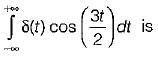All Exams >
NEET >
AIIMS Mock Tests & Previous Year Question Papers >
All Questions
All questions of AIIMS Chemistry Mock Tests for NEET Exam
When vapours of isopropyl alcohol are passed over heated copper, the major product obtained is- a) Propane
- b) Propylene
- c) Acetaldehyde
- d) Acetone
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Propane
b)
Propylene
c)
Acetaldehyde
d)
Acetone

|
Soumya answered |
Isopropyl alcohol + Cu,573K----Propanone or acetone will be the major product.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:720g of water contains how many moles of water?- A:
20
- B:
40
- C:
60
- D:
80
The answer is b.
20
40
60
80
|
|
Varsha Mangla answered |
Weight of water=18g
given weight= 720g
number of moles=given weight/ molar mass
n= 720/18
n= 40
So, the answer is (b)40.
given weight= 720g
number of moles=given weight/ molar mass
n= 720/18
n= 40
So, the answer is (b)40.
Ultra-silicon is prepared by the process of- a)zone-refining
- b)sublimation
- c)crystallisation
- d)fractional distillation
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ultra-silicon is prepared by the process of
a)
zone-refining
b)
sublimation
c)
crystallisation
d)
fractional distillation
|
|
Baby Ghosh answered |
Ultra Pure Silicon is prepared by Zone refining. Zone Refining is based on the difference in solubility of impurities in molten and solid state of the metal. This technique is used for obtaining metals of very high imputity.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The maximum amount of BaCl₄ precipitated on mixing BaCl₂ (0.5 M) with H₂SO₄ (1M) will correspond to- A:
0.5 M
- B:
1.0 M
- C:
1.5 M
- D:
2.0 M
The answer is a.
0.5 M
1.0 M
1.5 M
2.0 M
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
1. The options provided by you are all in kg,and incorrect too. In question it is asked that amount BaSO4 in terms of moles.2. The reaction is : BaCl2 + H2SO4 →→ BaSO4 + 2HCl3. 1 mole of BaCl2 reacts with 1 mole of H2SO4 to give 1 mole of BaSO4. But here 0.5 M of BaCl2 is present for 1 mole of H2SO4.So.BaCl2 is the limiting reagent,and 0.5M of BaSO4 is obtained.
What is the rate of a reaction in mol-L⁻1-s⁻1in a first order reaction, if its half-life period is 693 s, and its concentration is 2 mol-L⁻1?- a)200
- b)100
- c)0.02
- d)0.002
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the rate of a reaction in mol-L⁻1-s⁻1in a first order reaction, if its half-life period is 693 s, and its concentration is 2 mol-L⁻1?
a)
200
b)
100
c)
0.02
d)
0.002
|
|
Navya Choudhury answered |
First Order Reaction and Half-life
A first order reaction is a chemical reaction in which the rate of the reaction is proportional to the concentration of only one reactant. The rate of a first order reaction can be expressed as:
Rate = k[A]
where k is the rate constant and [A] is the concentration of the reactant.
The half-life of a reaction is the time it takes for the concentration of the reactant to decrease to half of its initial value. For a first-order reaction, the half-life can be expressed as:
t1/2 = (ln2)/k
where t1/2 is the half-life and ln2 is the natural logarithm of 2.
Calculating the Rate of the Reaction
Given:
t1/2 = 693 s
[A] = 2 mol/L
Using the equation for the half-life of a first-order reaction, we can solve for the rate constant:
693 s = (ln2)/k
k = (ln2)/693 s
k ≈ 0.001
Now that we have the rate constant, we can use the equation for the rate of a first-order reaction to calculate the rate of the reaction:
Rate = k[A]
Rate = (0.001 mol/L/s)(2 mol/L)
Rate = 0.002 mol/L/s
Therefore, the rate of the reaction in mol/L/s is 0.002. The correct answer is option D.
A first order reaction is a chemical reaction in which the rate of the reaction is proportional to the concentration of only one reactant. The rate of a first order reaction can be expressed as:
Rate = k[A]
where k is the rate constant and [A] is the concentration of the reactant.
The half-life of a reaction is the time it takes for the concentration of the reactant to decrease to half of its initial value. For a first-order reaction, the half-life can be expressed as:
t1/2 = (ln2)/k
where t1/2 is the half-life and ln2 is the natural logarithm of 2.
Calculating the Rate of the Reaction
Given:
t1/2 = 693 s
[A] = 2 mol/L
Using the equation for the half-life of a first-order reaction, we can solve for the rate constant:
693 s = (ln2)/k
k = (ln2)/693 s
k ≈ 0.001
Now that we have the rate constant, we can use the equation for the rate of a first-order reaction to calculate the rate of the reaction:
Rate = k[A]
Rate = (0.001 mol/L/s)(2 mol/L)
Rate = 0.002 mol/L/s
Therefore, the rate of the reaction in mol/L/s is 0.002. The correct answer is option D.
Which type of glass has a property to cut off ultra-violet rays?- a)hard glass
- b)pyrex glass
- c)crook's glass
- d)soft glass
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of glass has a property to cut off ultra-violet rays?
a)
hard glass
b)
pyrex glass
c)
crook's glass
d)
soft glass

|
Mamali . answered |
Crooked Glass is a special type of glass which contains Cerium Oxide [CeO2]. Crooked Glass can cut off the ultraviolet rays making it exclusively use in Sunglasses.....
A current liberates 0.504 g of hydrogen in 2 hours, the amount of copper liberated from a solution of CuSO₄ by the same current flowing for the same time would be- a)31.8 g
- b)63.6 g
- c)15.9 g
- d)6.36 g
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A current liberates 0.504 g of hydrogen in 2 hours, the amount of copper liberated from a solution of CuSO₄ by the same current flowing for the same time would be
a)
31.8 g
b)
63.6 g
c)
15.9 g
d)
6.36 g
|
|
preeti answered |
My ans is 15.9 gm .anyone who post this ques pls reply right answer
Cuprous ion is colourless while cupric ion is coloured because- a)Both have half filled p- and d-orbitals
- b)Cuprous ion has incomplete d-orbital and cupric ion has a complete d-orbital
- c)Both have unpaired electrons in the d-orbital
- d)Cuprous ion has a complete d-orbital and cupric ion has an incomplete d-orbital
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Cuprous ion is colourless while cupric ion is coloured because
a)
Both have half filled p- and d-orbitals
b)
Cuprous ion has incomplete d-orbital and cupric ion has a complete d-orbital
c)
Both have unpaired electrons in the d-orbital
d)
Cuprous ion has a complete d-orbital and cupric ion has an incomplete d-orbital

|
Aaksc Chemistry answered |
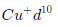
have zero unpaired electron so colourless but cupric ion have one unpaired electron so it shows colour due to d-d transition.
Which out of the following is chiral in nature?- a)CH3CH(OH)CH3
- b)CH3CH(OH)C2H5
- c)CH3CH2OH
- d)CH3CH(OCH3)CH3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which out of the following is chiral in nature?
a)
CH3CH(OH)CH3
b)
CH3CH(OH)C2H5
c)
CH3CH2OH
d)
CH3CH(OCH3)CH3
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Chiral carbon: The carbon atom which is attached to four different groups is called a chiral center.
In CH3CHOHCH2CH3 the second carbon from is chiral carbon because it is attached to four different groups.
Select incorect statement(s):- a)SN1 reaction also take place with some elimination
- b)SN2 reaction with chiral compounds give racemic mixture
- c)S N1 reaction is faster in more polar solvents
- d)All are incorrect statements
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select incorect statement(s):
a)
SN1 reaction also take place with some elimination
b)
SN2 reaction with chiral compounds give racemic mixture
c)
S N1 reaction is faster in more polar solvents
d)
All are incorrect statements

|
Kruti Patel answered |
Option B is correct as SN2 reaction do not give racemic mixture , it gives compound with inverted configuration ,racemic mixture is given by SN1 reaction and not SN2 reaction
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion(A): Carbonyl compounds react with phenyl hydrazine to form phenyl hydrazones.
Reason(R): Hydrozones of aldehydes and ketones are prepared in highly acidic medium.- a)Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)Assertion is true but Reason is false.
- d)Assertion is false but Reason is true.
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion(A): Carbonyl compounds react with phenyl hydrazine to form phenyl hydrazones.
Reason(R): Hydrozones of aldehydes and ketones are prepared in highly acidic medium.
a)
Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
Assertion is true but Reason is false.
d)
Assertion is false but Reason is true.
|
|
Jyoti Aiims Aspirant answered |
Reason is false because in highly acidic medium protonation of hydrazine occur which decrease nucleophilic character of NH2=NH2!
Which of the following is heterogeneous mixture?- a)gasoline
- b)water vapour
- c)carbon dioxide
- d)common salt and sulphur
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is heterogeneous mixture?
a)
gasoline
b)
water vapour
c)
carbon dioxide
d)
common salt and sulphur
|
|
Deepanshi Mishra answered |
A heterogenous mixture is a mixture having non uniform composition throughout the mixture. So here common salt and sulphur is a heterogenous mixture.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Which reaction sequence would be best to prepare 3-choloraniline from benezene ?- A:
Cholorination ,nitration ,reduction
- B:
Nitration , chlorination, reduction
- C:
Nitration , reduction , chlorination
- D:
Nitration, reduction ,acylation, chlorination ,hydrolysis
The answer is b.
Cholorination ,nitration ,reduction
Nitration , chlorination, reduction
Nitration , reduction , chlorination
Nitration, reduction ,acylation, chlorination ,hydrolysis

|
Bhawesh answered |
First nitration is done then which forms nitrobenzene. then chlorination is done which adds cl at the meta position because NO2 is meta directing . them to reduce NO2 to nh2 reduction is done.
An aqueous solution of glucose is 10% in strength. The volume in which 1 gm mole of it is dissolved will be- a)18 litres
- b)9 litres
- c)0.9 litres
- d)1.8 litres
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An aqueous solution of glucose is 10% in strength. The volume in which 1 gm mole of it is dissolved will be
a)
18 litres
b)
9 litres
c)
0.9 litres
d)
1.8 litres

|
Isha Kar answered |
10g glucose dissolved in 100ml of solution
so 180 g will be dissolved in 100/10 ×180 ml
=1.8L
may be it helps..
so 180 g will be dissolved in 100/10 ×180 ml
=1.8L
may be it helps..
A man can swim in still water with a speed of 3 m/s. x and y axis are drawn along and normal to the bank of river flowing to right with a speed of 1 m/s. The man starts swimming from origin O at t = 0 second. Assume size of man to be negligible. Locus of all the possible points where man can reach at t = 1 sec. is (x–a)2 + y2 = c2 Find value of ac2.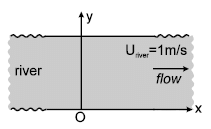
Correct answer is '9'. Can you explain this answer?
A man can swim in still water with a speed of 3 m/s. x and y axis are drawn along and normal to the bank of river flowing to right with a speed of 1 m/s. The man starts swimming from origin O at t = 0 second. Assume size of man to be negligible. Locus of all the possible points where man can reach at t = 1 sec. is (x–a)2 + y2 = c2 Find value of ac2.
|
|
Sarita Yadav answered |
Method -1
If the river is still, the man will be at a distance 3 metres from origin O after 1 second. The locus of all the point where man can reach at t = 1 second is a semicircle of radius 3 and centre at O (dotted semicircle shown in figure).
The river flows to right with a speed 1 m/s. Hence there shall be additional shift in position by 1 m/s x 1 sec = 1m towards right. Hence the locus of all points giving possible position after one second will be the dotted semicircle shifted to right by 1 m as shown in figure.
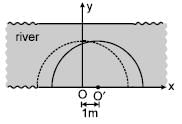
If the river is still, the man will be at a distance 3 metres from origin O after 1 second. The locus of all the point where man can reach at t = 1 second is a semicircle of radius 3 and centre at O (dotted semicircle shown in figure).
The river flows to right with a speed 1 m/s. Hence there shall be additional shift in position by 1 m/s x 1 sec = 1m towards right. Hence the locus of all points giving possible position after one second will be the dotted semicircle shifted to right by 1 m as shown in figure.

Hence locus all the points where the man can be at t = 1 sec. is a semicircle of radius 3 and centre at 0' (1 m, 0 m)
∴ Equation of locus of all the points is
(x - 1)2 + (y - 0)2 = 32
or (x - 1)2 + y2 = 9
Method - 2
Let the relative velocity of the man make angle 'θ' with the x-axis.
Then at time 't' :
x = (3 cosθ + 1) t
and y = 3 sinθ t
⇒(x - t)2 + y2 = (3 cosθ)2 t2 + (3 sinθ)2 t2
(x - t)2 + y2 = 9t2
at t = 1 sec. the required equation is
(x - 1)2 + y2 = 9.
∴ Equation of locus of all the points is
(x - 1)2 + (y - 0)2 = 32
or (x - 1)2 + y2 = 9
Method - 2
Let the relative velocity of the man make angle 'θ' with the x-axis.
Then at time 't' :
x = (3 cosθ + 1) t
and y = 3 sinθ t
⇒(x - t)2 + y2 = (3 cosθ)2 t2 + (3 sinθ)2 t2
(x - t)2 + y2 = 9t2
at t = 1 sec. the required equation is
(x - 1)2 + y2 = 9.
The species isoelectronic with C₂H₄ is- a)CN-
- b)O₂
- c)N₂⁺
- d)O₂⁺
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The species isoelectronic with C₂H₄ is
a)
CN-
b)
O₂
c)
N₂⁺
d)
O₂⁺
|
|
Tarun Saha answered |
Isoelectronic refers to molecules, ions or atoms that have the same count of valence electrons and the same electronic structure.
Now,
The atomic number of O₂ = 8
The atomic number of C = 6
The atomic number of H = 1
The atomic number of N = 7
We are given with,
C2H4 = 2×6 + 4×1 = 16 electrons
O₂⁺ = 2×8-1 = 15 electrons
CN⁻ = 1×6 + 1×7 +1 = 14 electrons
N₂⁺ = 2×7 -1 = 13 electrons
O₂ = 2×8 = 16 electrons
As we can see that, C2H4 and O₂ have same number of electrons, hence they are isoelectronic.
The vapour pressure at a given temperature of an ideal solution containing 0.2 mol of a non-volatile solute and 0.8 mol of solvent is 60 mm of Hg. The vapour pressure of the pure solvent at the same temperature will be- a)120 mm of Hg
- b)150 mm of Hg
- c)60 mm of Hg
- d)75 mm of Hg
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The vapour pressure at a given temperature of an ideal solution containing 0.2 mol of a non-volatile solute and 0.8 mol of solvent is 60 mm of Hg. The vapour pressure of the pure solvent at the same temperature will be
a)
120 mm of Hg
b)
150 mm of Hg
c)
60 mm of Hg
d)
75 mm of Hg
|
|
Shounak Dasgupta answered |
Given:
Moles of non-volatile solute (n₁) = 0.2 mol
Moles of solvent (n₂) = 0.8 mol
Vapour pressure of solution (P) = 60 mm of Hg
To find:
Vapour pressure of the pure solvent (P₀)
Explanation:
According to Raoult's law,
P = P₀X₂
where P₀ is the vapour pressure of the pure solvent, X₂ is the mole fraction of the solvent.
The mole fraction of the solvent is given by,
X₂ = n₂/(n₁ + n₂)
Substituting the given values,
X₂ = 0.8/(0.2 + 0.8) = 0.8
Now,
P = P₀X₂
P₀ = P/X₂ = 60/0.8 = 75 mm of Hg
Therefore, the vapour pressure of the pure solvent at the given temperature is 75 mm of Hg.
Hence, the correct option is (d) 75 mm of Hg.
Moles of non-volatile solute (n₁) = 0.2 mol
Moles of solvent (n₂) = 0.8 mol
Vapour pressure of solution (P) = 60 mm of Hg
To find:
Vapour pressure of the pure solvent (P₀)
Explanation:
According to Raoult's law,
P = P₀X₂
where P₀ is the vapour pressure of the pure solvent, X₂ is the mole fraction of the solvent.
The mole fraction of the solvent is given by,
X₂ = n₂/(n₁ + n₂)
Substituting the given values,
X₂ = 0.8/(0.2 + 0.8) = 0.8
Now,
P = P₀X₂
P₀ = P/X₂ = 60/0.8 = 75 mm of Hg
Therefore, the vapour pressure of the pure solvent at the given temperature is 75 mm of Hg.
Hence, the correct option is (d) 75 mm of Hg.
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-Assertion(A): For caogulating AS2 , S3 , Al3 + ions an better than Na⁺ ions.
Reason(R): Size of Al3 + is smaller than Na⁺.- a)Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)Assertion is true but Reason is false.
- d)Assertion is false but Reason is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion(A): For caogulating AS2 , S3 , Al3 + ions an better than Na⁺ ions.
Reason(R): Size of Al3 + is smaller than Na⁺.
Reason(R): Size of Al3 + is smaller than Na⁺.
a)
Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
Assertion is true but Reason is false.
d)
Assertion is false but Reason is true.
|
|
Anshu Saha answered |
Assertion and Reasoning
Assertion(A): For calculating AS2-, S3-, Al3+ ions are better than Na+ ions.
Reason(R): Size of Al3+ is smaller than Na.
Explanation:
The Assertion(A) states that calculating AS2-, S3-, Al3+ ions is better than Na+ ions.
The Reason(R) states that the size of Al3+ is smaller than Na.
Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
The size of the ions is significant in determining the strengths of their respective acids.
The smaller the size of the ion, the stronger the acid.
Al3+ ions are smaller in size than Na+ ions, so Al3+ is a stronger acid than Na+.
Therefore, it is not correct to say that the size of Al3+ is the reason why it is better to calculate AS2-, S3-, Al3+ ions than Na+ ions.
Instead, the reason is that Al3+ is a stronger acid than Na+.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
Assertion(A): For calculating AS2-, S3-, Al3+ ions are better than Na+ ions.
Reason(R): Size of Al3+ is smaller than Na.
Explanation:
The Assertion(A) states that calculating AS2-, S3-, Al3+ ions is better than Na+ ions.
The Reason(R) states that the size of Al3+ is smaller than Na.
Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
The size of the ions is significant in determining the strengths of their respective acids.
The smaller the size of the ion, the stronger the acid.
Al3+ ions are smaller in size than Na+ ions, so Al3+ is a stronger acid than Na+.
Therefore, it is not correct to say that the size of Al3+ is the reason why it is better to calculate AS2-, S3-, Al3+ ions than Na+ ions.
Instead, the reason is that Al3+ is a stronger acid than Na+.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option B.
The compound used as refrigerant is- a)CCl₄
- b)COCl₂
- c)CF₄
- d)CCl₂F₂
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
CCl₄
b)
COCl₂
c)
CF₄
d)
CCl₂F₂

|
Rutuja Pawar answered |
Freon is used as a refrigerant Most widely used freons are CCl2F2,CCl3F,CHClF2..
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Acetone is prepared by- A:
Oxidation of n-propyl alcohol
- B:
Oxidation of acetaldehyde
- C:
Pyrolysis of calcium acetate
- D:
Pyrolysis of calcium formate
The answer is c.
Oxidation of n-propyl alcohol
Oxidation of acetaldehyde
Pyrolysis of calcium acetate
Pyrolysis of calcium formate

|
Jayesh Majgunkar answered |
(CH3COO)2 Ca when you heat it that means pyrolysis ....CaC03 comes out and u get acetone as the product further CaC03 decomposes to form Ca0 and C02.
Which of the following is the second most abundant element in the earth's crust?- a)carbon
- b)oxygen
- c)silicon
- d)nitrogen
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the second most abundant element in the earth's crust?
a)
carbon
b)
oxygen
c)
silicon
d)
nitrogen

|
Mamali . answered |
Silicon - 27.7% Silicon is the second most common element present in the crust with an abundance of 276,900 ppm. ...
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-Assertion(A): Inversion of cane sugar is catalysed by invertase from yeast.
Reason(R): The conversion of starch into maltase is catalysed by diastase.- a)Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)Assertion is true but Reason is false.
- d)Assertion is false but Reason is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion(A): Inversion of cane sugar is catalysed by invertase from yeast.
Reason(R): The conversion of starch into maltase is catalysed by diastase.
Reason(R): The conversion of starch into maltase is catalysed by diastase.
a)
Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
Assertion is true but Reason is false.
d)
Assertion is false but Reason is true.

|
abhishek patel answered |
Cane sugar is sucrose which is catalysed by invertase to form glucose and fructose.
Diastase as a enzyme which converts starch into maltose.
So both are true but we can see that they are not related in any way so option B is correct.
Diastase as a enzyme which converts starch into maltose.
So both are true but we can see that they are not related in any way so option B is correct.
A solution is obtained by dissolving 12 g of urea (mol.wt. 60) in one litre of water. Another solution is obtained by dissolving 68.4 g of cane sugar (mol.wt. 342) in one litre of water at same temperature. The lowering of vapour pressure in first solution is- a)same as that of 2nd solution
- b)one-fifth of the 2nd solution
- c)double that of 2nd solution
- d)five times that 2nd solution
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A solution is obtained by dissolving 12 g of urea (mol.wt. 60) in one litre of water. Another solution is obtained by dissolving 68.4 g of cane sugar (mol.wt. 342) in one litre of water at same temperature. The lowering of vapour pressure in first solution is
a)
same as that of 2nd solution
b)
one-fifth of the 2nd solution
c)
double that of 2nd solution
d)
five times that 2nd solution
|
|
Divya Pol Divya Pol answered |
Option A is correct
we known that in the first solution number of the moles of urea.
mass of urea 1
= -------------------------- × ---------
m.wt. of urea V
12 1
= ------------------- × ----------- = 0.2
60 1
In second solution the number of moles of cane sugar.
mass of cane sugar
= --------------------------------------
m. wt. of cane sugar
68.4 1
= ------------- × ------- = 0.2
342 1
A metal oxide is reduced by heating it in a stream of hydrogen. It is found that after complete reduction, 3.15 g of the oxide has yielded 1.05 g of the metal. We may deduce that- a)The atomic weight of the metal is 8
- b)The atomic weight of the metal is 4
- c)The equivalent weight of the metal is 4
- d)The equivalent weight of the metal is 8
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A metal oxide is reduced by heating it in a stream of hydrogen. It is found that after complete reduction, 3.15 g of the oxide has yielded 1.05 g of the metal. We may deduce that
a)
The atomic weight of the metal is 8
b)
The atomic weight of the metal is 4
c)
The equivalent weight of the metal is 4
d)
The equivalent weight of the metal is 8

|
Harshitha Dey answered |
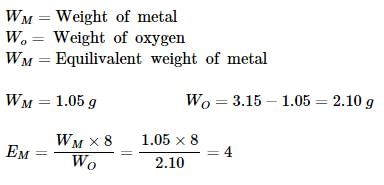
So the equivalent weight of the metal is 4.
The mole fraction of the solute in one molal aqueous solution is- a)0.027
- b)0.036
- c)0.018
- d)0.009
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The mole fraction of the solute in one molal aqueous solution is
a)
0.027
b)
0.036
c)
0.018
d)
0.009
|
|
Shounak Dasgupta answered |
Calculation of Molality:
Molality is defined as the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. In this case, one molal aqueous solution means that one mole of solute is dissolved in one kilogram of water.
Therefore, Molality = 1 mole / 1 kg = 1 mol/kg
Calculation of Mole Fraction:
Mole fraction is defined as the ratio of moles of solute to the total number of moles of solute and solvent in a solution.
Let's assume that the molar mass of the solute is 'x' g/mol. Then, the number of moles of solute in one kilogram of water is given by:
Number of moles of solute = (1 mol / 1000 g) * (1000 g / 1 kg) * x g = x/1000 mol
The total number of moles in the solution is given by:
Number of moles of solute + Number of moles of solvent = x/1000 mol + 1000/18 mol
Here, we have assumed that the density of water is approximately 1 g/mL and its molar mass is 18 g/mol.
Therefore, the mole fraction of the solute is given by:
Mole fraction of solute = (Number of moles of solute) / (Number of moles of solute + Number of moles of solvent)
= x/1000 mol / (x/1000 mol + 1000/18 mol)
= (18x) / (1000x + 18000)
Putting x = 36 g/mol (as given in the question), we get:
Mole fraction of solute = (18*36) / (1000*36 + 18000)
= 0.018
Hence, the correct option is C) 0.018.
Molality is defined as the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. In this case, one molal aqueous solution means that one mole of solute is dissolved in one kilogram of water.
Therefore, Molality = 1 mole / 1 kg = 1 mol/kg
Calculation of Mole Fraction:
Mole fraction is defined as the ratio of moles of solute to the total number of moles of solute and solvent in a solution.
Let's assume that the molar mass of the solute is 'x' g/mol. Then, the number of moles of solute in one kilogram of water is given by:
Number of moles of solute = (1 mol / 1000 g) * (1000 g / 1 kg) * x g = x/1000 mol
The total number of moles in the solution is given by:
Number of moles of solute + Number of moles of solvent = x/1000 mol + 1000/18 mol
Here, we have assumed that the density of water is approximately 1 g/mL and its molar mass is 18 g/mol.
Therefore, the mole fraction of the solute is given by:
Mole fraction of solute = (Number of moles of solute) / (Number of moles of solute + Number of moles of solvent)
= x/1000 mol / (x/1000 mol + 1000/18 mol)
= (18x) / (1000x + 18000)
Putting x = 36 g/mol (as given in the question), we get:
Mole fraction of solute = (18*36) / (1000*36 + 18000)
= 0.018
Hence, the correct option is C) 0.018.
Assuming complete ionization, the pH of 0.1 M, HCl is 1. The molarity of H₂SO₄ with the same pH is- a)0.1
- b)0.2
- c)0.05
- d)2.0
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assuming complete ionization, the pH of 0.1 M, HCl is 1. The molarity of H₂SO₄ with the same pH is
a)
0.1
b)
0.2
c)
0.05
d)
2.0
|
|
Jaya Singh answered |
Explanation:
pH of 0.1 M HCl:
HCl is a strong acid that dissociates completely in water.
HCl → H+ + Cl-
Since the concentration of HCl is 0.1 M, the concentration of H+ ions is also 0.1 M.
pH = -log[H+]
Therefore, pH = -log[0.1] = 1
pH of HSO:
HSO is a diprotic acid that can donate two protons.
HSO → H+ + SO2-
SO2- → H+ + SO32-
The dissociation constants for the two steps are:
K1 = [H+][HSO]/[SO42-] and K2 = [H+][SO42-]/[SO32-]
Since the pH of the solution is 1, the concentration of H+ ions is 0.1 M.
Assuming complete ionization, the concentration of HSO is equal to the concentration of H+ ions.
Therefore, [HSO] = 0.1 M
Using the first dissociation constant, we can calculate the concentration of SO42- ions.
K1 = [H+][HSO]/[SO42-]
0.1 = (0.1)(0.1)/[SO42-]
[SO42-] = 0.1 M
Using the second dissociation constant, we can calculate the concentration of SO32- ions.
K2 = [H+][SO42-]/[SO32-]
0.1 = (0.1)(0.1)/[SO32-]
[SO32-] = 1 M
The total concentration of sulfate ions is the sum of the concentrations of SO42- and SO32- ions.
[SO42-] + [SO32-] = 0.1 + 1 = 1.1 M
The molarity of HSO is the same as the concentration of H+ ions, which is 0.1 M.
Conclusion:
The molarity of HSO with the same pH as 0.1 M HCl is 0.05 M (Option C).
Which of the following gas molecule has the maximum specific heat at constant pressure?- a)argon
- b)helium
- c)oxygen
- d)nitrogen
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following gas molecule has the maximum specific heat at constant pressure?
a)
argon
b)
helium
c)
oxygen
d)
nitrogen
|
|
Shanaya Roy answered |
Explanation:
Specific heat is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree Celsius. At constant pressure, the specific heat is known as the specific heat capacity at constant pressure (Cp).
The specific heat capacity is dependent on the molecular structure of the substance. The gas molecule with more degrees of freedom has a higher value of Cp.
The degree of freedom of a gas molecule is the number of independent ways in which it can move. The degree of freedom for monoatomic gases is 3 and for diatomic gases is 5.
Out of the given options, oxygen is a diatomic gas, and it has five degrees of freedom. Hence, it has the highest specific heat capacity at constant pressure among the given options.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C, oxygen.
Specific heat is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree Celsius. At constant pressure, the specific heat is known as the specific heat capacity at constant pressure (Cp).
The specific heat capacity is dependent on the molecular structure of the substance. The gas molecule with more degrees of freedom has a higher value of Cp.
The degree of freedom of a gas molecule is the number of independent ways in which it can move. The degree of freedom for monoatomic gases is 3 and for diatomic gases is 5.
Out of the given options, oxygen is a diatomic gas, and it has five degrees of freedom. Hence, it has the highest specific heat capacity at constant pressure among the given options.
Therefore, the correct answer is option C, oxygen.
Electrophile N ⊕O2 attacks the following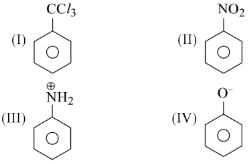
In which cases N ⊕O2 will be at meta-postition?- a)II and IV
- b)I,II and III
- c)II and III
- d)I only
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Electrophile N ⊕O2 attacks the following

In which cases N ⊕O2 will be at meta-postition?
a)
II and IV
b)
I,II and III
c)
II and III
d)
I only

|
Rajeev Kumar Gupta answered |
In Ist 2nd and 3rd we can electron withdrawing groups attached thus only meta position possible (as you can see forming resonating structure of them) where electron density is higher thus electrophile (e Ka bhukha) will come and attack on meta
The mass of 1 x 1022 molecules of CuSO₄.5H₂O is- a)41.59 g
- b)415.9 g
- c)4.159 g
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The mass of 1 x 1022 molecules of CuSO₄.5H₂O is
a)
41.59 g
b)
415.9 g
c)
4.159 g
d)
None of these
|
|
Shivani Gupta answered |
See no of moles =given wt/molar wt=no of molecules/avogadro number
.so w/250=10^22/6×10^
w=250/60=4.16 g .
.so w/250=10^22/6×10^
w=250/60=4.16 g .
The edge length of face centred unit cubic cell is 508 pm. If the radius of the cation is 110 pm, the radius of the anion is- a)228 pm
- b)398 pm
- c)144 pm
- d)618 pm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The edge length of face centred unit cubic cell is 508 pm. If the radius of the cation is 110 pm, the radius of the anion is
a)
228 pm
b)
398 pm
c)
144 pm
d)
618 pm
|
|
Divya Shah answered |
To find the radius of the anion, we can use the concept of the face-centered unit cubic cell and the given information about the cation's radius.
Given:
- Edge length of the face-centered unit cubic cell = 508 pm
- Radius of the cation = 110 pm
We need to determine the radius of the anion.
Formula:
In a face-centered unit cubic cell, the cations are located at the corners of the cube, and the anions are located at the center of each face.
1. Calculate the diagonal of the face-centered unit cubic cell:
Using the Pythagorean theorem, we can find the diagonal of the cube using the edge length.
- Diagonal of the cube = √(3 * (edge length)^2)
- Diagonal of the cube = √(3 * (508 pm)^2) = √(3 * 258064 pm^2) = √774192 pm = 878.21 pm
2. Calculate the distance between the cation and the center of the face:
The distance between the cation and the center of the face is half the diagonal of the cube.
- Distance between cation and center of the face = Diagonal of the cube / 2 = 878.21 pm / 2 = 439.105 pm
3. Calculate the radius of the anion:
The radius of the anion is the difference between the distance between the cation and the center of the face and the radius of the cation.
- Radius of the anion = Distance between cation and center of the face - Radius of the cation = 439.105 pm - 110 pm = 329.105 pm
Therefore, the radius of the anion is 329.105 pm, which is approximately 329 pm. None of the given options match this value. Thus, the correct answer may not be option 'C'.
Given:
- Edge length of the face-centered unit cubic cell = 508 pm
- Radius of the cation = 110 pm
We need to determine the radius of the anion.
Formula:
In a face-centered unit cubic cell, the cations are located at the corners of the cube, and the anions are located at the center of each face.
1. Calculate the diagonal of the face-centered unit cubic cell:
Using the Pythagorean theorem, we can find the diagonal of the cube using the edge length.
- Diagonal of the cube = √(3 * (edge length)^2)
- Diagonal of the cube = √(3 * (508 pm)^2) = √(3 * 258064 pm^2) = √774192 pm = 878.21 pm
2. Calculate the distance between the cation and the center of the face:
The distance between the cation and the center of the face is half the diagonal of the cube.
- Distance between cation and center of the face = Diagonal of the cube / 2 = 878.21 pm / 2 = 439.105 pm
3. Calculate the radius of the anion:
The radius of the anion is the difference between the distance between the cation and the center of the face and the radius of the cation.
- Radius of the anion = Distance between cation and center of the face - Radius of the cation = 439.105 pm - 110 pm = 329.105 pm
Therefore, the radius of the anion is 329.105 pm, which is approximately 329 pm. None of the given options match this value. Thus, the correct answer may not be option 'C'.
Which of the following is a method of converting a ketone to hydrocarbon with same number of carbon atoms?- a)Clemensen's reduction
- b)Reimer-Tiemann reaction
- c)Cannizzaro's reaction
- d)Rosenmund's reaction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a method of converting a ketone to hydrocarbon with same number of carbon atoms?
a)
Clemensen's reduction
b)
Reimer-Tiemann reaction
c)
Cannizzaro's reaction
d)
Rosenmund's reaction
|
|
Rhea Sharma answered |
Clemensens Reduction
Clemensens reduction is a method of converting a ketone to hydrocarbon with same number of carbon atoms. This reaction involves the reduction of a ketone to a hydrocarbon by reaction with zinc amalgam and hydrochloric acid.
Mechanism:
1. In the first step, the ketone is converted to its enol tautomer by reaction with zinc amalgam and hydrochloric acid.
2. The enol tautomer is then reduced to a hydrocarbon by reaction with more zinc amalgam and hydrochloric acid.
Overall reaction:
Ketone + Zn/HCl → Enol + Zn/HCl → Hydrocarbon
Advantages:
- High yield of product
- Mild reaction conditions
- No need for strong reducing agents
Limitations:
- Only works for ketones with alpha hydrogen atoms
- Requires careful control of reaction conditions to avoid over-reduction or side reactions
Example:
Acetone can be converted to propane by Clemensens reduction.
Acetone + Zn/HCl → Propene
Overall, Clemensens reduction is a useful method for converting ketones to hydrocarbons with the same number of carbon atoms. The reaction is relatively simple and mild, making it a valuable tool in organic synthesis.
Clemensens reduction is a method of converting a ketone to hydrocarbon with same number of carbon atoms. This reaction involves the reduction of a ketone to a hydrocarbon by reaction with zinc amalgam and hydrochloric acid.
Mechanism:
1. In the first step, the ketone is converted to its enol tautomer by reaction with zinc amalgam and hydrochloric acid.
2. The enol tautomer is then reduced to a hydrocarbon by reaction with more zinc amalgam and hydrochloric acid.
Overall reaction:
Ketone + Zn/HCl → Enol + Zn/HCl → Hydrocarbon
Advantages:
- High yield of product
- Mild reaction conditions
- No need for strong reducing agents
Limitations:
- Only works for ketones with alpha hydrogen atoms
- Requires careful control of reaction conditions to avoid over-reduction or side reactions
Example:
Acetone can be converted to propane by Clemensens reduction.
Acetone + Zn/HCl → Propene
Overall, Clemensens reduction is a useful method for converting ketones to hydrocarbons with the same number of carbon atoms. The reaction is relatively simple and mild, making it a valuable tool in organic synthesis.
Sodium sulphate is soluble in water but barium sulphate is insoluble because- a)the hydration energy of Na2SO4 is more than its lattice energy
- b)the lattice energy of BaSO4 is more than its hydration energy
- c)the hydration energy of Na2SO4 is less than its lattice energy
- d)Both A and B
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Sodium sulphate is soluble in water but barium sulphate is insoluble because
a)
the hydration energy of Na2SO4 is more than its lattice energy
b)
the lattice energy of BaSO4 is more than its hydration energy
c)
the hydration energy of Na2SO4 is less than its lattice energy
d)
Both A and B

|
Abhishek Choudhary answered |
Hydration energy of Na2SO4 is more than its lattice energy and lattice energy of Ba2SO4 is more than its hydration energy.
A substance 'A' decomposes in solution following the first order kinetics. Flask I contains 1 L of 1 M solution of A and flask II contains 100 ml of 0.6 M solution. After 8 hrs, the concentration of A in flask I becomes 0.25 M, what will be the time for concentration of A in flask II to become 0.3 M?- a)0.4 hr
- b)2.4 hr
- c)4.0 hr
- d)unpredictable as rate constant is not given
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A substance 'A' decomposes in solution following the first order kinetics. Flask I contains 1 L of 1 M solution of A and flask II contains 100 ml of 0.6 M solution. After 8 hrs, the concentration of A in flask I becomes 0.25 M, what will be the time for concentration of A in flask II to become 0.3 M?
a)
0.4 hr
b)
2.4 hr
c)
4.0 hr
d)
unpredictable as rate constant is not given
|
|
Akshat Goyal answered |
Solution:
Given, flask I contains 1 L of 1 M solution of A and flask II contains 100 ml of 0.6 M solution.
The decomposition of A follows first-order kinetics. Hence, the rate of decomposition is proportional to the concentration of A.
Rate of decomposition of A in flask I can be given as:
k = (2.303/t) log (C0/Ct)
Where,
k = rate constant
t = time taken
C0 = initial concentration of A = 1 M
Ct = concentration of A after time t = 0.25 M
Substituting the values in the above equation, we get:
k = (2.303/8) log (1/0.25)
k = 0.0674 hr^-1
Now, we can use the same rate constant to find the time taken for the concentration of A in flask II to become 0.3 M.
Rate of decomposition of A in flask II can be given as:
k = (2.303/t) log (C0/Ct)
Where,
C0 = initial concentration of A = 0.6 M
Ct = concentration of A after time t = 0.3 M
Substituting the values in the above equation and using the rate constant calculated earlier, we get:
0.0674 = (2.303/t) log (0.6/0.3)
t = 4.02 hrs
Hence, the correct option is (c) 4.0 hrs.
Given, flask I contains 1 L of 1 M solution of A and flask II contains 100 ml of 0.6 M solution.
The decomposition of A follows first-order kinetics. Hence, the rate of decomposition is proportional to the concentration of A.
Rate of decomposition of A in flask I can be given as:
k = (2.303/t) log (C0/Ct)
Where,
k = rate constant
t = time taken
C0 = initial concentration of A = 1 M
Ct = concentration of A after time t = 0.25 M
Substituting the values in the above equation, we get:
k = (2.303/8) log (1/0.25)
k = 0.0674 hr^-1
Now, we can use the same rate constant to find the time taken for the concentration of A in flask II to become 0.3 M.
Rate of decomposition of A in flask II can be given as:
k = (2.303/t) log (C0/Ct)
Where,
C0 = initial concentration of A = 0.6 M
Ct = concentration of A after time t = 0.3 M
Substituting the values in the above equation and using the rate constant calculated earlier, we get:
0.0674 = (2.303/t) log (0.6/0.3)
t = 4.02 hrs
Hence, the correct option is (c) 4.0 hrs.
Two moles of an ideal gas are compressed at 300 K from a pressure of 1 atm to a pressure of 2 atm. The change in free energy is- a)1.46 KJ-mol⁻1
- b)3.46 KJ-mol⁻1
- c)5.46 KJ-mol⁻1
- d)7.46 KJ-mol⁻1
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two moles of an ideal gas are compressed at 300 K from a pressure of 1 atm to a pressure of 2 atm. The change in free energy is
a)
1.46 KJ-mol⁻1
b)
3.46 KJ-mol⁻1
c)
5.46 KJ-mol⁻1
d)
7.46 KJ-mol⁻1

|
Vanya Singh answered |
Free energy change =2.303×2×8.314×300log(2/1)
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion(A): Iodination of alkane is made in presence of HgO or HIO3.
Reason(R): Iodination is very slow and reversible process.- a)Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)Assertion is true but Reason is false.
- d)Assertion is false but Reason is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion(A): Iodination of alkane is made in presence of HgO or HIO3.
Reason(R): Iodination is very slow and reversible process.
Assertion(A): Iodination of alkane is made in presence of HgO or HIO3.
Reason(R): Iodination is very slow and reversible process.
a)
Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
Assertion is true but Reason is false.
d)
Assertion is false but Reason is true.
|
|
Jyoti Shah answered |
The reaction of I2 with alkanes is reversible because the HI formed as a by-product is a moderate reducing agent and hence reduces the iodoalkane back to alkane.
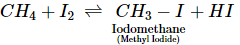
Thus, the iodination can be carried out in presence of an oxidising agent such as iodic acid (HIO3) or HgO which converts HI to I2 as it is formed:
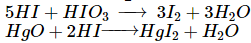
Thus, the iodination can be carried out in presence of an oxidising agent such as iodic acid (HIO3) or HgO which converts HI to I2 as it is formed:
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion(A): Vitamin B5 is also called pyridoxin.
Reason(R): Deficiency of vitamin B5 causes determatitis and dementia.- a)Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)Assertion is true but Reason is false.
- d)Assertion is false but Reason is true.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion(A): Vitamin B5 is also called pyridoxin.
Reason(R): Deficiency of vitamin B5 causes determatitis and dementia.
Assertion(A): Vitamin B5 is also called pyridoxin.
Reason(R): Deficiency of vitamin B5 causes determatitis and dementia.
a)
Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
Assertion is true but Reason is false.
d)
Assertion is false but Reason is true.
|
|
Jaga Priyan answered |
Because vitamin B5 also called panthothenic acid
otherwise vitamin B6 is called pyridoxin
otherwise vitamin B6 is called pyridoxin
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion(A): Ionic solids are characterised by high melting and boiling point.
Reason(R): Ionic solids have coulombic forces of attraction between their ions.- a)Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)Assertion is true but Reason is false.
- d)Assertion is false but Reason is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion(A): Ionic solids are characterised by high melting and boiling point.
Reason(R): Ionic solids have coulombic forces of attraction between their ions.
Assertion(A): Ionic solids are characterised by high melting and boiling point.
Reason(R): Ionic solids have coulombic forces of attraction between their ions.
a)
Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
Assertion is true but Reason is false.
d)
Assertion is false but Reason is true.
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Ionic solids have high melting and boiling point because cations and anions present in them are bounded by coulombic forces of attraction
The number of moles of oxygen in one litre of air containing 21% oxygen by volume, in standard conditions, is- a)0.186 mol
- b)0.21 mol
- c)2.10 mol
- d)0.0093 mol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of moles of oxygen in one litre of air containing 21% oxygen by volume, in standard conditions, is
a)
0.186 mol
b)
0.21 mol
c)
2.10 mol
d)
0.0093 mol

|
Kajal Bose answered |
At standard conditions, 1 liter of air at 21% oxygen possesses 0.21 L of oxygen. Since at STP 1 mole of gas occupies 22.4 L, simply divide 0.21/22.4, to arrive at0.0094 moles of oxygen.
Among KO₂, AlO₂-, BaO₂ and NO₂⁺, unpaired electron is present in- a)NO₂⁺ and BaO₂
- b)KO₂ and AlO₂-
- c)KO₂ only
- d)BaO₂ only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Among KO₂, AlO₂-, BaO₂ and NO₂⁺, unpaired electron is present in
a)
NO₂⁺ and BaO₂
b)
KO₂ and AlO₂-
c)
KO₂ only
d)
BaO₂ only

|
Rocky Handsome answered |
KO2 contains one unpaired electron due to presence of O-2 ion in it.
If the number of electrons present are in even numbers then it well may be completely paired(but not sure though) but if it is odd in number then there surely are unpaired electron(s) .
Here in this case only KO2 had odd(35) electrons in it & so it clearly has unpaired ellctrons in it !!
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion(A):An electron jumps from 5th to 2nd shell,number of possible transition state = 3.
Reason(R): Possible transition state
= ∑Δn = ∑5 − 2 .- a)Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)Assertion is true but Reason is false.
- d)Assertion is false but Reason is false.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion(A):An electron jumps from 5th to 2nd shell,number of possible transition state = 3.
Reason(R): Possible transition state
= ∑Δn = ∑5 − 2 .
Assertion(A):An electron jumps from 5th to 2nd shell,number of possible transition state = 3.
Reason(R): Possible transition state
= ∑Δn = ∑5 − 2 .
a)
Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
Assertion is true but Reason is false.
d)
Assertion is false but Reason is false.
|
|
Preethi Saha answered |
Number of initial states - number of final states.
A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
C) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
D) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
The answer is A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Explanation:
When an electron jumps from the 5th to the 2nd shell, it can do so in three possible ways:
1. Directly from the 5th to the 2nd shell
2. From the 5th to the 4th shell, then from the 4th to the 2nd shell
3. From the 5th to the 3rd shell, then from the 3rd to the 2nd shell
Therefore, the number of possible transition states is 3. This is correctly explained by the Reason given.
A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
C) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
D) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
The answer is A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Explanation:
When an electron jumps from the 5th to the 2nd shell, it can do so in three possible ways:
1. Directly from the 5th to the 2nd shell
2. From the 5th to the 4th shell, then from the 4th to the 2nd shell
3. From the 5th to the 3rd shell, then from the 3rd to the 2nd shell
Therefore, the number of possible transition states is 3. This is correctly explained by the Reason given.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:How many atoms are contained in one mole of sucrose (C12H22O11)?
- A:
45 x6.02 x 1023 atoms/mole
- B:
5 x 6.62 x 1023 atoms/mole
- C:
5 x 6.02 x 1023 atoms/mole
- D:
None of these
The answer is a.
How many atoms are contained in one mole of sucrose (C12H22O11)?
45 x6.02 x 1023 atoms/mole
5 x 6.62 x 1023 atoms/mole
5 x 6.02 x 1023 atoms/mole
None of these

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
C12H22O11 contains a total of 45 atoms ≅ 45 x 6.02 x 1023 atoms/mole
Which has the highest molar heat of vaporization?- a)HF
- b)HCl
- c)HBr
- d)HI
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which has the highest molar heat of vaporization?
a)
HF
b)
HCl
c)
HBr
d)
HI

|
Anusha Sontakke answered |
Due to extensive H-bonding in HF(ll) more energy is required to convert a given amount (say one mole) of HF from liquid to vapour state. Thus out of different hydrogen halides, molar enthalpy of vaporisation of HF is maximum.
The pH of solution formed by mixing 40 ml of 0.10 M HCl with 10 ml of 0.45 M of NaOH is- a)10
- b)12
- c)8
- d)6
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The pH of solution formed by mixing 40 ml of 0.10 M HCl with 10 ml of 0.45 M of NaOH is
a)
10
b)
12
c)
8
d)
6
|
|
Shivi Singh answered |
Nmix = NbVb-NaVa/Vb+Va, here Nb= 0.45M for NaOH and Vb is 10ml , Na= 0.10M for HCl and Va= 40ml , Nmix= (0.45×10)-(0.1×40)/10+40, Nmix= 4.5-4/50,. Nmix=0.5/50 = 0.01 Base concentration is more then overall concentration is basic so pOH=-log10 [OH-] ,. pOH= -log10 [0.01],. pOH= -log10 [10^-2] , pOH= -(-2), pOH = 2 , and we find pH so 14=pH+pOH , 14= pH+2, pH=14-2= 12 ANS .
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-Assertion(A): Hard water is more suitable than soft water for laundary and dying.
Reason(R): Hard water can be used in steam boilers.- a)Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
- b)Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
- c)Assertion is true but Reason is false.
- d)Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following question, a Statement of Assertion (A) is given followed by a corresponding Reason (R) just below it. Read the Statements carefully and mark the correct answer-
Assertion(A): Hard water is more suitable than soft water for laundary and dying.
Reason(R): Hard water can be used in steam boilers.
Reason(R): Hard water can be used in steam boilers.
a)
Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b)
Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c)
Assertion is true but Reason is false.
d)
Both Assertion and Reason are false.
|
|
Palak Basu answered |
Answer:
Assertion: Hard water is more suitable than soft water for laundry and dying.
Reason: Hard water can be used in steam boilers.
Correct answer: Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Explanation:
The given Assertion and Reason are both incorrect. Hard water contains dissolved minerals such as calcium and magnesium, which can leave deposits on clothes and reduce the effectiveness of detergents. Soft water, on the other hand, is better for laundry and dying because it does not contain these minerals.
The Reason given is also incorrect. While hard water can be used in steam boilers, this fact has no relation to the suitability of hard water for laundry and dying.
Therefore, the correct answer is that both Assertion and Reason are false.
Assertion: Hard water is more suitable than soft water for laundry and dying.
Reason: Hard water can be used in steam boilers.
Correct answer: Both Assertion and Reason are false.
Explanation:
The given Assertion and Reason are both incorrect. Hard water contains dissolved minerals such as calcium and magnesium, which can leave deposits on clothes and reduce the effectiveness of detergents. Soft water, on the other hand, is better for laundry and dying because it does not contain these minerals.
The Reason given is also incorrect. While hard water can be used in steam boilers, this fact has no relation to the suitability of hard water for laundry and dying.
Therefore, the correct answer is that both Assertion and Reason are false.
Chapter doubts & questions for AIIMS Chemistry Mock Tests - AIIMS Mock Tests & Previous Year Question Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of AIIMS Chemistry Mock Tests - AIIMS Mock Tests & Previous Year Question Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup