATP is synthesised.
- d)Oxygen is vital in respiration for the removal of hydrogen.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct statement.
a)
There is a complete breakdown of glucose during fermentation.
b)
Pyruvate is formed in the mitochondrial matrix.
c)
During the conversion of succinyl CoA to succinic acid, a molecule of ATP is synthesised.
d)
Oxygen is vital in respiration for the removal of hydrogen.
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
- Oxygen sits at the end of the electron transport chain, where it accepts electrons, hydrogen and picks up protons to form water.
- Pyruvate is formed in the cytoplasm.
- During fermentation glucose is partially broken down by glycolysis.
- During the conversion of succinyl CoA to succinic acid a molecule of GTP is synthesized.
So, the correct option is 'Oxygen is vital in respiration for removal of hydrogen'.
In which of the following do the two names refer to one and the same thing?- a)Krebs cycle and Calvin cycle
- b)Citric acid cycle and Calvin cycle
- c)Tricarboxylic acid cycle and citric acid cycle
- d)Tricarboxylic acid cycle and urea cycle
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following do the two names refer to one and the same thing?
a)
Krebs cycle and Calvin cycle
b)
Citric acid cycle and Calvin cycle
c)
Tricarboxylic acid cycle and citric acid cycle
d)
Tricarboxylic acid cycle and urea cycle
|
|
Akash Saini answered |
Explanation:
The correct answer is option C, which states that the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same thing. Let's understand why this is the correct answer.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle:
The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle, is a series of chemical reactions that occur in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. It is an essential metabolic pathway that plays a key role in the oxidation of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to generate energy in the form of ATP.
Citric Acid Cycle:
The citric acid cycle, as the name suggests, is named after citric acid. It is a series of chemical reactions that take place in the mitochondria of cells. The cycle starts with the condensation of acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate to form citrate, which is then metabolized through a series of enzymatic reactions to regenerate oxaloacetate.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle = Citric Acid Cycle:
The tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same metabolic pathway. The cycle was initially named after its intermediate product, citric acid, and later came to be known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle due to the presence of three carboxylic acid groups in the cycle.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option C, where the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same thing. The other options, including the Krebs cycle and Calvin cycle, the citric acid cycle and Calvin cycle, and the tricarboxylic acid cycle and urea cycle, are incorrect as they refer to different metabolic pathways or processes.
The correct answer is option C, which states that the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same thing. Let's understand why this is the correct answer.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle:
The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle, is a series of chemical reactions that occur in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. It is an essential metabolic pathway that plays a key role in the oxidation of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to generate energy in the form of ATP.
Citric Acid Cycle:
The citric acid cycle, as the name suggests, is named after citric acid. It is a series of chemical reactions that take place in the mitochondria of cells. The cycle starts with the condensation of acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate to form citrate, which is then metabolized through a series of enzymatic reactions to regenerate oxaloacetate.
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle = Citric Acid Cycle:
The tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same metabolic pathway. The cycle was initially named after its intermediate product, citric acid, and later came to be known as the tricarboxylic acid cycle due to the presence of three carboxylic acid groups in the cycle.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option C, where the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the citric acid cycle refer to the same thing. The other options, including the Krebs cycle and Calvin cycle, the citric acid cycle and Calvin cycle, and the tricarboxylic acid cycle and urea cycle, are incorrect as they refer to different metabolic pathways or processes.
A piece of steel has a weight W in air, W1 when completely immersed in water and W2 when completely immersed in an unknown liquid. The relative density (specific gravity) of liquid is :- a)
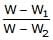
- b)
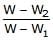
- c)
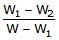
- d)
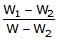
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A piece of steel has a weight W in air, W1 when completely immersed in water and W2 when completely immersed in an unknown liquid. The relative density (specific gravity) of liquid is :
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
If the loss of weight of a body in water is 'a' while in liquid is 'b' then
Sigma in liquid / sigma in water = upthrust on body in liquid / upthrust on body in water
Then a / b = (W air - W liquid) / (W air - W water).
Sigma in liquid / sigma in water = upthrust on body in liquid / upthrust on body in water
Then a / b = (W air - W liquid) / (W air - W water).
A beaker containing water is placed on the platform of a spring balance. The balance reads 1.5 kg. A stone of mass 0.5 kg and density 500 kg/m3 is immersed in water without touching the walls of beaker. What will be the balance reading now ?- a)2 Kg
- b)2.5 Kg
- c)1 KG
- d)3 Kg
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A beaker containing water is placed on the platform of a spring balance. The balance reads 1.5 kg. A stone of mass 0.5 kg and density 500 kg/m3 is immersed in water without touching the walls of beaker. What will be the balance reading now ?
a)
2 Kg
b)
2.5 Kg
c)
1 KG
d)
3 Kg
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
Since the weight of the block must be equal to the buoyant force acting on the block for it to remain in equilibrium,
B=0.5kg
The reading of the spring balance = Weight of water + Buoyant force' reaction pair force downwards
=1.5kg+0.5kg=2kg
A boy carries a fish in one hand and a bucket (not full) of water in the other hand. If the places the fish in the bucket, the weight now carried by him (assume that water does not spill) :- a)Is less than before
- b)Is more than before
- c)Is the same as before
- d)Depends upon his speed
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A boy carries a fish in one hand and a bucket (not full) of water in the other hand. If the places the fish in the bucket, the weight now carried by him (assume that water does not spill) :
a)
Is less than before
b)
Is more than before
c)
Is the same as before
d)
Depends upon his speed
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Buoyant force on fish due to water will be equal and opposite to the force on water by fish.
These two forces are internal forces for the fish bucket system.
Hence, they will not affect the weight the boy carries.
These two forces are internal forces for the fish bucket system.
Hence, they will not affect the weight the boy carries.
A light semi cylindrical gate of radius R is piovted at its mid point O, of the diameter as shown in the figure holding liquid of density r. The force F required to prevent the rotation of the gate is equal to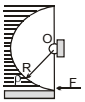
- a) 2pR3rg
- b)2rgR3l
- c)
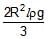
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A light semi cylindrical gate of radius R is piovted at its mid point O, of the diameter as shown in the figure holding liquid of density r. The force F required to prevent the rotation of the gate is equal to
a)
2pR3rg
b)
2rgR3l
c)
d)
None of these
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
The force is normal to the surface of the cylinder and hence will pass through the centre. And since the forces pass through the centre it means that the net torque will be zero.
Which of the following on the addition will cause deep red colour to disappear?
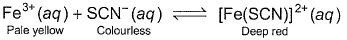
- a)AgNO3
- b)HgCI2
- c)H2C2O4
- d)H2O
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following on the addition will cause deep red colour to disappear?
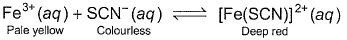
a)
AgNO3
b)
HgCI2
c)
H2C2O4
d)
H2O
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
The correct answers are option A,B,C
Because of silver salt ie . silver nitrate with powerful germicidal activity
Ag+ + SCN− → AgSCN↓
Hg2+ + SCN− → Hg(SCN)2↓
4Fe3+ + 3(COO)2−2 → 2Fe2(COO)3↓
Because of silver salt ie . silver nitrate with powerful germicidal activity
Ag+ + SCN− → AgSCN↓
Hg2+ + SCN− → Hg(SCN)2↓
4Fe3+ + 3(COO)2−2 → 2Fe2(COO)3↓
Consider the following equilibrium,N2(g) + 3H2(g)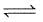 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)
If N2(g) is added to the above mixture in equilibrium,[IIT JEE 2006]- a)the equilibrium will shift to forward direction as entropy increases in the direction of spontaneous reaction
- b)the equilibrium constant Kp increases
- c)partial pressure of NH3 as well as that of N2 increases when equilibrium is reached
- d)the equilibrium constant Kp remains constant
Correct answer is option 'C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following equilibrium,
N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)
If N2(g) is added to the above mixture in equilibrium,
 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)If N2(g) is added to the above mixture in equilibrium,
[IIT JEE 2006]
a)
the equilibrium will shift to forward direction as entropy increases in the direction of spontaneous reaction
b)
the equilibrium constant Kp increases
c)
partial pressure of NH3 as well as that of N2 increases when equilibrium is reached
d)
the equilibrium constant Kp remains constant
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Partial pressure of each component in the mixture increases on increasing concentration. Also,according to Le Chatelier's principle the reaction would shift such that kp does not change.
A fluid container is containing a liquid of density r is is accelerating upward with acceleration a along the inclined place of inclination a as shwon. Then the angle of inclination q of free surface is : 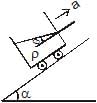
- a)tan_1
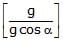
- b)
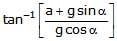
- c)
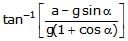
- d)
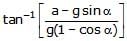
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A fluid container is containing a liquid of density r is is accelerating upward with acceleration a along the inclined place of inclination a as shwon. Then the angle of inclination q of free surface is :
a)
tan_1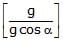
b)
c)
d)

|
Lohit Matani answered |
First resolve all components in the along and perpendicular to incline. Pressure difference is created in a vertical column full of liquid. This is because of gravity acting in downward direction. Similarly, pressure difference will be created too along the incline. So, p = h * d * g * cosa (in perpendicular direction) and
p = hd (a + g sina) (along incline).
So, tan(theta) = (a + gsina)/(gcosa)
p = hd (a + g sina) (along incline).
So, tan(theta) = (a + gsina)/(gcosa)
When hydrochloric acid is added to cobalt (II) nitrate solution at room temperature, the following reaction takes place
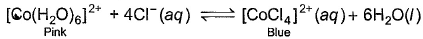 Q. The solution is blue at room temperature. However, it turns pink when cooled in a freezing mixture. Based upon this information, which of the following expression is correct for the forward reaction?
Q. The solution is blue at room temperature. However, it turns pink when cooled in a freezing mixture. Based upon this information, which of the following expression is correct for the forward reaction?- a)ΔH > 0
- b)ΔH < 0
- c)ΔH = 0
- d)The sign of ΔH can’t be predicted based on the given information
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When hydrochloric acid is added to cobalt (II) nitrate solution at room temperature, the following reaction takes place
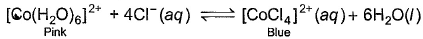
Q. The solution is blue at room temperature. However, it turns pink when cooled in a freezing mixture. Based upon this information, which of the following expression is correct for the forward reaction?
a)
ΔH > 0
b)
ΔH < 0
c)
ΔH = 0
d)
The sign of ΔH can’t be predicted based on the given information
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
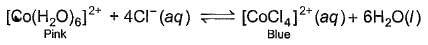
According to the given information, the solution turns pink when cooled in freezing mixture. So, the equilibrium has shifted in backward direction. So we can say that the reaction is endothermic and ∆H for the reaction is greater than zero. This is because, endothermic reactions have ∆H > 0 and they proceed in reverse direction.
AgCI(s)is sparingly soluble salt,AgCl (s)  Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
There is- a)increase in solubility if NH3(ag) is added
- b)increase in solubility if NaCI or AgNO3 is added
- c)decrease in solubility if KCI is added
- d)decrease in solubility if H2O is added
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
AgCI(s)is sparingly soluble salt,
AgCl (s) 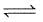 Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
There is
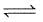 Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq)There is
a)
increase in solubility if NH3(ag) is added
b)
increase in solubility if NaCI or AgNO3 is added
c)
decrease in solubility if KCI is added
d)
decrease in solubility if H2O is added

|
Pioneer Academy answered |
When ammonia is added, solubility of AgCl increases due to formation of complex salt which decreases the concentration of radicals in the product side and tus drives the reaction in forward direction.
When we add KCl common ion effect is applied in presence of common ion solubility decreases and reaction goes in backward direction.
When we add KCl common ion effect is applied in presence of common ion solubility decreases and reaction goes in backward direction.
A rectangular tank is placed on a horizontal ground and is filled with water to a height H above the base. A small hole is made on one vertical side at a depth D below the level of the water in the tank. The distance x from the bottom of the tank at which the water jet from the tank will hit the ground is- a)
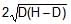
- b)
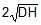
- c)
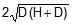
- d)
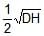
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A rectangular tank is placed on a horizontal ground and is filled with water to a height H above the base. A small hole is made on one vertical side at a depth D below the level of the water in the tank. The distance x from the bottom of the tank at which the water jet from the tank will hit the ground is
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
Time taken by liquid drop to fall
S=ut+(1/2)at2
t=√2(H−D)/g
Horizontal velocity of liquid =√2gD
Range =√2(H−D)/g× √2gD
Range =2√D(H−D)
S=ut+(1/2)at2
t=√2(H−D)/g
Horizontal velocity of liquid =√2gD
Range =√2(H−D)/g× √2gD
Range =2√D(H−D)
A cuboidal piece of wood has dimensions a, b and c. Its relative density is d. It is floating in a larger body of water such that side a is vertical. It is pushed down a bit and released. The time period of SHM executed by it is :- a)
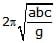
- b)
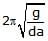
- c)
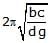
- d)
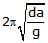
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A cuboidal piece of wood has dimensions a, b and c. Its relative density is d. It is floating in a larger body of water such that side a is vertical. It is pushed down a bit and released. The time period of SHM executed by it is :
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Time period of SHM of small vertical oscillations in a liquid is given by T=2π√l/g, where l is the length of cube/cylinder dipped in the water.
So according to law of floatation,
weight of the cube = weight of the water displaced
abc × d × g=bcl × 1×g
⇒l=da
⇒T=2π√da/g
So according to law of floatation,
weight of the cube = weight of the water displaced
abc × d × g=bcl × 1×g
⇒l=da
⇒T=2π√da/g
Combustion of CO(g)can be increased in the following reaction by
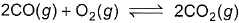
- a)decreasing volume at constant temperature
- b)adding argon gas
- c)adding O2 gas
- d)decreasing pressure at constant temperature
Correct answer is 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Combustion of CO(g)can be increased in the following reaction by
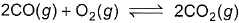
a)
decreasing volume at constant temperature
b)
adding argon gas
c)
adding O2 gas
d)
decreasing pressure at constant temperature

|
Manish Aggarwal answered |
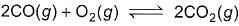
For option a; with decrease in volume or with increase in pressure, reaction shifts towards less no. of moles. So, here combustion of CO will increase.
For option b; adding argon at constant volume doesn’t make any effect on equilibrium. Also, if we add argon at constant pressure, the reaction will shift towards more no. of moles and so the combustion of CO will decrease.
For option c; adding O2 will shift the reaction in forward direction (according to Le Chatelier principle), so combustion of CO will increase.
For option d; with decrease in pressure or increases in volume, reaction shifts towards more no. of moles and so combustion of CO will decrease.
A body is just floating in a liquid (their densities are equal) If the body is slightly pressed down and released it will -
- a) Start oscillating
- b)Sink to the bottom
- c)Come back to the same position immediately
- d)Come back to the same position slowly
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A body is just floating in a liquid (their densities are equal) If the body is slightly pressed down and released it will -
a)
Start oscillating
b)
Sink to the bottom
c)
Come back to the same position immediately
d)
Come back to the same position slowly
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The body will sink to the bottom as it gains a downward velocity and has no force to bring it back up. The weight becomes greater than upwards thrust.
As body is just floating, its density is same as that of the liquid.
If pressed below, it will gain momentum downwards, and continue to sink till bottom.
When the body is slightly pressed, the contraction in volume decreases upthrust, so weight becomes greater than upthrust, body moves down. The upthrust further decreases, since more and more contraction occurs as the body moves down. The body thus, sinks to the bottom.
If pressed below, it will gain momentum downwards, and continue to sink till bottom.
When the body is slightly pressed, the contraction in volume decreases upthrust, so weight becomes greater than upthrust, body moves down. The upthrust further decreases, since more and more contraction occurs as the body moves down. The body thus, sinks to the bottom.
Figure shows a three arm tube in which a liquid is filled upto levels of height l. It is now rotated at an angular frequency w about an axis passing through arm B. The angular frequency w at which level of liquid of arm B becomes zero. 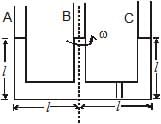
- a)
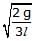
- b)
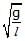
- c)
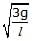
- d)
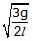
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Figure shows a three arm tube in which a liquid is filled upto levels of height l. It is now rotated at an angular frequency w about an axis passing through arm B. The angular frequency w at which level of liquid of arm B becomes zero.
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The pressure at the bottom of a tank of water is 3P where P is the atmospheric pressure. If the water is drawn out till the level of water is lowered by one fifth., the pressure at the bottom of the tank will now be
- a)2 P
- b)(13/5) P
- c)(8/5) P
- d)(4/5) P
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The pressure at the bottom of a tank of water is 3P where P is the atmospheric pressure. If the water is drawn out till the level of water is lowered by one fifth., the pressure at the bottom of the tank will now be
a)
2 P
b)
(13/5) P
c)
(8/5) P
d)
(4/5) P

|
Stepway Academy answered |

The cross sectional area of a horizontal tube increases along its length linearly, as we move in the direction of flow. The variation of pressure, as we move along its length in the direction of flow (x-direction), is best depicted by which of the following graphs- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The cross sectional area of a horizontal tube increases along its length linearly, as we move in the direction of flow. The variation of pressure, as we move along its length in the direction of flow (x-direction), is best depicted by which of the following graphs
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
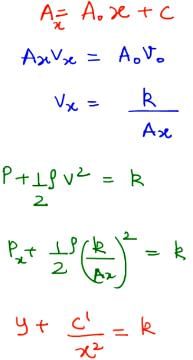
So, it will be a downward facing parabola.
For the reaction,2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) 2SO3 (g) + 188.3 KJ
2SO3 (g) + 188.3 KJ
the number of moles of SO3 formed is increased if- a)temperature is increased at constant V
- b)inert gas is added to the mixture
- c)O2 is removed from the mixture
- d)volume of the reaction flask is decreased
Correct answer is option 'B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
For the reaction,
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) 2SO3 (g) + 188.3 KJ
2SO3 (g) + 188.3 KJ
the number of moles of SO3 formed is increased if
 2SO3 (g) + 188.3 KJ
2SO3 (g) + 188.3 KJthe number of moles of SO3 formed is increased if
a)
temperature is increased at constant V
b)
inert gas is added to the mixture
c)
O2 is removed from the mixture
d)
volume of the reaction flask is decreased
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Volume decreased
i.e p increased
no.of moles reactant more
A jet of water with cross section of 6 cm2 strikes a wall at an angle of 60º to the normal and rebounds elastically from the wall without losing energy. If the velocity of the water in the jet is 12 m/s, the force acting on the wall is- a)0.864 Nt
- b)86.4 Nt
- c)72 Nt
- d)7.2 Nt
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A jet of water with cross section of 6 cm2 strikes a wall at an angle of 60º to the normal and rebounds elastically from the wall without losing energy. If the velocity of the water in the jet is 12 m/s, the force acting on the wall is
a)
0.864 Nt
b)
86.4 Nt
c)
72 Nt
d)
7.2 Nt
|
|
Bhargavi Yadav answered |
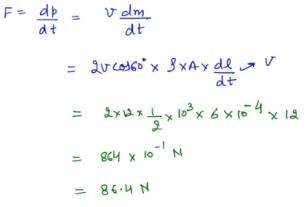
For the reaction,
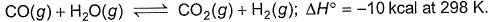
Equilibrium amount of CO2(g) can be increased by- a)decreasing temperature
- b)adding an inert gas
- c)decreasing the volume of the container
- d)increasing the amount of CO (g)
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
For the reaction,
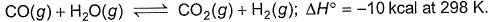
Equilibrium amount of CO2(g) can be increased by
Equilibrium amount of CO2(g) can be increased by
a)
decreasing temperature
b)
adding an inert gas
c)
decreasing the volume of the container
d)
increasing the amount of CO (g)
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The correct answers are option A & D
As the reaction is exothermic decreasing the temperature will move it in forward direction in order to maintain equilibrium . increasing the amount of CO would increase the reactant concentration so in order to balance it out the reaction moves forward . hence the amount of CO2 increases. so options A and D , both are correct.
As the reaction is exothermic decreasing the temperature will move it in forward direction in order to maintain equilibrium . increasing the amount of CO would increase the reactant concentration so in order to balance it out the reaction moves forward . hence the amount of CO2 increases. so options A and D , both are correct.
End-product of citric acid/Krebs cycle is- a)Citric acid
- b)CO2 + H2O
- c)Lactic acid
- d)Pyruvic acid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
End-product of citric acid/Krebs cycle is
a)
Citric acid
b)
CO2 + H2O
c)
Lactic acid
d)
Pyruvic acid
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
The eight steps of the citric acid cycle are a series of redox, dehydration, hydration, and decarboxylation reactions. Each turn of the cycle forms one GTP or ATP as well as three NADH molecules and one FADH2 molecule, which will be used in further steps of cellular respiration to produce ATP for the cell.
Which of the following is the key intermediate compound linking glycolysis to the Krebs cycle?- a)ATP
- b)Malic acid
- c)Acetyl CoA
- d)NADH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the key intermediate compound linking glycolysis to the Krebs cycle?
a)
ATP
b)
Malic acid
c)
Acetyl CoA
d)
NADH
|
|
H2O answered |
Acetyl CoA is the key intermediate between the Krebs cycle of glycolysis. After glycolysis, the glucose converts to pyruvic acid which is a three-carbon molecule. It is converted into acetyl coenzyme a by oxidative decarboxylation This, Acetyl CoA enters the Krebs cycle and along with oxaloacetic acid forms the citric acid which is a 6C compound.
A U-tube having horizontal arm of length 20 cm, has uniform cross-sectional area = 1 cm2. It is filled with water of volume 60 cc. What volume of a liquid of density 4 g/cc should be poured from one side into the U-tube so that no water is left in the horizontal arm of the tube?- a)60 cc
- b)45 cc
- c)50 cc
- d)35 cc
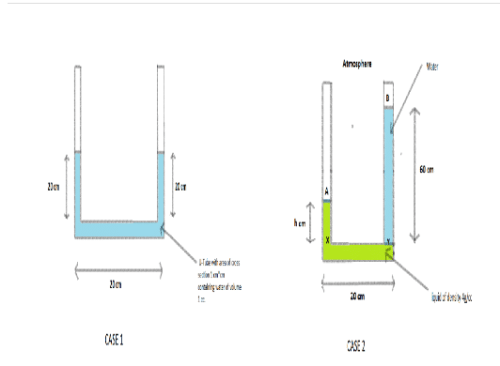
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A U-tube having horizontal arm of length 20 cm, has uniform cross-sectional area = 1 cm2. It is filled with water of volume 60 cc. What volume of a liquid of density 4 g/cc should be poured from one side into the U-tube so that no water is left in the horizontal arm of the tube?
a)
60 cc
b)
45 cc
c)
50 cc
d)
35 cc
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |

In each of the following equilibria, pressure is made four times after equilibrium is set up. In which case yield of the product(s) is maximum?
- a)N2O4 (g)
 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
- b)C(s) + H2O(g)
 CO(g) +H2(g)
CO(g) +H2(g)
- c)N2(g) + 3H2(g)
 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)
- d)2Fe(s) +3H2O (g)
 Fe2O3(s) + 3H2(g)
Fe2O3(s) + 3H2(g)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In each of the following equilibria, pressure is made four times after equilibrium is set up. In which case yield of the product(s) is maximum?
a)
N2O4 (g) 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)
 2NO2(g)
2NO2(g)b)
C(s) + H2O(g)  CO(g) +H2(g)
CO(g) +H2(g)
 CO(g) +H2(g)
CO(g) +H2(g)c)
N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)
 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)d)
2Fe(s) +3H2O (g)  Fe2O3(s) + 3H2(g)
Fe2O3(s) + 3H2(g)
 Fe2O3(s) + 3H2(g)
Fe2O3(s) + 3H2(g)

|
Bs Academy answered |

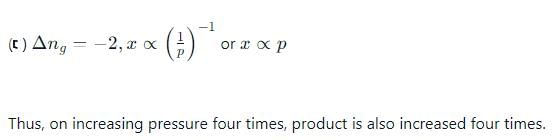
increase in pressure on the following equilibriumH2O(l) H20(g)results is
H20(g)results is- a)liquefaction of steam
- b)formation of more steam
- c)decrease in boiling point of H2O
- d)increase in boiling point of H2O
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
increase in pressure on the following equilibrium
H2O(l)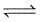 H20(g)
H20(g)
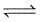 H20(g)
H20(g)results is
a)
liquefaction of steam
b)
formation of more steam
c)
decrease in boiling point of H2O
d)
increase in boiling point of H2O
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
The correct answers are Options A and D.
As in this equilibrium, liquid converts into gas so increase in the pressure will favour reverse reaction; so formation of more H2O(l). Also, as we increase pressure boiling point of water increases.
As in this equilibrium, liquid converts into gas so increase in the pressure will favour reverse reaction; so formation of more H2O(l). Also, as we increase pressure boiling point of water increases.
Two stretched membranes of areas 2 and 3 m2 are placed in a liquid at the same depth. The ratio of the pressure on them is -- a) 1 : 1
- b) 2 : 3
- c)
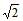 :
: 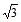
- d)22 : 32
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two stretched membranes of areas 2 and 3 m2 are placed in a liquid at the same depth. The ratio of the pressure on them is -
a)
1 : 1
b)
2 : 3
c)
d)
22 : 32
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Pressure depends on depth of container irrespective of its shape and in the above case depth for both the vessels are given same. Therefore the hydraulic pressure for the containers will be in the ratio 1: 1
A metal ball of density 7800 kg/m3 is suspected to have a large number of cavities. It weighs 9.8 kg when weighed directly on a balance and 1.5 kg less when immersed in water. The fraction by volume of the cavities in the metal ball is approximately :- a)20%
- b)30%
- c)16%
- d)11%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A metal ball of density 7800 kg/m3 is suspected to have a large number of cavities. It weighs 9.8 kg when weighed directly on a balance and 1.5 kg less when immersed in water. The fraction by volume of the cavities in the metal ball is approximately :
a)
20%
b)
30%
c)
16%
d)
11%
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
Answer- volume of cavity/ball=0.16
Explaination-
Here when put in water the water displaces/fills the empty cavity.
Volume of only metal=mass/density =9.8/7800=1.25X10^-3cu.m
Volume of whole ball including cavity= weight of water dispaced/density of water
Density of water is 1000kg/cu.m.
Volume of whole ball=1.5X10^-3cu.m
Volume of cavity=Volume of ball-volume of metal
=1.5X10^-3 - 1.25X10^-3
=0.25X10^-3cu.m
Ratio of volume of cavity/ball = 0.25X10^-3 / 1.5X10^-3 = 0.16 = 16%
0.16 fraction of whole ball is a cavity. i.e.16%.
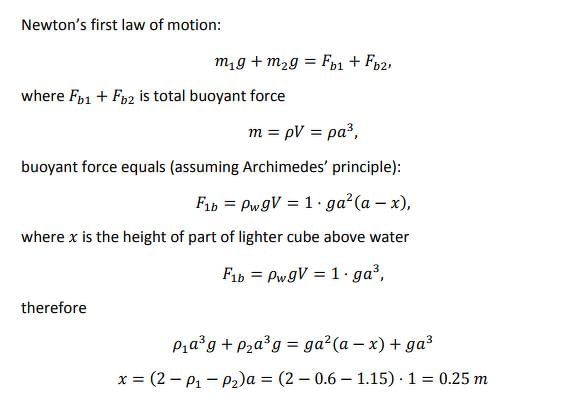
Two cubes of size 1.0 m sides, one of relative density 0.60 and another of relative density = 1.15 are connected by weightless wire and placed in a large tank of water. Under equilibrium the lighter cube will project above the water surface to a height of- a)50 cm
- b)25 cm
- c)10 cm
- d)Zero
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two cubes of size 1.0 m sides, one of relative density 0.60 and another of relative density = 1.15 are connected by weightless wire and placed in a large tank of water. Under equilibrium the lighter cube will project above the water surface to a height of
a)
50 cm
b)
25 cm
c)
10 cm
d)
Zero
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
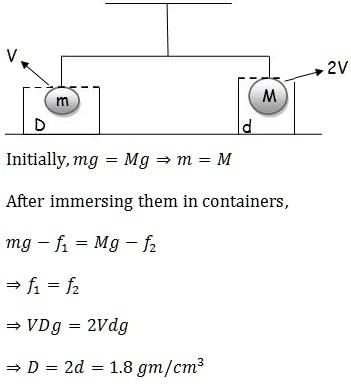
Two bodies having volumes V and 2V are suspended from the two arms of a common balance and they are found to balance each other. If larger body is immersed in oil (density d1 = 0.9 gm/cm3) and the smaller body is immersed in an unknown liquid, then the balance remain in equilibrium. The density of unknown liquid is given by :- a)2.4 gm/cm3
- b)1.8 gm/cm3
- c) 0.45 gm/cm3
- d)2.7 gm/cm3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two bodies having volumes V and 2V are suspended from the two arms of a common balance and they are found to balance each other. If larger body is immersed in oil (density d1 = 0.9 gm/cm3) and the smaller body is immersed in an unknown liquid, then the balance remain in equilibrium. The density of unknown liquid is given by :
a)
2.4 gm/cm3
b)
1.8 gm/cm3
c)
0.45 gm/cm3
d)
2.7 gm/cm3
|
|
Ram Mohith answered |
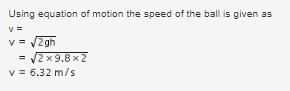
A ball of relative density 0.8 falls into water from a height of 2m. The depth to which the ball will sink is (neglect viscous forces) :- a)8m
- b)2m
- c)6m
- d)4m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A ball of relative density 0.8 falls into water from a height of 2m. The depth to which the ball will sink is (neglect viscous forces) :
a)
8m
b)
2m
c)
6m
d)
4m
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
Let us calculate the buoyancy force by water try to stop the ball.
Buoyancy force = weight of displaced water
= Density of water x Volume of the ball x g
= d x V x g (Equation 1)
But buoyant force = ma
Therefore, ma = d x V x g
or a = (dVg) / m (Equation 2)
Let the density of the ball be d'.
→ m = d'V
Substituting in equation 2, we get
a = (dVg) / d'V
= dg / d'
=(d/d') x g
Given that relative density, (d / d') = 0.8
So, a = g / (0.8)
= 10 / 0.8
→ a = 12.5 m/s^2
Net deceleration of ball,a' = a - g = 12.5 - 10
= 2.5 m/s^2
Final speed of ball v' = 0
Using the equation - v'^2 = v^2 + 2a's..(where s = depth of ball in the water)
Substituting the values in the above equation, we get
40 = 0 + 2 x 2.5 x s
s = 8m
A bucket contains water filled upto a height = 15 cm. The bucket is tied to a rope which is passed over a frictionless light pulley and the other end of the rope is tied to a weight of mass which is half of that of the (bucket + water). The water pressure above atmosphere pressure at the bottom is :- a)0.5 kPa
- b)1 kPa
- c) 5 kPa
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A bucket contains water filled upto a height = 15 cm. The bucket is tied to a rope which is passed over a frictionless light pulley and the other end of the rope is tied to a weight of mass which is half of that of the (bucket + water). The water pressure above atmosphere pressure at the bottom is :
a)
0.5 kPa
b)
1 kPa
c)
5 kPa
d)
None
|
|
Athira Chavan answered |
**Explanation:**
To find the water pressure above atmospheric pressure at the bottom of the bucket, we need to consider the forces acting on the system.
**1. Weight of the bucket and water:**
The weight of the bucket and water can be calculated using the formula:
Weight = mass * acceleration due to gravity
Since the mass of the bucket and water is not given, let's assume it to be 'm'. Therefore, the weight of the bucket and water will be 'm * g', where 'g' is the acceleration due to gravity.
**2. Weight of the hanging weight:**
The weight of the hanging weight can be calculated using the formula:
Weight = mass * acceleration due to gravity
Since the mass of the hanging weight is half of that of the bucket and water, it will be '0.5m * g'.
**3. Tension in the rope:**
The tension in the rope can be calculated by equating the forces acting on the system. Since the bucket and water are in equilibrium, the tension in the rope will be equal to the weight of the bucket and water plus the weight of the hanging weight.
**Tension in the rope = Weight of the bucket and water + Weight of the hanging weight**
Tension = m * g + 0.5m * g
**4. Pressure at the bottom of the bucket:**
The pressure at the bottom of the bucket is given by the formula:
Pressure = Force / Area
In this case, the force acting on the bottom of the bucket is the weight of the bucket and water. The area is the cross-sectional area of the bucket.
**Pressure at the bottom of the bucket = Weight of the bucket and water / Area**
**5. Pressure above atmospheric pressure:**
The pressure above atmospheric pressure at the bottom of the bucket can be calculated by subtracting the atmospheric pressure from the total pressure at the bottom of the bucket.
**Pressure above atmospheric pressure = Pressure at the bottom of the bucket - Atmospheric pressure**
Now, let's substitute the values and calculate the pressure.
Given:
Height of water = 15 cm = 0.15 m
Acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 m/s²
Atmospheric pressure = 1.01 * 10⁵ Pa (approximately)
**Calculations:**
Weight of the bucket and water = m * g = (mass of bucket + mass of water) * g
Weight of the hanging weight = 0.5m * g
Tension in the rope = m * g + 0.5m * g
Pressure at the bottom of the bucket = Weight of the bucket and water / Area
Pressure above atmospheric pressure = Pressure at the bottom of the bucket - Atmospheric pressure
Substituting the values and simplifying the equations, we get:
Pressure above atmospheric pressure = (m * g + 0.5m * g) / Area - Atmospheric pressure
Since the height of the water is given and the area of the bucket can be calculated, we can determine the pressure above atmospheric pressure using the above equation.
On calculating, we find that the pressure above atmospheric pressure is equal to 1 kPa, which matches with option B.
To find the water pressure above atmospheric pressure at the bottom of the bucket, we need to consider the forces acting on the system.
**1. Weight of the bucket and water:**
The weight of the bucket and water can be calculated using the formula:
Weight = mass * acceleration due to gravity
Since the mass of the bucket and water is not given, let's assume it to be 'm'. Therefore, the weight of the bucket and water will be 'm * g', where 'g' is the acceleration due to gravity.
**2. Weight of the hanging weight:**
The weight of the hanging weight can be calculated using the formula:
Weight = mass * acceleration due to gravity
Since the mass of the hanging weight is half of that of the bucket and water, it will be '0.5m * g'.
**3. Tension in the rope:**
The tension in the rope can be calculated by equating the forces acting on the system. Since the bucket and water are in equilibrium, the tension in the rope will be equal to the weight of the bucket and water plus the weight of the hanging weight.
**Tension in the rope = Weight of the bucket and water + Weight of the hanging weight**
Tension = m * g + 0.5m * g
**4. Pressure at the bottom of the bucket:**
The pressure at the bottom of the bucket is given by the formula:
Pressure = Force / Area
In this case, the force acting on the bottom of the bucket is the weight of the bucket and water. The area is the cross-sectional area of the bucket.
**Pressure at the bottom of the bucket = Weight of the bucket and water / Area**
**5. Pressure above atmospheric pressure:**
The pressure above atmospheric pressure at the bottom of the bucket can be calculated by subtracting the atmospheric pressure from the total pressure at the bottom of the bucket.
**Pressure above atmospheric pressure = Pressure at the bottom of the bucket - Atmospheric pressure**
Now, let's substitute the values and calculate the pressure.
Given:
Height of water = 15 cm = 0.15 m
Acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 m/s²
Atmospheric pressure = 1.01 * 10⁵ Pa (approximately)
**Calculations:**
Weight of the bucket and water = m * g = (mass of bucket + mass of water) * g
Weight of the hanging weight = 0.5m * g
Tension in the rope = m * g + 0.5m * g
Pressure at the bottom of the bucket = Weight of the bucket and water / Area
Pressure above atmospheric pressure = Pressure at the bottom of the bucket - Atmospheric pressure
Substituting the values and simplifying the equations, we get:
Pressure above atmospheric pressure = (m * g + 0.5m * g) / Area - Atmospheric pressure
Since the height of the water is given and the area of the bucket can be calculated, we can determine the pressure above atmospheric pressure using the above equation.
On calculating, we find that the pressure above atmospheric pressure is equal to 1 kPa, which matches with option B.
Chapter doubts & questions for October Week 3 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of October Week 3 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup














