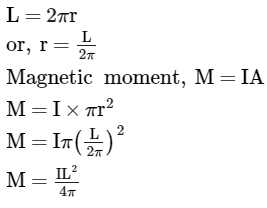All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of September Week 2 for NEET Exam
If the susceptibility of a metal at saturation is 4500, then what is the permeability of this metal at saturation?- a)5.684 X 10-4 T-m/A
- b)5.654 X 10-3 T-m/A
- c)5.654 X 10-7 T-m/A
- d)5.658 X 10-5 T-m/A
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the susceptibility of a metal at saturation is 4500, then what is the permeability of this metal at saturation?
a)
5.684 X 10-4 T-m/A
b)
5.654 X 10-3 T-m/A
c)
5.654 X 10-7 T-m/A
d)
5.658 X 10-5 T-m/A
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
μr=μ/μ0
μ= μr x μ0
μ=4500 x 4πx 10-7
μ=56520x10-7
μ=5.652x10-3
μ= μr x μ0
μ=4500 x 4πx 10-7
μ=56520x10-7
μ=5.652x10-3
What kinds of materials are used for coating magnetic tapes?- a)Diamagnetic Materials
- b)Ferrites
- c)Electromagnet
- d)Paramagnetic materials
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What kinds of materials are used for coating magnetic tapes?
a)
Diamagnetic Materials
b)
Ferrites
c)
Electromagnet
d)
Paramagnetic materials

|
Divey Sethi answered |
Ceramics are used for coating magnetic tapes in a cassette player or for building memory stores in a modern computer. Ceramics are specially treated barium-iron oxides and are also called ferrites.
The units of magnetic pole strength and magnetic dipole moment of a bar magnet are- a)A-m, JT-1
- b)JT-1, Am-1
- c)JT-1, Am
- d)Am-1, JT-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The units of magnetic pole strength and magnetic dipole moment of a bar magnet are
a)
A-m, JT-1
b)
JT-1, Am-1
c)
JT-1, Am
d)
Am-1, JT-1
|
|
Anaya Patel answered |
The units of magnetic pole strength is (A-m) and magnetic dipole moment of a bar magnet is (JT-1)
In the complex PtCl4.3NH3 the number of ionisable chlorines is- a)1
- b)3
- c)2
- d)0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the complex PtCl4.3NH3 the number of ionisable chlorines is
a)
1
b)
3
c)
2
d)
0

|
Srishti Kaur answered |
Pt has coordination number of 4 so 3 chlorine will come outside the coordination sphere.
What is the unit of susceptibility?- a)Am-1
- b)Am2
- c)No units
- d)Am
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the unit of susceptibility?
a)
Am-1
b)
Am2
c)
No units
d)
Am
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
In electromagnetism the magnetic susceptibility (Latin: susceptibilis, “receptive”; denoted X) is a measure of how much a material will become magnetized in an applied magnetic field. Mathematically, it is the ratio of magnetization M(magnetic moment per unit volume) to the applied magnetizing field intensity H.
KCl.MgCl2.6H2O is a- a)Double salt
- b)Mixed salt
- c)Basic salt
- d)Complex salt
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
KCl.MgCl2.6H2O is a
a)
Double salt
b)
Mixed salt
c)
Basic salt
d)
Complex salt

|
Srestha Choudhury answered |
KCl.MgCl2.6H2O is double salt
In the formation of complex entity, the central atom/ion acts as- a)Bronsted acid
- b)Lewis base
- c)Lewis acid
- d)Bronsted base
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the formation of complex entity, the central atom/ion acts as
a)
Bronsted acid
b)
Lewis base
c)
Lewis acid
d)
Bronsted base
|
|
Arka Das answered |
Explanation:
In the formation of a complex entity, a central atom/ion acts as a Lewis acid. This can be explained as follows:
Lewis Acid and Lewis Base:
According to Lewis acid-base theory, a Lewis acid is a species that accepts a pair of electrons to form a coordinate covalent bond, while a Lewis base is a species that donates a pair of electrons to form a coordinate covalent bond.
Formation of Complex Entity:
A complex entity is formed by the coordination of a central atom/ion with one or more ligands. Ligands are molecules or ions that donate a pair of electrons to the central atom/ion to form a coordinate covalent bond.
Role of Central Atom/Ion:
In the formation of a complex entity, the central atom/ion acts as a Lewis acid because it accepts a pair of electrons from the ligands to form a coordinate covalent bond. The central atom/ion has an incomplete outer shell, which makes it electron deficient and thus able to accept electrons from other species.
Examples:
Some examples of complex entities and their central atom/ion are as follows:
- In [Fe(CN)6]4-, Fe2+ acts as the central ion, which accepts electrons from the CN- ligands.
- In [Cu(NH3)4]2+, Cu2+ acts as the central ion, which accepts electrons from the NH3 ligands.
- In [Ag(NH3)2]+, Ag+ acts as the central ion, which accepts electrons from the NH3 ligands.
Conclusion:
Thus, we can conclude that in the formation of a complex entity, the central atom/ion acts as a Lewis acid because it accepts a pair of electrons from the ligands to form a coordinate covalent bond.
In the formation of a complex entity, a central atom/ion acts as a Lewis acid. This can be explained as follows:
Lewis Acid and Lewis Base:
According to Lewis acid-base theory, a Lewis acid is a species that accepts a pair of electrons to form a coordinate covalent bond, while a Lewis base is a species that donates a pair of electrons to form a coordinate covalent bond.
Formation of Complex Entity:
A complex entity is formed by the coordination of a central atom/ion with one or more ligands. Ligands are molecules or ions that donate a pair of electrons to the central atom/ion to form a coordinate covalent bond.
Role of Central Atom/Ion:
In the formation of a complex entity, the central atom/ion acts as a Lewis acid because it accepts a pair of electrons from the ligands to form a coordinate covalent bond. The central atom/ion has an incomplete outer shell, which makes it electron deficient and thus able to accept electrons from other species.
Examples:
Some examples of complex entities and their central atom/ion are as follows:
- In [Fe(CN)6]4-, Fe2+ acts as the central ion, which accepts electrons from the CN- ligands.
- In [Cu(NH3)4]2+, Cu2+ acts as the central ion, which accepts electrons from the NH3 ligands.
- In [Ag(NH3)2]+, Ag+ acts as the central ion, which accepts electrons from the NH3 ligands.
Conclusion:
Thus, we can conclude that in the formation of a complex entity, the central atom/ion acts as a Lewis acid because it accepts a pair of electrons from the ligands to form a coordinate covalent bond.
Declination is the angle between:- a)horizontal and vertical components of earth’s magnetic field
- b)horizontal component and total magnetic field of the earth
- c)geographic and magnetic meridian
- d)geographic meridian and horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Declination is the angle between:
a)
horizontal and vertical components of earth’s magnetic field
b)
horizontal component and total magnetic field of the earth
c)
geographic and magnetic meridian
d)
geographic meridian and horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Magnetic declination, or magnetic variation, is the angle on the horizontal plane between magnetic north (the direction the north end of a compass needle points, corresponding to the direction of the Earth's magnetic field lines) and true north (the direction along a meridian towards the geographic North Pole).
In the complex Fe(CO)x, the value of x is
- a)3
- b)2
- c)4
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the complex Fe(CO)x, the value of x is
a)
3
b)
2
c)
4
d)
5

|
Maitri Sharma answered |
Complex carbonyls follow Sidwick's EAN rule i.e compound with EAN 36 will be relatively more stable than other metal carbonyls. Iron pentacarbonyl has EAN number of 36 = Z−X+Y = (26−0+2x)
[Z = atomic number, X = oxidation state of metal, Y= total electrons donated by ligand]
∴x = 5. So, the formula will be Fe(CO)5.
[Z = atomic number, X = oxidation state of metal, Y= total electrons donated by ligand]
∴x = 5. So, the formula will be Fe(CO)5.
The IUPAC name [CoCl(NO2)(en)2]Cl is- a)Chloridonitrobis (ethylenediamine) cobalt(II) chloride
- b)Chloridobis (ethylenediamine) nitrito-N-cobalt(III) chloride
- c)Bis(ethylenediamine) chloronitrocobalt(III) chloride
- d)Chloridonitrobis (ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name [CoCl(NO2)(en)2]Cl is
a)
Chloridonitrobis (ethylenediamine) cobalt(II) chloride
b)
Chloridobis (ethylenediamine) nitrito-N-cobalt(III) chloride
c)
Bis(ethylenediamine) chloronitrocobalt(III) chloride
d)
Chloridonitrobis (ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride

|
Baishali Chakraborty answered |
Name of ligands name first in alphabetical order followed by anme of central ion.
Which among the following has square pyramidal geometry?- a)Tetracarbonylnickel(0)
- b)Hexaamminecobalt(II) nitrate
- c)Pentacarbonyliron(0)
- d)Bis(acetylacetonato)oxovanadium(IV)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following has square pyramidal geometry?
a)
Tetracarbonylnickel(0)
b)
Hexaamminecobalt(II) nitrate
c)
Pentacarbonyliron(0)
d)
Bis(acetylacetonato)oxovanadium(IV)

|
Malavika Shah answered |
Bis(acetylacetonato)oxovanadium(IV) has square pyramidal geometry.
The correct IUPAC name of Mn3(C0)12 is- a)Dodecacarbonylmanganate(0)
- b)Manganicdodecacarbonyl(0)
- c)Dodecacarbonylmanganese(0)
- d)Dodecacarbonylmaganic(II)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct IUPAC name of Mn3(C0)12 is
a)
Dodecacarbonylmanganate(0)
b)
Manganicdodecacarbonyl(0)
c)
Dodecacarbonylmanganese(0)
d)
Dodecacarbonylmaganic(II)

|
Kunal Pillai answered |
Ligands are named 1st followed by the name of central metal ion.
The ferromagnetic materials can be magnetised easily because- a)Ferromagnetic materials have low susceptibility and permeability
- b)Ferromagnetic materials have high susceptibility and low permeability
- c)Ferromagnetic materials have high susceptibility and permeability
- d)Ferromagnetic materials have low susceptibility and high permeability
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The ferromagnetic materials can be magnetised easily because
a)
Ferromagnetic materials have low susceptibility and permeability
b)
Ferromagnetic materials have high susceptibility and low permeability
c)
Ferromagnetic materials have high susceptibility and permeability
d)
Ferromagnetic materials have low susceptibility and high permeability

|
Rounak Goyal answered |
Such materials are called ferromagnetic, after the Latin word for iron, ferrum. Not only do ferromagnetic materials respond strongly to magnets (the way iron is attracted to magnets), they can also be magnetized themselves—that is, they can be induced to be magnetic or made into permanent magnets.
The hybridization of nickel in tetracarbonyl nickel is- a)sp3
- b)sp3d2
- c)dsp2
- d)sp3d
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The hybridization of nickel in tetracarbonyl nickel is
a)
sp3
b)
sp3d2
c)
dsp2
d)
sp3d

|
Ashwini Chakraborty answered |
The hybridization of an atom refers to the mixing of atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals, which have different shapes and energies than the original atomic orbitals. In the case of tetracarbonyl nickel, the nickel atom is bonded to four carbon monoxide (CO) ligands.
The central nickel atom in tetracarbonyl nickel is surrounded by four ligands, which means it has a coordination number of 4. In order to determine the hybridization of the nickel atom, we can use the concept of the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory.
According to VSEPR theory, the electron pairs around the central atom will arrange themselves in a way that maximizes the distance between them, resulting in a geometry that minimizes electron-electron repulsion. In the case of tetracarbonyl nickel, the four CO ligands are arranged in a symmetrical tetrahedral geometry around the central nickel atom.
To determine the hybridization of the nickel atom, we can count the number of electron pairs around it. In tetracarbonyl nickel, there are four sigma bonds between the nickel atom and the four CO ligands, as well as four lone pairs on the nickel atom. This gives a total of eight electron pairs around the nickel atom.
The hybridization of an atom is determined by the number of sigma bonds and lone pairs around it. In this case, since there are four sigma bonds and four lone pairs, the nickel atom in tetracarbonyl nickel is sp3 hybridized.
The sp3 hybrid orbitals are formed by the mixing of one s orbital and three p orbitals on the nickel atom. These hybrid orbitals are oriented in a tetrahedral arrangement, pointing towards the four CO ligands.
In summary, the hybridization of the nickel atom in tetracarbonyl nickel is sp3, as there are four sigma bonds and four lone pairs around the central atom.
The central nickel atom in tetracarbonyl nickel is surrounded by four ligands, which means it has a coordination number of 4. In order to determine the hybridization of the nickel atom, we can use the concept of the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) theory.
According to VSEPR theory, the electron pairs around the central atom will arrange themselves in a way that maximizes the distance between them, resulting in a geometry that minimizes electron-electron repulsion. In the case of tetracarbonyl nickel, the four CO ligands are arranged in a symmetrical tetrahedral geometry around the central nickel atom.
To determine the hybridization of the nickel atom, we can count the number of electron pairs around it. In tetracarbonyl nickel, there are four sigma bonds between the nickel atom and the four CO ligands, as well as four lone pairs on the nickel atom. This gives a total of eight electron pairs around the nickel atom.
The hybridization of an atom is determined by the number of sigma bonds and lone pairs around it. In this case, since there are four sigma bonds and four lone pairs, the nickel atom in tetracarbonyl nickel is sp3 hybridized.
The sp3 hybrid orbitals are formed by the mixing of one s orbital and three p orbitals on the nickel atom. These hybrid orbitals are oriented in a tetrahedral arrangement, pointing towards the four CO ligands.
In summary, the hybridization of the nickel atom in tetracarbonyl nickel is sp3, as there are four sigma bonds and four lone pairs around the central atom.
The IUPAC name of AlCl3.4(EtOH) is- a)Aluminium(III) chloride-4-ethanol
- b)Aluminium (IV) chloride-4-hydroxyethane
- c)Aluminium (II) chloride-4-ethanol
- d)Aluminium chloride-4-ethanol
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The IUPAC name of AlCl3.4(EtOH) is
a)
Aluminium(III) chloride-4-ethanol
b)
Aluminium (IV) chloride-4-hydroxyethane
c)
Aluminium (II) chloride-4-ethanol
d)
Aluminium chloride-4-ethanol

|
Ashish Nambiar answered |
This is double salt so name is written in sequential manner.
According to Werner’s theory , the primary valences of the central atom- a)Are equal to its coordination number
- b)Decide the geometry of the complex
- c)Are satisfied by negative ions
- d)Are satisfied by negative ions or neutral molecules
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
According to Werner’s theory , the primary valences of the central atom
a)
Are equal to its coordination number
b)
Decide the geometry of the complex
c)
Are satisfied by negative ions
d)
Are satisfied by negative ions or neutral molecules

|
Nidhi Nambiar answered |
Primary valency is equal to no. of ligands attachted which are negatively charges.
Which of the following ligand gives chelate complexes?- a)NH3
- b)SCN--
- c)Pyridine
- d)C2O42-
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following ligand gives chelate complexes?
a)
NH3
b)
SCN--
c)
Pyridine
d)
C2O42-

|
Samridhi Bajaj answered |
Oxalate is a bidentate ligand.
What was the result of S.L. Miller's 1953 experiment?- a)Proved the theory of panspermia
- b)Formation of amino acids under simulated early Earth conditions
- c)Discovery of DNA
- d)Disproved the Big Bang theory
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Proved the theory of panspermia
b)
Formation of amino acids under simulated early Earth conditions
c)
Discovery of DNA
d)
Disproved the Big Bang theory

|
Stepway Academy answered |
In 1953, S.L. Miller conducted an experiment where he created conditions similar to early Earth with a mixture of gases and electrical discharges. This resulted in the formation of amino acids, supporting the idea of chemical evolution as a precursor to the origin of life.
Topic in NCERT: Origin of life
Line in NCERT: "he created electric discharge in a closed flask containing ch4, h2, nh3 and water vapour at 800°c. he observed formation of amino acids."
The following are some major events in the early history of life
P. First heterotrophic prokaryotes
Q. First genes
R. First eukaryotes
S. First autotrophic prokaryotes
T. First animals
Which option below places these events in the correct order?
- a)PQSRT
- b)QSPTR
- c)QPSRT
- d)QSPRT
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The following are some major events in the early history of life
P. First heterotrophic prokaryotes
Q. First genes
R. First eukaryotes
S. First autotrophic prokaryotes
T. First animals
Which option below places these events in the correct order?
P. First heterotrophic prokaryotes
Q. First genes
R. First eukaryotes
S. First autotrophic prokaryotes
T. First animals
Which option below places these events in the correct order?
a)
PQSRT
b)
QSPTR
c)
QPSRT
d)
QSPRT
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Organisms have evolved from simpler forms to complex form. Hence the order of the events are genes first, then heterotrophic prokaryotes, then autotrophic prokaryotes, then eukaryotes and then animals.
Which of the following can be termed as mixed complex?- a)[Co(NH3)4NO2Cl]Cl
- b)K4[Fe(CN)6]
- c)K2FeSO4
- d)[Cu(NH4)]SO4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following can be termed as mixed complex?
a)
[Co(NH3)4NO2Cl]Cl
b)
K4[Fe(CN)6]
c)
K2FeSO4
d)
[Cu(NH4)]SO4

|
Niti Saha answered |
In A one and more different types of ligands are present.
Which is used in cancer therapy?- a)Cyanocobalamine
- b)Cis-Platin
- c)Zeise’s salt
- d)EDTA
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is used in cancer therapy?
a)
Cyanocobalamine
b)
Cis-Platin
c)
Zeise’s salt
d)
EDTA

|
Vandana Menon answered |
Cis Platin (cis – [Pt(NH3)2(Cl)2] is a anti cancer drug.
Which is not true about a ligand?- a)A monodentate ligand cannot be chelating ligand
- b)A multidentate ligand cannot cause chelation
- c)It can be monodentate of multidentate
- d)It can act as a Lewis Base
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is not true about a ligand?
a)
A monodentate ligand cannot be chelating ligand
b)
A multidentate ligand cannot cause chelation
c)
It can be monodentate of multidentate
d)
It can act as a Lewis Base

|
Anu Basu answered |
Multidentate ligand always act as chelating Ligand
The oxidation state of Ag in tollen’s reagent is- a)+1.5
- b)0
- c)+2
- d)+1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxidation state of Ag in tollen’s reagent is
a)
+1.5
b)
0
c)
+2
d)
+1

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
The silver-producing reaction in this demonstration is one that is commonly used in basic organic laboratory classes to identify aldehydes. The reaction called "The Silver Mirror Test" or Tollens' Test is accomplished by mixing aqueous silver nitrate with aqueous ammonia to produce a solution known as Tollens' reagent. Although this solution contains only a very weak oxidizing agent, it is strong enough to oxidize the aldehyde functional group. As this oxidation occurs, silver is reduced from the +1 oxidation state to metallic silver. This metallic silver is deposited on the walls of the test tube producing a reflective "mirror".
Who proposed that the first form of life could have come from pre-existing nonliving organic molecules?- a)SL Miller
- b)Oparin and Haldane
- c)Charles Darwin
- d)Alfred Wallace
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who proposed that the first form of life could have come from pre-existing nonliving organic molecules?
a)
SL Miller
b)
Oparin and Haldane
c)
Charles Darwin
d)
Alfred Wallace
|
|
Jaspreet answered |
This theory was given by A. L.Oparin and J.B.S. haldane !!!
The magnetic induction left behind in the sample after the magnetizing field has been removed is called- a)Hyteresis
- b)Retentivity
- c)Coercivity
- d)Ferromagnetism
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The magnetic induction left behind in the sample after the magnetizing field has been removed is called
a)
Hyteresis
b)
Retentivity
c)
Coercivity
d)
Ferromagnetism
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
Remanence or remanent magnetization or residual magnetism is the magnetization left behind in a ferromagnetic material (such as iron) after an external magnetic field is removed. It is also the measure of that magnetization. Colloquially, when a magnet is "magnetized" it has remanence.The remanence of magnetic materials provides the magnetic memory in magnetic storage devices, and is used as a source of information on the past Earth's magnetic field in paleomagnetism.The equivalent term residual magnetization is generally used in engineering applications. In transformers, electric motors and generators a large residual magnetization is not desirable (see also electrical steel) as it is an unwanted contamination, for example a magnetization remaining in an electromagnet after the current in the coil is turned off. Where it is unwanted, it can be removed by degaussing.Sometimes the term retentivity is used for remanence measured in units of magnetic flux density.
Which of the following complex will give white precipitate with barium chloride solution?
- a)[Co(NH3)4Cl2]NO2
- b)[Cr(NH3)5Cl]SO4
- c)[Co(NH3)6]Br3
- d)[Cr(NH3)5SO4]Cl
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following complex will give white precipitate with barium chloride solution?
a)
[Co(NH3)4Cl2]NO2
b)
[Cr(NH3)5Cl]SO4
c)
[Co(NH3)6]Br3
d)
[Cr(NH3)5SO4]Cl

|
Nidhi Yadav answered |
Since the reagent is BaCl2(aq), displacement reaction will take place. The resulting solution, if insoluble in water, will form a white precipitate. Both BaNO2 and BaCl2 are soluble in water and hence will not form a precipitate. BaSO4, however, is insoluble in water and hence forms a white precipitate.
A particle of charge q and mass m moves in a circular orbit of radius r with angular speed. The ratio of the magnitude of its magnetic moment to that of its angular momentum depends on- a)q and m
- b)ω and q
- c)ω, q and m
- d)ω and m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle of charge q and mass m moves in a circular orbit of radius r with angular speed. The ratio of the magnitude of its magnetic moment to that of its angular momentum depends on
a)
q and m
b)
ω and q
c)
ω, q and m
d)
ω and m

|
Sanchita Iyer answered |
To find the magnetic moment due to a single particle, it is advisable to consider the equivalent current due to it
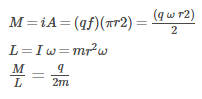
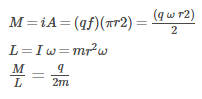
What does the Big Bang theory suggest about the universe's origin?- a)It originated from the condensation of gases
- b)It began with a singular huge explosion
- c)It was always in a steady state
- d)It formed through gradual accumulation of matter
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
It originated from the condensation of gases
b)
It began with a singular huge explosion
c)
It was always in a steady state
d)
It formed through gradual accumulation of matter

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
The Big Bang theory suggests that the universe originated from a singular, immense explosion, leading to its ongoing expansion and cooling, eventually forming stars, galaxies, and other celestial bodies.
Topic in NCERT: Origin of universe
Line in NCERT: "the big bang theory attempts to explain to us the origin of universe. it talks of a singular huge explosion unimaginable in physical terms."
According to Oparin and Haldane, what preceded the formation of life?- a)Formation of water from oxygen and hydrogen
- b)Disappearance of the dinosaurs
- c)Chemical evolution from inorganic constituents
- d)Development of multicellular organisms
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Formation of water from oxygen and hydrogen
b)
Disappearance of the dinosaurs
c)
Chemical evolution from inorganic constituents
d)
Development of multicellular organisms

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Oparin of Russia and Haldane of England proposed that the formation of life was preceded by chemical evolution, which involved the formation of diverse organic molecules from inorganic constituents under Earth's early conditions.
Topic in NCERT: Origin of life
Line in NCERT: "oparin of russia and haldane of england proposed that the first form of life could have come from pre-existing non-living organic molecules (e.g. rna, protein, etc.) and that formation of life was preceded by chemical evolution, i.e., formation of diverse organic molecules from inorganic constituents."
The coordination number of Cr in [Cr (NH3)3 (H2O)3]- a)3
- b)6
- c)4
- d)2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The coordination number of Cr in [Cr (NH3)3 (H2O)3]
a)
3
b)
6
c)
4
d)
2

|
Sanchita Reddy answered |
Understanding Coordination Number
The coordination number of a metal ion in a complex refers to the number of ligand donor atoms that are bonded to it. In the case of the complex [Cr(NH3)3(H2O)3], we need to analyze the ligands attached to chromium (Cr).
Identifying Ligands
- The complex contains two types of ligands:
- Ammonia (NH3), which is a neutral ligand.
- Water (H2O), which is also a neutral ligand.
Counting the Ligands
- There are three NH3 ligands.
- There are three H2O ligands.
Calculating the Coordination Number
- To find the coordination number, we simply add the number of donor atoms from each ligand type:
- From NH3: 3 ligands x 1 donor atom each = 3
- From H2O: 3 ligands x 1 donor atom each = 3
- Total coordination number = 3 (from NH3) + 3 (from H2O) = 6
Conclusion
Thus, the coordination number of Cr in the complex [Cr(NH3)3(H2O)3] is 6. This means that option 'B' is correct. The coordination number reflects how many atoms are directly bonded to the metal ion, which in this case is chromium.
The coordination number of a metal ion in a complex refers to the number of ligand donor atoms that are bonded to it. In the case of the complex [Cr(NH3)3(H2O)3], we need to analyze the ligands attached to chromium (Cr).
Identifying Ligands
- The complex contains two types of ligands:
- Ammonia (NH3), which is a neutral ligand.
- Water (H2O), which is also a neutral ligand.
Counting the Ligands
- There are three NH3 ligands.
- There are three H2O ligands.
Calculating the Coordination Number
- To find the coordination number, we simply add the number of donor atoms from each ligand type:
- From NH3: 3 ligands x 1 donor atom each = 3
- From H2O: 3 ligands x 1 donor atom each = 3
- Total coordination number = 3 (from NH3) + 3 (from H2O) = 6
Conclusion
Thus, the coordination number of Cr in the complex [Cr(NH3)3(H2O)3] is 6. This means that option 'B' is correct. The coordination number reflects how many atoms are directly bonded to the metal ion, which in this case is chromium.
The first life originated- a)on land
- b)in air
- c)in water
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The first life originated
a)
on land
b)
in air
c)
in water
d)
all of these
|
|
Jaspreet answered |
It's a Ncert line life originated first in water 😊✌️
Theory of spontaneous generation was rejected because:- a)It explained origin of first life from non-living or inanimate matter and lacked experimental evidence.
- b)It was based on the biogenesis concept.
- c)It did not explain about the origin of first life on earth.
- d)It proposed origin of life from outer space.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Theory of spontaneous generation was rejected because:
a)
It explained origin of first life from non-living or inanimate matter and lacked experimental evidence.
b)
It was based on the biogenesis concept.
c)
It did not explain about the origin of first life on earth.
d)
It proposed origin of life from outer space.
|
|
Advait Joshi answered |
Theory of Spontaneous Generation Rejection Explanation
Theory of Spontaneous Generation:
- The theory of spontaneous generation proposed that life could arise from non-living or inanimate matter through a process of spontaneous generation.
Reasons for Rejection:
- Lack of Experimental Evidence:
- One of the main reasons why the theory of spontaneous generation was rejected was due to the lack of experimental evidence to support it.
- Scientists found no concrete proof that life could spontaneously arise from non-living matter.
- Biogenesis Concept:
- The concept of biogenesis, which states that living organisms can only arise from pre-existing living organisms, gained more support as it was backed by experimental evidence.
- This contradicted the idea of spontaneous generation.
- Origin of First Life on Earth:
- The theory of spontaneous generation did not provide a satisfactory explanation for the origin of the first life on Earth.
- It failed to address the specific mechanisms by which life could arise from non-living matter.
- Origin of Life from Outer Space:
- Some proponents of the theory of spontaneous generation suggested that life could have originated from outer space.
- However, this idea lacked substantial evidence and was not widely accepted by the scientific community.
In conclusion, the theory of spontaneous generation was rejected primarily because it lacked experimental evidence to support its claims and failed to provide a comprehensive explanation for the origin of life on Earth. The concept of biogenesis, which has experimental backing, gained more acceptance in the scientific community.
Theory of Spontaneous Generation:
- The theory of spontaneous generation proposed that life could arise from non-living or inanimate matter through a process of spontaneous generation.
Reasons for Rejection:
- Lack of Experimental Evidence:
- One of the main reasons why the theory of spontaneous generation was rejected was due to the lack of experimental evidence to support it.
- Scientists found no concrete proof that life could spontaneously arise from non-living matter.
- Biogenesis Concept:
- The concept of biogenesis, which states that living organisms can only arise from pre-existing living organisms, gained more support as it was backed by experimental evidence.
- This contradicted the idea of spontaneous generation.
- Origin of First Life on Earth:
- The theory of spontaneous generation did not provide a satisfactory explanation for the origin of the first life on Earth.
- It failed to address the specific mechanisms by which life could arise from non-living matter.
- Origin of Life from Outer Space:
- Some proponents of the theory of spontaneous generation suggested that life could have originated from outer space.
- However, this idea lacked substantial evidence and was not widely accepted by the scientific community.
In conclusion, the theory of spontaneous generation was rejected primarily because it lacked experimental evidence to support its claims and failed to provide a comprehensive explanation for the origin of life on Earth. The concept of biogenesis, which has experimental backing, gained more acceptance in the scientific community.
What role does the ozone layer play in the context of early Earth's atmosphere?- a)It protected early forms of life from ultraviolet radiation
- b)It contributed to the formation of oceans
- c)It helped in the synthesis of organic molecules
- d)It was responsible for the development of multicellular life
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
It protected early forms of life from ultraviolet radiation
b)
It contributed to the formation of oceans
c)
It helped in the synthesis of organic molecules
d)
It was responsible for the development of multicellular life

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The formation of the ozone layer was crucial in early Earth's history as it helped to shield the surface from harmful ultraviolet rays from the sun, thereby protecting the nascent forms of life and allowing biological processes to occur more safely.
Topic in NCERT: Origin of life
Line in NCERT: "the ozone layer was formed."
What theory did Louis Pasteur's experiment help to dismiss?- a)Big Bang Theory
- b)Panspermia
- c)Spontaneous Generation
- d)Chemical Evolution
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Big Bang Theory
b)
Panspermia
c)
Spontaneous Generation
d)
Chemical Evolution

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Louis Pasteur's experiment, which involved pre-sterilized flasks to show that no life arose from "killed yeast" unless exposed to air, helped to dismiss the theory of spontaneous generation, proving that life comes only from pre-existing life.
Topic in NCERT: Origin of life
Line in NCERT: "louis pasteur by careful experimentation demonstrated that life comes only from pre-existing life. he showed that in pre-sterilised flasks, life did not come from killed yeast while in another flask open to air, new living organisms arose from ‘killed yeast'. spontaneous generation theory was dismissed once and for all."
बाह्य अंतरिक्ष में अपनी यात्रा से लौट रहे अंतरिक्ष यान पृथ्वी के वायुमंडल में बड़ी तेजी से प्रवेश करते हैं, जिससे वे गर्म जलते हैं। इन उच्च तापमानों का सामना करने के लिए ढाल के रूप में किस धातु का उपयोग किया जाता है?- a)टाइटेनियम
- b)लोहा
- c)लीड
- d)निकल
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
बाह्य अंतरिक्ष में अपनी यात्रा से लौट रहे अंतरिक्ष यान पृथ्वी के वायुमंडल में बड़ी तेजी से प्रवेश करते हैं, जिससे वे गर्म जलते हैं। इन उच्च तापमानों का सामना करने के लिए ढाल के रूप में किस धातु का उपयोग किया जाता है?
a)
टाइटेनियम
b)
लोहा
c)
लीड
d)
निकल

|
Akash Kumar7351 answered |
A
In the experiment in given diagram which of the following groups of gases were used to simulate primitive atmosphere?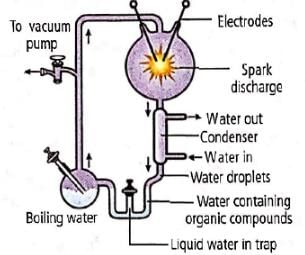
- a)N2, H2, CH4 C2H6
- b)NH3, H2O, CH4 H2
- c)N2O, H2O, NO2, SO2
- d)CH4, H2, NO2, SO2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the experiment in given diagram which of the following groups of gases were used to simulate primitive atmosphere?

a)
N2, H2, CH4 C2H6
b)
NH3, H2O, CH4 H2
c)
N2O, H2O, NO2, SO2
d)
CH4, H2, NO2, SO2
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Stanley Miller in 1953 took an air tight apparatus and circulated four gases - CH4, NH3, H2 and water vapour through it. He passed electrical discharges from electrodes at 800∘C. Then he passed the mixture through a condenser He performed this experiment continuously in this way for a week and analysed the composition of the liquid inside the apparatus. He found a large number of simple organic compounds including some amino acids such as alanine, glycine and aspartic acid. Miller, thus, proved that organic compounds were basis of life.
Chapter doubts & questions for September Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of September Week 2 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup