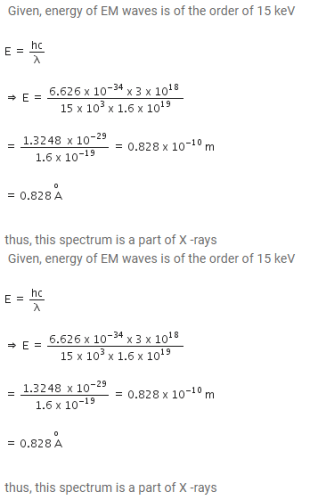All Exams >
NEET >
Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation >
All Questions
All questions of November Week 1 for NEET Exam
Which one is not an electromagnetic wave?- a)ultraviolet rays
- b)ultrasound waves
- c)X- rays
- d)radio waves
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is not an electromagnetic wave?
a)
ultraviolet rays
b)
ultrasound waves
c)
X- rays
d)
radio waves
|
|
Shivaraju. K Shivaraju. answered |
These are not audible because high frequency wave
Weather forecasting uses- a)Visible Rays
- b)Micro waves
- c)Infra red Rays
- d)Gamma Rays
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Weather forecasting uses
a)
Visible Rays
b)
Micro waves
c)
Infra red Rays
d)
Gamma Rays
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
It's an infrared sensor that reads temperatures.This sensor allows satellites to measure the amount of energy radiated by Earth's surface, clouds, oceans, air, and so on. Infrared sensors can be used at night—a helpful feature for forecasters, considering that the imager can only pick up data during daylight hours.
Infra red rays are used
- a)radar systems
- b)In green house to keep plants warm
- c)To treat muscular pain
- d)Both b and c
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Infra red rays are used
a)
radar systems
b)
In green house to keep plants warm
c)
To treat muscular pain
d)
Both b and c

|
Niki Niki answered |
Infra red rays are basically heat radiation it gives warmth which support the plant growth. It also helps in treating muscle pain in the same way we use hot water massage for muscle cramps. Hope it helps:)
The physical properties of electromagnetic waves are decided by their- a)Method of excitation
- b)Wavelength
- c)Frequency
- d)Amplitude
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The physical properties of electromagnetic waves are decided by their
a)
Method of excitation
b)
Wavelength
c)
Frequency
d)
Amplitude
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
These electric and magnetic waves travel perpendicular to each other and have certain characteristics, including amplitude, wavelength, and frequency. General Properties of all electromagnetic radiation: Electromagnetic radiation can travel through empty space.
Electromagnetic Spectrum is- a)Orderly distribution of the electromagnetic radiations according to their amplitude only.
- b)Orderly distribution of the electromagnetic radiations according to their wavelength or frequency.
- c)Orderly distribution of the electromagnetic radiations according to their wavelength or amplitude.
- d)Orderly distribution of the electromagnetic radiations according to their amplitude or frequency.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Electromagnetic Spectrum is
a)
Orderly distribution of the electromagnetic radiations according to their amplitude only.
b)
Orderly distribution of the electromagnetic radiations according to their wavelength or frequency.
c)
Orderly distribution of the electromagnetic radiations according to their wavelength or amplitude.
d)
Orderly distribution of the electromagnetic radiations according to their amplitude or frequency.
|
|
Swati Verma answered |
The orderly distribution of electromagnetic radiations according to their wavelength or frequency as called the electromagnetic spectrum. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of the frequency range from few Hz to 106 Hz.
Oscillating circuits produce- a)Radio frequencies
- b)Power frequencies
- c)Microwaves
- d)Ultra violet Rays
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Oscillating circuits produce
a)
Radio frequencies
b)
Power frequencies
c)
Microwaves
d)
Ultra violet Rays

|
Rajeev Sen answered |
The utility frequency, (power) line frequency (American English) or mains frequency (British English) is the nominal frequency of the oscillations of alternating current (AC) in an electric power grid transmitted from a power station to the end-user.An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillating electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave. An RF oscillator produces signals in the radio frequency (RF) range of about 100 kHz to 100 GHz.
What is the role of α-interferon in cancer treatment?- a)It directly kills cancer cells.
- b)It helps in preventing the formation of tumors.
- c)It activates the immune system to destroy tumor cells.
- d)It prevents DNA damage in normal cells.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
It directly kills cancer cells.
b)
It helps in preventing the formation of tumors.
c)
It activates the immune system to destroy tumor cells.
d)
It prevents DNA damage in normal cells.
|
|
Baishali Desai answered |
Role of α-Interferon in Cancer Treatment
α-Interferon (IFN-α) is a type of cytokine that plays a crucial role in the immune response and has therapeutic applications in cancer treatment.
Mechanism of Action
- Immune Activation: α-Interferon primarily functions by enhancing the immune system's ability to identify and destroy tumor cells.
- Cytokine Release: It stimulates the production of other cytokines and enhances the activity of immune cells such as T-cells and natural killer (NK) cells.
Enhancement of Antitumor Activity
- Immune Surveillance: By activating immune cells, α-Interferon improves the body's surveillance against cancer cells, making it more effective in recognizing and eliminating them.
- Inhibition of Tumor Growth: It has been shown to inhibit the proliferation of certain tumor cells, indirectly contributing to the management of cancer.
Clinical Applications
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma: α-Interferon is used in treating liver cancer, particularly in patients with hepatitis C virus.
- Melanoma and Renal Cell Carcinoma: It is also utilized in managing melanoma and renal cell carcinoma, among other cancers.
Conclusion
In summary, α-Interferon does not directly kill cancer cells, prevent DNA damage, or stop tumor formation. Instead, its primary role in cancer therapy is to activate the immune system, which leads to the targeted destruction of tumor cells. This immune-mediated approach is a vital aspect of modern cancer treatment strategies.
α-Interferon (IFN-α) is a type of cytokine that plays a crucial role in the immune response and has therapeutic applications in cancer treatment.
Mechanism of Action
- Immune Activation: α-Interferon primarily functions by enhancing the immune system's ability to identify and destroy tumor cells.
- Cytokine Release: It stimulates the production of other cytokines and enhances the activity of immune cells such as T-cells and natural killer (NK) cells.
Enhancement of Antitumor Activity
- Immune Surveillance: By activating immune cells, α-Interferon improves the body's surveillance against cancer cells, making it more effective in recognizing and eliminating them.
- Inhibition of Tumor Growth: It has been shown to inhibit the proliferation of certain tumor cells, indirectly contributing to the management of cancer.
Clinical Applications
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma: α-Interferon is used in treating liver cancer, particularly in patients with hepatitis C virus.
- Melanoma and Renal Cell Carcinoma: It is also utilized in managing melanoma and renal cell carcinoma, among other cancers.
Conclusion
In summary, α-Interferon does not directly kill cancer cells, prevent DNA damage, or stop tumor formation. Instead, its primary role in cancer therapy is to activate the immune system, which leads to the targeted destruction of tumor cells. This immune-mediated approach is a vital aspect of modern cancer treatment strategies.
Radioactive decay of the nucleus leads to the emission of- a)visible light
- b)gamma rays
- c)radio waves
- d)microwaves
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Radioactive decay of the nucleus leads to the emission of
a)
visible light
b)
gamma rays
c)
radio waves
d)
microwaves

|
Rounak Goyal answered |
The emission of gamma rays does not alter the number of protons or neutrons in the nucleus but instead has the effect of moving the nucleus from a higher to a lower energy state (unstable to stable). Gamma ray emission frequently follows beta decay, alpha decay, and other nuclear decay processes.
Which of the following statements about the treatment of HIV/AIDS is/are correct?
i. Anti-retroviral drugs can completely cure HIV/AIDS.
ii. Anti-retroviral drugs help control the replication of the virus and prolong the life of the patient.
iii. There is no vaccine available for HIV prevention, but safe sex practices can reduce transmission.
iv. HIV treatment is only effective during the early stages of infection.- a)i and ii
- b)ii and iii
- c)iii and iv
- d)i and iv
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
i. Anti-retroviral drugs can completely cure HIV/AIDS.
ii. Anti-retroviral drugs help control the replication of the virus and prolong the life of the patient.
iii. There is no vaccine available for HIV prevention, but safe sex practices can reduce transmission.
iv. HIV treatment is only effective during the early stages of infection.
a)
i and ii
b)
ii and iii
c)
iii and iv
d)
i and iv
|
|
Mohit Choudhury answered |
Understanding HIV/AIDS Treatment
HIV/AIDS treatment involves a series of statements regarding the effectiveness and management of the disease. Let's break down the provided options to understand the correct answer.
Statement Analysis
- i. Anti-retroviral drugs can completely cure HIV/AIDS.
- This statement is incorrect. Anti-retroviral therapy (ART) does not cure HIV/AIDS; it is designed to manage the virus and prevent its progression.
- ii. Anti-retroviral drugs help control the replication of the virus and prolong the life of the patient.
- This statement is correct. ART effectively reduces the viral load in the body, helping individuals live longer and healthier lives by managing the virus.
- iii. There is no vaccine available for HIV prevention, but safe sex practices can reduce transmission.
- This statement is also correct. Currently, no vaccine exists for HIV, but using condoms and other safe sex practices significantly lowers the risk of transmission.
- iv. HIV treatment is only effective during the early stages of infection.
- This statement is incorrect. While early treatment is beneficial, ART can be effective at any stage of HIV infection.
Correct Answer Explanation
The correct answer is option 'b' (ii and iii).
- Reasoning:
- Statement ii accurately reflects the role of anti-retroviral drugs in managing HIV, highlighting their importance in controlling the virus and extending life.
- Statement iii correctly acknowledges the absence of a vaccine while emphasizing that safe sex practices can mitigate transmission risk.
In summary, while ART is crucial for managing HIV, it does not provide a cure, and preventive measures like safe sex are essential for reducing transmission.
HIV/AIDS treatment involves a series of statements regarding the effectiveness and management of the disease. Let's break down the provided options to understand the correct answer.
Statement Analysis
- i. Anti-retroviral drugs can completely cure HIV/AIDS.
- This statement is incorrect. Anti-retroviral therapy (ART) does not cure HIV/AIDS; it is designed to manage the virus and prevent its progression.
- ii. Anti-retroviral drugs help control the replication of the virus and prolong the life of the patient.
- This statement is correct. ART effectively reduces the viral load in the body, helping individuals live longer and healthier lives by managing the virus.
- iii. There is no vaccine available for HIV prevention, but safe sex practices can reduce transmission.
- This statement is also correct. Currently, no vaccine exists for HIV, but using condoms and other safe sex practices significantly lowers the risk of transmission.
- iv. HIV treatment is only effective during the early stages of infection.
- This statement is incorrect. While early treatment is beneficial, ART can be effective at any stage of HIV infection.
Correct Answer Explanation
The correct answer is option 'b' (ii and iii).
- Reasoning:
- Statement ii accurately reflects the role of anti-retroviral drugs in managing HIV, highlighting their importance in controlling the virus and extending life.
- Statement iii correctly acknowledges the absence of a vaccine while emphasizing that safe sex practices can mitigate transmission risk.
In summary, while ART is crucial for managing HIV, it does not provide a cure, and preventive measures like safe sex are essential for reducing transmission.
Which of the following is the primary mechanism by which HIV attacks the immune system?- a)By directly attacking red blood cells
- b)By infecting helper T-lymphocytes
- c)By causing mutations in the DNA of immune cells
- d)By inhibiting the production of antibodies
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
By directly attacking red blood cells
b)
By infecting helper T-lymphocytes
c)
By causing mutations in the DNA of immune cells
d)
By inhibiting the production of antibodies

|
EduRev NEET answered |
HIV specifically targets and infects helper T-lymphocytes (TH cells), which play a key role in the immune system's response. This leads to a weakened immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections.
Topic in NCERT: Hiv replication and impact on helper t-lymphocytes
Line in NCERT: "hiv enters into helper t-lymphocytes (t), replicates and produce progeny viruses. the progeny viruses released in the blood attack other helper t-lymphocytes."
Microwaves have wavelength in the range of- a)400 nm to 1 nm
- b)1mm to 1m
- c)< 10 -12m
- d)400nm to 700 nm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Microwaves have wavelength in the range of
a)
400 nm to 1 nm
b)
1mm to 1m
c)
< 10 -12m
d)
400nm to 700 nm

|
Anshika Rane answered |
Microwaves have wavelengths in the range of 1mm to 1m.
Explanation:
Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation that falls between infrared radiation and radio waves on the electromagnetic spectrum. They are widely used in technology and everyday life, particularly in microwave ovens for cooking food.
1. Definition of microwaves:
Microwaves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with longer wavelengths than visible light but shorter wavelengths than radio waves. They have frequencies ranging from 300 MHz (0.3 GHz) to 300 GHz.
2. Wavelength range of microwaves:
Microwaves have wavelengths ranging from 1mm to 1m. This range corresponds to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. The specific wavelength of a microwave depends on its frequency, which can vary depending on the application.
3. Importance of wavelength in microwaves:
The wavelength of microwaves is important because it determines their interaction with matter. For example, microwaves with longer wavelengths are more easily absorbed by water molecules, which is why they are used in microwave ovens to heat food. The shorter wavelengths of microwaves are used in communication systems, such as satellite communication and radar.
4. Applications of microwaves:
Microwaves have numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Communication: Microwaves are used in mobile phones, satellite communication, and wireless internet to transmit and receive signals.
- Cooking: Microwave ovens use microwaves to heat food quickly and efficiently.
- Radar: Microwaves are used in radar systems for navigation, weather forecasting, and military applications.
- Medical imaging: Microwaves are used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to generate images of the human body.
- Astronomy: Microwaves are used in radio telescopes to study celestial objects and phenomena.
In conclusion, microwaves have wavelengths in the range of 1mm to 1m, which corresponds to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. Understanding the wavelength range of microwaves is crucial for their various applications in communication, cooking, radar, medical imaging, and astronomy.
Explanation:
Microwaves are a form of electromagnetic radiation that falls between infrared radiation and radio waves on the electromagnetic spectrum. They are widely used in technology and everyday life, particularly in microwave ovens for cooking food.
1. Definition of microwaves:
Microwaves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with longer wavelengths than visible light but shorter wavelengths than radio waves. They have frequencies ranging from 300 MHz (0.3 GHz) to 300 GHz.
2. Wavelength range of microwaves:
Microwaves have wavelengths ranging from 1mm to 1m. This range corresponds to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. The specific wavelength of a microwave depends on its frequency, which can vary depending on the application.
3. Importance of wavelength in microwaves:
The wavelength of microwaves is important because it determines their interaction with matter. For example, microwaves with longer wavelengths are more easily absorbed by water molecules, which is why they are used in microwave ovens to heat food. The shorter wavelengths of microwaves are used in communication systems, such as satellite communication and radar.
4. Applications of microwaves:
Microwaves have numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Communication: Microwaves are used in mobile phones, satellite communication, and wireless internet to transmit and receive signals.
- Cooking: Microwave ovens use microwaves to heat food quickly and efficiently.
- Radar: Microwaves are used in radar systems for navigation, weather forecasting, and military applications.
- Medical imaging: Microwaves are used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to generate images of the human body.
- Astronomy: Microwaves are used in radio telescopes to study celestial objects and phenomena.
In conclusion, microwaves have wavelengths in the range of 1mm to 1m, which corresponds to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. Understanding the wavelength range of microwaves is crucial for their various applications in communication, cooking, radar, medical imaging, and astronomy.
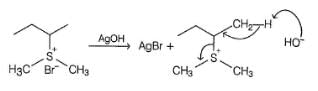
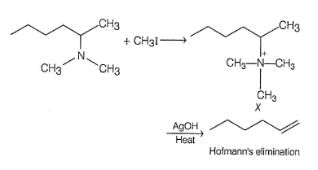
One or More than One Options Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 6-8) This section contains 3 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.Q. Which of the following gives methanol as the major product when heated with AgOH?- a)(CH3)4NI
- b)CH3CH2—N(CH3)3I
- c)(C6H5)2SCH3I
- d)(CH3)3SI
Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
One or More than One Options Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 6-8) This section contains 3 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONE or MORE THAN ONE are correct.
Q.
Which of the following gives methanol as the major product when heated with AgOH?
a)
(CH3)4NI
b)
CH3CH2—N(CH3)3I
c)
(C6H5)2SCH3I
d)
(CH3)3SI

|
Athul Patel answered |
Explanation:
Organic compounds:
- Methanol can be obtained when organic compounds containing a leaving group (-I) are heated with AgOH.
Correct options:
- (CH₃)₄NI: This compound contains a leaving group (-I), so it can give methanol as a major product when heated with AgOH.
- (C₆H₅)₂SCH₃I: This compound also contains a leaving group (-I), so it can give methanol as a major product when heated with AgOH.
- (CH₃)₃SI: This compound contains a leaving group (-I), so it can give methanol as a major product when heated with AgOH.
Which type of cancer is associated with the presence of viral oncogenes?- a)Lung cancer
- b)Breast cancer
- c)Liver cancer
- d)Cancer caused by chemical carcinogens
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Lung cancer
b)
Breast cancer
c)
Liver cancer
d)
Cancer caused by chemical carcinogens
|
|
Shubham Kulkarni answered |
Understanding Viral Oncogenes and Cancer
Cancer can arise from various factors, and one significant contributor is the presence of viral oncogenes. These are genes that can transform normal cells into cancerous ones when introduced by certain viruses.
Association with Liver Cancer
- Liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is strongly linked to viral oncogenes.
- The most notable viruses are Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and Hepatitis C virus (HCV).
- These viruses can integrate their genetic material into the host's DNA, leading to uncontrolled cell growth.
Mechanism of Action
- Viral oncogenes can disrupt normal cell regulatory mechanisms:
- They may inhibit tumor suppressor genes.
- They can activate proto-oncogenes that promote cell division.
- The chronic inflammation caused by these viruses also contributes to liver damage, which increases cancer risk.
Other Cancers and Viral Oncogenes
- While liver cancer is the most prominent example, other cancers can also be associated with viral oncogenes:
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is linked to cervical cancer.
- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is associated with certain lymphomas.
- However, the question specifically emphasizes liver cancer due to its direct association with viral oncogenesis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, liver cancer stands out as the type of cancer most commonly associated with viral oncogenes, particularly due to the significant roles of HBV and HCV. Understanding these connections is crucial for cancer prevention and treatment strategies.
Cancer can arise from various factors, and one significant contributor is the presence of viral oncogenes. These are genes that can transform normal cells into cancerous ones when introduced by certain viruses.
Association with Liver Cancer
- Liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is strongly linked to viral oncogenes.
- The most notable viruses are Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and Hepatitis C virus (HCV).
- These viruses can integrate their genetic material into the host's DNA, leading to uncontrolled cell growth.
Mechanism of Action
- Viral oncogenes can disrupt normal cell regulatory mechanisms:
- They may inhibit tumor suppressor genes.
- They can activate proto-oncogenes that promote cell division.
- The chronic inflammation caused by these viruses also contributes to liver damage, which increases cancer risk.
Other Cancers and Viral Oncogenes
- While liver cancer is the most prominent example, other cancers can also be associated with viral oncogenes:
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is linked to cervical cancer.
- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is associated with certain lymphomas.
- However, the question specifically emphasizes liver cancer due to its direct association with viral oncogenesis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, liver cancer stands out as the type of cancer most commonly associated with viral oncogenes, particularly due to the significant roles of HBV and HCV. Understanding these connections is crucial for cancer prevention and treatment strategies.
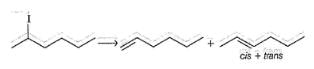
Passage IIWhen compound 1 is heated with C2H5ONa compound 2 and 3 are formed: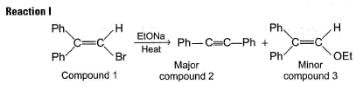
Two mechanisms were proposed for reaction I.
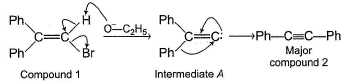
Mechanism A HBr is eliminated from compound 1 to form a symmetrical vinyl carbene intermediate A, which then rearranges to compound 2.
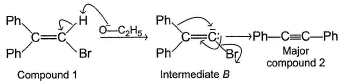
Mechanism B Ethoxide ion first abstract a proton to form a carbanion intermediate B which then rearranges with loss of bromide ion to form compound 2
To distinguish between the two machanisms, an isotopic labeling experiment was designed. Two compounds (Compound 4 and 5) were labelled with C-14 and each was treated separately with sodium ethoxide under identical experimental condition where following results were obtained.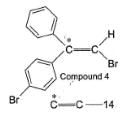
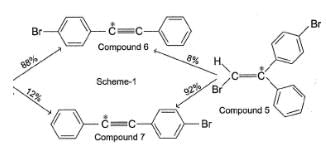 Q. In reaction scheme 1, had the α-C to bromine be labelled with C-14
Q. In reaction scheme 1, had the α-C to bromine be labelled with C-14- a)no change in observation regarding % of various products would have been observed
- b)percentage of the compounds 6 and 7 formed from compound 4 would have been interchanged
- c)percentage of the compounds 6 and 7 formed from compound 5 would have been interchanged
- d)percentage of the compounds 6 and 7 formed from both compounds 4 and 5 would have been interchanged
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage II
When compound 1 is heated with C2H5ONa compound 2 and 3 are formed:

Two mechanisms were proposed for reaction I.
Mechanism A HBr is eliminated from compound 1 to form a symmetrical vinyl carbene intermediate A, which then rearranges to compound 2.
Mechanism B Ethoxide ion first abstract a proton to form a carbanion intermediate B which then rearranges with loss of bromide ion to form compound 2
To distinguish between the two machanisms, an isotopic labeling experiment was designed. Two compounds (Compound 4 and 5) were labelled with C-14 and each was treated separately with sodium ethoxide under identical experimental condition where following results were obtained.


Q.
In reaction scheme 1, had the α-C to bromine be labelled with C-14
a)
no change in observation regarding % of various products would have been observed
b)
percentage of the compounds 6 and 7 formed from compound 4 would have been interchanged
c)
percentage of the compounds 6 and 7 formed from compound 5 would have been interchanged
d)
percentage of the compounds 6 and 7 formed from both compounds 4 and 5 would have been interchanged

|
Rishika Chauhan answered |
Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent: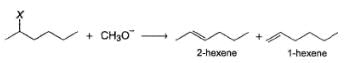
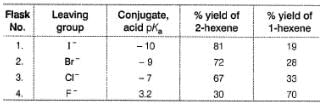 From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O- to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q. Highest percentage yield of 1-hexene in flask 4 leads us to conclude that
From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O- to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q. Highest percentage yield of 1-hexene in flask 4 leads us to conclude that- a)1-hexene is more stable than 2-hexene
- b)Leaving group is not important in E2 reaction
- c)Fluoride, being the poorest leaving group, steric factor control the orientation of elimination, no matter how much elimination product is formed.
- d)None of the above correctly explain the % yield of 1-hexene in yield
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage I
The following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:


From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O- to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.
Q.
Highest percentage yield of 1-hexene in flask 4 leads us to conclude that
a)
1-hexene is more stable than 2-hexene
b)
Leaving group is not important in E2 reaction
c)
Fluoride, being the poorest leaving group, steric factor control the orientation of elimination, no matter how much elimination product is formed.
d)
None of the above correctly explain the % yield of 1-hexene in yield

|
Bhavana Banerjee answered |
Fluorine being the poorest leaving group, major product is one that is formed at fastest rate,
Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:
 From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O- to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q. During formation of products in the given elimination reaction, the highest energy transition state would have been produced when methoxide ion reacts with
From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O- to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q. During formation of products in the given elimination reaction, the highest energy transition state would have been produced when methoxide ion reacts with- a)2-iodohexane to form 2-hexene
- b)2-iodohexane to form 1-hexene
- c)2-fluorohexane to form 1-hexene
- d)2-fluorohexane to form 2-hexene
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage I
The following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:


From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O- to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.
Q.
During formation of products in the given elimination reaction, the highest energy transition state would have been produced when methoxide ion reacts with
a)
2-iodohexane to form 2-hexene
b)
2-iodohexane to form 1-hexene
c)
2-fluorohexane to form 1-hexene
d)
2-fluorohexane to form 2-hexene

|
Vaishnavi Dasgupta answered |
Fluorine is poorest leaving group and formation of 2-hexene involve greater steric hindrance hence, highest energy transition state,
Which of the following methods is used to detect early-stage cancers by examining tissue samples?- a)PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
- b)Biopsy
- c)MRI
- d)Radiography
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
b)
Biopsy
c)
MRI
d)
Radiography

|
Lead Academy answered |
A biopsy involves taking a tissue sample from the suspected area and examining it under a microscope to detect cancerous changes in the cells.
Topic in NCERT: Biopsy and histopathological studies
Line in NCERT: "in biopsy, a piece of the suspected tissue cut into thin sections is stained and examined under microscope (histopathological studies) by a pathologist."
Which of the following statements regarding benign and malignant tumors is/are correct?
i. Benign tumors grow uncontrollably and spread to other organs.
ii. Malignant tumors have the ability to invade surrounding tissues and spread to distant parts of the body (metastasis).
iii. Benign tumors do not cause significant damage and remain localized.
iv. Malignant tumors are typically slow-growing and confined to their original location.- a)i and iv
- b)ii and iii
- c)ii and iv
- d)i and ii
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
i. Benign tumors grow uncontrollably and spread to other organs.
ii. Malignant tumors have the ability to invade surrounding tissues and spread to distant parts of the body (metastasis).
iii. Benign tumors do not cause significant damage and remain localized.
iv. Malignant tumors are typically slow-growing and confined to their original location.
a)
i and iv
b)
ii and iii
c)
ii and iv
d)
i and ii

|
Top Rankers answered |
Statement i is incorrect because benign tumors do not spread; they remain localized.
Statement ii is correct as malignant tumors invade surrounding tissues and can spread to distant sites (metastasis).
Statement iii is correct as benign tumors usually do not cause significant damage and stay localized.
Statement iv is incorrect because malignant tumors are usually fast-growing and not confined to their original location.
Thus, the correct answer is Option B: ii and iii.
Statement ii is correct as malignant tumors invade surrounding tissues and can spread to distant sites (metastasis).
Statement iii is correct as benign tumors usually do not cause significant damage and stay localized.
Statement iv is incorrect because malignant tumors are usually fast-growing and not confined to their original location.
Thus, the correct answer is Option B: ii and iii.
Topic in NCERT: Tumors: benign and malignant
Line in NCERT: "benign tumors normally remain confined to their original location and do not spread to other parts of the body and cause little damage. the malignant tumors, on the other hand are a mass of proliferating cells called neoplastic or tumor cells. these cells grow very rapidly, invading and damaging the surrounding normal tissues. cells sloughed from such tumors reach distant sites through blood, and wherever they get lodged in the body, they start a new tumor there. this property called metastasis is the most feared property of malignant tumors."
Which of the following is/are true regarding the treatment and prevention of cancer?
i. Chemotherapy is the only treatment for cancer and is effective in all types of cancer.
ii. Radiotherapy is used to target and kill cancerous cells by irradiating the tumor.
iii. Immunotherapy is a newer method that enhances the immune system’s ability to detect and destroy cancer cells.
iv. Early detection of cancer has no impact on the treatment success.- a)ii and iii
- b)i and ii
- c)iii and iv
- d)i and iv
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are true regarding the treatment and prevention of cancer?
i. Chemotherapy is the only treatment for cancer and is effective in all types of cancer.
ii. Radiotherapy is used to target and kill cancerous cells by irradiating the tumor.
iii. Immunotherapy is a newer method that enhances the immune system’s ability to detect and destroy cancer cells.
iv. Early detection of cancer has no impact on the treatment success.
i. Chemotherapy is the only treatment for cancer and is effective in all types of cancer.
ii. Radiotherapy is used to target and kill cancerous cells by irradiating the tumor.
iii. Immunotherapy is a newer method that enhances the immune system’s ability to detect and destroy cancer cells.
iv. Early detection of cancer has no impact on the treatment success.
a)
ii and iii
b)
i and ii
c)
iii and iv
d)
i and iv

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Statement i is incorrect because chemotherapy is one treatment, but not the only one, and it is not effective for all types of cancer.
Statement ii is correct as radiotherapy is used to irradiate and kill cancer cells, particularly in localized tumors.
Statement iii is correct as immunotherapy boosts the immune system to help identify and destroy cancer cells.
Statement iv is incorrect because early detection significantly improves the chances of successful treatment.
Thus, the correct answer is Option A: ii and iii.
Statement ii is correct as radiotherapy is used to irradiate and kill cancer cells, particularly in localized tumors.
Statement iii is correct as immunotherapy boosts the immune system to help identify and destroy cancer cells.
Statement iv is incorrect because early detection significantly improves the chances of successful treatment.
Thus, the correct answer is Option A: ii and iii.
Topic in NCERT: Treatment of cancer
Line in NCERT: "treatment of cancer: the common approaches for treatment of cancer are surgery, radiation therapy and immunotherapy. in radiotherapy, tumor cells are irradiated lethally, taking proper care of the normal tissues surrounding the tumor mass."
"many cancers are curable if detected early and appropriate therapeutic measures are taken."
"many cancers are curable if detected early and appropriate therapeutic measures are taken."
Comprehension TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 9-17) This section contains 2 paragraphs, each describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Nine questions related to the paragraphs have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent: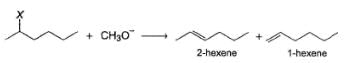
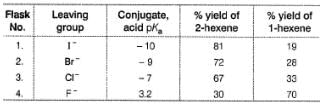 From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O- to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q. Based to the above observation, which flask will have the largest amount of 1-hexene?
From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O- to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q. Based to the above observation, which flask will have the largest amount of 1-hexene?- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Comprehension Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 9-17) This section contains 2 paragraphs, each describing theory, experiments, data, etc. Nine questions related to the paragraphs have been given. Each question has only one correct answer among the four given options (a), (b), (c) and (d).
Passage I
The following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:


From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O- to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.
Q.
Based to the above observation, which flask will have the largest amount of 1-hexene?
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4

|
Ashish Nambiar answered |
Maximum elimination products would be formed in flask 1 and minimum elimination products would be formed in flask 4. Hence, even the 19% of total products in flask 1 would be much greater than 70% of total products in flask 4.
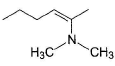
Only One Option Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 1-5) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. What is the major alkene product in the following reaction?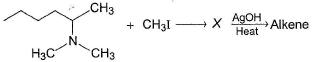
- a)
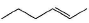
- b)
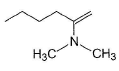
- c)
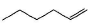
- d)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Only One Option Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-5) This section contains 5 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q.
What is the major alkene product in the following reaction?
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Bhavana Banerjee answered |
Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:
 From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O- to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q. Transition state with least double bond character will be formed when methoxide reacts with
From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O- to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q. Transition state with least double bond character will be formed when methoxide reacts with- a)2-iodohexane to form 2-hexene
- b)2-iodohexane to form 1-hexene
- c)2-fluorohexane to form 2-hexene
- d)2-fluorohexane to form 1-hexene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage I
The following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:


From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O- to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.
Q.
Transition state with least double bond character will be formed when methoxide reacts with
a)
2-iodohexane to form 2-hexene
b)
2-iodohexane to form 1-hexene
c)
2-fluorohexane to form 2-hexene
d)
2-fluorohexane to form 1-hexene

|
Janhavi Kaur answered |
It forms the highest energy transition state.
Passage IIWhen compound 1 is heated with C2H5ONa compound 2 and 3 are formed:
Two mechanisms were proposed for reaction I.
Mechanism A HBr is eliminated from compound 1 to form a symmetrical vinyl carbene intermediate A, which then rearranges to compound 2.

Mechanism B Ethoxide ion first abstract a proton to form a carbanion intermediate B which then rearranges with loss of bromide ion to form compound 2

To distinguish between the two machanisms, an isotopic labeling experiment was designed. Two compounds (Compound 4 and 5) were labelled with C-14 and each was treated separately with sodium ethoxide under identical experimental condition where following results were obtained.
 Q. Based on the results of scheme 1, the chemist most likely ruled out mechanism A because they assumed that intermediate A should have formed
Q. Based on the results of scheme 1, the chemist most likely ruled out mechanism A because they assumed that intermediate A should have formed- a)compound 6 only
- b)compound 7 only
- c)equal amounts of 6 and 7
- d)neither compound 6 nor 7
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage II
When compound 1 is heated with C2H5ONa compound 2 and 3 are formed:

Two mechanisms were proposed for reaction I.
Mechanism A HBr is eliminated from compound 1 to form a symmetrical vinyl carbene intermediate A, which then rearranges to compound 2.
Mechanism B Ethoxide ion first abstract a proton to form a carbanion intermediate B which then rearranges with loss of bromide ion to form compound 2
To distinguish between the two machanisms, an isotopic labeling experiment was designed. Two compounds (Compound 4 and 5) were labelled with C-14 and each was treated separately with sodium ethoxide under identical experimental condition where following results were obtained.


Q.
Based on the results of scheme 1, the chemist most likely ruled out mechanism A because they assumed that intermediate A should have formed
a)
compound 6 only
b)
compound 7 only
c)
equal amounts of 6 and 7
d)
neither compound 6 nor 7

|
Bhavana Banerjee answered |
Which part of the body does HIV primarily target to cause immune deficiency?- a)Red blood cells
- b)Helper T-lymphocytes
- c)Macrophages
- d)Neutrophils
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Red blood cells
b)
Helper T-lymphocytes
c)
Macrophages
d)
Neutrophils

|
Bs Academy answered |
HIV primarily infects helper T-lymphocytes (TH cells), which are critical for coordinating the immune response. As these cells are destroyed, the immune system becomes weakened.
Topic in NCERT: Human health and disease
Line in NCERT: "hiv enters into helper t-lymphocytes (t), replicates and produce progeny viruses."
One Integer Value Correct TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 20 and 21) This section contains 2 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).Q. In the reaction given below how many elim ination products are formed in principle if reaction proceeds by E1 cb mechanism?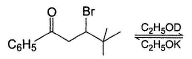
Correct answer is '4'. Can you explain this answer?
One Integer Value Correct Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 20 and 21) This section contains 2 questions. When worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q.
In the reaction given below how many elim ination products are formed in principle if reaction proceeds by E1 cb mechanism?

|
Bhavana Banerjee answered |
Consider the following reaction,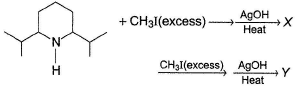 Q. How many different stereoisomers of the major elimination product Y are possible?
Q. How many different stereoisomers of the major elimination product Y are possible?
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following reaction,
Q.
How many different stereoisomers of the major elimination product Y are possible?

|
Rishika Chauhan answered |
The major elimination product is

Since, the diene above is symmetrical, only three geometrical isomers exist.
Since, the diene above is symmetrical, only three geometrical isomers exist.
Consider the following reaction and the product formed.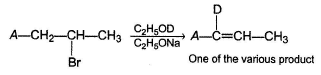 Q. The most likely mechanism of the above reaction is
Q. The most likely mechanism of the above reaction is- a)E2
- b)E2C
- c)E1
- d)E1cb
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following reaction and the product formed.
Q.
The most likely mechanism of the above reaction is
a)
E2
b)
E2C
c)
E1
d)
E1cb

|
Janhavi Kaur answered |
Above equilibrium can explain the formation of given product, hence reaction must proceed by E1 cb mechanism
Passage IIWhen compound 1 is heated with C2H5ONa compound 2 and 3 are formed:
Two mechanisms were proposed for reaction I.
Mechanism A HBr is eliminated from compound 1 to form a symmetrical vinyl carbene intermediate A, which then rearranges to compound 2.

Mechanism B Ethoxide ion first abstract a proton to form a carbanion intermediate B which then rearranges with loss of bromide ion to form compound 2

To distinguish between the two machanisms, an isotopic labeling experiment was designed. Two compounds (Compound 4 and 5) were labelled with C-14 and each was treated separately with sodium ethoxide under identical experimental condition where following results were obtained.
 Q. Compound 2 and 6 can be distinguished from each other by all of the following techniques except:
Q. Compound 2 and 6 can be distinguished from each other by all of the following techniques except:- a)gas chromatography
- b)mass spectrometry
- c)dipole moment measurement
- d)polarimetry
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage II
When compound 1 is heated with C2H5ONa compound 2 and 3 are formed:

Two mechanisms were proposed for reaction I.
Mechanism A HBr is eliminated from compound 1 to form a symmetrical vinyl carbene intermediate A, which then rearranges to compound 2.
Mechanism B Ethoxide ion first abstract a proton to form a carbanion intermediate B which then rearranges with loss of bromide ion to form compound 2
To distinguish between the two machanisms, an isotopic labeling experiment was designed. Two compounds (Compound 4 and 5) were labelled with C-14 and each was treated separately with sodium ethoxide under identical experimental condition where following results were obtained.


Q.
Compound 2 and 6 can be distinguished from each other by all of the following techniques except:
a)
gas chromatography
b)
mass spectrometry
c)
dipole moment measurement
d)
polarimetry

|
Srestha Choudhury answered |
2 and 6 are different compounds, can be separated by gas chromatography. They have different mass, can be distinguished by mass-spectrometry. 2 and 6 have different polarity, can be distinguished by dipole moment measurement. However both are achiral, cannot be distinguished by polarimetry.
1-butene would be formed most easily in the following reaction when X is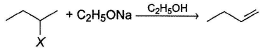
- a)
- b)Br-
- c)Cl-
- d)F-
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
1-butene would be formed most easily in the following reaction when X is
a)
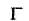
b)
Br-
c)
Cl-
d)
F-

|
Keerthana Mehta answered |
Rate of reaction in E2 reaction depends on acidity of β—H as well as steric hindrance at β-carbon. When X is F, acidity is maximum and there is less steric hindrance at less substituted β-carbon.
Which of the following statements about HIV transmission is/are correct?
i. HIV is transmitted only through sexual contact and contaminated needles.
ii. HIV can be transmitted through casual contact such as hugging, shaking hands, or sharing food.
iii. HIV can be transmitted from an infected mother to her child during pregnancy or childbirth.
iv. Blood transfusions with contaminated blood are a common mode of HIV transmission.- a)i and iii
- b)ii and iv
- c)i, iii, and iv
- d)ii and iii
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about HIV transmission is/are correct?
i. HIV is transmitted only through sexual contact and contaminated needles.
ii. HIV can be transmitted through casual contact such as hugging, shaking hands, or sharing food.
iii. HIV can be transmitted from an infected mother to her child during pregnancy or childbirth.
iv. Blood transfusions with contaminated blood are a common mode of HIV transmission.
i. HIV is transmitted only through sexual contact and contaminated needles.
ii. HIV can be transmitted through casual contact such as hugging, shaking hands, or sharing food.
iii. HIV can be transmitted from an infected mother to her child during pregnancy or childbirth.
iv. Blood transfusions with contaminated blood are a common mode of HIV transmission.
a)
i and iii
b)
ii and iv
c)
i, iii, and iv
d)
ii and iii

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Statement i is correct as HIV is primarily transmitted through sexual contact and contaminated needles.
Statement ii is incorrect as HIV is not transmitted through casual contact like hugging or shaking hands.
Statement iii is correct because HIV can be transmitted from an infected mother to her child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
Statement iv is correct as HIV can be transmitted via blood transfusions with contaminated blood.
Thus, the correct answer is Option C: i, iii, and iv.
Statement ii is incorrect as HIV is not transmitted through casual contact like hugging or shaking hands.
Statement iii is correct because HIV can be transmitted from an infected mother to her child during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
Statement iv is correct as HIV can be transmitted via blood transfusions with contaminated blood.
Thus, the correct answer is Option C: i, iii, and iv.
Topic in NCERT: Transmission of hiv infection
Line in NCERT: "hiv infection generally occurs by (a) sexual contact with infected person, (b) by transfusion of contaminated blood and blood products, (c) by sharing infected needles as in the case of intravenous drug abusers and (d) from infected mother to her child through placenta."
Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:
 From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O- to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q. Transition state with maximum double bond character will be formed when methoxide reacts with
From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O- to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q. Transition state with maximum double bond character will be formed when methoxide reacts with- a)2-iodohexane to form 2-hexene
- b)2-iodohexane to form 1-hexene
- c)2-fluorohexane to form 1-hexene
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage I
The following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:


From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O- to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.
Q.
Transition state with maximum double bond character will be formed when methoxide reacts with
a)
2-iodohexane to form 2-hexene
b)
2-iodohexane to form 1-hexene
c)
2-fluorohexane to form 1-hexene
d)
none

|
Rishika Chauhan answered |
Iodine is best leaving group and 2-hexene is more substituted product, hence major product,
Passage IThe following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:

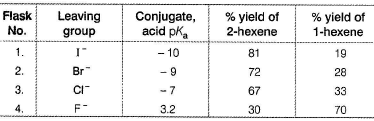 From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O- to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q. If we consider X to be iodine in the given elimination reaction, the number of different elimination products present in the flask-1 would be?
From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O- to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.Q. If we consider X to be iodine in the given elimination reaction, the number of different elimination products present in the flask-1 would be?- a)2
- b)3
- c)4
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Passage I
The following E2 is carried out with different halogen substituent:


From the percentage yield of two products observed with different leaving group, it was concluded that both ease of leaving group and steric hindrance to the approach of base CH3O- to β-H affect the orientation of elimination reaction.
Q.
If we consider X to be iodine in the given elimination reaction, the number of different elimination products present in the flask-1 would be?
a)
2
b)
3
c)
4
d)
5

|
Anu Basu answered |
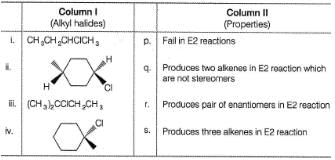
Matching List TypeDirection (Q. Nos. 18 and 19) Choices for the correct combination o f elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.Q. Match the reaction from Column I with the type of m echanism from Column II and mark the correct option from the codes given below.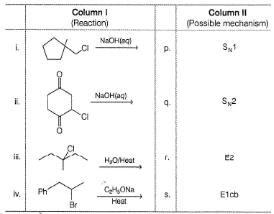

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Matching List Type
Direction (Q. Nos. 18 and 19) Choices for the correct combination o f elements from Column I and Column II are given as options (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which one is correct.
Q.
Match the reaction from Column I with the type of m echanism from Column II and mark the correct option from the codes given below.

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Nidhi Nambiar answered |
(i) Given halide is a primary, predominantly undergo SN2 reaction.
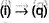
(ii) Given halide is secondary, can undergo SN2 reaction. Also, E2 reaction leads to a conjugated system. Also it may react by E1 cb mechanism because it forms resonance stabilised carbanion.
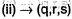
(iii) It is a 3° halide and in the presence of weak base H2O, weak nucleophile H2O , it may undergo unimolecular substitution (SN1) and elimination (E1) reaction.
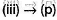
(iv) It may form a stable benzylic carbocation after hydride shift, hence may react by SN1 mechanism. Also it is a secondary halide, may undergo SN2 reaction. It may also react by E2 reaction ai it gives conjugated system. Carbanion. formed at β-C will be stabilised by resonance from ring, hence may undergo E1 cb mechanism.
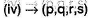
(ii) Given halide is secondary, can undergo SN2 reaction. Also, E2 reaction leads to a conjugated system. Also it may react by E1 cb mechanism because it forms resonance stabilised carbanion.
(iii) It is a 3° halide and in the presence of weak base H2O, weak nucleophile H2O , it may undergo unimolecular substitution (SN1) and elimination (E1) reaction.
(iv) It may form a stable benzylic carbocation after hydride shift, hence may react by SN1 mechanism. Also it is a secondary halide, may undergo SN2 reaction. It may also react by E2 reaction ai it gives conjugated system. Carbanion. formed at β-C will be stabilised by resonance from ring, hence may undergo E1 cb mechanism.
What is the primary method used to detect cancer in internal organs?- a)Biopsy
- b)Chemotherapy
- c)MRI and CT scan
- d)Blood tests
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Biopsy
b)
Chemotherapy
c)
MRI and CT scan
d)
Blood tests

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and CT (Computed Tomography) scans are commonly used to detect cancers in internal organs. These imaging techniques provide detailed pictures of the body's internal structures, helping to identify tumors.
Topic in NCERT: Cancer detection and diagnosis
Line in NCERT: "techniques like radiography (use of x-rays), ct (computed tomography) and mri (magnetic resonance imaging) are very useful to detect cancers of the internal organs."
Chapter doubts & questions for November Week 1 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of November Week 1 - Weekly Tests for NEET Preparation in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Related NEET Content

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup